Thursday, January 31, 2019
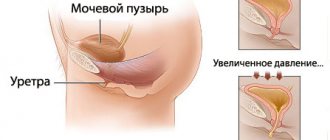
Rare urination is often the reason for a visit to the doctor. The essence of the pathology is a very slow, uneven and scanty urine output, often accompanied by pain. In especially severe cases, the patient has virtually no normal urination.
This disorder occurs in representatives of both sexes, it can have a different nature and origin and is a symptom of a number of diseases of the urinary system.
Urinary standards
A healthy adult should visit the toilet 4 to 7 times a day (women - up to 9 times). In children, this normal indicator is higher and varies depending on age (a newborn can urinate up to 25 times a day, and as the child grows older, the number of urinations decreases).
To determine the normal activity of the genitourinary system, the daily volume of urine (diuresis) and the portion of urine per act of urination (mictition) are taken into account. Normally, these figures average 1.5 liters and 300 ml.
The normal process of urination is characterized by a number of other signs:
- no difficulties during the act of excreting urine - there is no need for special tension or relaxation;
- after going to the toilet, a person does not experience the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- the duration of the period of urinary fluid release is up to one minute;
- urine leaves in the form of a stream with pressure;
- there is no pain during the act of urination and after it;
- going to the toilet when you feel the urge does not require urgency - a person is able to control the process;
- there are no problems of urinary incontinence (both with strong urge and with tension in the form of coughing, laughter, physical activity).
The key to normal functioning of the urinary organs is the absence of disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys, although other factors can also lead to disturbances in the form of rare and small urination.
Statistics
Among all pathologies of the genitourinary system, urolithiasis is one of the most common. It is diagnosed in 33-40% of cases when urological pathologies are suspected. At the same time, males may be much more susceptible to this disease.
However, specific preparation is required for certain types of analysis. For example, before testing urine for catecholamines, it will be important to refuse treatment with certain medications, and you will also need to limit physical and mental stress. A few days before the oxalate test, you will not need to take medications with increased vitamin C content. A specialist should tell you about the nuances. Only after all preparatory procedures have been completed is it possible to begin collecting urine.
Let's pay attention to the fact that you can slightly violate certain rules for passing urine so that the result is negative. As you can see, you don't have to put in a lot of effort to break these rules. And the question of how to make a general urine test bad can be considered closed.

Main causes of pathology
Such an unpleasant phenomenon as rare urination can have different causes. The occurrence of pathology can be caused by both physiological and pathological factors.
Typical pathological causes are certain diseases, namely:
- urolithiasis (kidney stones affect the ureter);
- acute renal failure and kidney inflammation (renal tissue dystrophy, pyelonephoritis);
- malignant tumors;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- nervous disorders;
- gynecological diseases;
- prostate diseases;
- genitourinary infections.
Formations in the form of stones, tumors, stenoses or strictures (narrowings of the lumen) in the genitourinary organs become mechanical barriers that prevent the passage of urinary fluid.
The transmission of nerve impulses about the urge to urinate may be a consequence of dysfunction of the central nervous system organs, including the spinal cord and brain.
Physiological factors include situational reasons: heavy physical exertion (due to insufficient volume of fluid drunk and heavy sweating), dehydration due to intoxication (with vomiting and diarrhea). Normal urination can also be disrupted by alcohol, certain pharmaceutical drugs, or injuries to the urinary system, particularly the kidneys.
Causes of urinary retention in children
The appearance of the symptom of rare urination in pediatric patients has its own specifics.
If the nature of the disorder is physiological, the cause of the disorder in infants in the first months of life may be too high a fat content in breast milk or formula. In a child aged six months or older, pathology may be caused by changes in diet and the amount of liquid the baby drinks.
To reduce urination in a child, any infectious diseases accompanied by an increase in temperature, which causes dehydration, are carried out.

