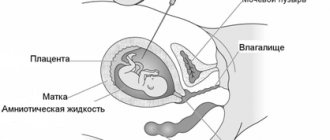
Ultrasound is widely used for examination during pregnancy. After all, this method is easy to carry out, does not cause discomfort, is safe for the mother and developing child, and is also informative. A special type of such diagnostics is ultrasound screening. It is included in the standard examination of pregnant women and is carried out strictly at certain stages of gestation, regardless of the individual characteristics of the course of pregnancy. Screening can be carried out by referral within the framework of compulsory medical insurance or for a fee.
What is perinatal screening
The content of the article
Perinatal screening is a set of diagnostic measures that allow prenatal examination of the fetus and identify expectant mothers with an increased risk of congenital pathologies and child development disorders. This screening in many countries is recognized as a basic test that provides the most complete information to the specialist managing the pregnancy and future parents regarding the health of the baby.
Many women, speaking about this examination, often confuse two concepts - prenatal and perinatal. So, prenatal diagnosis is carried out before conception, i.e. in this case, the expectant mother is examined. Doctors use different methods to determine the risks of having a sick child. Perinatal screening is an examination during pregnancy and the object of study in this case is the fetus. The importance of such a study, especially in the early stages, is undeniable: if the screening shows disappointing results, the patient always has a choice - to continue the pregnancy or terminate it.
Stages of perinatal screening
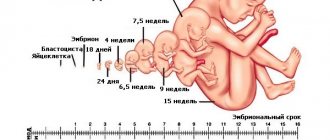
The entire complex of activities within the framework of perinatal research is divided into three stages, each of which the woman must go through at a certain stage of pregnancy. The first part of the diagnostic procedures occurs at 11-13 weeks of pregnancy, the second time you need to go for diagnostics upon reaching 18-24 weeks, the third perinatal screening is carried out at 30-34 weeks of pregnancy. The first 2 stages consist of two basic diagnostic procedures, each of which helps to identify genetic abnormalities
- Ultrasound – Ultrasound gives the most complete picture of the structure of organs, the functioning of the heart, as well as the external signs of the baby and its position in space.
- Biochemical blood test - this analysis is aimed at identifying in the patient’s blood certain substances of a protein nature that are produced by the fetus and amniotic membranes and may indicate the presence of chromosomal pathologies and disorders of the formation of the neural tube.
In our medical center, fetal examination is carried out using a modern 3D, 4D device with Doppler from SAMSUNG MEDISON
Clinical blood test
A complete blood test (CBC) is a mandatory test prescribed every time you visit a therapist (and almost all other medical specialists). The data from this examination allows you to get a general idea of the condition of the patient’s body.
In the first half of pregnancy, the analysis is carried out once a month, in the second half - every 2 weeks.
Main indicators of UAC:
- Hemoglobin. The main component of erythrocytes (red blood cells). The function of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen from the lungs to organs and tissues and remove carbon dioxide. The presence of anemia is determined by the hemoglobin concentration.
- Hematocrit is the ratio of cellular elements and the fluid medium of the blood. This indicator reflects the severity of anemia and shows how thick the blood is (the risk of thrombosis increases).
- Erythrocytes are red blood cells. When screening pregnant women, only the number of red blood cells is determined, without assessing their characteristics.
- Color index. Reflects the hemoglobin content in a red blood cell. It evaluates the nature of anemia and the presence of iron deficiency in the body.
- Platelets are a formed element of blood that participates in its coagulation and fibrinolysis (resorption of blood clots).
- Leukocytes are white blood cells that participate in immune reactions. Their function is to protect the body from viruses, bacteria and other foreign particles. Leukocytosis (increased white blood cells) indicates the presence of inflammation or other pathologies. However, in pregnant women, moderate leukocytosis is the norm.
- Leukocyte formula. This is the percentage of different types of leukocytes in the blood: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes and monocytes). Using this formula, we can approximately guess the cause of the pathological process (viruses, bacteria, parasites, allergies, etc.).
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). An increase in this indicator indicates the presence of inflammation or disease. In pregnant women, ESR is normally up to 2 times higher than in non-pregnant women.
Stage I of perinatal screening (11-13 weeks)
Examination of the expectant mother during this period allows us to obtain a huge amount of information regarding the condition of the baby and the general course of pregnancy. Ultrasound examination at 11-13 weeks of pregnancy in modern clinics is carried out using three-dimensional echography - 3D ultrasound (3D), thereby obtaining the following data regarding pregnancy:
- The number of viable embryos implanted in the uterus.
