Medical editor: Strokina O.A. - therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. January, 2021.
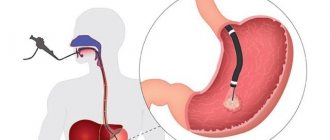
Gastroscopy is a method of endoscopic examination of the stomach with its visual inspection using a special instrument - a gastroscope with illumination and a camera. The gastroscope is inserted through the mouth and esophagus into the stomach cavity.
Gastroscopy is usually prescribed as one of the components of esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or separately, depending on the purpose of the study and the capabilities of the equipment.
Indications for gastroscopy
The list of indications for gastroscopy is very long; it is indicated for any diseases of the upper digestive system and stomach; in addition, gastroscopy is also used to treat some gastric diseases.
The procedure is prescribed for cases of stomach pain, frequent heartburn, belching, nausea and vomiting, and constant heaviness and distension in the stomach.
Gastroscopy is also applicable in the following cases:
- suspicion of esophageal diseases, esophagitis, esophageal stenosis, GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease);
- suspicion of the presence of a foreign body in the esophagus and stomach;
- stomach diseases (gastritis, peptic ulcer, polyps and stomach cancer),
- performing a biopsy of the esophagus or stomach;
- stopping bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus,
- bougienage of the esophagus;
- removal of polyps;
- stopping bleeding from a stomach ulcer;
- applying medications directly to erosions and ulcers.
Gastroscopy can be used in other cases when it is necessary to provide access to the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach, as well as to carry out diagnostics.
Expert commentary
Alexander Druzhinenko, gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences:
– Of course, gastroscopy is not the most pleasant procedure and requires some courage from the patient. But, unfortunately, other studies - X-ray and ultrasound - do not allow us to determine the smallest changes in the mucous membrane in the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, if the doctor insists, you will still have to swallow the endoscope.
Previously, patients were wary of gastroscopy for another reason. They were afraid of contracting various infections through the endoscope. In a good clinic there is no such danger. The current standards for processing instruments are very strict: mechanical cleaning of the endoscope, soaking in special solutions. Disinfection and sterilization in special devices are guaranteed to disinfect the device. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid of the risk of infection.
Contraindications
Gastroscopy is a fairly safe and simple examination method, but despite this, there are certain contraindications to it.
Absolute contraindications include:
- shock;
- severe shortness of breath with decreased blood oxygen levels;
- myocardial infarction in the acute stage;
- stroke;
- aortic aneurysm;
- coma (except in situations where the patient is intubated);
- convulsions;
- perforation of the esophagus, stomach.
Relative contraindications include a fairly broad group of diseases and conditions - severe heart and pulmonary failure, blood clotting disorders (coagulopathy), conditions after a heart attack or stroke suffered less than six months ago, serious diseases of the nervous system, conditions when the patient cannot independently follow commands doctor (for example, severe obesity, general exhaustion), enlarged thyroid gland, spasm and cicatricial narrowing of the esophagus, severe spinal deformity,
If the patient has acute processes in the oropharynx, runny nose, enlarged retrosternal and cervical lymph nodes, large diverticula of the esophagus, the endoscopist should be notified
What diseases can gastroscopy detect?
It is necessary to perform a gastroscopy of the stomach if you suspect a wide range of diseases and pathological conditions of the digestive system:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- atrophic metaplastic gastritis;
- Barrett's esophagus;
- esophagitis (inflammation of the esophageal mucosa);
- duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum);
- polyposis;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
Modern video gastroscopy is a painless, safe and highly informative method for diagnosing various diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Preparation for gastroscopy
In order for the study to provide maximum information for diagnosing diseases of the esophagus and stomach, proper preparation is important.
First of all, it is necessary to indicate to the doctor about drug allergies, especially to drugs for local anesthesia, and also inform about the constant use of medications.
It is also important to name chronic diseases - problems with the heart, blood, breathing.
You should not eat food for at least 8 hours before gastroscopy so that your stomach is completely empty. No liquids should be taken 1-2 hours before the procedure. The presence of food in the stomach makes diagnosis and diagnosis difficult.
How is gastroscopy performed?
The results of endoscopy are most informative when conducting the study on an empty stomach. Before a scheduled visit to the endoscopist, you must refrain from eating and drinking for 8-12 hours. To diagnose the organs of the gastrointestinal system, the doctor uses a gastroscope - a flexible optical device with a built-in camera.
When this procedure is mentioned, patients usually say that they are instructed to swallow a tube. Many people remember from childhood that this process is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. They vary from person to person, but if you avoid FDGS due to fear of pain, we recommend that you contact our medical center. Our clinic has modern equipment for endoscopic diagnosis of diseases of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
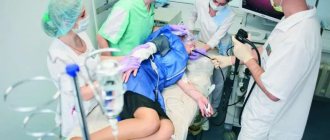
Anesthesia is used to increase patient comfort. The doctor will perform the procedure under general anesthesia. This method of pain relief is called sedation. It has minimal anesthetic risk, since the drugs are not narcotic analgesics. The anesthesiologist is responsible for pain management.
