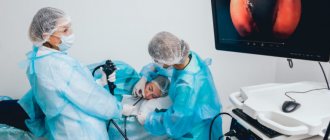
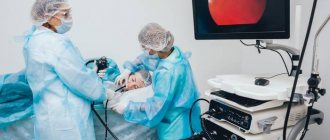
Gastroscopy and colonoscopy are modern research methods that allow diagnosing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the early stages. However, both during gastroscopy and colonoscopy, patients experience very unpleasant sensations caused by a state of discomfort, and in some cases, pain (in particular, during colonoscopy), which can prevent the doctor from efficiently performing the required manipulation. In this regard, recently it has become increasingly important to perform these procedures during sleep, and especially to perform them simultaneously (gastroscopy and colonoscopy) during a single administration of anesthesia.
If the patient has a pronounced gag reflex, or has had an unsuccessful experience with a previous similar study, there is an option to carry out all the necessary procedures in the most comfortable conditions for the patient, namely during medicated sleep. At the same time, he does not experience stress, the feeling of anxiety and fear goes away.
Such a study is carried out under the supervision of an anesthesiologist, who conducts a preliminary survey of the patient, after which he carries out an individual selection of the drug and its subsequent administration. Unlike anesthesia, this method is easier to tolerate. After waking up (usually after 5-10 minutes), the patient fully recovers within 30-45 minutes. During the day, he is not allowed to drive a car or work with complex technical equipment.
We have at our disposal a full arsenal of modern endoscopic equipment from Pentax Medical. The versatility of our center allows the patient to receive advice from specialists in related specialties, gastroenterologists, proctologists in one place and without wasting extra time.
In our center, you can combine gastroscopy (FGDS) and colonoscopy, doing both of these not very pleasant procedures simultaneously and under anesthesia, saving your body from repeated exposure to drugs.
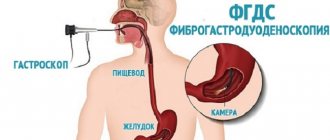
Gastroscopy, FGDS - endoscopic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum), has great diagnostic value and allows you to identify many diseases at an early stage. The procedure also allows for therapeutic measures, cytology and histology. The advantage of the method is that it allows you to see the slightest changes in the mucosa with the highest accuracy.
What is EGD analysis?
First of all, let’s figure out what an endoscopy examination is. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a diagnostic procedure aimed at examining the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, which is carried out by introducing a special device into the patient’s gastrointestinal tract - an endoscope. In fact, fibrogastroduodenoscopy allows you to evaluate the same parts of the digestive system, but usually takes place without examining the esophagus.
You can find out more about the service and its cost here >>
As for the recently widespread video gastroscopy , it differs from previous techniques by the location of a small video camera at the end of the endoscope tube. This addition allows the specialist to obtain a visual picture of the condition of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum on the computer screen by controlling a moving camera. In addition, it should be noted that the ability to save a video protocol of the study allows you to confirm the diagnosis and can save the patient from repeating the procedure.
To understand what EGDS is in medicine, you should realize that this technique, along with FGDS, allows you to identify many gastrointestinal diseases in the initial stages of development , when other diagnostic methods cannot give reliable results. These research methods are of particular importance in determining oncological tumors, even with small tumor sizes.
endoscopic used in the NEOMED clinic is equipped with the “i-scan” function (virtual chromoendoscopy), thanks to which it is possible to diagnose cancer at a very early stage . In addition, EGDS, unlike FGDS, makes it possible during the research process to take a small section of tissue for cytological and microscopic analyses, while minimizing discomfort for the patient.
You can find out more about the service and its cost here >>
Where else are FGDS and FGS of the stomach done?
District, city and rural hospitals still use endoscopes with outdated technology - fiberglass, the main method of obtaining images in endoscopes of the early 20th century. Therefore, the studies are called FGDS of the stomach or FGS of the stomach (fibrogastroduodenoscopy and fibrogastroscopy, respectively). Such equipment is no longer produced by leading import concerns Olympus, Pentax, Fuji.