- Determining the exact duration of pregnancy.
- The presence or absence of gross malformations.
- Nuchal translucency thickness TVP (used as an indicator of some chromosomal syndromes).
- Visualization of the nasal bone is important to exclude the possibility of Down syndrome.
After undergoing a classic ultrasound, a pregnant woman undergoes a biochemical blood test, which at this stage is called a “double test”, due to the fact that the quantitative levels of two protein components are measured: PAPPA and hCG (free β subunit).
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
- one of the main pregnancy hormones contained in the mother’s blood serum. Its reduced level indicates placental pathologies, and its increased content may indicate chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
PAPP-A – also called protein A
. Its concentration in maternal blood may indicate the presence of chromosomal diseases such as Down and Edwards syndromes.
How to do 1 screening during pregnancy
As a rule, the first screening is carried out at the antenatal clinic and usually takes place within one hour. An ultrasound examination is completely painless, but a blood test may cause you a little trouble.
To ensure that the screening results are not distorted, it is advisable to prepare for the procedure the day before:
- do not eat chocolate, seafood, fatty meat;
- abstain from sexual intercourse.
Before taking blood and performing an ultrasound, the gynecologist weighs the pregnant woman and asks her to either not drink water at all or limit its consumption to half a glass.
Stage II of perinatal screening (16-18 weeks)
At this stage, it is quite possible to conduct a 3D or 4D ultrasound, which makes it possible to evaluate all the external aspects of the baby, and also, in the case of four-dimensional echography, determine the mobility of the fetus and its gender.
The biochemical component of the second stage is a “triple” test, which involves identifying and measuring the following protein components in the blood of the expectant mother:
- Free β subunits of hCG.
- Alphafetoprotein.
- Free estradiol.
ACE (Alpha Fetoprotein)
- a specific protein that is produced directly by the fetus and enters the mother’s blood through the placenta. Its increased content may indicate defects of the fetal neural tube and defects of other vital organs. A decrease in ACE can be recorded in chromosomal diseases such as Down syndrome.
Free estradiol
is a female steroid hormone that must be produced by the placenta during pregnancy. A decrease in the level of estradiol in a woman’s blood may indicate a violation of fetal development.
Possible risks that the first ultrasound will show
The above indicators are very important already in the first stages of screening, because obvious discrepancies with normal indicators can indicate the presence of possible pathologies in the fetus:
- risk of Down syndrome : if the nasal bone of the fetus is poorly identified on ultrasound, if its size is significantly below normal and the facial contours are not clearly expressed;
- risk of Edwards syndrome : if the nasal bone is practically invisible or its size is very small; an umbilical hernia has formed; instead of two umbilical arteries there is only one, the heart rate is extremely low;
- risk of Patau syndrome : if the umbilical hernia is clearly visible on ultrasound; heart rate is extremely high; pathologies of fetal development are observed.
Perinatal screening results
Despite the fact that perinatal genetic screening is recommended for all pregnant women, there are a number of families for whom a thorough diagnosis and consultation with a geneticist during pregnancy is mandatory:
- The spouses have relatives with severe genetic diseases.
- In a consanguineous marriage.
- During late pregnancy (mother is over 35 and father is over 40 years old);
- If the couple has already had children with genetic disorders.
- If the mother has severe somatic diseases (heart or kidney pathologies, diabetes mellitus);
- During difficult pregnancy;
- If you suspect the presence of genetic pathologies identified during ultrasound.
Evaluation of results
Data from ultrasound diagnostics and blood biochemistry are assessed together using special programs, which makes it possible to determine a woman’s individual risk. The risk group includes expectant mothers whose results are 1:300 – the risk of having a baby with a chromosomal abnormality. However, it should be understood that this result is not yet a diagnosis. To establish more accurate results, the pregnant woman is sent for additional studies in the form of invasive diagnostics. Now let's take a closer look at the most important part of perinatal screening during pregnancy - ultrasound.
Clinical urine analysis
The examination is carried out to assess the condition of the kidneys, the load on which in women during pregnancy increases several times. Prescribed monthly in the first half of pregnancy, then once every 2 weeks.
