Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the heart or echocardiography (ECHO-CG) of the fetus – an important part of the study during pregnancy.
Heart development is a complex and interesting process. The rudiment of the heart muscle is formed in the 4th week of pregnancy and is a hollow tube. Around the 5th week, the first pulsating contractions occur, and by 8-9 weeks the heart becomes four-chambered - 2 atria, 2 ventricles, that is, like in an adult.
To assess cardiac activity, ECHO-CG, auscultation, that is, listening to the heartbeat, and cardiotocography (CTG) are used.
Starting from 5-7 weeks and throughout pregnancy, as well as childbirth, doctors carefully monitor the contractions of the fetal heart. The nature and frequency of the heartbeat reflect its general condition.
Heart rate (HR) is an important indicator of fetal viability. The normal heart rate depends on the stage of pregnancy:
- 110-130 beats per minute at 6-8 weeks;
- 170-190 beats per minute at 9-10 weeks;
- 140-160 beats per minute from 11 weeks until birth.
ECHO-CG of the fetus is the most in-depth way to diagnose its heart. During the examination, the doctor assesses the position of the organ in the chest, measures its size, as well as the size of the chambers and vessels, and assesses blood flow.
By order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 1130n of 2021, expectant mothers are recommended to undergo two ultrasound screening procedures - at 11-14 weeks of pregnancy and 19-21 weeks.
Ultrasound screening (from the Latin “screening” - sifting) is a medical examination of the fetus aimed at identifying abnormalities in its development, including identifying chromosomal abnormalities and malformations.
A screening study does not establish, but does not completely exclude the diagnosis of chromosomal pathologies - screenings using special ultrasound signs and biochemical results identify patients with a high risk of developing defects who need to undergo additional examination.
Cardiac ultrasound is a routine part of screening. The most accurate result is obtained at a period of 18-24 weeks, since in the early stages not all features and structures of the heart muscle are noticeable, and in later stages the study is limited by the fetal skeleton and the noticeably enlarged abdomen of the pregnant woman. The basic evaluation procedure includes a 4-chamber study and a view through three vessels and the trachea. A detailed ultrasound is prescribed in cases where a planned examination, in the form of ultrasound screening, has shown pathology and requires a targeted assessment of the heart muscle and blood vessels.
Indications for in-depth research:
- If a pregnant woman, her husband, or their children have congenital heart disease (CHD);
- The effect of unfavorable factors during pregnancy (long-term and severe toxicosis, accompanied by physical exhaustion, living in environmentally unfavorable conditions, taking alcohol, drugs, etc.);
- Diseases that require treatment of a pregnant woman with antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant and other groups of drugs (HIV, rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis, etc.);
- Maternal diseases such as diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus and others;
- If abnormalities are detected during routine ultrasound examination.
Ultrasound of the fetal heart in pregnant women
May 26, 2016
In Russia, about 10,000 children are born annually with congenital heart defects (CHD), 30-50% of them are “critical defects of the newborn period,” i.e. CHD, for which specialized care is indicated in the first year, month, day, and sometimes in the first hours of a child’s life. This circumstance dictates the need to identify congenital defects of the circulatory system even before the birth of the child.
Considering the need to conduct an echocardiographic examination (ultrasound of the heart) of the fetus in pregnant women, the medical specialist trained an ultrasound specialist, pediatric cardiologist S.A. Aleksandrova, at the Scientific Center for Cardiovascular Surgery named after. A.N. Bakuleva, Moscow, in the additional professional program “Intrauterine diagnosis of pathology of the cardiovascular system.”
The most in-depth and productive study of the cardiac system is ultrasound of the fetal heart. It is prescribed after three previous checks: auscultation, cardiotocography and ultrasound examination. In case of detection of violations and preliminary indications for serious diagnosis, ultrasound of the fetal heart (echocardiography) is necessary. Fetal echocardiography is a method of examining the heart using special ultrasound equipment with built-in cardiac programs. The procedure does not pose any danger or pain to the mother and fetus. This method allows you to diagnose heart defects in a child in the prenatal period, before birth.
In order to identify congenital heart disease in the fetus, it is advisable to conduct a single complex echocardiographic examination of the fetus at 20-22 weeks of pregnancy in women with a normal pregnancy who are not at risk. Women belonging to the high-risk category are required to undergo echocardiographic monitoring of the fetus at 18-20, 26-28 weeks of pregnancy.
The ultrasound method really makes it possible to determine disorders in the cardiovascular system of an unborn child. Some pathologies may be so severe that the child will not be able to independently exist with them outside the mother’s body. At the moment when, after birth, the umbilical cord blood stops flowing to the baby and he takes his first breath, his pulmonary circulation starts, and an increased load falls on the heart. This may cause the condition to worsen, perhaps even to a critical level.
