- Mom's health
Medicine has advanced a lot in recent years. If just ten years ago, during the entire pregnancy, women took only a few tests and underwent an ultrasound scan 1-2 times, now expectant mothers are under the constant close supervision of doctors and undergo thorough examinations. And, of course, this is not the whims of doctors, but an urgent need, because modern diagnostic methods make it possible to detect various anomalies and developmental defects in the fetus already in the early stages of pregnancy.
Hypoplasia of the nasal bone in the fetus - what is it?

So if your doctor has prescribed this procedure for you, do not refuse. The harm from ultrasound during pregnancy is nothing more than a myth, but there can be a lot of benefits from this examination. The nasal bones are quadrangular, elongated bones that are visible as early as –11 weeks of pregnancy. If the length of the nasal bone in the fetus is less than it should be at this stage of pregnancy, then in this case they speak of hypoplasia of the nasal bone. If the fetus's nasal bone is completely absent, the condition is called aplasia.
Causes of nasal bone hypoplasia
Previously, the fact of nasal bone hypoplasia did not attract much attention, but relatively recently, thanks to scientific research, it was possible to establish the relationship of such an anomaly with the possibility of having a child with Down syndrome and other chromosomal pathologies.

Numerous studies in this area have shown that hypoplasia was detected in 80% of children born with genomic pathology. This gave reason to believe that such an anomaly is a sign of congenital abnormalities. Factors that provoke hypoplasia are varied:
- taking potent medications in the first trimester of pregnancy, including antibacterial drugs;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- marriage between blood relatives;
- gamma radiation from a woman during pregnancy;
- injuries and bruises from falls;
- harmful working conditions;
- intoxication with hazardous chemicals;
- heredity;
- infectious diseases (herpes, rubella, smallpox, toxoplasmosis, hepatitis, ARVI);
- prolonged overheating of a pregnant woman under the sun or in a sauna;
- the age of the expectant mother, after 40 years the risk of having a sick child increases;
- environmental factors that negatively affect a pregnant woman’s body.
Shortening of the nasal bone may be the result of genetic predisposition and poor lifestyle choices, the influence of negative factors that pregnant women often overlook. Even severe toxicosis can provoke the development of such a serious pathology.
Thanks to modern diagnostic methods used in obstetrics, it is possible to detect hypoplasia of the nasal bones in the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy. This anomaly is a clinical indication for artificial termination of pregnancy. But if the parents are ready to accept such a child, the embryo is saved. The main thing is to listen to the advice of doctors and make the right decision.
Why do you need to know the length of the fetal nasal bone?
Hypoplasia of the nasal bones in the fetus or their aplasia is considered one of the most important signs (markers) of some chromosomal abnormalities, for example, Down's disease, Edwards, Turner, Patau syndromes and some others.
True, in the very early stages, the very presence of nasal bones in the fetus is much more important than their size. And you can determine the size no earlier than the 12th week of pregnancy.
Here are a few examples as an example:
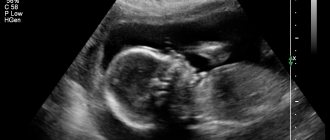
1. Below on the ultrasound we see a normal nasal bone. 3 clear lines can be distinguished.
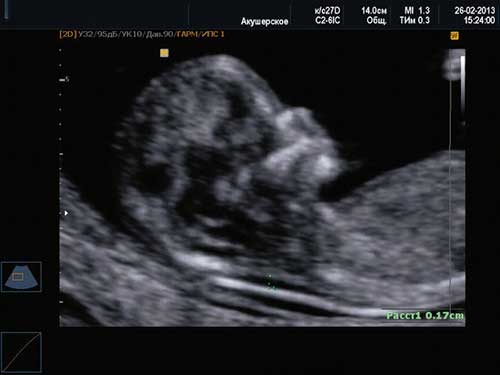
2. Hypoplasia of the nasal bone. Ultrasound done at 12 weeks of pregnancy. Length - 1.4 mm (below the normal limit).
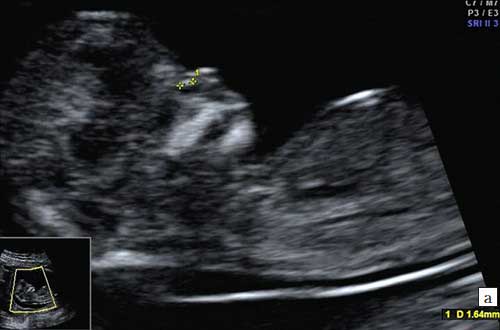
Signs of hypoplasia
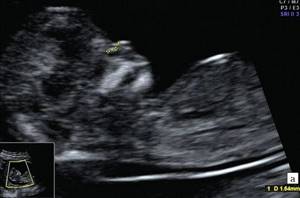
It is important to detect hypoplasia of the nasal bones in the fetus before 20 weeks of pregnancy. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a clear discrepancy between the actual length and acceptable standards. There is a special table that determines the minimum and maximum size of the nasal bone depending on the stage of its growth and development. For example, the norm at 12-13 weeks is 2-4.2 mm; at 20-21 - 5.7-8.3 mm. The data was obtained by WHO during a survey of hundreds of healthy babies.