We can say, out of habit or the old fashioned way, these terms - FGDS of the stomach or FGS of the stomach are distributed and used by doctors themselves, and are picked up by patients if the study is carried out on modern video equipment. This is not literate, which also often misleads the doctors themselves. Because with FGDS of the stomach or FGS of the stomach, other technologies and limited capabilities of equipment and equipment are implied - the lack of registration of photo and video fragments, the lack of an image magnification mode and an electron chromoscopy mode (for example, in the Exera system from Olympus - narrow-spectrum NBI analysis).
Gastroscopy using the PENTAX MEDICAL endoscope
Why is gastroscopy necessary?
The procedure is performed in order to:
- Detect gastritis, ulcers, erosions, polyps
- Perform a biopsy
- Detect stomach cancer
- Definition of Helicobacter pylori
- Determine stomach acidity.
Gastroscopy is required when the patient experiences nausea, vomiting, heartburn, stomach pain, loss of appetite, causeless weight loss, difficulty swallowing, and discomfort in the upper abdomen.
How is gastroscopy done?
The patient is placed on the couch, local anesthesia is performed (irrigation of the root of the tongue with lidocaine). The doctor inserts a gastroscope, the patient must breathe through his nose. When the endoscope reaches the esophagus, the patient takes a sip, the tube passes further and rushes to the stomach, and then into the duodenum. If necessary, tissue samples are taken. The entire procedure takes 2-3 minutes if no additional steps are required.
Our diagnostic center has endoscopes that make the gastroscopy procedure much more effective and expand its capabilities. Excellent image quality, digital color video processor, high resolution images are a guarantee of correct diagnosis and comfort for the patient. Our gastroscopes have been tested in the world's best clinics and meet hygiene and safety standards. The picture quality is ideal (there is structural enhancement, electronic zoom and other options). The clinic offers a full range of gastroscopy procedures and guarantees excellent results and maximum comfort for the patient.
What to expect during a gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy is a painless examination method in most cases. Pain can be caused by ulcers, inflammatory processes, injuries to the stomach and esophagus. The patient feels a slight tingling, “tickling”; there may be slight discomfort when the gastroscope tube passes from the stomach to the duodenum.
Preparation for gastroscopy
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. 8-10 hours before the test you should not eat or drink; only clean water is allowed. You can't drink water for 3 hours. It is necessary to warn the doctor about all medications taken and report chronic diseases.
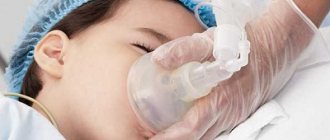
Gastroscopy “in a dream”
A new direction in the diagnosis of diseases is gastroscopy “in a dream”. Intravenous sedation causes superficial drug sleep. The patient does not feel any discomfort, the procedure takes a few minutes. After 30-40 minutes you can leave the clinic.
Gastroscopy under anesthesia is carried out with complete switching off of consciousness. The manipulations performed by the doctor are not felt by the patient. You can leave the clinic after the anesthesiologist is sure that consciousness has been restored.
With conventional gastroscopy, there is still a possibility of reflex vomiting. The “dream” procedure minimizes this possibility, makes the doctor’s task easier, and the patient does not experience any discomfort. Complications after anesthesia (respiratory disturbances, heart rhythm disturbances, confusion) are also unlikely, since the staff uses safe drugs, and all vital functions are monitored by an anesthesiologist.
How should you behave after gastroscopy and gastroscopy “in your sleep”?
After a regular gastroscopy, you can eat, drink, and drive immediately. If the procedure was performed under anesthesia, an accompanying person is needed so that the patient can go home. You can't drive. Your doctor will tell you about additional restrictions (if they are necessary in your case).
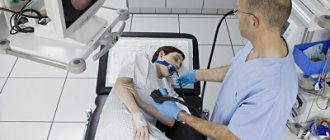
How is esophagogastroduodenoscopy performed without sedation?
