The electrocardiography method, which involves recording the electrical fields of the heart and displaying a graph on a display or paper, has for many years been considered the most effective way to diagnose heart diseases and disorders of its functioning.
Thanks to an electrocardiogram, a special graphic image, the doctor can assess the quality of the heart and promptly identify possible pathologies and deviations from the norm.
To carry out the procedure, an electrocardiograph is used, which is a device with a recording device and an amplifier of the biopotential of the heart.
A nurse will be allowed to work with an ECG machine only if she has undergone special training. The technique of taking an electrocardiogram requires a specialist not only knowledge and experience, but also an understanding of certain symbols of the graphic image.
The procedure is performed in a room equipped with special equipment, as well as at the patient’s bedside or when working outside the hospital in emergency cases.
In the room where ECG registration is carried out, the following conditions must be met: it must be located far from sources of electrical interference, the couch must be covered with a blanket with a metal grounded mesh.
Why is electrocardiography performed?
Electrocardiography is one of the mandatory points of any planned medical examination. All patients, even in the absence of complaints and symptoms, must be periodically diagnosed, as this allows possible health problems to be detected in a timely manner and treatment can be started immediately.
In patients with cardiovascular diseases, electrocardiography should be performed more often to monitor heart function and well-being, as well as assess the quality of therapy.
The method is used regularly if the patient has problems with blood pressure, obesity, or irregular heart rhythm.
Options
List of parameters determined by electrocardiography:
- Potassium imbalance.
- Magnesium imbalance.
- Heart rate.
- Zones of necrosis.
- Possible disturbances in the blood supply to the myocardium.
- Thickening of the walls of the heart.
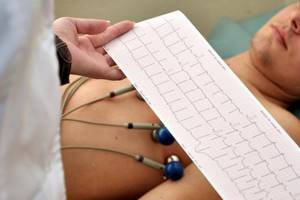
Preparing for electrocardiography
- The specialist must save the necessary personal data of the patient, indicating the date and time of ECG registration, as well as the medical history number.
- Preparation involves positioning the patient correctly during the procedure and connecting the electrodes. The patient should lie down on the couch. In rare cases, for certain illnesses or injuries, a sitting position is acceptable.
- After the patient is in the desired position, the nurse will clean the areas of the skin where the electrodes will be attached. To do this, she uses a special degreasing agent.
- Each electrode is treated with sodium chloride solution. A special gel is applied to them to improve conductivity.
What is meant by leads?
Schemes that record differences in indicators are usually called “leads”. During electrocardiography, a specialist monitors the work of the heart in different leads on a graphic image. It is customary to consider standard leads, enhanced leads and chest leads.
Standard leads:
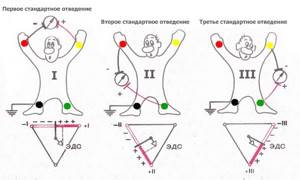
- I standard lead - the difference in potentials on the right and left hands.
- II standard lead - the difference in potentials on the left and right legs.
- III standard lead - difference in potentials on the left arm and left leg.
Reinforced leads:
- AVL (left hand).
- AVF (left leg).
- AVR (right hand).
Chest leads – 6 leads V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6.
Correct fixation of electrodes
When conducting electrocardiography, electrodes are used for fixation on the lower and upper extremities, as well as electrodes for the chest. The quality of perception of electrical impulses depends on the quality of the location of the electrodes on the patient’s body. Therefore, the algorithm of actions should be as strict as possible.
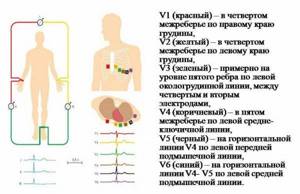
Electrodes for standard leads have special colors:
- Right hand – red electrode.
- Left hand – yellow electrode.
- Right leg – black electrode.
- The left leg is a green electrode.
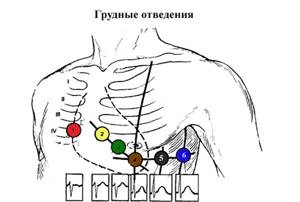
After fixing the electrodes on the limbs, electrodes are applied to certain areas of the patient’s chest:
- Electrode V1 is the area at the level of the fourth intercostal space on the right side of the sternum.
- Electrode V2 is the area at the level of the fourth intercostal space on the left side of the sternum.
- Electrode V4 is fixed earlier than V3. Electrode V4 should be attached in the area of the fifth intercostal space on the left side, taking into account the midclavicular line.
- Electrode V3 is the area between electrodes V2 and V4.
- Electrode V5 is the area of the fifth intercostal space, taking into account the anterior axillary line.
- Electrode V6 – area at the level of the fifth intercostal space (in the center of the axillary line).
