Timing of ultrasound during pregnancy
The first screening is carried out between 10-14 weeks. Usually this is double testing - in addition to ultrasound diagnostics, the blood of the expectant mother is also checked. Based on the results, possible pathologies and deviations in the development of the developing fetus are determined.
The second ultrasound is performed from 16 to 20 weeks. The best time for examination is 17-19 weeks. Perinatal screening is carried out later, after a blood test - in the period 20-24 weeks. The second examination also includes ultrasound and biochemistry. If desired, a woman can refuse the 2nd part of the examination, but this is not recommended to avoid negative consequences.
The third ultrasound scan is performed between 30 and 34 weeks. During this period, obvious pathologies of the child’s development can be detected. If deviations were noticed earlier, then the third time they are confirmed or refuted. Some changes are noticeable only in the third trimester.
How reliable are the research results?
Pregnant women should refrain from interpreting screening results on their own. Each of the obtained indicators is assessed by doctors not individually, but only in conjunction with other parameters.
Important! Risk calculations are based on the results of a blood test for biochemical markers and data from the first ultrasound performed at 11-13 weeks.
Initially, research data is interpreted by an obstetrician-gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy. If discrepancies are detected, the woman is referred to a geneticist, who, together with an obstetrician-gynecologist, determines further examination tactics.
When is a second ultrasound necessary?
A second screening is needed even if there are no problems during pregnancy and the woman has no complaints. Ultrasound is mandatory for expectant mothers in the following risk groups:
- suffered ARVI in the period from 14 to 20 weeks. gestation;
- age – from 35 years;
- if one or both parents were alcoholics or drug addicts;
- there is a risk of miscarriage;
- the radiation dose received (by one or both parents) before or after conception;
- oncology, which was discovered after 2 weeks of pregnancy;
- parents who are closely related;
- hereditary genetic abnormalities;
- involuntary self-abortions;
- pathologies of the fetus and deviations in its development identified during the 1st examination.
Also included in the indications is a previously frozen pregnancy or the birth of a stillborn baby. If a woman took medications that are prohibited when carrying a child or worked in difficult (or hazardous) work. Screening should not be skipped by those whose first children were born with developmental disabilities.
When is ultrasound diagnostics prescribed?
Screening ultrasound is usually performed 3 times, since it is customary to divide the gestation period into 3 trimesters.
The first screening is done from the 10th to the 14th week of pregnancy , and often only this study involves a double test: in addition to ultrasound, an analysis of the venous blood of the pregnant woman is performed. The results of such a procedure determine with precise statistical probability the extent to which dangerous anomalies may develop in the fetus.
The second ultrasound screening usually does not include other tests . An exception is suspicion of pathology during the first examination or women from so-called risk groups. Ultrasound of the 2nd trimester is done from the 18-20th to the 24th week from the date of the last menstruation. Compliance with exact deadlines is very important, since if they do not comply, the interpretation of the ultrasound is considered inaccurate.
And finally, the third screening corresponds to the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, performed from the 30th to the 34th week.
Features of the second screening
By the time the second ultrasound is performed during pregnancy, the fetus has already grown noticeably, and its physical appearance has also changed. During an ultrasound examination, a number of parameters are assessed:
- Face – the presence of a mouth, nose, eyes, ears is checked. The size of the bones of the nasal part is determined, whether there are clefts in the oral cavity, and how the eyeballs develop.
- Fetometry (otherwise known as fetal size).
- How developed are the lungs?
- The structure of all organs is checked.
- The level of amniotic fluid is determined.
- Fingers and toes are counted.
- The placenta is assessed – its maturity and thickness.
It is at the 2nd ultrasound that the sex of the future newborn is determined for the first time, as the primary signs are clearly visualized. The results obtained during ultrasound diagnostics are often supplemented by blood biochemistry. This is especially necessary if developmental abnormalities have been identified in the fetus. When everything is normal, there is no need to do a blood test.
Biochemistry helps determine the concentration of free estriol, hCG (human gonadotropin), inhibin A and AFP protein (alpha fetoprotein). In case of previously identified deviations, the indicators show the dynamics of development of previously identified deviations. If the blood was not tested during the 2nd examination, then there is no point in doing the analysis later - it becomes irrelevant and uninformative. Then Doppler measurements and CTG are performed. This allows you to assess the blood supply to the fetus, placenta, and umbilical cord.
What does a second trimester ultrasound show?
An ultrasound of the fetus, performed on a modern device, allows you to see almost everything that may interest a doctor at this stage.
Placenta
Its placement relative to the outlet of the uterus gives grounds to state the presentation, low position or normal position of the child. In the first two cases, it is necessary to take measures and optimize the pregnant woman’s lifestyle, as well as undergo an unscheduled ultrasound examination after 5-7 weeks.
