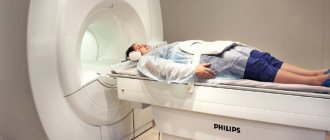
MR scanning of the abdominal cavity Magnetic resonance imaging is used to diagnose pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) and other abdominal organs. The advantages of the MRI procedure are non-invasive, painless and harmless. Many patients ask the doctor to replace fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) with a more comfortable MRI scan. This is possible in some cases.
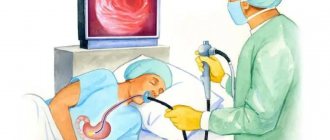
FGDS is used to identify pathologies of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. The research technology involves inserting a probe into the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth, which is unpleasant for the patient. People do not like the procedure because of the gagging that occurs during the process of swallowing the endoscope.
Magnetic resonance imaging does not cause any discomfort and is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods. But despite the high accuracy of the results, it cannot replace invasive examination of the digestive organs. What is better is FGDS or MRI of the stomach, the specialist leading the patient decides.
Indications for the procedure
There are a number of indications for magnetic resonance imaging of the stomach that are directly related to diseases and symptoms.
Stomach ulcer
This disease can be prevented if a procedure such as an MRI of the stomach is performed in a timely manner and the right diet is chosen already at the stage of gastritis.
Chronic or acute gastritis
One of the most common stomach diseases - gastritis - after some time can become chronic and develop into an ulcer. This can be avoided if you undergo a timely examination of the stomach and esophagus using magnetic resonance imaging.
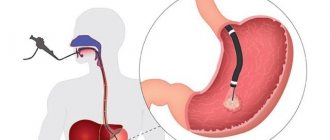
Stomach cancer
MRI of the stomach allows you to get clear and clear images, thanks to which you can identify tumors with 100% accuracy.
Esophageal spasm
This rather painful process can occur not only due to a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, but also due to the presence of concomitant diseases. An MRI of the esophagus shows what is causing the unpleasant symptoms. Doctors recommend undergoing a tomography examination to be sure of the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Diaphragmatic hernias and more
It is not always possible that a routine examination and questioning by a general practitioner allows one to make the most accurate diagnosis, so one has to resort to various diagnostic methods that can show a clear picture. The same is the case with diaphragmatic hernias. Experts recommend examining the stomach and esophagus using MRI.
FGDS
FGDS is one of the most informative methods that should be used specifically to determine the current state of the intestines. During the examination, a special probe with a camera installed on it is used.
When performing an FGDS, it is possible to examine the esophagus, check the condition of the stomach, and also take various types of biological material for testing.
There are many symptoms that indicate that a patient needs to undergo an FGDS. These include heartburn, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, belching, severe weight loss for no particular reason.
Typically, FGDS is prescribed by gastroenterologists based on the results of data obtained by other diagnostic methods. These include data such as ultrasound data of the abdominal organs, stool, urine, and blood tests.
The method helps to accurately determine the presence of many types of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as to find signs of the presence of Helicobacter in the human body.
It is worth remembering that many patients try not to use FGDS due to the fact that the procedure itself causes severe discomfort. A long tube is inserted into the mouth - this provokes panic and a strong gag reflex.
There is a possibility of damage to the esophagus, as well as many other potential problems. For this reason, if symptoms permit, many choose an MRI.
How to prepare for an MRI examination?
This procedure does not require special preparation. Your doctor will recommend that you stop eating and drinking immediately before the test. To obtain the most accurate result, it is recommended to limit yourself in the consumption of tea, coffee and flour products a few days before the procedure. The tomograph creates a special magnetized field, as a result of which before the procedure it is necessary to remove jewelry and metal objects, glasses, piercings, watches, belts, remove your mobile phone, flash cards, coins, bank and transport cards from your pockets. Females are advised to limit themselves to minimal makeup, as some products contain metal particles.
How is it carried out?
Fluoroscopy begins with the use of a contrast agent. Next, a vertical study , which allows one to evaluate the passage of barium suspension through the stomach and its distribution in the folds. After this, the patient is asked to take a horizontal position in order to study the pneumorelief and the duodenal bulb. To study the stomach under conditions of complete filling, the doctor asks you to drink barium sulfate in one gulp.
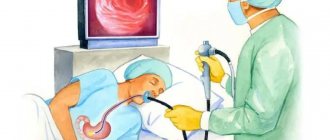
When performing an FGDS, the patient swallows a special flexible endoscope and lies on his left side. With the help of swallowing movements, the probe is advanced to the stomach, after which air is pumped to straighten the walls of the stomach. After removing excess mucus, an examination of the entire mucous membrane of the walls, as well as the duodenum, begins.
Important Lidocaine is used to reduce the gag reflex and reduce sensitivity. This is the only drug that can cause allergies.
Carrying out the procedure
Before starting the procedure, the doctor explains the entire examination process to the patient, talks about the rules and contraindications. Next, the patient lies down on a special table, which then smoothly moves into the tomograph. To obtain the most accurate results, you should remain calm and still. Often, during the examination, the stomach walls are straightened by slightly stretching with the help of an iron-containing solution, which is prescribed to the patient and relieves pain. Sometimes a specialist administers intravenous contrast, shows the most clearly needed areas, and this does not cause any discomfort.
Examination using CT or gastroscopy. What to choose?
A good mood, a cheerful state - all these are signs of a healthy person, but what to do if you are suffering from stomach pain? To identify the cause of the discomfort, of course, you need to immediately visit your therapist, who will prescribe the accompanying tests. Unfortunately, the palpation method does not guarantee the correct diagnosis, so the doctor may prescribe a CT scan of the stomach or gastroscopy.
A CT scan of the stomach is the fastest diagnostic procedure, with which you can obtain maximum information about your organ. The examination is based on the passage of X-rays through the patient's body. They are sent to special sensors and take snapshots, after which the computer processes them and turns them into a 3D image. During the procedure, you cannot move; complete immobility is necessary, since the slightest movement can spoil the analysis result. The patient is placed on a moving table-couch, and the diagnostician directs the gantry to the anatomical part of the human body being examined. Pictures are taken from different angles and perspectives, thanks to this the doctor will be able to prescribe the correct treatment for you. The procedure takes about 20 minutes; if a contrast study is prescribed in the referral, then the diagnostic time will increase to 50 minutes. The cost of a CT scan of the stomach will be much less than that of an abdominal CT scan due to the smaller diagnostic area. The following symptoms are indications for such an examination:
- Pain in the stomach area;
- Frequent heartburn;
- A sharp decrease in body weight;
- Suspicion of gastritis, peptic ulcer;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Sourish or bitter taste in the mouth;
- Heaviness in the stomach;
- Various neoplasms;
- Inflammation;
- Identifying causes of bleeding;
- To control treatment;
- Any abnormal processes in the stomach.
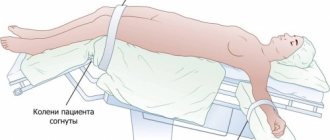
Exactly the same indications apply to gastroscopy. This diagnostic method uses an endoscope. It has a camera and a cold light bulb. With it, the doctor can monitor the condition of the stomach in real time. The device is inserted through the oral cavity, with the patient lying on his side and bending his knees. During the procedure, anesthesia is given, but this does not prevent the gag reflex. The study takes about 5 minutes.
Only your doctor decides which method of diagnosing the stomach to use, based on your body characteristics. Basically, computed tomography is prescribed because it is painless and informative. It shows not only the internal state of the organ, but can also provide information about nearby soft tissues and bones. Also, thanks to it, it is possible to visualize malignant and benign tumors and foreign bodies. Registration for the procedure is carried out on our website “link”. With gastroscopy, it is possible to remove a foreign body, eliminate bleeding, take tests to diagnose gastric juice, or remove polyps; tomography certainly cannot do this.
Contraindications
Many medical diagnostic methods have contraindications, and MRI of the stomach is no exception.
Pregnancy, lactation period
MRI during pregnancy must be agreed upon with your doctor. Pregnancy is not a strict contraindication, but it is not advisable to carry out this diagnosis before 12 weeks, since during this period the organs of the unborn baby begin to form. The lactation period is also not a contraindication for MRI of the stomach. You should not be afraid of the effect of contrast on breast milk, since the time it takes to be removed from the body is no more than 2-3 days.
Presence of foreign metal objects in the body
Patients should definitely inform the specialist about the presence of foreign metal or electronic objects in the body, such as pins, prostheses, implants, etc. They may distort the results or fail. It is possible that such objects may cause injury to the patient during the examination.
What it is?
X-ray of the stomach is an instrumental technique for examining the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, which may be accompanied by the introduction of a contrast agent. A double contrast study can also be used, when additional air injection is performed. The substance that acts as a contrast is barium sulfate.
FGDS is a method of examining the gastrointestinal tract using a special device - a gastroscope. A gastroscope is a special device with a lighting device at the end. Modern devices have a camera that transmits the image to a computer screen.
CT scan of the stomach: price in Moscow
The cost of CT scan in Moscow depends on many factors:
- Clinic locations.
- Equipped with modern equipment.
- Doctor's qualifications.
- Areas of research.
- From the presence or absence of contrast.
A CT scan of the stomach in Moscow can be performed at a price of 3,200 rubles and more, depending on the reputation of the clinic and the equipment used. You can also undergo computed tomography at a low price during the promotion and through a system of discounts on services.
The process of gastroscopy
This procedure is performed only by an experienced endoscopist under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. A gastroscope is a thin, flexible and smooth tube (5 to 11 mm in diameter) with a lens or optical camera at the end. The tube is inserted into the patient's mouth and then into the esophagus. If desired, local anesthesia of the pharynx is performed, and the examination can also be performed under anesthesia (during sleep).
The doctor makes observations and records the examination. The use of a gastroscope allows, simultaneously with diagnosis, to take tissue samples for biopsy, remove polyps and foreign objects that have entered the esophagus.
The entire procedure lasts from 3 to 15 minutes; experienced doctors have no complications or consequences after the examination.
To prepare for the examination, you must not eat for 8-10 hours before the procedure, and you also need to warn the doctor:
- about the presence of certain diseases, such as diabetes;
- about the presence of drug intolerance and taking any medications;
- about blood pathologies (for example, low coagulability);
- about the presence of heart pathologies, pregnancy or epilepsy.