Therefore, it is necessary to know in advance what heart pathologies the fetus has. Thanks to this information, doctors will be able to fully provide the necessary care to the newborn. And if the child needs surgery, the expectant mother will also make sure in advance that the child she is expecting has a place prepared in the clinic where he can undergo it.
Factors that require further fetal echocardiography on the maternal side include:
- congenital heart defect in the child’s parent;
- previous pregnancy with congenital heart disease or atrioventricular block;
- general maternal diseases: diabetes Type 1, Type 2, phenylketonuria; use of medications before and after conception: antiepileptic drugs, lithium, antidepressants, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
- maternal use of nonspecific anti-inflammatory medications during pregnancy 25-30 weeks;
- Detection of infectious and viral diseases in a pregnant woman (toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, parvovirus B19;
- Autoimmune diseases that affect several organs at once;
- Thyroid diseases;
- High blood pressure;
- Mother's use of alcoholic beverages and drugs during pregnancy, such as cocaine and marijuana;
- Pregnancy using in vitro fertilization method.
Factors that require further echocardiography from the fetus include:
- Heart rhythm disturbances with suspected congenital heart disease;
- Violations of the thickness of the collar space;
- Bradycardia (less than 100 beats per minute) and tachycardia (more than 180 beats per minute)
- Fetal factors causing cardiac failure, such as: tricuspid valve insufficiency, abnormal blood flow in the ductus venosus, feto-fetal transfusion syndrome, monozygotic twins, abnormal development of the venous system, fetal iron deficiency, congenital anastomosis between the artery and vein, single umbilical cord artery.
- Hereditary diseases with a violation of the structure of chromosomes. (Down, Patau, Edward, DiGeorge, Turner syndrome)
- Genetic diseases with concomitant cardiomyopathy.
A timely visit to a doctor will help with earlier diagnosis and successful treatment of the identified disease!
Medical is located in the public business area at the address: Shakhty, st. Shishkina 162.
Phone numbers for making an appointment: 8 (8636) 288-433, 8 (8636) 236-934.
Request a call back for a consultation and make an appointment with a specialist!
Preparation
No preparation is required before the procedure. For short periods of time, a “vaginal” sensor is used for better visualization. The study at a later stage is carried out using an “external” sensor, that is, through the abdomen. The pregnant woman applies the gel to her stomach, examines the fetal heart, and measures the heart rate.
If an examination reveals a developmental abnormality in the fetus, the parents are informed about the severity of the pathological changes, treatment options and how viable the child will be. A woman can decide to terminate or continue the pregnancy.
Features of the procedure
Echocardiography of the fetus is carried out using a color ultrasound diagnostic device and a Doppler ultrasound device. Most often, the sensor is installed on the pregnant woman’s abdomen, but if there is a need for early examination, it can be inserted vaginally.
The most accurate results are obtained between 18 and 22 weeks. This is explained by the fact that in the early stages not all features of the heart may be noticeable or they are not visualized clearly enough, and later difficulties are associated with the pregnant woman’s belly becoming too enlarged and the sensor being located too far away, and the formation of the fetal bone skeleton (in particular, the chest). In the latter case, the image also comes out less clear. The procedure usually takes about 45 minutes, but can last longer if abnormalities are detected.
Based on the results of the study, an experienced cardiologist will be able to examine the exact structure of the heart chambers, valves, arteries, veins and any other structures. In M-mode, the size of the heart and the correct functioning of the ventricles are determined. And Doppler echocardiography allows the doctor to evaluate the heart rhythm, direction and speed of blood flow.
If abnormalities are detected during fetal echocardiography, it is important to undergo a repeat examination. In addition, congenital heart disease requires childbirth to take place in specialized medical institutions that have equipment for performing cardiac surgery on newborns.
Why is it important to perform an ultrasound of the heart during pregnancy?
A timely ECHO-CG of the fetus makes it possible to identify congenital malformations, including those of the heart. Congenital heart disease is a developmental anomaly in which certain structures of the heart muscle have not formed or are incorrectly located. A child with a pathology must be born in a specially equipped institution, where he will have the opportunity to receive the help of a resuscitator, cardiovascular surgeon and obstetrician-gynecologist.
Medical equipment uses expert class equipment with the possibility of Dopplerography and color Doppler mapping. The knowledge of specialists and high-class equipment allows you to obtain detailed, accurate information about the state of the child’s cardiovascular system.