Holter (24-hour) ECG monitoring – complete instructions for the patient
Pulling behind the sternum? Rapid heartbeat or slow pulse? Do you experience a fluttering feeling in your chest? How can a modern method of heart research, Holter ECG monitoring, also known in common parlance as Holter, help in such cases?
To find out this, we visited an appointment with a general practitioner, cardiologist at the Expert Voronezh Clinic, Angelina Anatolyevna Kalinina.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, what is Holter monitoring and why is it prescribed?
Holter ECG monitoring or, in other words, daily monitoring of heart function is a method of electrophysiological instrumental diagnostics that allows continuous recording of an electrocardiogram using a special device.
This method is used in clinical practice in the field of cardiology, therapy to identify disturbances in the rhythm and conductivity of the heart, ischemic changes (especially with contraindications to the so-called “stress tests” - for example, bicycle ergometry), as well as for monitoring and control in the treatment of rhythm disturbances and coronary heart disease.
You can sign up for Holter monitoring here
— What symptoms of the cardiovascular system are an indication for Holter monitoring?
These are spontaneous, inexplicable episodes of loss of consciousness, dizziness, especially without any obvious reason (staying in a stuffy room, excitement, etc.); any sensations of heart rhythm disturbances (rapid or rare pulse; interruptions, “freezing”, “tumbling” in the heart area; shortness of breath, chest pain; night awakenings, especially accompanied by shortness of breath, breathing problems).
A leading neurologist talks about the possible causes and diagnosis of dizziness
"Clinic Expert Kursk" Umerenkova Natalya Vladimirovna
The study is also advisable if the patient or his relatives have a certain heart pathology (including hereditary pathology), and it can be carried out even in the complete absence of complaints. These are diseases such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, long QT syndrome, short QT syndrome, and ventricular preexcitation syndromes. Additionally, Holter ECG monitoring can be prescribed to evaluate the performance of an artificial pacemaker after a myocardial infarction.
— Is this diagnosis carried out only for adults? Or do children also undergo a daily ECG?
Of course, Holter monitoring is also used to examine children. Of course, the child’s adequate and conscious behavior is important (following any doctor’s instructions during the study, avoiding unintentional breakdown of the electrodes or damage to the device, etc.). Those. These are organizational and technical aspects. In principle, there are no obstacles to researching children.
— How does Holter monitoring differ from a simple ECG? Why is a regular ECG not enough?
The fundamental difference is the likelihood of detecting some pathological abnormalities. It is incomparably higher during Holter monitoring. It often happens that a doctor, during an objective examination of a patient, clearly records rhythm disturbances, but there is nothing on the ECG. The problem with an ECG in such cases is the short duration of the study and the absence of a person’s usual load (for example, walking). Rhythm disturbances, especially if they are unstable, may not “get” on a regular ECG purely statistically.
Heart, why don't you want peace? What causes tachycardia? Cardiologist says
"Clinic Expert Kursk" Novikova Elena Viktorovna
— Patients often ask questions: what is better: Holter monitoring or cardiac echo, Holter or cardiac ultrasound? Tell us, is there an alternative to the method of daily ECG monitoring?
Holter does not have an alternative that is identical in terms of capabilities. The fact is that echocardiography and Holter monitoring evaluate different aspects related to the structure and function of the heart.
Ultrasound allows you to “see” the structure of the organ, its parts (chambers, valve apparatus), their sizes, the presence of some structural features, functional characteristics associated with the operation of the valves, the movement of blood and the walls of the heart. However, it will not say anything about the type of heart rhythm disturbances, possible myocardial ischemia, which is especially important - outside of a state of rest.
Holter monitoring answers these questions. On the other hand, Holter will not help in any way to evaluate, for example, the valve apparatus, or to determine the presence of defects or blood clots in the cavities of the heart.
When is it prescribed and what will a heart ultrasound show? Read more
Therefore, these studies are not mutually exclusive, but complementary, and to complete the picture, it is recommended to perform both diagnostics.
— Are there any contraindications to Holter monitoring?
There are no such restrictions, rather restrictions. There may be, for example, some difficulties when applying electrodes (severe deformation of the chest, acute inflammatory processes on the skin in this area); mental disorders and corresponding behavior, which may create a risk of incorrect data collection or damage to the device, leading to inaccurate keeping of the research diary; You may be allergic to the adhesive plaster used to secure the electrodes.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, how to properly prepare for a daily ECG?
No special preparation of the patient for daily ECG monitoring is required. If a man has thick hair on his chest, it is recommended to shave it off where the electrodes are applied for optimal contact of the electrodes with the skin.
— How is the Holter monitoring procedure performed?
