Development of teeth in the embryonic period and after birth
At the 6-7th week of embryogenesis, the first signs of teeth appear. At the time of birth, the crowns of the central incisors are formed in the child, the crowns of the lateral incisors are not fully formed, half of the crown of the canines is present, as well as the chewing surfaces of the remaining teeth. Many surfaces have incomplete mineralization.
In each jaw of a newborn there are 18 dental follicles, including 8 permanent and 10 temporary. They all have different degrees of mineralization. By about five years of age, the growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth is activated and the process of physiological resorption of the roots of baby teeth begins. Against the background of these changes, a change in bite begins - temporary to permanent.
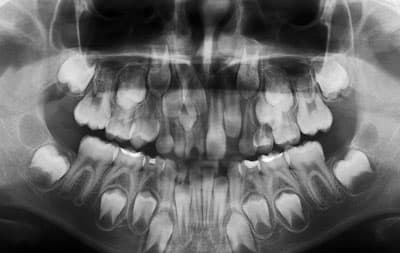
X-ray of baby teeth
Every doctor will confirm that without diagnosis it is almost impossible to select adequate treatment for any organ and system of the human body, and the oral cavity is no exception. However, it is not always possible to fully assess its condition using an external examination, because this method allows you to see only the external periodontal tissues and enamel. In modern dentistry, just like several years ago, radiography remains one of the most informative diagnostic methods. It can be prescribed not only to an adult, but also to a child to determine the condition of baby or permanent teeth.
What happens during a dental x-ray
During the examination, a film or a special sensor is applied to the area indicated by the doctor and X-rays are sent. They pass through tissue, weakening on denser structures. The resulting image is recorded on an X-ray sensitive film or electronic matrix. This way, a clear picture of the examined area is obtained, which shows not only the outer coverings of the oral cavity, but also the deep tissues, tooth roots, etc.
Types of X-rays of children's teeth
In modern dentistry, the following types of x-ray examination of the oral cavity are used.
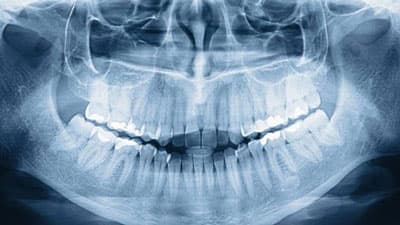
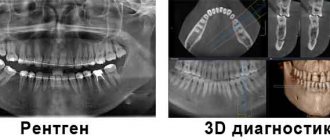
Panoramic photo (orthopantomogram)
. This is an image that covers the entire oral cavity and even adjacent parts of the skull, such as the maxillary sinuses. An orthopantomogram allows you to get a general idea of the condition of the entire oral-maxillary apparatus. Such research is indispensable when carrying out implantations, flap operations, surgical and orthodontic treatment.
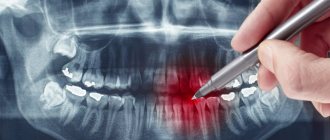
Sight shot
. This type of examination can help examine in detail a specific area of the mouth, such as one problem tooth, its roots and surrounding tissue. A targeted x-ray of a baby tooth allows you to better examine its condition, determine the source of the pathological process, and its location. The method is important not only during diagnosis, but also during the treatment process to control its quality.
A snapshot of a bite
. Thanks to this examination, it is possible to photograph individual areas of the jaw (4 or more teeth). Bite photography can be used as an auxiliary method to detect tartar or caries in hard-to-reach areas.
Today, dental radiography involves the use of high-resolution digital equipment. Such equipment allows you to obtain a clear image with the possibility of its detailing and, accordingly, better diagnostics. In addition, in this case, images can be processed on a computer (to improve their quality, contrast, brightness), and also saved on electronic media or transmitted via the Internet, if the opinion of another specialist is required.
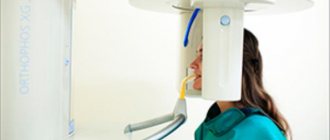
How is a dental x-ray performed?