UPS is not the end and not a death sentence. Most are operable, which means the baby has every chance of a healthy life. It is only important not to miss the moment and find out about the problem in time.
Abnormalities of fetal heart position
The content of the article
Among the anomalies of the location of the heart, ectopia of the heart (placement outside the chest) is distinguished. Such pathologies include dextrocardia (displacement of the heart to the right side relative to the normal position) and mesocardia (the location of the heart is not on the left side of the sternum, but along the midline of the body).
Ectopy of the heart in the fetus occurs 14-18 days after conception, the mesaderm begins to develop incorrectly, which causes improper fusion of the abdominal wall. The fetus either has no diaphragm at all or no diaphragmatic segment of the pericardium.
Due to the hole in the wall between the right and left ventricles, intracardiac murmurs are heard. Also, in the fetus, ectopia of the heart is often accompanied by other anomalies - hydrocephalus, encephalocele, etc.
It must be said that there is a high probability of misdiagnosis based on the position of the heart. With a breech presentation of the fetus, the heart is visualized on the right side on ultrasound, although in fact it is located in the right place.
In 71% of cases, ectopia of the heart is caused by pleural effusion, cystic adenomatous malformation of the lung, or diaphragmatic hernia.
There are four types of ectopia:
- abdominal (the heart is located in the peritoneum);
- thoracic (the heart comes out through defects in the sternum);
- thoracoabdominal (Cantrell's pentad is a complex pathology with a complex of deviations from the norm);
- cervical (the heart moves to the heart area).
Thoracic ectopia occurs in 55-60% of cases, thoracoabdominal - in 38%, cervical - in almost 3%. Survival rate is about 10%. In most cases, with ectopia, the baby is either stillborn or dies immediately after birth.
The pathology is accompanied by displacement of other internal organs, which are not protected from mechanical damage and are more susceptible to infections and viruses than usual.
Heart ultrasound at home
Our clinic offers to conduct ultrasound examinations at the patient’s home. To do this, first leave a request by phone and select a convenient time for the appointment. In the process of communicating with the operator, you need to answer a number of questions, describe symptoms, voice a previously made diagnosis (if any), leave your personal data and coordinates.
At the appointed time, a doctor will arrive at the patient’s home with a portable ultrasound machine, which is no different in efficiency from the usual stationary equipment. A small design will allow you to make a full diagnosis and get maximum useful information.
With the help of Doppler, ultrasonic waves penetrate the tissue and, when reflected from the organ, return with the necessary indicators, which appear on the monitor in the form of an image.
This service will make people's lives much easier:
- with pastel mode;
- disabled;
- in old age;
- with small children;
- after a complex operation.
Ultrasound at home will become indispensable for people with limited free time.
Where to do an ultrasound of the heart
Even if you do not have symptoms indicating the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system, experts recommend undergoing an ultrasound scan 2-3 times a year for preventive purposes. However, not everyone has the opportunity to take time off from work and stand in long lines waiting to see a doctor.
A way out of this situation may be to undergo this examination in a private clinic. After all, you can make an appointment at any time convenient for you, and highly qualified staff will conduct all the necessary research. Ultrasound results are processed immediately, so you do not have to wait long to receive a medical report.
Find a qualified cardiologist and make an appointment with him, as well as make an appointment with a sonologist for a preventive ultrasound, the help desk for private clinics in Moscow “Your Doctor” will help you.
Publication date: 2019-12-13
Preparing for the study
Although most ultrasound examinations do not require preparation, there are a few exceptions:
- before an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the patient is asked not to eat or drink anything 6 hours before the procedure;
- a full bladder may be required during pelvic ultrasound;
- to improve image clarity, a harmless substance called contrast agent is injected before the examination;
- If necessary, intravenous tranquilizers are used.
Young children may require additional preparation for an ultrasound. We are talking about the use of sedatives to prevent the child from being overly active during the procedure.
Is it safe for the fetus and mother?
Ultrasound diagnostics are performed several times throughout pregnancy to monitor the condition of the internal organs and the dynamics of the baby’s development. Some mothers are worried about the possibility of negative effects on his body, but there is no need to worry.
Heart ultrasound is one of the few diagnostic methods that are allowed during pregnancy. This procedure is completely safe for mother and child, no matter what line it is performed on. The technique is based on the use of sound waves in the 20 kHz range. They are reflected from the tissues of the organs, captured by the sensor and converted into an image on the monitor. The vibrations produced by the sensor are painless and do not cause tissue damage or the development of fetal defects.