Main indicators of general urine analysis:
- Quantity;
- Color;
- Transparency;
- Density (specific gravity);
- pH is the concentration of free hydrogen ions in urine. It depends on the amount of acids and acid salts in it;
- Protein. There is practically no protein in the urine of a healthy person;
- Glucose. Glucosuria (increased glucose in the urine) indicates diabetes mellitus in the patient. In pregnant women, it is gestational, that is, it appears during pregnancy and goes away after childbirth;
- Bilirubin. Normally, it is not present in the urine; it appears with jaundice;
- Urobilinogen. This is a substance formed in the intestines from bilirubin. There may be traces of it in the urine; its complete absence means that bile does not enter the intestines, which means there are problems with the liver or gall bladder;
- Ketone bodies. Formed during the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver. Normally absent in urine;
- Erythrocytes (red blood cells). Normally, there are no or single occurrences in urine;
- Leukocytes (white blood cells). Single ones may be detected;
- Epithelium. In a healthy woman, there are no epithelial cells in the TAM;
- Cylinders are protein and cellular particles. Appears in renal pathology;
- Bacteria. Normally they are not present in urine;
- Salt. Should not be detected.
Online consultation with a gynecologist
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
The role of 3D ultrasound in perinatal screening: 3D or 2D?
Today, no one doubts that ultrasound diagnostic techniques are the most important aspect of monitoring intrauterine development, age and position of the fetus. At the same time, the technical base of medicine does not stand still, and in addition to the classic, two-dimensional ultrasound, such a useful diagnostic practice as 3D ultrasound or three-dimensional echography has come. The advantages of this research method lie in the possibility of obtaining a three-dimensional image, which in all colors demonstrates to the specialist and future parents all aspects of the external manifestations and organs of the baby.
Differences between 3D ultrasound and classical ultrasound
All ultrasonic research methods have a common principle, which is based on the use of ultrasonic radiation, the wave frequency of which does not exceed 20 kHz. Applying such a wave load in a pulsed mode makes it possible to assess the functional normality and morphological structure of tissues, organs and systems of the fetus. At the same time, the traditional two-dimensional method displays a flat image on the dashboard monitor, which is understandable to doctors, but is not informative for non-professionals, namely for the child’s parents who are looking forward to meeting the baby for the first time. It should be noted that this method of diagnostic monitoring is important for medical specialists managing pregnancy, as it makes it possible to fully assess the structure of the internal organs of the fetus, which is incredibly important when organizing comprehensive monitoring.
Three-dimensional echography produces a full-fledged three-dimensional image that does not require decoding and clearly reflects the external features and position of the baby in the womb.
Advantages of 3D ultrasound in perinatal screening
3D ultrasound provides doctors with a number of obvious advantages:
- A clearer image
makes it possible to identify a number of defects that cannot be identified during classical ultrasound screening: hand anomalies, facial clefts, skeletal malformations, disturbances in the formation of the anterior abdominal wall, placenta anomalies, structural features of the external genitalia, non-fusion of the spinal cord, etc. . Identification of all of these abnormalities requires a change in the strategy for managing such a pregnancy. - 3D ultrasound allows you to determine the sex of the baby
more accurately in the early stages of pregnancy, which may be necessary not only to satisfy the curiosity of future parents, but also from the point of view of eliminating the likelihood of hereditary pathologies associated with gender. - The psychological readiness of the mother and father
for the birth of the long-awaited child, of course, increases after the initial acquaintance with the baby, even through a monitor and a photograph, which, at the request of the parents, can be provided after this manipulation.
Features of three-dimensional echography
According to the results of numerous medical studies, 3D ultrasound is an absolutely safe diagnostic method that is used for medical reasons. The features of 3D ultrasound during screenings during pregnancy include the following factors:
- Three-dimensional echography is most informative at 22-33 weeks of pregnancy, since during this period the external signs of the fetus are already sufficiently formed, and its size does not interfere with visual inspection.
- The duration of a three-dimensional ultrasound is about 40 minutes, which is much longer than the time required for classical two-dimensional screening.
- The bladder does not have to be full before performing a 3D ultrasound.
- The diagnostic capabilities of the technique drop significantly in the presence of such characteristics of the patient or the course of pregnancy as severe obesity of the expectant mother, oligohydramnios, the presence of scars on the woman’s abdominal wall, or uncomfortable position of the fetus.
Three-dimensional echography is a diagnostic practice that has earned the trust of doctors and patients around the world, confirming its exceptional effectiveness and safety for both women and babies. At the same time, today, 3D ultrasound remains the “gold standard” for intrauterine study of the structure of facial structures, limbs, sexual characteristics and space-occupying formations in the fetus, as well as a backup method for identifying such chromosomal abnormalities as Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, etc.