The procedure for obtaining a panoramic, bitewing or targeted X-ray of a tooth is quite simple and usually does not take much time. Before undergoing it, it is necessary to perform oral hygiene to remove food debris. The person being examined wears a special apron that protects the body from x-ray radiation. Then the patient’s head is fixed in the desired position, the examined area is scanned and an image is formed. During the procedure, the patient must remain motionless, otherwise the x-ray will be distorted.
To clarify prices for dental x-rays at Martinka Dentistry in Moscow or to sign up for a procedure, please contact our help desk by phone listed in the “Contacts” section.
Features of the shadow picture of temporary teeth
On x-rays, the roots of primary teeth are shorter and the bifurcation angle of molars is greater than that of permanent teeth. The root canals are wider, and the dental cavity is larger in volume. The size of the periodontal gap in a child may vary, and this is considered a normal variant.
The dental follicle appears on an x-ray as a rounded clearing and has a clear rim of compaction. In its cavity there is a rudiment, which changes at different stages. First, points are visible along the cutting edge, which gradually form a single contour of the crown.
Types of X-rays at the Anderson Clinic
Modern digital radiography used in our clinic is a painless and safe procedure that allows a detailed examination of the entire maxillofacial area of the patient. There are 2 main types of radiographs, differing in the area of the studied zones.
Sight shot
Concentration on one or several adjacent teeth is ensured by the so-called targeted image, and is carried out on a visiograph - a component of X-ray equipment that displays the image on the monitor.
Indications for prescribing a targeted X-ray:
- caries diagnosis;
- diagnostics of the general condition of teeth;
- detection of pulpitis or periodontitis;
- identification of inflammatory processes in soft tissues;
- recording and monitoring treatment results.
What unformed root tips look like on an x-ray
In unformed tips, the length of the root is almost normal, the walls are parallel to each other. The wide root canal ends in a funnel-shaped extension. In the area of the apex, the periodontal fissure merges with the growth zone, which incompetent specialists sometimes identify as a pathology.
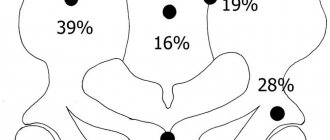
Throughout the entire length of the root and at the apex, a compact plate of the socket wall is differentiated. This picture is typical for the upper central and lateral incisors in 8-year-old children, for the lower central incisors in 6-year-old children, as well as for the lower lateral incisors and first lower molars in 7-8 year old children.
Types of x-rays when examining children
Depending on the goals of the study, there is a need to obtain one or another type of x-ray. Among them:
- targeted radiographs - show one or a pair of teeth and nearby soft tissues;
- panoramic image of the jaw - displays a picture of the dentition along with the rudiments of the radical elements;
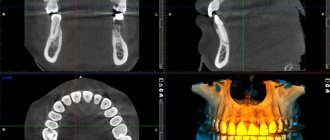
- 3D images are three-dimensional images of the entire jaw (upper, lower row) or a section of it.
The difference between panoramic and targeted radiographs
The difference between a panoramic X-ray and a targeted X-ray is the area of study. In the first case, the object of study is the jaw row, in the second - a specific area of the child’s gums, jaw or oral cavity.
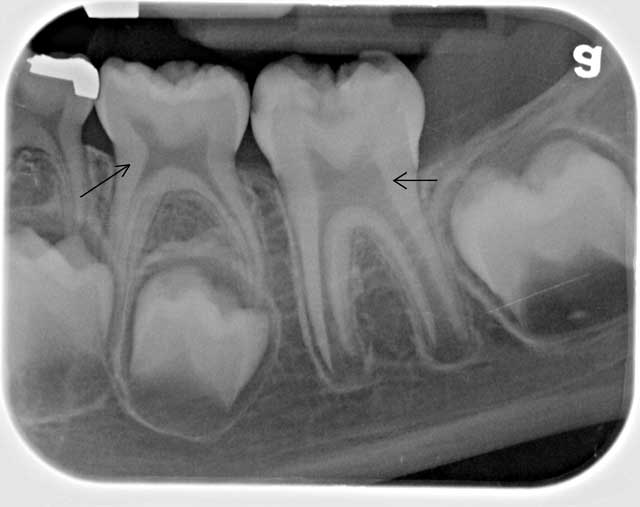
Sight shot
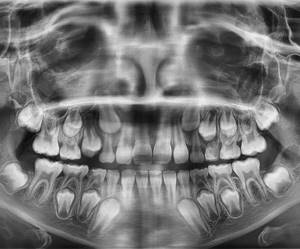
Panoramic shot
In the process of targeted radiography, the beam tube is brought closer to the soft tissues. A successful shot shows one or two elements adjacent to each other.
