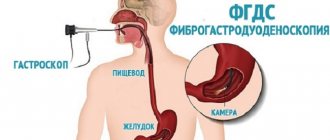
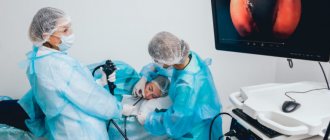
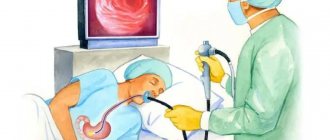
If a patient complains about the digestive system, the gastroenterologist prescribes various diagnostic techniques that help identify the cause and make the correct diagnosis. A fairly common and effective procedure in this case is FGDS.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a direct visualization method that allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach, esophagus, and intestines. The examination is carried out using an endoscope. This device is a thin tube with a built-in camera. For adults, a tube with a diameter of about 1 cm is used, for children the diameter is smaller. On the monitor, the doctor sees the condition of the tissues, the presence of inflammation, neoplasms, and damage. The equipment also allows for treatment and collection of biomaterials for study in the laboratory.
Indications for FGDS
Examination and treatment of the stomach and duodenum using endoscopic equipment is prescribed:
- For abdominal pain that is regular.
- In case of discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen.
- For heartburn that does not go away for a long time.
- For anemia.
- In case of nausea and vomiting for a long time.
- When belching occurs.
- For problems with appetite.
- With sudden weight loss.
- For diseases of the liver, gall bladder.
- Before preparing for surgical interventions.
- To exclude ulcers, cancer, gastritis.
The examination is also recommended for chronic gastrointestinal diseases, to assess the effectiveness of the treatment, and to prepare the patient before a number of surgical interventions.
Recommended Diet
A condition for successful invasive diagnostics is that the patient follows a certain diet before FGDS. It is maintained for 3 days. During this short period, provided that all recommendations are followed, the stomach will be cleansed as much as possible. The patient must properly coordinate his diet.
A detailed menu will be created by your doctor, who will definitely tell you what you can eat before gastroscopy and how many hours after FGDS you absolutely cannot eat. Among the most popular tips is to eat foods that contain well-ground ingredients. This will avoid irritation of the mucous membranes, and the doctor will receive a reliable picture of the disease.
What is allowed to eat during the examination?
Foods should be eaten before gastroscopy of the stomach or intestines only in warm, stewed, steamed and baked form. Gastroenterologists advise giving preference to light foods that are quickly digested and low in fat. The list of permitted products includes:
- well-cooked cereals;
- lean fish;
- white poultry fillet;
- baked fruits and vegetables;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- compotes, weak green tea, mineral water.
You are allowed to include porridge in your diet. It is important that it is not damp.

Prohibited Products
A few days before the FGS, it is forbidden to eat spicy food, dishes seasoned with various spices and herbs. Gastroenterologists recommend refraining from drinking alcoholic beverages. During FGDS, you should also not consume the following foods:
- chocolate confectionery;
- fresh vegetables and fruits, as they are rich in coarse fiber;
- seeds (pumpkin, sunflower) and nuts;
- dairy products;
- legumes (beans, peas, lentils, etc.);
- fatty meat and fish;
- rich flour products and brown bread.
Prohibited drinks include:
- packaged or natural juices;
- coffee;
- sparkling water;
- jelly.
In addition to the products listed above, the consumption of smoked meats, pickled foods, fast food, and fried foods is strictly prohibited. This is a harmful and difficult to digest food that you should definitely exclude from your menu. This recommended diet before gastroscopy of the stomach will fully prepare your body for FGDS.
In addition, those patients who already have gastritis and ulcers are advised to follow a dietary diet for several weeks between the first and repeat examinations. This will give the doctor the opportunity to get a complete picture of the health of the gastrointestinal tract and monitor improvements in health.

Side effects
Typically, FGDS is well tolerated by patients, but sometimes after the procedure the following are noted:
- Feeling of bloating, fullness in the intestines.
- Pain in the stomach, lower abdomen.
- Sore sensation in the throat.
The discomfort goes away during the day; if necessary, you can take a drug with an antispasmodic effect.
If the symptoms have not gone away the next day, or there is an increase in temperature to 38°C or higher, sharp pain, stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, then you should consult a doctor.
Using additional oral hygiene products
Know! We have sorted out the fact that brushing your teeth before gastroscopy is allowed, while being careful.
But what about other products designed to care for the oral cavity? After all, many people are accustomed to using mouthwash and chewing gum every day to freshen their breath.