The value of 4D ultrasound in perinatal diagnosis: advantages and features
In modern practice of medical management of pregnancy, such a procedure as 4D ultrasound has become basic, both for a specialist monitoring the course of gestation and for impatient parents who are waiting to meet their child. This technique has several significant advantages over classical two-dimensional screening and is very often used as an addition to the basic course of mandatory research.
4D ultrasound will provide an opportunity not only to fully assess the health and development of the baby, but will also give parents the joy of first visual contact with the child, who will be in the natural intrauterine environment.
4D ultrasound - capabilities and advantages
The capabilities of the 4D ultrasound procedure are somewhat expanded in comparison with the usual two-dimensional echography. This is ensured by the fact that the examination (also called color ultrasound) allows you to evaluate the external manifestations of the fetus using four dimensions simultaneously: depth, height, length and time. As a result of the procedure, the image displayed on the dashboard monitor will resemble a video that in real time demonstrates not only the appearance and main morphological features of the baby, but also his movements, facial expressions, gestures and smile.
If the baby has not turned his back to the ultrasound scanner, such a sight evokes a lot of positive emotions among parents and provides certain diagnostic information to the specialist.
Positive aspects of 4D ultrasound for a pregnancy specialist
In addition to data that is standard for all ultrasound methods regarding the age, size and position of the fetus, 4D ultrasound gives the specialist the opportunity to determine the presence of the following anomalies in the baby’s development:
- Facial defects (facial clefts)
- Skeletal malformations (non-fusion of the spinal cord)
- Anomalies of the hands (quantitative pathologies of the fingers)
- Presence of space-occupying formations in the fetus
- Pathological changes in the placenta
- Defects of the anterior abdominal wall
- Abnormal development of the external genitalia
4D ultrasound makes it possible to track the natural movements of the fetus. This can also become important information in the process of confirming a particular developmental pathology. Thanks to the expanded review that this option of ultrasound screening implies, it is also possible to visually assess the structure of all external signs. This is especially true for facial structures (nasolabial triangle, lips, ears, chin, nose, etc.).
It should also be noted that the 4D technique provides more accurate information regarding the baby’s gender. This information is of interest to the doctor due to the presence of a hereditary pathology factor or genetic abnormalities linked to sex. And this is one of the main tasks of perinatal screening.
Positive aspects of 4D ultrasound for expectant parents:
- The opportunity to see the baby long before his birth, establish a certain psychological contact with him, and also prepare for the external characteristics of the baby.
- You can find out exactly the gender and even see the confirmation in person, on the monitor screen. This aspect almost always worries parents, as well as the developmental characteristics of the child.
- Parents can receive a video that will remain an unusual memory of such an important period in the life of every family as pregnancy. We are giving a CD with the recording as a gift!
How does 4D ultrasound work?
The procedure is practically no different from standard ultrasound screening. However, four-dimensional echography takes almost three times longer than black-and-white ultrasound (about 45 minutes). At the same time, a pregnant woman should know that filling the bladder does not affect the results obtained. In addition, it is worth understanding that the 4D technique has a maximum level of information content in the period from 22 to 33 weeks, which is due to the development and size of the fetus.
Patients suffering from severe forms of obesity or having scars on the abdomen, as well as when diagnosing a condition such as oligohydramnios, should be prepared for the fact that the picture may not be clear enough. In almost all other cases, 4D ultrasound will be an excellent way to get to know the baby and get a guarantee of its normal intrauterine development. The Diana Clinic offers its patients a 4D ultrasound procedure, guaranteeing information content and safety for the baby and the expectant mother.
Analysis for hCG β - unit for perinatal diagnosis
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is a hormone whose concentration increases sharply during pregnancy. Its increase indicates that conception has occurred, which is extremely important during pregnancy resulting from infertility treatment. HCG is not strictly a “female” hormone. This substance is specifically administered to men in order to improve sperm count in cases of suspected male infertility.
What is hCG and β – hCG
This substance consists of two components:
- α-unit similar to other hormones;
- β is a unit unique to hCG, distinguishing it from other hormonal substances.
That is why it is the β - unit that is analyzed, and the analysis itself is often called β - hCG.
