Ultrasound diagnostics is the most popular diagnostic method in the modern world. This is the safest, painless and non-invasive way to obtain information about the state of human internal organs.
Eco fertilization What is it?
The method of ultrasound diagnostics of the body is carried out using a sound wave, which is sent by the device’s sensor through a nozzle. This wave is reflected from the organs, displaying the state of the organs being examined on the screen. But this method, unfortunately, cannot be used in diagnosing the condition of bone tissue and gastrointestinal tract organs. In this case, of course, it is more informative to use radiography and endoscopic methods.
Ultrasound diagnostics has no side effects, since, compared to x-rays, there is no exposure to x-rays. This allows you to carry out this procedure as many times as necessary to clarify the diagnosis or track the course of the diagnosed condition, as well as control the transfer of embryos during IVF.
In obstetric and gynecological practice, the ultrasound diagnostic method is valuable and indispensable in diagnosing the development of pregnancy. Diagnosis using ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to examine the condition of the abdominal organs in a woman and examine the condition of the fetus. This allows early detection of developmental defects in the fetus and suspicion of a threat from the woman’s organs. With the development of new modern technologies, future parents have the opportunity to see their baby using the latest technology of 3D and 4D images displayed on a large screen. This image is three-dimensional and you can clearly see the child, his arms, fingers and all his movements.
IVF - first ultrasound during pregnancy
During pregnancy resulting from IVF, the method of ultrasound examination in terms of technique is completely no different from this diagnostic method for a sudden pregnancy. An uzologist has the right to use two types of diagnostics:
- transabdominal examination is performed using a high-frequency transducer that transmits waves through the layers of the anterior abdominal wall. This type of diagnosis is most used in later stages of pregnancy. It is worth noting that the ultrasonic wave does not harm health, both for the woman and her unborn child;
- transvaginal examination. This type of diagnosis is recommended for use in the early stages of pregnancy. During the procedure, a sensor is inserted directly into the vagina. This is necessary due to the fact that during this period the developing fetus is too small in size and the transabdominal method will be of little information. In addition, with this diagnostic method, the cervix is clearly visible, the condition of which is of great importance during pregnancy.
Like any research method, ultrasound diagnostics also requires preparation. Thus, before the transvaginal examination method, it is necessary to empty the bladder. But before the transabdominal method, you should drink one liter of still water. But at the moment, with the help of modern technologies, there are no fundamental guidelines for conducting screening studies.
So, by what indicators is it possible to determine the onset of pregnancy after in vitro fertilization? I would like to note that they are completely identical to the manifestations of signs of pregnancy that occurs suddenly in natural conditions, but it may also turn out that the pregnancy is multiple, that is, twins during IVF.
According to the IVF protocol, the embryo transfer stage requires 3-5 days. This time is necessary for the egg to enter the blastocyst stage. This in turn gives a greater chance of successful implantation. In some cases, implantation may occur only 10 days after transplantation. This type of development is also considered normal and is called late implantation.
How does the cryoprotocol work?
How long after a fresh cycle, in which embryos are obtained and frozen, is cryopreservation performed? The decision is made by the doctor depending on the condition of the patient’s reproductive system and her general health. On average, the break is two cycles.
If we are talking about embryos that were once vitrified for the future, then the duration of the break depends only on the spouses. When they decide that it is time for pregnancy, then they return to our clinic.
There are two main options for carrying out a cryoprotocol: the transfer can be carried out in a natural cycle (NC) or on hormone replacement therapy (HRT). The best option is selected by the attending fertility specialist.
Natural cryocycle
Cryotransfer to the EC is carried out under conditions close to physiological. Hormones are prescribed to a minimum - only to support the luteal phase and thereby increase the chances of pregnancy. For this purpose, before and after the transfer of vitrified embryos, the expectant mother takes progesterone preparations.
From the very beginning of the cycle, the doctor uses ultrasound to monitor how the egg matures and the endometrium grows. When ovulation is confirmed, the specialist prescribes the transfer of vitrified embryos.