The procedure lasts on average 30 – 60 minutes. Before the procedure begins, the root of the tongue area is anesthetized with a special anesthetic spray. This allows you to relax the muscles of the pharynx and reduce the intensity of the gag reflex.
The patient lies on the couch, on his left side, swallows the endoscope probe, after which the doctor carefully moves the flexible tube further into the stomach. The tube itself is significantly smaller in size than a bolus of food, so patients do not experience any problems with swallowing or breathing.
During the procedure, your doctor will advise you to refrain from swallowing. If saliva accumulates in the mouth, it is removed using a saliva ejector. To examine the mucous membrane of the organs of the upper digestive system, the specialist will carefully advance the endoscope, examining the condition of the walls of the esophagus, stomach, and then the duodenum. If problems arise with visualizing the walls of organs, water or air is supplied through a special endoscope channel into the lumen of the stomach, which will clean the area to be examined. Any liquid or air that enters the stomach is immediately removed using a special suction.
Preparation for gastroscopy
Preparation for the study begins 2-3 days in advance. Foods rich in nitrogen compounds and fiber - meat products, bread, fresh fruits and vegetables - are excluded from the diet. On the eve of the examination, the last meal is at 19-00 (do not overeat). At 6 am you are allowed to drink a glass of clean water without gas (if thirsty), you can take prescribed medications. Taking anticoagulants and smoking on the day of gastroscopy is prohibited. You need to take the results of previous examinations with you Gastrointestinal tract (endoscopic, x-ray, ultrasound), general blood test.
Contraindications
Contraindications to gastroscopy are divided into absolute and relative. The study is not possible in severe general conditions, in particular those caused by myocardial infarction and acute cerebrovascular accidents. The procedure is not performed in cases of severe cardiovascular and pulmonary insufficiency. The technique is not used for hemophilia due to the high risk of bleeding. Relative contraindications to endoscopy include acute inflammatory diseases of the tonsils, pharynx, mediastinum and other nearby organs due to the risk of spreading infection (except when the study is performed for health reasons). Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is limited in patients suffering from epilepsy and mental disorders. In this case, the decision is made individually; the use of general anesthesia is mandatory.
Indications for endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract
The procedure is carried out only according to medical indications. Diagnostics is prescribed for patients who contact a gastroenterologist with the following symptoms:
- digestive problems that do not disappear after normalization of nutrition and conservative treatment;
- weight loss with the usual diet;
- bowel problems: chronic diarrhea or constipation;
- bloody, purulent, mucous inclusions in the stool;
- bloating;
- abdominal pain;
- persistent heartburn, belching;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
Other indications:
- the need for targeted biopsy of altered areas of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract;
- conducting a test for the activity of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, which cause gastritis and stomach ulcers;
- monitoring the effectiveness of previously performed therapy for gastrointestinal diseases;
- determining the level of stomach acidity;
- removal of polypous tumors.
Emergency endoscopic examination is indicated in the following situations:
- penetration of a foreign body into the stomach;
- uncontrolled gastrointestinal bleeding;
- complications of gastric and intestinal ulcers
Indications
Both methods are prescribed depending on the patient’s complaints and based on a doctor’s examination. If suspicions are limited only to damage to the stomach, FGS is performed. FGDS is relevant in cases where there is a risk of involvement of the duodenum, gallbladder and pancreas in the pathology. We provide basic information about the indications in the table below.
| Indications for FGS | Indications for FGDS |
|
|
Let us note the features of the indications for both procedures:
- FGS is prescribed when the doctor is sure that only the stomach is affected. This procedure will be faster and will cause the patient a minimum of discomfort, and when examined in a private clinic, it will also save money.
- FGDS is important for lesions of the duodenum. It is also prescribed for suspected diseases of the pancreas, liver and gall bladder. The doctor can judge the state of their work by the nature of the discharge and the results of changes in the papillary zone.