Doctors
Prices for services
| Name of service | Price |
| A03.16.001 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy | 3650 rub. |
| FGDS (including IV anesthesia) | 7200 rub. |
| Research complex: FGD+COLONOSCOPY (including IV anesthesia) | 13000 rub. |
Dear patients! You can find a complete list and cost of services at the reception or by calling 8,.
In the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of various diseases of the human digestive system, today a research method such as FGDS is actively used. This procedure helps to timely determine the source of the problem and establish the correct diagnosis. For this reason, let us further in this article discuss everything about the FGDS procedure: what it is and how it is done.
| Procedure name: | Fibrogastroduodenoscopy, FGDS |
| Alternative: | radiography, videoendoscopy, hydrosonography |
| Contraindications: | pronounced curvature of the spine; ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke; myocardial infarction in the acute stage; diseases of the mediastinum that have led or may lead to displacement of the esophagus (neoplasms, aortic aneurysm and others); pathology of the blood coagulation system; significant enlargement of the thyroid gland; esophageal stenosis; bronchial asthma in the acute stage; categorical refusal of the patient from the study; acute inflammatory processes in the pharynx and larynx (including tonsils); enlarged cervical lymph nodes; stage 3 hypertension; angina pectoris; mental illnesses (patients’ inability to control themselves) |
| Patients: | Women, children, men |
| Preparation: | 10-12 hours before the procedure, you should not eat or smoke right before the test |
| Who appoints: | Gastroenterologist |
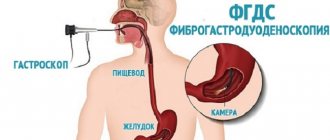
How is the gastrointestinal tract examined?
This type of medical manipulation involves studying the condition of the epithelium of these organs using an endoscope. How is this analysis done?
The research consists of the following stages:
- the pharynx area is treated with drugs for local anesthesia;
- an endoscope is inserted using a dental instrument;
- the study is recorded using video and photography;
- in some cases a biopsy is performed.
An endoscope is an optical device in the form of a long flexible tube, which is equipped with a small camera. To carry out manipulations, there is a special channel through which the doctor can use miniature instruments. The diameter of the endoscope tube is significantly smaller than the diameter of the duodenum and esophagus, and pediatric endoscopes do not exceed 6-8 mm.
The analysis can also examine the duodenum.
What is a gastric biopsy
What is a biopsy - this is the process of obtaining a sample of altered tissues with their subsequent morphological (histological) examination. The material is collected during gastroscopy (EGD, FGDS). Why is it carried out - to establish an accurate diagnosis if a malignant process is suspected.
To obtain a piece of tissue from the stomach, the doctor uses a special device - a flexible esophagogastroscope equipped with fiber optics. The esophagogastroscope is characterized by elasticity, the ability to clearly visualize and record images, and a low risk of trauma to the digestive tract.
Before the procedure, the patient is given premedication and the oropharynx area is treated with lidocaine using a special spray. According to indications, medicated sleep is used, but usually the patient remains fully conscious. The patient takes a position on his left side and clamps an endoscopy mouthpiece in his mouth - a special device to protect the endoscope from accidental biting. Through the mouthpiece, the doctor inserts the endoscope into the pharynx and esophagus. When passing the mouth of the esophagus, a gag reflex occurs. To overcome it, the patient makes a swallowing movement.
Next, air is supplied inside in small portions, mucus and gastric juice are sucked out. The doctor examines the inner surfaces of the walls and plucks off several pieces with a diameter of 2–3 mm from the required areas. It is important to obtain at least 5 samples. Pinching is performed using biopsy forceps. Biopsy forceps are adapted to the curves of the gastrointestinal tract and allow obtaining good tissue samples. If it is necessary to remove a large fragment, an electrosurgical loop is used.
Patients are concerned about whether it hurts to do a biopsy. The most uncomfortable moment in the entire procedure is the passage of the endoscope through the oropharynx area. No pain is felt during tumor tissue collection.
What does the study show?
Such an analysis helps to determine the functioning of the human digestive tract, as well as to determine the anatomical changes in its organs (for example, the intestines or duodenum). The interpretation of the research results should be carried out by a specialized doctor, which will guarantee their reliability and subsequent effective treatment.
Also, a study of this nature gives the endoscopist the opportunity to carefully examine the condition of the mucous membranes of such organs of the gastrointestinal tract as the esophagus or duodenum. With the help of FGDS, doctors detect even microscopic changes that are perfectly treatable today.
During the procedure and if necessary, a biopsy can be performed. What it is? FGDS makes it possible to take a sample of neoplasm cells for further study in the laboratory. This is extremely important, because timely detection of malignant tumors is the key to successful treatment of cancer.