There are several conditions for choosing cryotransfer to the EC. These are age under 35 years, regularity of the menstrual cycle and absence of problems with ovulation.
Cryotransfer for HRT
It involves managing the menstrual cycle of the expectant mother; hormonal agents are used for this. This type of cryoprotocol is indicated for women of late reproductive age, patients with irregular cycles, reduced follicular reserve, and lack of ovulation.
Scheme of cryoprotocol for HRT
From the beginning of the cycle, estrogen drugs are used. They cause endometrial growth, which is monitored by ultrasound. When the uterine mucosa reaches the desired parameters, estrogens are replaced with progesterone preparations (to maintain the luteal phase), and a transfer procedure is prescribed.
Sometimes doctors fail to achieve normal endometrial growth in the EC or on HRT. Then the protocol includes small doses of medications to stimulate the ovaries.
The transfer procedure itself, regardless of the cryoprotocol scheme, proceeds in the same way as in the classic IVF program
Signs of pregnancy on ultrasound after embryo transfer during IVF
As soon as the fertilized egg is implanted into the uterine cavity, implantation occurs, and then the formation of the placenta from the endometrium and cytotrophoblast. After this, the chorion tissue begins to produce the so-called “pregnancy hormone” hCG. Due to its appearance in a woman’s body, some changes appear that are considered the first, but not reliable, signs of pregnancy. Such as:
- early toxicosis;
- slight increase in basal temperature;
- sudden changes in mood, from depression to aggression, tearfulness or, on the contrary, cheerfulness and good mood;
- an increase in breast volume and characteristic changes in the color of the nipples.
In medical practice, there are cases when, during in vitro fertilization in the early stages, pregnancy develops without any signs. Therefore, after some time it is necessary to conduct a test to determine the level of hCG in the blood serum; its increase will serve as a positive result of fertilization. But the most accurate and informative way to tell about the development of pregnancy is the ultrasound diagnostic method. This procedure does not require much preparation effort. One of the requirements is an empty bladder.
What does the law say about ecology?
The first ultrasound during IVF is performed only using a transvaginal sensor. This is necessary in order to be able to more informatively and reliably obtain information about the implanted embryo and its location. Over time, the doctor has the right to repeat the transvaginal diagnostic procedure, but in the future, at a later date, use only a transabdominal sensor. The importance of ultrasound after embryo transfer during IVF lies in the fact that only in 60% of cases the transfer ends in pregnancy. And another important, but very rare reason is the possibility of pregnancy developing outside the uterine cavity. An initial ultrasound examination is carried out on the 21st day after embryo transfer to ensure successful transfer and pregnancy. The value of the first ultrasound after IVF is too great and significant not only for confirming successful transplantation and engraftment, but also for identifying particularly dangerous pathologies on the part of the woman and the fetus (frozen pregnancy). The first ultrasound diagnosis allows you to determine:
- location in the uterus of the fertilized egg;
- the number of implanted embryos obtained as a result of in vitro fertilization;
- determine the viability of the embryo(s) after transplantation;
- functional state of the ovaries;
- the presence or absence of increased uterine tone;
- the presence or absence of detachment of the ovum;
- relationship between term and fetal development.
Is there a need for an examination after a miscarriage?
It is important to emphasize that expectant management is only suitable in a situation where a woman has no external symptoms of miscarriage. She has no bleeding, nagging pain in the lower abdomen or dizziness. If such signs still exist, you should not delay your visit to the clinic. Doctors will help you safely remove the dead embryo and, if necessary, send it for histological examination. Such research will help to understand what the root cause of miscarriage is.
A single case of frozen pregnancy, according to the clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health and the world's leading associations of reproductive medicine, is not an indication for diagnosis. It is assumed that the miscarriage occurred due to an error in the chromosomal structure of the embryo and is a random one-time occurrence.
If miscarriages and spontaneous pregnancy loss occur repeatedly, you need to understand the reasons. The exact examination plan is drawn up by the attending physician individually, based on the specific clinical picture. The only thing that is recommended under any circumstances is to conduct a study of the karyotype of the deceased embryo.