The person arrives at the appointed time. Several electrodes are placed on his chest, fixed and connected with wires to a portable recording device.
For additional support of the electrodes, a cotton T-shirt or T-shirt is put on top, tightly fitting to the body.
The person is given instructions, including how to keep a diary, and is released for a day. A day later he returns, the device is removed and the data is decrypted.
— Please give an example of how to correctly fill out a Holter monitoring diary?
First of all, it describes what the patient did during the entire study period and his physiological state. The time of sleep, wakefulness, physical exercise, walking, running, eating and taking medications (as agreed with the attending physician, with the name of the drug), driving, emotional stress (even quarrels, etc.) are noted. The exact time of occurrence of complaints is recorded: pain of any localization with its nature (dull, squeezing, stabbing, burning, etc.) and duration; feelings of tightness in the chest; palpitations or rare pulse, “fading” of the heart; episodes of weakness; dizziness, etc. It is very advisable to indicate under what circumstances the complaints appeared (during exercise or at rest, after emotional stress, etc.), how they went away (after stopping the exercise, taking medication, calming down, etc.).
In other words, the more detailed the diary, the more valuable information the doctor will receive.
— Does the patient need to take sick leave during 24-hour monitoring?
No, it is not issued.
— What can and cannot be done under any circumstances while wearing a Holter monitoring device?
The rules for wearing a halter are relatively simple, but at the same time important.
It is possible and advisable to wear a tight-fitting cotton tank top or T-shirt to ensure that the electrodes adhere more closely to the skin.
At night, do not remove the device, choosing a comfortable position in bed.
If the electrode comes off, call your doctor or nurse immediately and wait for further instructions.
Do not wet the electrodes (showering, swimming). It is undesirable to be in an area with electromagnetic radiation (microwave oven, etc.). You should not carry your mobile phone in your pocket or talk on it for a long time.
Otherwise, you can lead your usual lifestyle, with the possible exception of active sports.
— Is it possible to use a computer for Holter monitoring?
This is not desirable, at least not for long.
Other
Lead registration
When registering standard leads, the location of the electrodes should be as follows:
- First standard lead: right hand (-), left hand (+).
- Second standard lead: right arm (-), left leg (+).
- Third standard lead: left leg (+), left arm (-).
The patient should be at rest. The specialist asks him not to be nervous and not to move. Then the ECG is recorded in leads I, II and III, followed by recording in the enhanced and chest leads. In this case, at least 4 cardiac cycles are recorded in each lead.
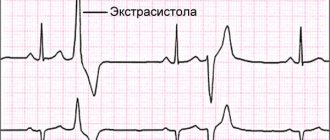
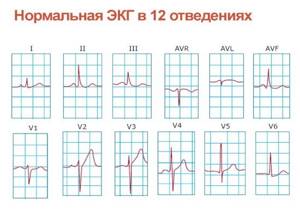
How to interpret an ECG?
One of the purposes of electrocardiography is to obtain an electrocardiogram, a special graphic image with a broken curve and sharp peaks. The peaks (or spikes) are located above the horizontal line on the graph.
They indicate the depth and frequency of rhythm changes. When deciphering the results of ECG registration, the spaces between these teeth are of great importance. They are designated in the electrocardiogram by letter combinations: “TP”, “QRST”, “TP”.
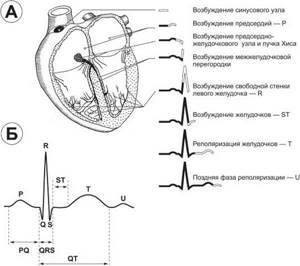
The recovery phase between muscle contractions is designated “T” on the graph. Atrial excitation and depolarization are indicated by the letter “P”, the recovery cycle of the ventricles is indicated by the letter “U”, and ventricular excitation is indicated by the letters “S”, “Q”, “R”.
Cardiogram of a healthy patient
The specialist focuses on the established standards and compares them with the indicators of the obtained cardiogram. If the patient’s health is good, the cardiogram should display the following parameters:
- QT – no more than 450 milliseconds.
- P – positive.
- EOS – not rejected.
- S – negative, below the R wave.
- T – positive.
- Q – negative.
- Heart rate – from 60 to 80.
- QRS is about 120 milliseconds.
Possible deviations
The specialist must determine the distance from one R wave to the other.
- If there are differences in distance between the R waves, this may indicate that the patient has a cardiac arrhythmia.
- Low heart rates may indicate bradycardia.
- If there is no P wave, the pacemaker has changed.
- If the heart rate is rapid, tachycardia is suspected.
- If the number of gastric complexes is above 105, this is a sign of tachycardia.
- But if the number of gastric complexes is below 60, then this is a sign of bradycardia.