The hormone is produced by the cells of the embryonic membrane to stimulate hormones that support pregnancy - progesterone and estrogen. This prevents the onset of menstruation and allows the embryo to “take root.” That is why, in case of infertility, doctors analyze the level of hCG in the patient’s body. If its content drops or lags behind the norm, the woman is prescribed hormonal drugs to support pregnancy. Monitoring the level of the hormone is necessary for women who are prone to recurrent miscarriage and have had frozen pregnancies.
The concentration of hCG increases rapidly until the placenta is formed, which later takes over the hormonal function. A rapid increase in hormone levels indicates that the pregnancy has continued and the embryo is developing. Subsequently, the hormone content decreases, remaining elevated before childbirth and somewhat after it.
Normal hCG levels vary greatly between women. The doctor determines whether everything is normal by the dynamics of changes in the indicator in a particular patient.
Approximate hormone concentrations during pregnancy are given in the table
| Duration, weeks | Concentration, honey/ml |
| 1 | 20-155 |
| 2 | 100-4850 |
| 3-4 | Up to 82,000 |
| 5-6 | Up to 151,000 |
| 7-8 | Up to 230,000 |
| 9-10 | Up to 290,000 |
| 11-16 | Decreases from 290,000 to 245,000 or less |
| 17-25 | Reduces to 50,000-80,000 |
| 25-37 | gradually decreases to 40,000 or less |
Inconsistency between the level of hCG and the period is observed in pathologies of pregnancy and abnormal development of the fetus
| promotion | demotion |
| hydatidiform mole | frozen pregnancy, embryo death |
| multiple pregnancy | risk of miscarriage |
| toxicosis | fetal underdevelopment |
| congenital hereditary diseases and fetal malformations | ectopic embryo implantation |
| hormonal pathologies in the mother | in the later stages indicates post-maturity |
Unlike pregnancy, in diseases that cause an increase in hCG levels (ovarian, stomach and breast cancer), the level of the hormone increases gradually and does not decrease. Therefore, a woman is prescribed such an analysis several times during pregnancy.
How is the β-hCG screening test performed?
For this study, blood from a vein or urine is donated, but the hormone is determined in urine later, and the result is not so accurate. Therefore, it is better to rely on a blood test showing the presence of the hormone and its concentration.
The material is collected in the morning on an empty stomach; if you need to take tests urgently, you need to fast for 4-6 hours. It is advisable not to take medications at this time. If the level of hCG in the early stages begins to rapidly decrease or increase, you need to consult a doctor and identify the cause.
What determines the information content and reliability of ultrasound screening?

Screening ultrasounds do not require special training from the woman, unlike the biochemical stage of the examination. To improve visualization of the uterus and appendages, it is advisable to exclude from the menu for several days foods that provoke gas formation in the intestines. If you are prone to constipation, you may need a cleansing enema or the use of laxatives. This will help avoid discomfort when inserting a vaginal sensor and will reduce the likelihood of increased uterine tone.
The information content and reliability of the data obtained largely depend on compliance with the recommended diagnostic time. Unfortunately, sometimes, due to the high workload of doctors in the compulsory medical insurance system, women are forced to undergo the first screening quite late, at the borderline. The effectiveness of ultrasound screening also increases significantly when the examination is carried out on modern expert-class equipment by an experienced, highly qualified specialist.
In addition, screening studies are an additional stress factor for a woman and can increase her level of internal anxiety. Comfortable conditions, the ability to visually monitor the progress of the study on a separate monitor, the “humane” attitude of the staff and the doctor - all this significantly improves the psychological state of the pregnant woman.
Currently, many women prefer to undergo ultrasound screening in specialized medical centers, such as the ICLINIC Clinic for Reproductive Medicine. The doctors working here are highly qualified and have all the necessary certificates, have the ability to conduct scrupulous research and do not avoid communicating with patients during diagnosis. Ultrasound at ICLINIC is carried out using modern certified expert-class equipment, which allows for good and accurate visualization of the organs being examined. If necessary, a pregnant woman can consult with experienced obstetricians and gynecologists and receive advice and support from a psychologist.
ICLINIC is one of the leading reproductive clinics in St. Petersburg, focused on the maximum possible assistance to couples in obtaining healthy offspring.
Where to do perinatal screening in St. Petersburg
The Diana Clinic in St. Petersburg offers all stages of perinatal screening, guaranteeing an individual approach to each woman and maximum reliability of the results obtained. Our specialists have extensive experience in the field of diagnostics during pregnancy. The medical center’s hardware makes it possible to carry out both basic and additional stages of screening.
<
p style=”text-align: justify;”>
CLICK TO SIGN UP
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter