- The first thing the gynecologist pays attention to during an external examination is the swelling of the genital organs. During pregnancy, due to increased blood circulation, the labia minora and majora lose their elasticity and become dense.
- The second sign of pregnancy is a change in the color of the internal genital organs. The vaginal walls take on a dark red or purple hue. The mucus released from the cervical canal becomes viscous and transparent.
- Then the doctor examines the cervix, appendages - fallopian or fallopian tubes, ovaries. During pregnancy, these organs enlarge and change their shape, so by palpation (manual examination) pregnancy is easy to determine.
- Next, the condition of the posterior vaginal vault is checked. Before pregnancy, the posterior vaginal vault has the shape of a retracted vault, and with the onset of pregnancy it becomes smooth.
Even during pregnancy, changes occur in a woman’s mammary glands.
Under the influence of hormones, the breasts begin to prepare for lactation (the process of feeding a child), more milk ducts are formed in it and the breasts increase in size. You should know that during an examination, a gynecologist can determine pregnancy, which is at least the fifth week, and to determine the onset of pregnancy earlier, an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) should be performed.
Pregnancy: where it all begins
Pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, or 280 days, from the first day of the last menstruation. Most women have a menstrual cycle of 28 days. However, the normal range extends from 21 to 35 days in adult women.
Pregnancy calendar - all information by week in one place
Between the 11th and 21st days of each menstrual cycle, the female body undergoes the process of ovulation, which can potentially lead to pregnancy. During ovulation, the egg released by the ovary moves down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. At the same time, the endometrium (mucosal surface) of the uterus is preparing to accept and support a future pregnancy: it thickens and its blood supply increases.
The uterus will remain in such readiness for about 14 more days. If the egg does not meet the sperm, it continues on its way to the uterus alone. In the absence of a fertilized egg, the uterus gets rid of the extra layer of endometrium along with the egg, and menstruation begins.
If the egg and sperm meet and fuse, pregnancy occurs.
Even though the egg has already been fertilized, it will take several more days before a home pregnancy test can show a positive result. This depends on the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) produced by the fertilized egg.
The hCG hormone tells the ovary that fertilization has occurred and maintains blood flow to the uterine lining so that the fertilized egg continues to develop.
The presence of the hCG hormone in the urine or blood directly indicates that pregnancy has begun. This can be confirmed at the very initial stage by urine tests (home pregnancy test) and blood tests (from a vein, laboratory test).
After establishing the fact of pregnancy, you yourself, and even more so your doctor, need to determine its duration. How it's done?
Why is it dangerous?
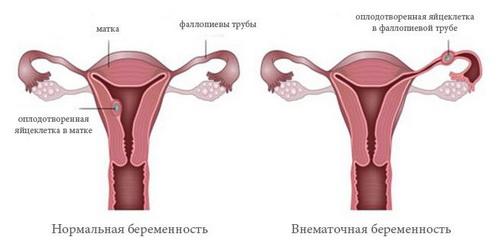
Why is ectopic pregnancy a dangerous pathology? This is due to the unnatural location of the fertilized egg, which can cause the size of the fallopian tube to increase. In such cases, it is necessary to promptly identify signs of deviation, since the pipe shell may become damaged or even rupture over time. As soon as this happens, the fertilized egg and mucus with blood will enter the patient’s abdominal cavity, which, in turn, will lead to the development of peritonitis.
On a note!
Ectopic pregnancy, or rather the lack of treatment, can also lead to severe internal bleeding. In this case, urgent hospitalization is required, and therapy will be carried out only in intensive care conditions.
The same symptoms may occur with the development of an abdominal or ovarian form of ectopic pregnancy, in which the risk of peritonitis and other serious complications is still very high.
How is gestational age determined?
Conception usually occurs two weeks after the start of the next menstrual cycle. To calculate the gestational age and calculate the approximate date of birth, obstetricians count 40 weeks from the first day of the last menstrual period.
To maintain a pregnancy calendar, obstetricians are guided by just such a reference system, in which the weeks are called “obstetric” and “advance” the actual pregnancy by 14 days. The actual pregnancy occurs on the date of conception.
The reason why obstetricians use their own scale for calculating the duration of pregnancy is simple: due to the fact that the cycle of different representatives of the fair half of humanity can vary greatly in duration, it can be difficult to determine the exact date of conception. Calculating the timing of pregnancy and the date of birth from the first day of the last menstruation in this case is a more reliable method.
You can calculate your expected due date yourself. Use Naegele's formula: count back 3 months from the first day of your last menstrual period and add 7 days. Any pregnancy calculator you find online will be based on this exact formula.