Among the specific pathological causes leading to very rare emissions in a child, specialists at our center identify the following disorders:
- congenital or acquired pathologies of the penis - the presence of an unresolved remnant of the embryonic urethra, phimosis (excess foreskin), paraphimosis (strangulation of the head of the penis);
- bladder injuries received during games (the reason for rare urination is swelling of the genitourinary organs caused by a blow, bruise, fall);
- urinary tract infections - most often the disorder is caused by acute cystitis (the disease occurs specifically in children, against the background of a rare urge to urinate) and nephritis;
- diseases of the nervous system (meningococcal and tuberculous meningitis, spinal poliomyelitis, concussions as a result of injuries);
- mental disorders (hysterical attacks, neuroses, tics).
Reflex urinary retention in a child is caused by prolonged forced abstinence during urge (due to spasm of the urethra and bladder), acute appendicitis or helminth infections (ascariasis).
If you notice that your child is urinating less frequently, you should see a doctor.

Bacteria in urine. Why don't they need to be treated?
Urologists often have to tell patients that the presence of bacteria in the urine is not a reason to prescribe treatment - unless other changes are detected in the tests and there are no other complaints. We explain why in the case of asymptomatic bacteriuria there is no need to look for its cause, “go to the doctor” and ruthlessly “remove bacteria” with antibiotics.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the release of a certain number of bacteria in a portion of properly collected urine from a patient without signs and symptoms of urinary tract inflammation.
The diagnosis of asymptomatic bacteriuria is established by the results of urine culture - when a bacterial concentration of ≥105 is detected in two consecutive analyzes in women and in one analysis in men.
The prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in women increases with age, from 1% in schoolgirls to >20% in women over 80 years of age.
There is a relationship between the presence of bacteria in urine and sexual activity: for example, studies have shown that sexually active women have a higher prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria than nuns of the same age.
However, in young healthy women, asymptomatic bacteriuria rarely lasts longer than a few weeks.
Normally, urine is sterile, but under certain conditions it can be a good breeding ground for bacteria, for example, in diabetes.
The presence of bacteria in a general urine test does not indicate that any bacteria must be cultured during bacteriological analysis (during urine culture). Likewise, an elevated white blood cell count does not always indicate the presence of bacteria in the urine.
In men, asymptomatic bacteriuria is rare. Detection of bacteria in urine is possible in 6-15% of elderly men over 75 years of age. In the presence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in young men, further examination is recommended to exclude bacterial prostatitis.
There is no need to treat asymptomatic bacteriuria.
Treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria is not required because:
- the presence of bacteria in the urine does not increase the likelihood of developing bladder and kidney diseases;
- does not lead to increased mortality;
- antibiotics initially sterilize the urine in almost all patients, but bacteriuria reappears after about 6 months. That is, treatment with antibiotics is not only useless, but also harmful, since bacteria develop immunity to antibiotics (resistance).
Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria is indicated in a small group of patients:
- patients who are planning to undergo surgical treatment with possible damage to the mucous membranes of the urinary tract and possible bleeding;
- patients who have undergone a kidney transplant;
- pregnant women.
With pregnant women, not everything is clear. According to statistics, 2-10% of pregnant women are diagnosed with asymptomatic bacteriuria. Often, if there are bacteria in a general urine test or the presence of bacteria in a low titer (for example, 10³), a woman is immediately prescribed an antibiotic, which, most likely, is not needed at all.
The fact is that most studies on the diagnosis and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women date back to the 70-80s of the last century. According to their results, 20-30% of pregnant women with BD develop acute pyelonephritis, which is associated with miscarriage, low fetal weight and other unfavorable factors. But over the past decades, many factors have changed, and modern studies (though not numerous) show a low risk of developing pyelonephritis in pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria - about 3%!
The official guidelines of the European Association of Urology and Russian recommendations indicate that it is necessary to treat asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women. Perhaps with more quality research on this topic, the recommendations will change. In the meantime, short courses of antibiotic therapy are indicated to reduce the incidence of side effects. It is possible to use fosfomycin (Monural) or a penicillin or cephalosporin antibiotic (Amoxiclav, Suprax).