Histological analysis will determine the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the development of the embryo. If such disorders are identified, the woman is given a favorable diagnosis and the likelihood of a favorable resolution of the second pregnancy is assessed as quite high. If the structure of the embryo is normal, then the causes of the miscarriage should be looked for in the parents. The doctor can prescribe a comprehensive examination of the health of men and women, smears for infections, checking hormonal levels and the functioning of the immune system, hysteroscopy, biopsy and other diagnostic procedures. It is the identification and elimination of the real cause of miscarriage that increases the chance of having a child.
Indications and contraindications
The short protocol is indicated in the following cases:
- woman's age over 35 years;
- regular menstrual cycle;
- male factor infertility with preserved female fertility;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- an unsuccessful attempt in a long IVF protocol.
The condition required for entry into the short protocol program is sufficient ovarian reserve.
Contraindications to the protocol are endometriosis, fibroids, endometrial hyperplastic diseases, irregular menstrual cycle, lack of ovulation, depletion of ovarian reserve.
When can I expect results after IVF?
As mentioned above, the result will be known for sure only after two or even three weeks of waiting. It should be said that a lot here depends on the choice of clinic, so you need to contact only trusted organizations that have everything necessary for you to become the parents of a beautiful baby.
Only competent work of all medical personnel will ensure high results and protect future parents from possible complications:
- negative IVF result;
- incorrectly identified cause of infertility;
- ovarian hyperstimulation;
- damage to the already fragile reproductive health of the couple, etc.
As you can see, there are many complications that can be encountered with IVF. After the transfer, the most important stage begins, during which much depends on the woman’s moral state, her mood and the availability of proper, not only medicinal, but also psychological support.
Summary
Embryo implantation is determined by many factors. And although enormous responsibility for the success of the program rests with reproductive specialists and embryologists, the prognosis for the effectiveness of the treatment course depends mainly on the initial parameters of the couple - age, cause and duration of infertility, concomitant gynecological pathologies, and the severity of the medical history. The usefulness of the transferred embryos, plus the readiness of the female body, in particular the endometrium, for their implantation significantly increases the chances of a favorable treatment outcome.
How is the transfer of thawed embryos carried out?
If you decide to use embryos stored in a cryobank, the first step should be to make an appointment with a fertility specialist. The doctor examines the patient, analyzes information about previous ART programs, prescribes examination to the required extent, and selects the optimal cryotransfer scheme. As a rule, the procedure is prescribed for the next menstrual cycle.
Cryotransfer scheme
There are two versions of the program. The first - cryopreservation in a natural cycle (NC) - is carried out according to the scheme given below.
- Using ultrasound monitoring, the reproductive specialist determines the fact of ovulation, and based on this information, sets the date of the procedure and the necessary drug support for the second phase of the cycle.
- Before transfer, the embryologist thaws and cultivates the embryos, assesses their quality, and performs assisted hatching, if indicated.
- The reproductive specialist places one, maximum two embryos into the patient’s uterine cavity. Embryo transfer is a painless procedure that is performed without anesthesia and takes about 5 minutes. An embryo placed in a special thin catheter is transferred into the uterine cavity under ultrasound control.
- After 14 days, the patient comes to the clinic for an hCG test.
Cryotransfer is less commonly prescribed during hormone replacement therapy (HRT). It involves the use of hormonal drugs to prepare the endometrium. While using medications, a reproductologist monitors the thickness of the endometrium using ultrasound. When she reaches the required levels, a cryotransfer date and drug support for the second phase of the cycle are set. Then the program proceeds in the same way as the transfer to the EC.
When is the test done after IVF?
A woman must undergo a number of examinations, including:
- hormonal analysis;
- blood tests for hCG;
- Ultrasound.
By looking at the results of examination tests over time, the doctor can assess the condition of the patient’s body, understand whether pregnancy has occurred, and whether IVF was successful. Moreover, at such an early stage, even a negative test result cannot be a sufficient basis to confirm an unsuccessful protocol, because in some cases the embryo is implanted later.
After unsuccessful IVF, new attempts to have a child should be made no earlier than six months later, because the female body must fully recover from the shock it suffered. That is why choosing the right reproductive center largely determines the success of the event.
What is IVF
With this type of fertilization, doctors remove an egg from a woman’s body, place it in special conditions and fertilize it with sperm. The embryo, which is formed during the process of fertilization, remains in the incubator for 3–5 days, then it is transferred to the uterus. Successful implantation of an embryo after IVF (pregnancy) is observed in every third case.
To carry out in vitro fertilization, the following conditions must be met:
- mutual consent of the parents,
- absence of chronic diseases in parents,
- the absence of any pathologies in the female genital organs (ovaries, uterine cavity) in the expectant mother.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the protocol include:
- good tolerance;
- can be used for any type of infertility;
- minimal number of complications, in particular ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome;
- no age restrictions;
- lower cost compared to a long protocol.
The short protocol has few disadvantages. The first is the relatively high probability of spontaneous ovulation. In this case, the circuit is interrupted. You can return to stimulation after a few months. Secondly, reproductive specialists are not always able to obtain a sufficient number of healthy eggs.
What to do after unsuccessful embryo implantation
No doctor guarantees a 100% chance of successful embryo implantation. In case of unsuccessful in vitro fertilization, the doctor finds out the reasons why the pregnancy did not occur. After this, the woman undergoes a course of treatment, then the IVF procedure can be repeated.
It is important not to lose heart after unsuccessful embryo implantation, to believe that the second or third attempt will definitely end in pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child.
If you dream of becoming a mother, see a future baby in a dream, but cannot get pregnant, contact the IVF Center in Petrozavodsk. Our gynecologists will consult you, make a diagnosis, examining you using the latest diagnostic equipment. We offer both conservative treatment and in vitro fertilization.
Embryological stage
Reproduction specialists are concerned about both reducing the incidence of multiple births and increasing the frequency of pregnancy and successful pregnancy. Practice shows that the majority of all miscarriages - about 60% - are caused by abnormalities associated with the embryo.
Therefore, not only the quantity, but also the quality of embryos for transfer plays an important role in the IVF program. Their classification based on various characteristics is the basis for selecting the most viable biomaterial. Embryologists do this. They decide which embryos will be transferred into the uterus and when.
Determining embryonic potential: basic principles
Selection based on assessing the prospects of embryos is an effective tool for a reproductologist. Along with the patient's age, fertility history and other information, it helps predict and implement successful embryo transfer.
Several embryo scoring systems have been developed. All of them are subjective, although they allow you to make educated guesses about the potential of the embryo. In practice, pregnancy may occur with a “bad” assessment and not occur with a “good” assessment. Moreover, regardless of the classification system, the criteria used by embryologists do not reflect what is happening inside cells at the genetic level.
Typically, in reproductive centers, embryo transfer occurs either 3 days (at the cleavage stage) or 5 days (at the blastocyst stage) after fertilization. Accordingly, they are assessed according to different classification systems.
Third day selection
At this stage, the cells in the embryo are fragmented. He himself does not grow and does not increase in size. Only its genetic material multiplies. Theoretically, one could assume that the embryo divides only in a certain sequence: 1 cell becomes two; 2 – four; 4 – eight and so on.
However, in fact, synchronous division does not always occur. Three, five, six cells can often be observed. This is not an indicator of a bad embryo - it grows like that. In addition, sometimes during division a small amount of the cytoplasm (the inner part of the cell) breaks and forms a bubble - the so-called fragment. It does not contain a nucleus and is not considered a cell.
The causes of fragmentation are not well understood. But it was found that embryos containing many fragments are at a disadvantage from a developmental point of view: their cells lose too much cytoplasm.
Embryos in the cleavage stage are classified according to two criteria:
- number of cells;
- appearance.
The first indicator is objective (the number of cells can be counted under a powerful microscope), the second is subjective. As laboratory studies show, “good” - normally growing - day 3 embryos ideally contain 8 cells. They have a better chance of developing into viable blastocysts.To select embryos based on their external characteristics, a 5-level scoring system is used. Number 1 (best position) marks embryos in which cells are the same size and there is no fragmentation; number 5 (worst position) – embryos with cells of different sizes and significant fragmentation.
Embryos from levels 1 to 3 have the greatest potential to develop to the blastocyst stage. At the same time, a level 4 embryo can also be of good quality if its morphology is associated with asynchronous cell division and is not caused by chromosomal abnormalities.
As practice shows, the number of cells on the third day is a more important indicator of embryonic potential than the level criterion. Thus, an 8-cell level 3 embryo is more promising than a 2-cell level 4 embryo.
Fifth day selection
On the 5th day, the cells of the embryo continue to multiply, but at the same time they are already growing and differentiating. The space inside the zone pellucida (ZP), the membrane surrounding the embryo, also begins to expand. When it becomes thinner, the blastocyst breaks through it. This “hatching” is necessary for implantation into the inner lining of the uterus.
There are two types of cells on the 5th day of embryonic development:
- intracellular mass (ECM), which becomes the basis for the formation of the fetus;
- trophectoderm (TE), from which tissues needed during pregnancy (for example, the placenta) are formed.
Together, these clusters of cells create a fluid-filled sphere. Inside the spherical formation there is an ECM, and outside there is an TE. Both types of cells are essential for a healthy pregnancy. Therefore, when evaluating a blastocyst, take into account: - condition – volume, compactness – VCM and TE (letter gradation is used: A (“excellent”) / B (“good”) / C (“satisfactory”) / D (“bad”);
- the degree of expansion of the fluid-filled cavity, or blastocoel (digital indicators from 1 to 6 are used).
Developed at the end of the last century (D. Gardner et al., 1999), this classification is widely used to this day.Classification of blastocysts is an extremely complex process that does not allow absolute estimates. An embryo with a grade D ECM, for example, may still develop and subsequently condense to grade B or even A.
The same is observed with the degree of expansion of growing embryos. An early 5-day blastocyst on the 6th day may become dilated and suitable for transfer or freezing if other indicators are as good. Determining the usefulness of an embryo is based on taking into account all its components.
The above classifications, based on the morphological principle, are considered necessary, but not sufficient for embryological prognosis. Therefore, other methods are being developed to assess the potential of an embryo: PGS, morphokinetic study, metabolite analysis. By complementing morphological parameters, they contribute to more effective selection of biomaterials.
Medicines used
The protocol uses the following groups of drugs:
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists - drugs compete with natural hormones and block the action of the pituitary gland - are prescribed from the first days of the protocol;
- ovulation stimulants - potentiate the maturation of several follicles in the ovaries at the same time;
- ovulation inducers - hCG - stimulate the ovulation process;
- Progesterone preparations - support the luteal phase of the cycle and promote implantation of the fertilized egg.
If the IVF regimen is successfully completed, progesterone is recommended to be taken throughout the first trimester.
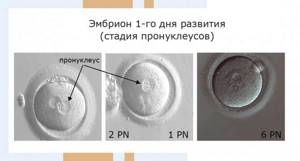
What happens on Day 1?
18-20 hours after the addition of sperm or ICSI (1st day), fertilization is assessed or not. If fertilization is normal, two pronuclei are formed. These are the precursors of the nuclei of future blastomere cells, into which the fertilized egg begins to divide. With proper fertilization, both pronuclei are clearly distinguishable and are designated 2pN.
If pronuclei are not visible, then most likely fertilization did not occur (0pN). Sometimes we observe 1 pronucleus (1 pN), in which case fertilization has occurred, but such embryos need to be closely monitored; as a rule, they have a reduced developmental potential. If we observe 3 or more pronuclei, then fertilization has not occurred correctly. “Incorrectly” fertilized oocytes are not suitable for further work and are disposed of.