In the future, the physical development of your unborn child, data about which can be obtained using a number of studies (including ultrasound), may make slight adjustments in determining the date of birth, but obstetricians’ forecasts are sometimes surprisingly accurate.
Ultrasound and doctor's examination
The doctor will be able to determine pregnancy, or rather, detect the fertilized egg, using an ultrasound examination with a transvaginal sensor approximately 5-6 days after the delay of menstruation or 3-4 weeks after fertilization. This method is considered the most reliable, although this study is usually prescribed at a later date. Without an ultrasound, during an external examination at the earliest stage of pregnancy, the doctor will be able to determine pregnancy.
History of contraception Ancient times One of the first mentions of a condom as a means of protection in antiquity - approximately 3000 BC. In Cretan... Read more
HIV infection: causes and symptoms of infection What is HIV infection HIV infection is a disease caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This virus is slowly...
More details
Intrauterine Device An intrauterine device is a small plastic device that is inserted inside the cervix and provides contraceptive…
Read more
1st month of pregnancy
1st week of pregnancy
Main event: menstruation.
2nd week of pregnancy
Main event: ovulation.
In fact, in the first and second weeks you are not yet pregnant.
The days of your last menstrual period and ovulation count as the first two weeks of your pregnancy, even taking into account the fact that the new life inside you has not yet been born.
3rd week of pregnancy
Main event: fertilization.
This is the week when pregnancy really begins.
The sperm and egg meet and fuse together in one of the fallopian tubes. The fertilized egg is called a "zygote". If more than one egg is fertilized, the pregnancy will be multiple (two children or more).
A normal zygote consists of 46 chromosomes: 23 chromosomes from you and 23 from your father. Chromosomes determine the sex of the unborn child, which depends on the sex chromosome of the father: if the sperm carries a Y chromosome, a boy will be born, if the X chromosome carries a girl.
More about the 3rd week of pregnancy
Chromosomes also determine such characteristic features as eye and hair color, hereditary psychotype, behavioral characteristics and, in a sense, the personality of the child.
24 hours after fertilization of the egg, the zygote begins to divide into two cells. Over the next 72 hours, cell division continues, resulting in a small group of cells that resembles a raspberry in appearance and is called a “morula.” During its internal fragmentation into new cells, the morula moves along the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
4th week of pregnancy
Main event: implantation.
Within about three days from the moment of fertilization of the egg, the morula reaches the uterus and penetrates it. Now the group of cells that continue to divide is called a “blastocyst.” It can be seen even with the naked eye.
The blastocyst floats freely in the uterine cavity for about two to three days, growing tiny protrusions on its surface that will help it attach to the uterine mucosa. It is surrounded by amniotic fluid - a biologically active environment that reliably protects the child and is a source of nutrients for him throughout pregnancy.
By the seventh day after fertilization of the egg, the blastocyst is ready for “implantation” - this is the name given to the process of attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus. It lasts approximately two days.
More about the 4th week of pregnancy
The blastocyst attaches to the walls of the uterus in the optimal place from the point of view of pregnancy development. This usually occurs in the area of the front or back wall.
Already by the time the egg begins to descend into the uterine cavity, the blastocyst is divided into two parts.
One part, the inner group of cells, forms the embryoblast, which later becomes the embryo.
The outer group of cells serves as a nutrient membrane - trophoblast, part of which goes to the beginning construction of the placenta.
The placenta will nourish and protect the fertilized egg, embryo, fetus and finally the unborn child throughout the entire intrauterine period of development.
Once implantation has occurred, conception can be considered complete. It is the fact of implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus and all subsequent hormonal processes in the female body that prevent the arrival of the next menstruation.
Women who know their body well or have increased sensitivity (both physiological and psychological) can already notice the first signs of pregnancy at this stage.
What changes are happening now in the female body, what new sensations may the expectant mother encounter?
How to listen to the fetal heartbeat
It is possible to assess fetal cardiac performance using:
- Ultrasound (in the early stages with an intravaginal sensor, then with a transabdominal one);
- cardiotocography (CTG);
- fetal Doppler;
- direct auscultation with a stethoscope.
Determination at home
Modern developments in the field of medical equipment offer portable devices that record fetal heart rate - fetal monitors.
This device allows you, regardless of time and place, to determine the baby’s cardiac activity or simply enjoy the sound of a beating heart.
The design of the Doppler is extremely simple:
- small-sized case with a digital display and buttons for sound control, recording and playback, which is powered by batteries;
- directly the sensor, which is connected to the base with a wire;
- headphones.
You can detect your heartbeat using a fetal monitor as early as the 12th week of pregnancy.