3D modeling in negative
We are talking about a procedure carried out using innovative equipment that allows one to obtain a 3D image of the jaw row or its area. Such an image helps to determine the location of pathological canals, areas of the root system, and fillings. A study is scheduled on the eve of endodontic therapy and implantation.
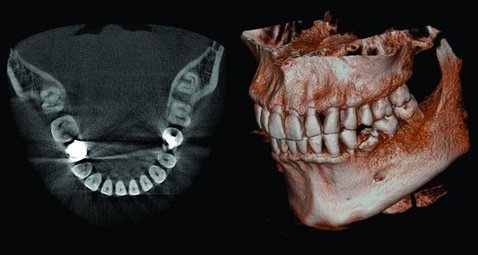
3D
Situations when taking photographs is strictly prohibited
Such situations practically never occur. On an individual basis, X-rays are considered in cases where the patient receives radiation in other areas of life: for example, in hazardous work, while undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy. But again, when X-raying the state of the jaw system, the radiation is so small that it will not affect the overall picture.
Thus, you should not be afraid to take photographs - in single quantities they are quite acceptable and will not affect your health at all.
It is important to understand that such diagnostic procedures allow for better treatment, especially with dental implantation, the results of which will last not a couple of years, but for many years of life. 1 Sanitary rules and regulations (SanPiN) 2.6. 2.6.1.1192-03 for the design and operation of X-ray rooms, devices and the conduct of X-ray examinations.
Is it dangerous to take pictures?
According to SanPiN1, when performing X-ray procedures for preventive purposes, radiation exposure should not exceed 1000 microsieverts (µSv) per year. We are talking specifically about prevention, since for medicinal purposes the indicator can be much higher.
In terms of the number of shots it looks like this:
- 500 targeted shots (1-3 µSv),
- 80 OPTG (13-17 µSv),
- 20 digital CT scans (50-60 µSv).
For comparison, here is a table that shows the radiation doses that a person receives during diagnostic procedures in dentistry, in other areas of medicine and in life in general. The last table shows parameters that are truly dangerous to the body and can be fatal.
| In dentistry | In other areas of medicine | In life | Dangerous indicators |
| 1-3 μSv – one targeted shot | 30-60 µSv – one digital fluorography, 150-250 µSv – old type film FOG | 5 µSv – 3 hours in front of a computer or TV | 750 thousand µSv – minor changes in blood composition |
| 13-17 μSv – one panoramic image (OPTG) | 500-700 µSv – one mammography procedure | 20-30 µSv – one 2-3 hour flight | 1 million µSv – mild radiation sickness |
| 50-60 μSv – one CT procedure in dentistry | 2000 μSv – one head CT procedure | 2000-3000 μSv – natural dose of radiation per person per year (food, solar radiation, air) | 7 million µSv – lethal dose of radiation |
As can be seen from the table, irradiation can cause harm (minor and short-lived) only when a dosage of 750 thousand µ3V is reached, while only one thousand µ3V is allowed for diagnosis. Therefore, 20 CT images or 80 panoramic images will not cause any harm to the body.
What does a dental x-ray show?
Implantation, prosthetics, sinus lifting, root canal treatment - all these operations are impossible without x-rays. It is necessary to take a photo of your teeth to assess the condition of the bone tissue, check the filling of the canals (photo of the roots of the teeth), and identify the development of hidden caries, which can appear under a filling, crown, or in the interdental spaces. An X-ray of the tooth also shows the condition of the periodontium (tissue around the root of the tooth) and periodontium (tissue around the entire tooth), cracks or inflammation of the canals. With the help of x-rays, the dentist can make an accurate diagnosis, especially if the patient's complaints and symptoms suggest several diseases or no obvious destruction. In this case, the dentist will not have to drill at random, which will save the patient from unnecessary painful manipulations.