As for the rinse aid , it to refuse it on the day of the study .
If the ingestion of toothpaste can be controlled, then a small amount of rinse aid will still enter the stomach, thereby distorting and complicating gastroscopy.
If we talk about chewing gum , it is also prohibited.
The problem is that when chewing gum, active salivation is observed, resulting in the release of gastric juice.
Stay up to date! To get a reliable gastroscopy result, it is better to rinse your mouth with water in the morning, trying not to swallow it.
Possibilities of FGDS
During the examination, the doctor assesses the condition of the mucous membranes of the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum. Foci of inflammation, tissue ulceration, and neoplasms are clearly visualized on the screen.
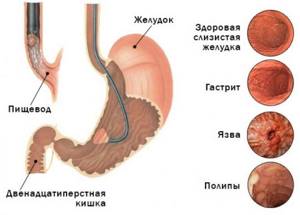
In addition, during the procedure you can:
- Remove the foreign object from the stomach.
- Get rid of benign formations.
- Perform a biopsy.
- Administer the necessary medications.
- Stop bleeding in the stomach.
Basic Rules
Proper breathing during gastric gastroscopy will facilitate the advancement of the gastroscope and make it less uncomfortable. In addition, it will help reduce the risk of damage to the walls of the esophagus and stomach, and also minimize pain.
Basic Rules:
- you need to breathe through your nose ;
- inhale and exhale as deeply as possible;
- take your time, breathe slowly;
- involve the stomach, not the chest, in the process;
- move as little as possible.
Important Do not try to swallow saliva or make swallowing movements while moving the gastroscope into the stomach - this can lead to injury to the walls of the larynx by the endoscope.
Belching may also occur during the procedure. There is no need to be ashamed of this: getting rid of air in the stomach will have a positive effect on the procedure.
The more relaxed you are during the procedure, the faster the doctor will be able to examine the gastrointestinal tract and the less you will damage the mucous membrane. If the mucous membrane in the throat is damaged, it can become infected and you may have a sore throat after the procedure.
Preparation
Preparation for EGD of the stomach begins several days before the procedure. Compliance with the recommendations will make diagnostic measures more informative, help conduct research without visualization difficulties and accurately identify possible pathologies.
Detailed information about preparation is provided to the patient by the gastroenterologist at the preliminary consultation. General recommendations are given below.
3 days before the test
Three days before the examination, it is recommended to exclude the following products from the menu:
- Seeds, nuts, legumes.
- Spicy, smoked, salty foods.
- Fried, fatty foods, mayonnaise.
- Carbonated drinks, alcohol, juices.
- Chocolate, coffee, ice cream.
- Baked goods made from wheat flour.
- Fruits and vegetables rich in fiber: cabbage, radishes, raw carrots. It is also not recommended to eat plums, apricots, tomatoes, and beets.
- Dairy products.
Preparation for FGDS is based on a diet that includes:
- Boiled or baked meat and vegetables.
- Rice, buckwheat, oatmeal porridge with water.
- Steam omelette.
- Crackers, dryers, biscuits.
- Compotes, jelly.
If the patient takes medications as part of the treatment of chronic diseases, the course of treatment is not interrupted, all recommendations are followed as prescribed.
It is advisable for the patient to quit smoking during the preparation period. Nicotine increases the intensity of gastric juice production, exacerbates the feeling of hunger, worsens the condition of blood vessels, causes spasms, and increases the urge to vomit.
Preparation for the examination also implies stabilization of the patient's chronic diseases. This applies to hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular pathologies and other diseases that require constant treatment. During periods of exacerbation, the procedure is not performed. All prescriptions must be mentioned to the gastroenterologist at the consultation before FGDS of the stomach.
The day before the procedure
The study is carried out on an empty stomach. The last meal is allowed no later than 8 hours before FGDS. This should be a light dinner. If the patient has digestive problems, then at least 12 hours should pass from dinner to the examination.
Patients with diabetes are allowed to drink sweet water or tea as needed, but no later than 5 hours before the procedure.
If there is a tendency to bloating or difficulty with bowel movements, then preparation for the procedure includes taking carminatives and cleansing the intestines with an enema or laxative. The patient must also notify the doctor about this.
On the day of the FGDS
- If the study is scheduled for the first half of the day, then you are not allowed to have breakfast, drink drinks or water. If you spend the afternoon, you can drink sweet tea in the morning.
- If the patient receives medications in the form of tablets and capsules, then, if possible, their intake is postponed until after the procedure. If medications that need to be absorbed or injections are used for therapy, then they are taken as usual. You must be informed about all medications taken before starting the study.
- No smoking.
It is recommended to wear loose-fitting clothing, without putting pressure on the abdomen and stomach. It is better to leave the neck free.
General requirements for conducting FGDS
Keep in mind! In order for gastroscopy to show a reliable clinical picture, a number of requirements must be met:
- Clean gastric mucosa . To do this, you should follow a special diet for several days before the test. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that settle on the mucous membrane. These include: legumes, milk, vegetables and fruits.
- Empty stomach. Food in the stomach does not allow gastroscopy. In addition, it can cause a gag reflex. In order for your stomach to be empty in the morning, you need to have dinner with easily digestible foods. Also, you should not drink anything before the diagnosis.
- Complete peace. The patient must undergo FGDS while completely calm - breathing is even. Otherwise, insertion of the gastroscope will be very painful. In addition, in a restless state, you can injure the esophagus during the examination.
- Withdrawal of medications . You should not take medications that coat the mucous membrane. You should also refrain from using painkillers, as they reduce peristalsis.
Note! When performing gastroscopy, it is important that there is no mucus in the stomach.
It is formed not only after eating food, but also as a result of smoking, even brushing your teeth.
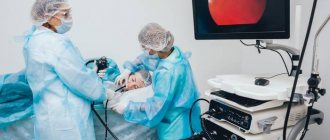
How is it carried out?
- The examination is carried out in a lying position on the left side.
- Patients using dentures need to free the oral cavity from foreign objects.
- Before the examination begins, the throat is irrigated with a local anesthetic. This reduces sensitivity and helps weaken the gag reflex.
- When the anesthetic begins to take effect, a clamp is inserted into the mouth, which prevents the jaw from accidentally closing.
- The doctor places the end of the endoscope at the root of the tongue and asks the patient to swallow. This way the tube enters the esophagus and moves along it. This is the most unpleasant moment of the procedure; then the feeling of discomfort goes away.
- The duration of the diagnostic test is about 15 minutes. If it is planned to take a biopsy, administer medications, or remove formations, then the time for performing an FGDS increases to half an hour.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy under sedation
To reduce discomfort in the patient and during upcoming long-term manipulations, FGDS can be performed with immersion in medicated sleep.
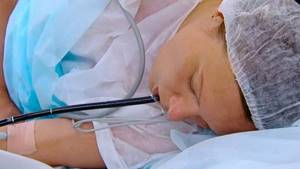
Also indications for sleep research are:
- Strong gag reflex.
- Psychomotor impairments that prevent you from remaining still during the examination.
- Patient's wishes.
Emergency EGD is not performed during sleep. The procedure is allowed for children from 7 years of age.
Preparing for such a test is different from preparing for a regular procedure. A consultation with an anesthesiologist and a number of tests are added.
Before the examination:
- A medical history is taken and a decision is made on the possibility of using a sedative.
- A general blood test, tests for HIV, hepatitis, and fluorography are performed.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient needs to remove jewelry and contact lenses. Next, the drug is administered, the patient falls asleep and the examination of the stomach begins.
Sleep time is calculated taking into account upcoming events. After waking up, you usually feel normal, without any significant discomfort. After 1 hour the patient is allowed to go home.
Preparation for gastroscopy under anesthesia
If you are planning examinations with sedation or anesthesia, it is strictly necessary to be on an empty stomach and not drink water for at least 3 hours before the examination. Features of preparation for gastroscopy are given above.
Tests for anesthesia (the need is determined by the anesthesiologist and the corporate requirements of the clinic; the Ministry of Health does not regulate the availability of these tests before endoscopic examination):
- HIV
- Hepatitis B and C
- Syphilis
- ECG (not more than 10 days old)
print version
TagsGastroscopy Health Endoscopy
"VIP Academy": European standards of medicine
The multifunctional uses Japanese equipment. We carry out diagnostics, treatment procedures, biopsies with further study of samples in our laboratory.
Endoscopes have high resolution, which makes it possible to examine mucous membranes with several times magnification to detect pathological changes up to 1 millimeter in size. The results are recorded on digital media.
We have doctors with more than 10 years of experience who specialize, among other things, in working with children.
Based on the results of endoscopy, you can consult a gastroenterologist and undergo a course of treatment from leading specialists in Nizhny Novgorod.