Before starting the study, the doctor will irrigate the patient’s oropharynx using an anesthetic solution to eliminate discomfort and reduce sensitivity. Then the patient is placed on his left side and, through a special mouthpiece, a thin, flexible gastroscope, equipped with a video camera, is carefully inserted into the esophagus, gradually descending to the stomach:
- the doctor carefully examines the mucous membrane and “pinches off” a piece of tissue from areas with a modified structure for subsequent histological analysis;
- if necessary, conducts a test for Helicobacter pylori infection;
- according to indications, performs minimally invasive operations (polyp removal, clipping or cauterization of a vessel, etc.).
The study takes from 15 to 40 minutes. The endoscopist spends 10-15 minutes processing the results, after which the patient is given a conclusion about the state of health of the gastrointestinal system.
The doctor draws conclusions directly during the examination. In the process of studying the mucous membrane of the digestive system and when re-viewing the recorded procedure. Then the doctor draws up an expert opinion on the condition of the mucous membrane, changes in color, the presence of ulcers, swelling, damage, etc. and gives recommendations for further treatment - conservative or surgical.
The progress of the procedure is recorded on a disk that the patient can take with him. This allows you to have diagnostic results with you when visiting a doctor.
Methodology
Gastroscopy is performed in the endoscopy room. The diagnosis is made based on the picture seen. If necessary, a biopsy and emergency treatment methods are performed (stopping bleeding from blood vessels, removing polyps).
An endoscopy device (endoscope) is a thin fiber-optic flexible tube that is sterilized before each examination. At its end there is a camera and lighting.
When examining under visual control, the doctor carefully inserts the instrument through the oral cavity into the esophagus and stomach (if necessary, then into the intestine).
The image is broadcast on the monitor and, if necessary, can be recorded on disk, zoomed in and examined in detail.
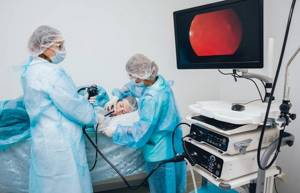
Gastroscopy in a dream
Gastroscopy in a dream helps to avoid discomfort during the procedure. This option is recommended for patients who are afraid of examinations and people with a strong gag reflex. During the study, the person is in a state of medicated sleep, that is, fully conscious. Thanks to this, the patient is relaxed and does not feel fear.
Intravenous administration of a sedative completely eliminates anxiety and discomfort. Since the person is in a dream, after completing the study there are no unpleasant memories left.
At the Moscow surgery center GMS Hospital, you can have a gastroscopy without unpleasant and uncomfortable sensations (not anesthesia). The patient is immersed in a medicated sleep, eliminating such inconveniences as the gag reflex, drooling, etc. Within an hour after the completion of the medical procedure and awakening, you will be able to go home.
After the examination under sedation, it is not immediately recommended to drive independently, since the reaction speed slows down.
Feelings during gastroscopy
Although the procedure is not painful, the sensation may cause some discomfort. It lasts on average 15-20 minutes.
However, the staff will do everything possible to facilitate the procedure: if the patient is nervous, sedative injections may be used, and to facilitate the passage of the endoscope through the throat, it is irrigated with an anesthetic solution (most often 1% lidocaine solution). A plastic mouthpiece is inserted between the teeth to prevent biting the endoscope tube.
When inserting the tube, you need to breathe deeply and relax; sometimes the doctor will ask you to swallow. A little air is supplied through the tube to straighten the walls of the esophagus and stomach.
After the examination, there may be an unpleasant sensation in the throat for 24 hours, which gradually disappears. Food can be taken 1 hour after the test.
Benefits of endoscopic examination
Unlike X-rays, gastroscopy is safe for health and takes only 10-20 minutes. The procedure can be performed in your sleep. Thanks to this, it is easily tolerated by the patient. The study does not create a radiation load on the body, does not injure tissue, and does not require complex preparation and rehabilitation.
Doctors at our clinic recommend regular endoscopic diagnostics for middle-aged and mature patients.
Preventive endoscopy allows you to detect pathological changes in the tissues of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Additionally, the doctor may recommend a biopsy - taking samples of biological material. It is carried out when a neoplasm is detected on the mucous membrane of the duodenum or stomach. The material is sent for histological or cytological examination to the laboratory. To make a final diagnosis, the doctor prescribes general and biochemical blood and urine tests to the patient.
In addition to routine examination, the doctor may perform an emergency procedure on the patient to stop gastric bleeding or remove a foreign body.
After FGDS
In the case of local anesthesia, the patient is usually sent home immediately after completion of the examination. If medication-induced sleep was used, the person is transferred to a ward, and after the medication wears off, he can also go home. Eating after FGDS is allowed after 1.5-2 hours.
After FGDS, unpleasant symptoms such as nausea, discomfort in the throat, and mild pain in the abdominal area may occur.
In very rare cases, after an FGDS, side effects may appear, which must be reported to the doctor:
- vomiting with blood;
- stool disorder (black loose stools);
- heat;
- unbearable abdominal pain.
If such signs appear a few hours or the next day after FGDS, you must urgently contact a specialist, because these may be symptoms of complications such as perforation of the stomach, esophagus, duodenum, internal bleeding, infections.