The cost of such devices in Russia is from 2 to 7 thousand rubles. More expensive models can transmit sound waves into the uterus. Manufacturers suggest playing slow music to calm a raging baby in the womb.
How to use a stethoscope and what it is
An obstetric (fetal) stethoscope is the simplest device for determining the functional state of a child and diagnosing fetal distress, available in every antenatal clinic.
Auscultation of the pregnant woman's abdomen is carried out from the second trimester during each visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist.
During auscultation of a pregnant woman’s abdomen with a stethoscope by an obstetrician-gynecologist, in addition to the baby’s heart sounds, the following can be heard:
- peristaltic sounds of the intestines and uterus;
- the sound of blood moving through the vessels of the umbilical cord;
- movements, fetal kicks;
- the beating of the abdominal aorta (must completely coincide with the pulse of the pregnant woman).
Reasons that make it difficult to listen to heart rate:
- significant fat layer of the anterior abdominal wall;
- attachment of the placenta to the anterior wall of the uterus;
- polyhydramnios.
Technique: the study is carried out when the pregnant woman lies on her back. Before listening, I determine the position, position, appearance and presentation of the fetus (its location in the uterus relative to the birth canal). This determines where to place the stethoscope. The heartbeat is best heard on the side of the fetal back, between its shoulder blades.
The fetal stethoscope is pressed with the wide end to the abdomen, and the other - tightly to the ear. The clarity and rhythm of heart sounds are determined, and the heart rate is calculated for 1 minute.
You can also listen to heart sounds using a standard phonendoscope.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination during pregnancy is an extremely important and reliable method for diagnosing fetal anomalies, monitoring its development, and determining delivery tactics.
This is a safe, fast, accessible and informative test for the mother and fetus, which does not require prior preparation (with the exception of a full bladder in early pregnancy).
Assessing fetal heart rate during ultrasound is most relevant before the second trimester. Next, the heartbeat is listened to with a stethoscope and CTG.
In addition to the rhythm, ultrasound examination at different stages of gestation determines:
- quantity, position and attachment of the fertilized egg;
- size, functional state of the placenta and umbilical cord;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- size, weight of the child, presence of intrauterine developmental delay syndrome;
- position, position, appearance and presentation of the fetus (cephalic, pelvic, transverse, oblique);
- all internal organs are visualized, which allows early identification of various developmental anomalies and chromosomal pathologies;
- condition of the cervix.
Data obtained from an ultrasound examination, together with CTG, make it possible to determine the biophysical profile of the fetus - an integrated indicator that most accurately predicts the possible intrauterine death of the embryo.
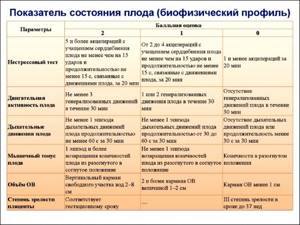
Rice. Algorithm for assessing BPP.
Further tactics directly depend on the amount of points:
- 12-8 - normal condition of the fetus;
- 7-6 - questionable result (possible hypoxia), dynamic observation, daily CTG, counting movements, Doppler measurements of uteroplacental blood flow in dynamics;
- less than 5 - severe fetal distress, threat of antenatal death of the child, immediate delivery.
Cardiotocography: description of the method and its information content
CTG is a method of assessing the condition of a child through parallel recording of the baby’s heartbeat and contractile activity of the uterus. This is an accessible, non-invasive method for early diagnosis of fetoplacental circulatory disorders and monitoring of treatment.
The monitoring result is presented on a specially plotted sheet in the form of two curves. Modern cardiotocographs are equipped with the function of mechanical recording of fetal movements.
The autonomic innervation of the heart matures by the 32nd week of gestation. Therefore, acceleration (acceleration) and deceleration (deceleration) on CTG recorded before the third trimester can only be caused by the influence of the maternal body and intrauterine conditions on the sinoatrial node.
CTG recorded after the 32nd week reaches maximum diagnostic significance in assessing the functional state of the fetus. During this period, the myocardial reflex, sleep and wakefulness patterns mature.
The CTG procedure is carried out for at least 40 minutes, since it is necessary to examine the child’s cardiac activity during the period of his activity. The baby's sleep duration fluctuates in the range of 15-30 minutes, and during this period of time the indicators will coincide with those if his condition is disturbed.
CTG can be recorded in a lying or semi-sitting position. A sensor is attached to the pregnant woman's stomach in the projection of the fetal back (for twins - one for each child), and she is given a button in her hands, which she must press as soon as she feels the fetal movements (kicks, turns, stretching). This will help you better assess heart rate variability.