Loktev Artem Valerievich andrologist
,
urologist
General symptoms
Symptoms of pathology may not always be obvious. In some cases, the violation is not always noticed immediately, and sometimes at first the problem is simply not given any importance.
Such inattention and recklessness is unacceptable, because the sooner you see a doctor, the less stress there will be for your body and the less time it will take for treatment.
Manifestations of urinary retention are the following:
- decreased frequency of the urge to urinate;
- reduction in daily urine volume;
- pain, cramping and discomfort in the lower abdomen during urination;
- urine does not come out in a stream, but intermittently, sometimes in the form of splashes or drops;
- the act of urination requires significant tension;
- Along with urinary retention, urinary incontinence is observed due to the appearance of sudden and too strong urges.
Often the patient also experiences an increase in temperature and constant pain in the lower abdomen.
If the disorder is not just a situational problem caused purely physiologically, then the symptoms will definitely make themselves felt.
Features of pathology in men
Rare urination in men is a serious reason for a visit to a urologist.
But, unfortunately, representatives of the stronger sex do not always rush to the clinic for such reasons. Rare urges and poor diuresis often go unnoticed by them.

As a result, the condition worsens and the disorder becomes more difficult to cure.
Often dysuria in men is caused by the formation of adhesions in the male urinary organs.
Spasms in pathology are accompanied by nervous stimulation, and in pathology of paralytic origin in men, on the contrary, nervous and physical activity is sharply reduced.
Urinary retention caused by mechanical factors (stones, sand in the kidneys) in the male half leads to severe pain and the appearance of bloody and mucous inclusions in the urine.
Rare urination in men without pain is already a good reason to visit a specialist. By contacting our clinic in a timely manner, you will avoid more serious urological problems.
Features of pathology in women
When the normal daily volume of urinary fluid decreases by 30% or more from the norm, doctors diagnose oliguria in women.
Rare urination in women (oliguria) may be due to the development of pathologies specific to the female body.
Among the relevant disorders are oncological formations in the female genitourinary organs (uterus, ovaries), the presence of hormonal imbalance during menopause, uterine bleeding, nervous disorders and other pathologies.

If female oliguria is physiological in nature, it is potentially not dangerous and can be eliminated by correcting the drinking regime and special therapy.
The pathological type of oliguria should cause serious concern. It is a symptom of many serious diseases that require long-term treatment, sometimes surgery.
In any case, a visit to a specialist is important.
In Moscow, experienced urologists work in our center. They will conduct a diagnosis and determine the most effective way to combat the disease.
| Code | Name | Price |
| 03.00 | Initial appointment with a urologist (candidate of medical sciences) | 2,000 rub. |
| 03.04 | Repeated appointment with a urologist (candidate of medical sciences) | 1,200 rub. |
| 03.60 | Initial appointment with a urologist (MD) | 5,000 rub. |
| 03.61 | Repeated appointment with a urologist (MD) | 3,000 rub. |
| All prices of the men's and women's health clinic | ||
Preparing for the study
- • Refrain from sexual intercourse for at least 2, but no more than 7 days before taking the test.
- • Avoid alcohol and strong medications.
- • Try to avoid overheating of the testicles - sauna, hot baths, too tight underwear.
- • Avoid physical fatigue and psycho-emotional stress on the eve of the study.
- • On the morning of the test, drink a glass of water with 3-5 g of baking soda added.
The study is carried out no earlier than 2 weeks after suffering inflammation of the urogenital tract, fever, acute infectious diseases.
Features in pregnant women
Rare urination during pregnancy is a very alarming symptom.
The physiology of pregnancy involves a significant increase in the load on the kidneys and a number of other organs, so as the duration of pregnancy increases, the disorder will worsen.