Results standards
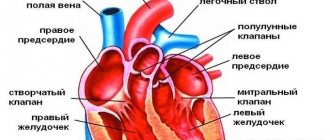
Indicators corresponding to generally accepted standards of ultrasound diagnostics:
- Stroke volume. This is the volume of blood pumped by the heart muscle per unit of time. Norm – 60 – 100 ml.
- Left ventricular volume at rest. Should not exceed 3.3 - 3.5 cm.
- Volume of the left ventricle at the time of contraction. The final systolic size is 2.3 – 4.1 cm.
- The area of the mitral valve in the open state is up to 4 cm2.
- Aortic valve dilatation of 1.5 cm or more.
- There is no transudate or exudate.
- The thickness of the posterior border of the left ventricle is 0.8 – 1.2 cm.
- There are no foreign inclusions.
- The mass of the muscular layer of the left stomach is 130 – 147 g. When assessing the indicators, the gender of the subject is taken into account.
These are the main indicators that the doctor pays attention to when interpreting the ultrasound results. Minor deviations of parameters in one direction or another are permissible provided there are no organic damages and serious disturbances in the functioning of the organ.
We will be waiting for you at the examination - make an appointment using the form on the website or by phone: +7.
Restrictions and contraindications
Ultrasound and echocardiography are absolutely safe for a pregnant woman, so there are no contraindications to the study or restrictions on the number of procedures. The only nuance that should be taken into account is the duration of pregnancy - the study does not make sense to do before the 5th week.
Echo-CG performed before the 5th week of gestation is not very informative, since the baby’s heart is still too small. A study in the 3rd trimester will also not provide the necessary information due to the woman’s large belly - the sensor will be located far away, the picture will be unclear.
Despite the advantages of diagnostics and its safety, experts are confident that one thorough study is enough. Each diagnostic procedure must be justified, so a repeated examination is carried out only if indicated.
Which doctor performs cardiac ultrasound?
An ultrasound examination of the heart is performed by an ultrasound specialist with the appropriate specialization or a cardiologist. The doctor conducts an examination, analyzes the information received, deciphers the readings and determines the diagnosis.
If the procedure is performed by a specialist, he can immediately make a diagnosis, determine the complexity of the current situation, give a prognosis and select effective treatment.
If it is possible to get by with drug treatment, the specialist will definitely take this chance and prescribe drug therapy. In the complex, nutrition, lifestyle, and psychological state must be adjusted.
The patient is advised to walk more, overwork less, eat light, healthy food, give up bad habits, avoid stress and nervous strain. Based on the ultrasound readings, the cardiologist will be able to calculate all possible risks.
Timing of ultrasound
The first ultrasound is performed at a period of 3 weeks and is a transvaginal examination familiar to all women (using a vaginal sensor). This examination allows you to confirm pregnancy, determine the number of fetuses and monitor the heartbeat of the embryo.
For a comprehensive assessment of the health of the body of the expectant mother and child, a screening examination is used, including a blood test for hormones and an expert screening ultrasound.
Routine screening ultrasound of pregnant women is carried out 3 times (according to the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated November 1, 2012 “On approval of the Procedure for providing medical care in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology”), one study in each trimester.
- Ultrasound 1 screening – period 11-14 weeks;
- Ultrasound 2 screening – period 18-21 weeks;
- Ultrasound 3 screening – period 30-34 weeks.
However, do not be alarmed if your obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes additional tests, since if there are certain indications, the number of ultrasound scans may increase to monitor the dynamics of fetal development.
Now let's take a closer look at exactly what information the study provides in each trimester.
What heart pathologies in the fetus are difficult to detect using screening ultrasound?
Difficulties in diagnosing heart diseases on ultrasound are caused by the following organ pathologies:
- atrial septal defect;
- ventricular septal defect;
- transposition of the main arteries.
If their presence is suspected, the patient should be regularly monitored and follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Why should you have an echocardiogram?
Heart ultrasound for pregnant women
is an important procedure, the results of which determine the health of not only the mother, but also the child. This study does not take much time, but it makes it possible to feel confident about the healthy future of your baby.
A healthy child is the key and guarantee of a happy family life. Cost for heart ultrasound for pregnant women
women is an acceptable and necessary payment for safe childbirth and a healthy life for the unborn child.
This article does not constitute medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for consultation with a physician.
Progress of the study
Ultrasound examination includes the following stages:
- Preparation. The diagnostician will ask the patient to remove clothing from the chest and sit comfortably on the couch. To improve the permeability of ultrasonic waves, a conductor gel is applied to the skin.
- Ultrasound of the heart. The procedure is performed in the supine position. Using an ultrasound sensor, the doctor moves it across the area under study, studying the organ in detail. If necessary, the diagnostician will ask you to change your body position, hold your breath or, conversely, speed it up. The ultrasound procedure lasts on average 15 – 20 minutes.