Based on the CTG results, the following are assessed:
- basal rhythm (averaged heart rate over 10 minutes of measurement);
- variability (the degree of deviation from the basal rhythm) - the number and amplitude of instantaneous oscillations are calculated;
- acceleration (heart rate acceleration by 15 beats/min or more for more than 15 seconds);
- decelerations (slowing down the rhythm) - types Dip1, 2, 3.
The obtained indicators are converted into points according to Fisher's criteria (Fig.).
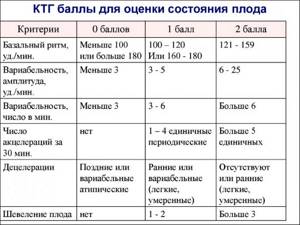
Signs of a normal CTG:
- basal heart rate 110-150/min;
- variability 5-25 beats/min;
- no decelerations;
- more than 2 accelerations in 10 minutes.
If the above criteria are met for 20 minutes, the CTG is not recorded further.
Tactics for managing a pregnant woman depending on the number of points:
- 9-12 – satisfactory condition. There is no threat to the fetus.
- 6-8 - signs of fetal hypoxia. CTG registration is carried out daily.
- 0—5—severe fetal distress, threat of antenatal death. Urgent hospitalization and delivery.
If CTG results are questionable, functional tests are additionally performed to assess the reserve capabilities of the fetal circulatory system and increase the reliability of diagnosis.
- Non-stress test (NST). Tracking changes in the fetal heart rate in response to its own movements, thereby assessing the work of the myocardial reflex and, accordingly, the baby’s nervous system. Absence of heart rate response is an indication for an oxytocion test.
- Oxytocin contractile test. Monitoring the fetal heart response to uterine contractions.
- Sound stimulation test. Using a vibroacoustic system, the doctor wakes up a sleeping baby, thereby potentially increasing his activity and the information content of the study and reducing the frequency of false-positive CTG results.
But it is worth noting that cardiotocography registers disorders only at the time of recording, and the scoring system has a reliability of about 75%. To predict the outcome of pregnancy, these data can be used exclusively in combination with other diagnostic methods.
First signs of pregnancy
- Changes in the mammary glands. Increased sensitivity of the mammary glands may occur. Some mothers experience pain when touching their breasts. Others notice that the vessels in the glands have become more visible through the skin. In addition, the color of the areolas and nipples begins to change (it becomes dark brown), and the tubercles on the nipples increase in size.
- Unusual sensations in the lower abdomen (stomach hurts and pulls).
- Slight increase in body temperature.
- Change in basal temperature.
- Decreased libido. If this worries you, don't worry, it will all come back by the second trimester.
- Increased reaction to certain smells and tastes.
- Frequent urge to urinate. Increased levels of progesterone cause increased blood flow to the uterus and thickening of its inner layer, which promotes good attachment of the fertilized egg to its wall. But this also creates a feeling of fullness and leads to an increased urge to urinate.
- Increased salivation, nausea, vomiting. These are symptoms of so-called morning sickness, which, despite its crafty name, can haunt you throughout the day and even at night.
- Lethargy, fatigue, drowsiness. In the first weeks after conception, it is not always easy to maintain the same level of activity. Now you need more and more energy for the processes occurring in your body. Fatigue may make you sleepy in the afternoon. Elevated progesterone levels act like a sleeping pill on you now.
- Fluctuations or changes in mood. The range of emotions and general emotional background is very wide - from irritability to complete peace.
- Delayed menstruation. If you usually have a regular cycle, then a delay is perhaps a fairly obvious sign of conception. If your cycle is not highly stable, then additional symptoms in the form of more frequent visits to the toilet, increased breast sensitivity and nausea will add arguments in favor of the assumption that pregnancy has occurred.
We’ll talk about the last symptom, nausea, separately.
Characteristic symptoms
A delay in the menstrual cycle is one of the main factors accompanying this pathology, therefore, if a woman experiences a delay, she should consult a doctor. But the course of ectopic pregnancy is not much different from the early stage of normal pregnancy, with the exception of some features.

The main symptoms of ectopic pregnancy that accompany a woman include:
- delayed menstruation;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloody issues;
- attacks of nausea and early toxicosis;
- hardening of the mammary glands, which are usually very painful;
- pain radiating to the lumbar region.
Many women mistakenly assume that the absence of a delay in menstruation can indicate the exclusion of the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Women often mistake bloody vaginal discharge for normal menstruation. According to experts, in approximately every fifth case, pathology can be detected even before menstruation is delayed. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis requires a complete examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis.
How to deal with toxicosis
No other symptom of pregnancy paints such gloomy colors on the first weeks of waiting as morning sickness or morning sickness in the early stages - a symptom that, unfortunately, is a faithful companion of this period in a woman’s life.
Early toxicosis during pregnancy occurs in more than half of expectant mothers. Its most striking representatives are nausea and vomiting, attacks of which usually occur in the first trimester, but some women may be bothered by these symptoms throughout pregnancy. As a rule, if toxicosis does not go away with the end of the first trimester, then by the 15th – 22nd week it still disappears.
There are several reasons for this condition - from increased hormone levels to nutritional disorders. Some chronic diseases, stress and emotional tension, characteristics of a woman’s nervous organization and other factors may also contribute.
Not all of them can be influenced by you to prevent symptoms of toxicosis or reduce their intensity. However, the arsenal of tools available to you is quite large:
- correction of diet and nutrition;
- adequate sleep and rest;
- physical activity;
- staying in the fresh air;
- avoiding smells, tastes and situations that provoke nausea and vomiting;
- snacks that help with nausea (a slice of lemon, a mint candy);
- rise slowly after waking up, preferably after snacking on a couple of crackers in bed.
We talk in more detail about ways to combat the symptoms of early toxicosis here
In addition to measures aimed at alleviating the condition due to early toxicosis of pregnant women, in the first weeks of pregnancy you need to take care of its very safety. What should you pay attention to?
Causes
There are many causative factors that prevent the normal location of the egg. These include:
- problems with the functioning (contraction) of the fallopian tubes
, as a result of which they cannot push the fertilized egg further; - structural feature of the pipe
. Sometimes it may be too scarred, tortuous or narrow, making it difficult for the egg to move; - a consequence of recent surgery
; - previous abortions
; - Slow sperm
can also trigger an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the egg, waiting for fertilization, is not able to get to the required place; - hormonal imbalance
; - the presence of benign tumors in the appendage area
. Tumors that arise in the uterine area can also lead to ectopic pregnancy; - negative changes in the functioning of the egg
(its properties change); - use of a special intrauterine device
. When wearing this contraceptive, a woman may experience problems, which ultimately leads to the described pathology; - consequences of using artificial insemination methods
; - severe stress and nervous overexcitation
, due to which the fallopian tube often spasms. As a rule, such fears most often arise due to reluctance to get pregnant.

Most of all these causes can be excluded, thereby avoiding the development of an ectopic pregnancy. Doctors recommend doing this at the pregnancy planning stage.
Precautions in the first weeks of pregnancy
- Nutrition. Rational nutrition is always important, but now especially, both for you and for your baby. Foods containing high doses of vitamins, such as eggs, meat, dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits, grains, seeds, nuts, vegetable oils, should form the basis of your diet. If you haven't been a meat and dairy eater before, know that you're in particular need of protein and calcium now. Avoid fast food, industrially processed foods such as processed foods, sausages, sausages, and confectionery. You can find out what foods are allowed and recommended for pregnant women here (https://agulife.ru/calendopedia/pitanie-i-dieta-po-trimestram-beremennosti).
- Rest and sleep. Often, a pregnant woman needs more sleep - about 8 - 10 hours. During sleep, your body begins to work more efficiently because it does not waste energy performing various functions in an active state.
- A good mood is the key to both your well-being and the normal development of your baby.
- Avoid lifting and carrying heavy objects. Physical activity and exercises for pregnant women are useful for you, but in moderate volumes and under moderate loads.
- Prenatal vitamins, especially folic acid (or vitamin B9), which can prevent some birth defects, including neural tube defects. It is recommended to start taking folic acid several weeks before pregnancy, or at least at the first signs of its onset.
- Stop drinking alcohol, nicotine, and large doses of caffeine. Otherwise, the risk of harming the normal development of all internal organs and systems of the unborn child increases.
- Avoid exposing your body to harmful chemicals, both industrial and household. Inhalation of vapors of harmful chemicals is associated with disturbances in the intrauterine development of the fetus, but it is in the first weeks of pregnancy that the formation of future organs and systems of the child’s body begins. Questions like “Can I dye my hair during pregnancy?” It's best to discuss it with a doctor you trust.
Diagnostics
As previously noted, pathological deviation can only be determined using ultrasound. During the examination, the gynecologist will look for the developing fetus in the uterus. But if an ectopic pregnancy develops, it will not be detected there. Then the doctor will continue searching in the area of the ovaries and cervix.
If you notice any suspicious symptoms, be sure to tell your doctor about them. The same applies to the appearance of spotting discharge from the vagina. You can’t delay the examination, just like you shouldn’t self-medicate. All this can cause irreparable damage to the health of a pregnant woman. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.