What gastrointestinal diseases can be detected during FGDS? During such manipulation in a medical facility, it is possible to identify:
- variceal bleeding, the source of which is the affected veins of the esophagus;
- esophageal stenosis caused by burns of the mucous epithelium by various chemicals;
- ulcerative formations;
- benign neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract (for example, in the duodenum) and the like.
In other words, a qualified interpretation of the analysis results makes it possible to promptly identify and begin treatment for extremely dangerous and common diseases of the stomach or intestines in our time.
Indications and contraindications

Stomach cancer is not the only gastrointestinal disease for which a biopsy is indicated. This is an informative study that can tell a lot about the state of the digestive tract. In what cases does the doctor prescribe a gastric biopsy:
- the patient has clinical symptoms suspicious for cancer: epigastric pain combined with nausea, vomiting and weight loss;
- other studies have shown the presence of a neoplasm;
- the patient has gastroesophageal reflux disease - the throwing of part of the gastric juice and stomach contents back into the esophagus;
- an ulcer or atrophic gastritis was previously diagnosed.
In the presence of gastric and duodenal ulcers, endoscopic examination is recommended once a year. Preventive FGDS allows timely tracking of the development of a malignant process, since ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane may have a tendency to malignancy (malignancy). If during a preventive FGDS the doctor notices suspicious areas on the mucous membrane, he will immediately take tissue samples. Early diagnosis of stomach cancer is good luck, since most patients see a doctor at the third stage of the tumor, when the chances of remission drop due to metastases.
The analysis is taken for an ulcer that does not heal for a long time, for chronic gastritis to clarify the stage of the process, to diagnose a polyp, and to monitor postoperative complications.
A biopsy is contraindicated in the presence of the following problems:
- stroke, heart attack and other acute vascular pathologies;
- esophageal stenosis;
- bronchial asthma in the acute stage;
- infectious process in the body;
- epilepsy.
It is necessary to stabilize the patient's condition as much as possible before examination, or find another way to study the tumor.
How is the preparation going?
Before conducting the analysis, a qualified specialist must explain in detail to the patient the rules for preparing for FGDS. They are as follows:
- 10-12 hours before the start of the procedure you should not eat. For this reason, FGDS is often carried out in the first half of the day;
- smoke right before the test. The fact is that nicotine can dramatically increase the volume of gastric juice secretion.
If the patient suffers from any diseases in acute or chronic form, this must be reported to the attending physician before the study. This also applies to the presence of allergic reactions to medications.
Everything for work: SOP FGDS
Full text of the article:
SOP “Fibrogastroduodenoscopy”
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. The purpose of this method is to visually determine the pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract, biopsy the affected tissue and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Target:
standardization of the fibrogastroduodenoscopy procedure.
Where:
endoscopic room of outpatient service (APS) and round-the-clock hospital (CSS).
When:
as prescribed by a doctor.
Responsibility:
The nurse in the endoscopy room is responsible for carrying out the manipulation in accordance with the requirements of the SOP. Monitoring compliance with SOPs is carried out by the senior nurse of the OPD.
Regulatory and reference documentation
• Federal Law of November 21, 2011 No. 323-FZ “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation” • Order of May 31, 1996 No. 222 “On improving the endoscopy service in healthcare institutions of the Russian Federation” • SP 3.1.3263-15 “Prevention of infectious diseases” diseases during endoscopic interventions" • SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities" • SanPiN 2.1.7.2790-10 "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the management of medical waste • MU 3.1.3420-17 "Provision epidemiological safety of non-sterile endoscopic interventions on the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract" • Letter of Rospotrebnadzor dated December 1, 2008 No. 01/14112-8-32 "On improving measures to ensure the epidemiological safety of manipulations with flexible endoscopes"
Resources
1. Equipment for endoscopy: Olympus GTF – E – 3, Videogastroscope VME – 98 VGT 220992. 2. Mouthpiece, tweezers, biopsy forceps. 3. Disposable gloves – 2 pairs. 4. Lidocaine solution 10% for throat irrigation. 5. Formalin solution 10%, bottles for histological material, container for transporting bottles to the laboratory. 6. Alcohol 70% – 50 g. 7. “Atmos” – suction device, enameled container for processing “Atmos” (can and hose), container for treating rinsing water. 8. Containers (3 l - 2 pcs., 10 l - 3 pcs.), filled with disinfectant solution according to the technological map for processing endoscopes. 9. Containers (1 liter - 2 pcs.), filled with disinfectant solution according to the technological map for processing mouthpieces. 10. Containers (1 liter – 2 pcs.) filled with disinfectant solution according to the technological map for processing instruments. 11. Glass containers for pre-treatment of an endoscope 0.5 l – 2 pcs. 12. Metal tray for napkins. 13. Brushes for processing endoscopes, syringes 20 ml - 5 pcs., Janet syringe. 14. Running water, distilled water, sterile water. 15. Disinfectant solutions according to the technological map. Hourglass at 1 min., 2 min., 5 min. 16. Gauze wipes, disposable absorbent diaper 1 pc. 17. Capacity for transporting endoscopes from a dirty area and from a clean area. 18. Leak test (pressure gauge), azopyram test and phenolphthalein test, test strip for TLD. 19. Metal stands and disposable covers for storing endoscopes. 20. Class A and Class B garbage bags. 21. Fleece napkins for surface treatment. 22. Soap, sanitizer and paper hand towels. 23. Emergency kit for anaphylactic shock, anti-HIV kit. 24. Registers for registering patients.
Main part of the SOP
1. Introduce yourself, identify the patient based on medical documentation or passport (ask for full name, date of birth). 2. Register the patient in the journal. 3. Inform the patient about the study, check for informed consent for the procedure. 4. Place a disposable sheet on the couch. 5. Carry out hand hygiene, put on gloves, a mask, a cap, an apron. 6. Invite the patient to the treatment room and anesthetize the throat with lidocaine. 7. Help the patient lie down on the couch and take the necessary position: on the left side with the left leg extended and the right leg bent at the knee and hip joints. The patient places his right arm along the body, bends his left arm at the elbow, straightens his back and places his head with his cheek on the pad, tilting down. 8. The nurse inserts a mouthpiece into the patient’s mouth and is located next to the endoscopist; during the examination, the nurse assists the doctor. 9. If a biopsy is necessary, he provides forceps and helps put the biopsy material into a bottle with formaldehyde. 10. After the procedure is completed, the nurse takes the endoscope and performs initial cleaning of the endoscope, then places the endoscope in a container and moves it to a dirty area, where the endoscope is processed in accordance with the requirements of SP 3.1.3263-15 “Prevention of infectious diseases during endoscopic interventions.” 11. After completing the procedure, it is necessary to help the patient get up from the table, after making sure that he is feeling well. 12. The patient must be warned not to eat for 1-2 hours after the examination. 13. Remove the sheet from the couch (class B medical waste), treat the couch with a napkin moistened with a disinfectant solution. 14. Treat hands hygienically, place gloves, mask and apron in a container for class “B” waste. 15. Register the doctor’s conclusion on the study in a journal, fill out a bottle with biopsy material and fill out a referral form to the histology laboratory, place the bottle and the referral in a container for transportation. 16. Give the patient a conclusion form and inform that the procedure is completed. 17. Invite the next patient to the office.
Preparation
· The FGDS procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach!! Last meal 12-14 hours before the test. You cannot take medications or smoke. · The patient must have a towel and the results of previous examinations with him.
Parameters for assessing and quality control of the method implementation
– Compliance with the technology of performing the manipulation, – timely execution of the procedure, – ensuring infectious safety of the procedure, – availability of a record of the fulfillment of the appointment in the medical documentation, – patient satisfaction with the quality of the procedure, – doctor’s satisfaction with the quality of the manipulation.
Distribution of this SOP
Copy Division Original Chief nurse Copy 2 Chief nurse OLD
Responsible executors are familiar with and undertake to comply with:
No. Last name Signature Date
What sensations may occur during the procedure?
Many patients are afraid of FGDS, considering this type of research extremely unpleasant. Progress in the field of medical equipment has reduced the level of human discomfort during analysis to almost zero.
A modern endoscope has a minimal size and therefore creates a minimum of unpleasant sensations for a person.
The medical procedure itself using an endoscope takes an average of 6 minutes. However, if any serious problems are detected, it can be increased to a quarter of an hour.
In most cases, the person does not feel any serious pain or particular discomfort. However, many patients state that they experienced unpleasant sensations during FGDS.
The following consequences of FGDS are considered the norm:
- belching;
- nausea;
- impulses to cough and sneeze;
- the appearance of tears;
- nasal discharge.
All these phenomena are considered completely normal, and in some patients they do not occur at all.
Is it possible to perform the procedure for examining the stomach or intestines under anesthesia? In fact, FGDS can be performed under both local and general anesthesia. This greatly simplifies the manipulation itself, since the patient does not feel any pain, which often complicates the study and even distorts its results.
In most cases, anesthesia is prescribed by a specialist when, in addition to the examination itself, long-term medical procedures are planned.
It is worth noting that the use of anesthesia is possible only if the patient does not suffer from allergic reactions to the components of the drug. In this case, anesthesia must be administered to the patient exclusively by a qualified anesthesiologist. And if a person has even the slightest contraindications, it is not worth performing FGDS under anesthesia.