A dangerous consequence of infrequent urination during pregnancy is the accumulation of decay products and toxins in the body, an imbalance of water and salt balance - this is detrimental to both the mother and especially the child. Ignoring the problem can lead to the most tragic consequences, so in this case the help of a qualified doctor is necessary.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you experience abnormalities in the process of urination (little urine and rare urination), even if this situation is not accompanied by additional alarming symptoms, you should still contact a urologist and undergo a diagnostic procedure.
The examination will determine the cause and nature of the pathology related to the problem, explain why infrequent urination occurred, and the doctor will be able to determine the optimal treatment path.
Diagnosis in our women's and men's health clinic is carried out comprehensively.
The first and mandatory stage of diagnosis is a medical appointment, which involves a conversation with the patient and a physical examination. During communication with the patient, the doctor finds out how long the symptom has been onset, the presence of additional pathologies, in particular, chronic diseases of the genitourinary organs, what operations the patient has undergone and what medications he has taken recently.
The further diagnostic process includes a number of laboratory and instrumental methods for examining the patient:
- conducting a general clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- bacteriological examination of smears from the genitourinary system;
- ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- X-ray of the pelvic and abdominal organs (general and excretory contrast urography).
If necessary, additional methods can also be used in the form of biochemical and hormonal analyzes of relevant biological media, as well as instrumental research methods (tomography, urocystoscopy, MRI and others).
In our center, diagnostics are performed using the latest generation equipment, and the examination results are guaranteed to be accurate.
The best specialists
All doctors undergo strict selection. They are professionals, polite and attentive to their patients.
Quality treatment
The results of the treatment are felt after the first visit. We guarantee you a solution to any problems
Modern diagnostics
We carry out diagnostics using modern European devices. Diagnostic reliability - 99%
Patient care
Our doctors treat everyone with care and understanding. Appointment with a doctor is completely confidential
Urine test
In order to take a urine test, you need to follow certain rules. There are certain rules that allow you to take the test and get the correct results. For example, before the test you should not eat anything that could affect the color of your urine. Such products include bright berries, and before donating urine, it is necessary to carry out personal hygiene procedures. As for the first portion of urine, there is no need to collect it, only the subsequent biomaterial. Using all this information, it will not be difficult to figure out how to make a bad urine test so that protein is found. You need to do the opposite.

Treatment
Treatment of rare urination does not consist in eliminating this individual symptom, but in combating the disease that is its etiopathogenetic root cause.
The direction and essence of the treatment process is determined by the results of the examination.

Our clinic offers patients predominantly conservative therapy. This technique is effective and not painful for the patient.
Among the corresponding treatment methods, the following methods have proven themselves to be positive:
- physiotherapeutic procedures in the form of warm compresses, sitz baths;
- gymnastics to train the muscles of the perineum;
- medications (drug treatment determines the factor provoking the pathology);
- special diet (exclusion of foods that retain fluid).
In emergency cases, when the disease is advanced, surgical intervention is not excluded - catheterization and necessary surgical operations (removal of stones, neoplasms).
What is retrograde ejaculation
Retrograde ejaculation is called ejaculation, in which the release of sperm, in whole or in part, does not occur in the urethra, but in the opposite direction - into the bladder. Normally, this is impossible, because at the moment of ejaculation, the neck of the bladder closes, preventing the return movement of the seed.
Impaired physiological closure of the bladder neck can be caused by certain medications, damage to the spinal cord and peripheral nerves, and congenital and acquired anatomical changes. Despite the wide variety of causes of pathology, the vast majority of patients with retrograde ejaculation are patients with diabetes mellitus.
The main danger of retrograde ejaculation is the development of male infertility. This type of infertility is called excretory infertility, since it is associated with insufficient ejaculate secretion or its complete absence.
Prevention of urinary retention
There are no targeted measures to prevent pathology.
A healthy and active lifestyle, proper nutrition, and avoidance of injuries will help you avoid the disorder. Monitor your body's water balance; in case of a cold or other illness accompanied by fever, drink more fluids.
If a symptom first appears, contact a specialist, do not self-medicate! Call the phone number listed on our website and make an appointment. Our urologists will definitely help you!