How accurately this indicator will be determined depends on the ultrasound machine and the qualifications of the specialist conducting the study. The risk of false conclusion remains when conducting any medical analysis, therefore, in the case of a positive/negative result, at least one repeat diagnostic procedure is performed.
If you find a shortened nasal bone on an ultrasound, you should not fall into despair. A thorough examination is a necessity that increases the chances of having a healthy baby, while the stress of interim results can harm the pregnant woman and her fetus.
Norms for nasal bone size by stage of pregnancy
The size of the fetal nasal bones depends on the stage of pregnancy. For example, at 12–13 weeks of pregnancy, the length of the nasal bone is only 3.0 mm. At -21 weeks it increases to 5.5 - 5.7 mm, and by the 35th week of pregnancy it reaches 9.0 mm.
In order to correctly and accurately assess the parameters of the nasal bone obtained during an ultrasound examination, the doctor must have extensive experience and high qualifications. In addition, it is necessary that the ultrasound be performed on a modern device - otherwise, obtaining reliable results is very doubtful.
Gnomik.ru recommends Rmh24.ru Refrigerator repair shop We repair refrigerators of all brands. Free visit of a specialist and diagnostics!
Use promo code: Gnomic.ru
and get a guaranteed 10% discount
We work in Moscow and the region.
Call
Call a specialist
Diagnosis of hypoplasia
Ultrasound at 10 weeks of pregnancy allows you to measure various fetal parameters necessary to assess its development. The discrepancy between the results obtained and the norm is grounds to assume the presence of possible deviations.
But even if an ultrasound showed that the nose is not developed enough, there is no need to panic ahead of time. The presence of one symptom is not always the basis for issuing a conclusion about the presence of a genomic disease. The results of the first screening are important in making a diagnosis, but at the same time it is necessary to conduct a more in-depth examination and only then draw conclusions.
Sometimes during examination there is a complete absence of the nasal bones. In such cases, aplasia is diagnosed.
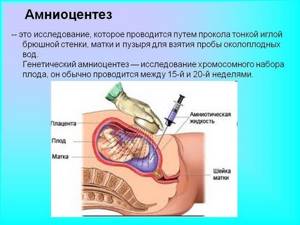
If the repeat ultrasound is similar to the first, amniocentesis is performed - analysis of amniotic fluid for the presence of chromosomal abnormalities. The study will allow us to collect data on the intrauterine development of the fetus and assess the degree of presence of genetic pathologies.
Doctors also usually prescribe:
- HCG analysis. The level of human chorionic gonadotropin allows you to detect pregnancy at an early stage and understand how successfully the fetus is developing. Genetic abnormalities can be indicated by either a sharp decrease or an increase in the concentration of the hormone.
- Blood test for PAPP-A. Plasma protein A is an important diagnostic indicator in the first trimester. A high level indicates a threat of miscarriage, a low level indicates the risk of genetic abnormalities in fetal development.
When diagnosing diseases, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of each organism, which are characteristic of it even at the level of intrauterine development. In some cases, the difference between real indicators and standard indicators is not critical. We can confidently talk about the presence of chromosomal abnormalities only in the case of hypoplasia of the fetus itself - short limbs, underdevelopment of internal organs. In any case, only a doctor can correctly decipher the research results and make a diagnosis.
Nasal bone hypoplasia and other indicators
Many parents, hearing from a doctor that the size of their unborn child’s nasal bone does not correspond to normal values, panic. In fact, it is too early to worry - it is simply impossible to accurately determine Down syndrome or any other chromosomal abnormality in a fetus just by the size of the nasal bones.
In order to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis, a pregnant woman is recommended to undergo a second ultrasound - with a different specialist and on a different device.
If, upon repeated examination, it is determined that the size of the baby’s nasal bone does not correspond to those that should be at this stage of pregnancy, then the woman is usually recommended to undergo additional examination - amniocentesis, i.e., sampling a small amount of amniotic fluid for subsequent genetic testing. analysis.
From 18 to 22 weeks
pregnancy, a second ultrasound screening of the fetus is performed. The main purpose of this study is to thoroughly evaluate fetal anatomy to diagnose the largest number of congenital malformations that are subject to prenatal detection. This is due to the possibility of termination of pregnancy for medical reasons in cases where congenital malformations are detected.