+
What diseases can be detected during a stomach examination?
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy can detect changes characteristic of the following pathologies:

- Gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa, sometimes superficial and deeper):
- catarrhal (wall hyperemia);
- erosive (defects of the mucosa with minor hemorrhages);
- atrophic (thinning of the membrane with a decrease in the number of mucous glands);
- Menetrier's disease (hypertrophic form of gastritis).
- Peptic ulcer (in the photo, a stomach ulcer looks like a local defect of the mucous membrane with swelling of the adjacent tissues).
- Duodenogastric reflux.
- Esophagitis.
- Barrett's esophagus (instead of flat epithelium, cylindrical epithelium appears in the lower sections).
- Crohn's disease is a specific inflammatory process that can affect all parts of the digestive system.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum or metastases of tumors from other locations.
- Chemical or radiation damage.
- Candidiasis (mainly in patients with immunosuppression, as a complication of HIV infection or chemotherapy).
- Portal hypertension in chronic liver failure (swelling and enlargement of the lower esophageal veins).
- Congenital anomalies of the digestive system.
- Hiatal hernia.
- CREST syndrome in systemic scleroderma (an autoimmune disease affecting connective tissue).
- Congenital Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (pigmentation of the mucous membrane with polyposis).
- Celiac disease (autoimmune intolerance to foods containing gluten protein).
- Whipple's disease (infectious lesion of the intestine, which is accompanied by the deposition of lipids in its wall).
- Insufficiency of the cardia (insufficient closure of the lower esophageal sphincter).
- Stomach tone (hypotension).
Interpretation of FGS results
Share information with your Facebook friends
VK
Question:
Hello, dear Andrey Viktorovich!
They gave me FGS. The diagnosis is not clear to me.
It is very difficult to get to a gastroenterologist in a clinic. There is no money for a paid doctor. Please help me decipher the description.
Description of FGS.
BDS is not visualized. - Is this good or bad? What to do about it?
Foci of hyperemia in the antrum of the stomach and in the duodenum, the pylorus does not close. Semolina in WPC.
I didn’t have any money with me for the biopsy. A doctor I know prescribed treatment for 10 days with 2 types of antibiotics, Controloc 20 mg twice a day, Enterol 3 times a day and Itopride 3 times a day. Then continue “Controloc” 2 times a day for 2 months and “Panzinorm 10000” 14 days 3 times a day. Medicines are expensive, but the main thing is that they help.
Doctor, please help me, describe the diagnosis in accessible language, whether everything is very bad or not. And was I given the right treatment?
While he was working as a taxi driver, he apparently spoiled his stomach, ate too much and quickly fell asleep from fatigue. I've been suffering for two years now. I drank both Nolpaza and Razo, after withdrawal the unpleasant symptoms returned, mainly heaviness, bloating, heartburn. The diet is now regular and stable. In the morning, a bowl of oatmeal, alternating with buckwheat, mixing it with olive oil. I eat it as a snack with cheese and bread. Snack – 1 egg or nuts, for lunch – low-fat pilaf with chicken without onions and carrots or boiled vegetables with chicken, pasta with chicken and carrots, for dinner – vegetable stew with chicken or cottage cheese with kefir. I eat bread only in the morning. Periodically I alternate chicken with pollock or flounder.
Answer:
Greetings! Don't be alarmed, there's nothing to worry about. The BDS is not visualized, because either the doctor could not remove it, or this is an anatomical feature, and the end device, which is usually used to look at everyone, does not always show the BDS. You need a special device with side optics - a duodenoscope - to be sure to remove the BDS. But this is a rare tool, and they need to be looked at with certain doubts in the field of BDS, which you have not described. It is now clear that there is gastritis with bile reflux, the so-called duodenogastric reflux. This is not good. You need to fight him. The semolina symptom indicates that the gallbladder or pancreas is not feeling well. You need to pay attention to this with a gastroenterologist - diet and regular meals. Discuss treatment with your doctor.
print version
Tagsbile Health pancreas Reflux
When to re-examine?
For a young patient, the need for preventive endoscopic examination of the stomach is low . Modern recommendations for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection generally advise avoiding FGDS if it is possible to repeat a fecal test for antigen to the pathogen.
It is rational to conduct a new study only if antibacterial therapy has not given the expected results, and the symptoms of pain and discomfort in the abdomen persist.
If areas of precancerous degeneration of the mucous membrane (polyps, Barrett's esophagus) are detected and surgical intervention is refused, it is recommended to repeat FGDS annually .
After surgical interventions, a repeat examination is carried out no earlier than six months later . It is indicated for patients who have persistent pain in the upper abdomen and symptoms of dyspepsia, despite adequate drug therapy.
The tips in this article will help you move through the procedure more easily.