- Getting results. The results of the study are issued immediately after filling out the ultrasound protocol form. You must show the document to the doctor who gave you the referral for diagnosis.
Decoding the results
Ultrasound and echo-CG help diagnose most pathologies of the heart muscle in a child. Such diagnostics makes it possible to predict the further course of pregnancy in the presence of abnormalities and the success of their correction through surgical intervention. The main criterion for the normal development of a child is heart rate. It should not deviate from the average statistical norms at a certain stage of pregnancy:
| Week of pregnancy | Heart rate (beats per minute) |
| 5 | 85 |
| 6 | 120 |
| 7 | 130–150 |
| 8–11 | 150–180 |
| 12–40 | 145–170 |
If the values are less than the specified standards, this indicates bradycardia, if more, this indicates tachycardia. Also during the research process, the specialist pays attention to other parameters that may indicate problems with the functioning of the heart muscle:
- a disturbance in the rhythm of the heartbeat may indicate hypoxia or fetal malformations;
- the presence of extraneous noise can indicate heart pathologies or oxygen starvation of the baby;
- The dull sound of heartbeats indicates hypoxia.
If a serious pathology is revealed in a child during the examination, it is necessary to undergo the procedure again after 7-14 days to exclude a medical error. If abnormalities in the development of the baby's heart muscle are detected, treatment or surgery can be prescribed after birth, and sometimes doctors take a wait-and-see approach - some pathologies in children go away with age. Sometimes specialists discover serious malformations that are incompatible with life, as a result of which the woman is offered to terminate the pregnancy.
At what time does BS appear in the fetus?
An ultrasound is used to listen to the baby's heartbeat. This is a special type of checks designed to determine the health of the baby. However, it will be problematic to hear the heartbeat within a certain period of time. Some people hear knocking sounds in the 4th month. For others, at 6-7 months of pregnancy. You can hear it thanks to ultrasound diagnostics. If you perform an ultrasound internally (transvaginally), you can hear heart sounds already at 4-5 weeks. If an ultrasound is performed externally, then readings can be obtained at 6-7 weeks.
In order to determine at what time SB appears in the fetus, it is necessary to establish the individual characteristics of the baby. Everyone's heartbeat can begin to be heard at different times.
Diagnostic methods:
- Using a stethoscope;
- Ultrasound.
A stethoscope is a special medical instrument that allows you to hear your heartbeat. This is done by a gynecologist. This instrument is made of wooden material and has an oblong shape. The examination is called ausculation. In order to increase sensitivity and hear better, there is a funnel at the end of the stethoscope, which has a wide diameter. This procedure is necessary. Because the presence or absence of a heartbeat is very important for the health of mother and baby. The longer the period, the better the beating is audible. This device has its own specifics. It is used at the 20th week of fetal ripening.
This is due to the fact that the device is not powerful enough to hear the beating of the heart under the skin. Until the heart gets stronger and gets bigger.
What diseases does ultrasound of the heart show?
A diagnostic test helps to identify:
- rheumatism;
- hypertension;
- myocarditis;
- disturbance of heartbeat rhythms;
- pericarditis;
- heart defects of various types;
- myocardial infarction;
- pathologies of arteries, aorta;
- ischemia.
Ultrasound also indicates the presence of intracardiac formations, hypotension, vegetative-vascular dystonia, cardiomyopathy, and diagnoses heart failure. The examination helps to detect neoplasms, hypo and hypertrophy of the myocardial walls, and expansion of cavities.
How is cardiac ultrasound performed?
The patient does not need special preparation for echocardiography. The procedure itself basically goes like this: the patient lies on the left side (in this position the lungs and ribs will not interfere with the passage of the ultrasound wave), after which the doctor applies a small amount of a special gel to the skin and applies a sensor. The signals received by the sensor will be transmitted, forming an image on the monitor screen, which can be two-dimensional or three-dimensional.
This type of study is called transthoracic. However, there are situations in which the cardiologist prescribes another type of echocardiography - transesophageal examination. It involves passing a scanning probe through the esophagus. Most often, such echocardiography is indicated during heart surgery and in the first time after heart surgery.
Useful information on diagnosing and treating heart disease:
- Diagnosis of cardiac diseases
- Consultation with a cardiologist
- Cardiology - the science of heart diseases
- Examination by a cardiologist
- Pediatric cardiologist
- Treatment of cardiac diseases
- Cardiologist appointment
- Prevention of cardiac diseases
- Paid cardiologist