Main fetal indicators during ultrasound at 18 weeks:
- BDP (biparietal size) - 37-47 mm.
- FZ (fronto-occipital size) - 49-59 mm.
- OG (fetal head circumference) - 131-161 mm.
- Coolant (fetal abdominal circumference) - 104 -144 mm.
Normal sizes of long bones on fetal ultrasound at 18 weeks of pregnancy:
- Femur 23-31 mm,
- Humerus 15-21mm,
- Forearm bones 17-23 mm,
- Tibia bones 23-31 mm.
Fetometry during fetal ultrasound at 19 weeks of pregnancy is normal:
- BDP (biparietal size) - 41-49 mm.
- FZ (fronto-occipital size) - 53-63 mm.
- OG (fetal head circumference) - 142-174 mm.
- Coolant (fetal abdominal circumference) - 114 -154 mm.
Normal sizes of long bones during fetal ultrasound at 19 weeks of pregnancy:
- Femur 26-34 mm,
- Humerus 23-31mm,
- Forearm bones 20-26 mm,
- Tibia bones 23-31 mm.
Also, during an ultrasound, the amount of amniotic fluid is assessed - the amniotic fluid index.
Normally, with an ultrasound at 18-19 weeks, it is 80-230 mm. Oligohydramnios can negatively affect the development of the fetal bone and nervous systems, and polyhydramnios can be a sign of intrauterine infection.
Localization of the placenta.
During the normal course of pregnancy, the placenta is usually located in the area of the fundus or body of the uterus, along the back wall, with a transition to the side walls. On the anterior wall the placenta is located somewhat less frequently.
Placenta previa is a pathology in which the placenta is located in the lower parts of the uterus along any wall, partially or completely blocking the area of the internal os. The incidence of placenta previa averages from 0.1% to 1% of the total number of births. If the placenta only partially covers the area of the internal os, then this is an incomplete presentation. If the placenta completely covers the area of the internal os, this is complete placenta previa. This option occurs with a frequency of 20-30%. There is also a low location of the placenta, when its edge is at a lower level than it should be normally, but does not overlap the area of the internal os.
Umbilical cord.
One of the important parameters is the location of the umbilical cord attachment. Pathology is considered to be a marginal, split or shell attachment, which is fraught with fetal hypoxia and is an indication for cesarean section.
Cervix.
The length of the cervix at this stage should be 40-45 mm. A short cervix means a risk of miscarriage.
Fetal malformations - reliability of ultrasound
Each person is individual and, naturally, this individuality can be traced even at the stage of intrauterine development. Therefore, the sizes of body parts, including the nasal bone, may differ from the table values.
It is possible to speak confidently about the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus only when not only underdevelopment of the nasal bones is detected, but also hypoplasia of the fetus itself - short arms and/or legs, too small sizes of some internal organs.
Therefore, if during the next ultrasound it turns out that the size of your baby’s nasal bones is smaller than normal, this does not mean that there is a genetic pathology. It is quite possible that this is simply an individual feature of the fetus and your baby will be born quite healthy and with a charming snub-nosed “button”. In any case, only your doctor can correctly interpret all the results obtained and make the correct diagnosis. Trust him.
Fetal development anomalies and diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound
As already noted, to make a diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities, one cannot judge only by the underdeveloped size of the nasal bones identified on ultrasound.
All people are individual by nature and this can be observed even during observation of intrauterine development. Therefore, tabulated values of fetal development are not always a criterion for determining various pathologies. And the length of the nasal bone is no exception.
It is possible to reliably determine whether the unborn child has chromosomal pathologies only if hypoplasia of the nasal bones is accompanied by fetal hypoplasia, i.e. In addition to a shortened nasal bone, he was found to have reduced dimensions of his limbs or internal organs.
Considering all this, there is no need to panic ahead of time. Even if the next ultrasound examination reveals that the size of the baby’s nasal bone is smaller than the table values, this is not yet a reason to diagnose a genetic anomaly. It is very possible that your baby is completely healthy and will be born with an elegant small nose. The final diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after various examinations and long-term observations of fetal development.
Further actions
If fetal nasal bone hypoplasia, diagnosed at 12 weeks, is subsequently confirmed, it is time to act. Chromosomal abnormalities cannot be treated. Having discovered such an anomaly in the fetus, the right thing to do would be to make an appointment with a good geneticist as soon as possible. There is no point in waiting for a scheduled appointment; you could waste a lot of time.
If the likelihood of giving birth to a child with abnormalities incompatible with life is too high, the doctor will most likely advise an abortion.