The structure of the placenta is studied to exclude intrauterine infections, which are indicated by compactions. A placenta thickness of more than 4.5 centimeters is an indicator of fetal hydrops, diabetes mellitus or Rh conflict. The thickness of the placenta also determines the degree of its maturity. A placenta thinner than two centimeters is considered prematurely aged and does not supply the fetus with a sufficient amount of necessary substances. In this case, the fetus will develop poorly. It is possible that the pregnancy will fail.
If placental abruption is detected in a pregnant woman, emergency hospitalization is necessary.
Amniotic fluid, umbilical cord
Their number is a dynamic value, therefore, in case of alarming indicators, it is necessary to control the situation by doing unscheduled ultrasounds. Low water may indicate the beginning of water leakage or the absence of kidneys in the fetus. Polyhydramnios is an indicator of Rh conflict or intrauterine infection. The latter is also evidenced by flakes in the water, clearly visible on ultrasound.
Umbilical cord. Examining it, the specialist counts the vessels, records the loops and the number of entanglements.
Preparation for the 2nd ultrasound and its implementation
No special preparation is required for an ultrasound. Due to the large volume of amniotic fluid, the examination will be of high quality. Preparation is required before donating blood. A couple of days before the procedure, you need to exclude from your diet any seafood, sweets, cocoa, citrus fruits, fatty, smoked and fried foods. Blood is taken on an empty stomach, so the last time you eat is 8-12 hours before donation.
Ultrasound is performed using a standard method. The woman lies down on the couch and exposes her stomach. A gel that conducts ultrasound is applied to it. The reflective signals are captured by the sensor and sent to the computer. Then, after instant processing, they are displayed on the screen as an image. If no violations are detected, then a blood test is not necessary.
Features of preparation for research
Prenatal screening does not require special or thorough preparation. A day before taking blood for analysis, a pregnant woman is advised to avoid eating fried, spicy and fatty foods, chocolate, citrus fruits and other allergenic foods.
Important! The doctor must be warned about all medications taken so that the specialist can take into account their effect on the mother’s body when conducting the study.
Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach. Immediately before collecting biomaterial, it is necessary to maintain a “fasting” interval of at least 8 hours. It is allowed to drink water without gas.
Performing an ultrasound requires even less preparation. A couple of hours before the test, it is recommended to stop eating citrus fruits, seafood and carbonated drinks.
Standards for 2nd screening
To determine possible pathologies, the condition of the placenta and the formation of the fetus, the threat of pregnancy, the results obtained at the 2nd screening are compared with standard values according to the tables. Weight is calculated using certain formulas. However, the values are not always accurate; it depends on the device, the position of the baby in the womb and the qualifications of the doctor.
Usually, by the 20th week, the internal organs have already managed to fully form, and the baby weighs about 300 g. For comparison, at the 16th week. – 100 g. After 7 days, 40 g are added, then at the same interval, twice 50 g and 60 g. Body length at the 16th week. approximately equal to 11.6 cm. During each 7-day period it increases by approximately a centimeter, and by the end of the 20th week. becomes 16.4.
Table of tummy and head circumferences
| Duration in weeks | Circumference – minimum/maximum (in mm) | |
| Belly | Heads | |
| 16-17 | 88-131 | 112-149 |
| 18-19 | 104-154 | 131-174 |
| 20 | from 124 to 164 | from 154 to 186 |
Table of BPR (biparietal) and LZR (frontal and occipital) head sizes
| Duration (in weeks) | Indicators – minimum/maximum (in mm) | |
| BPR | LZR | |
| 16 | from 31 to 37 | from 41 to 49 |
| 17 | from 34 to 42 | from 46 to 54 |
| 18 | from 37 to 47 | from 49 to 59 |
| 19 | from 41 to 49 | from 53 to 63 |
| 20 | from 43 to 53 | from 56 to 68 |
Length of bones - thighs, shins, shoulders and forearms
| Duration in weeks | Length – minimum/maximum (in mm) | |||
| Hips | Shin | Brachial | Forearms | |
| 16 | from 17 to 23 | 15-21 | from 15 to 21 | 12-18 |
| 17 | from 20 to 28 | 17-25 | from 17 to 25 | 15-21 |
| 18 | from 23 to 31 | 20-28 | from 20 to 28 | 17-23 |
| 19 | from 26 to 34 | 23-31 | from 23 to 31 | 20-26 |
| 20 | from 29 to 37 | 26-34 | from 26 to 34 | 22-29 |
AI (otherwise amniotic fluid index) is a very important indicator obtained by measuring the distance (at 3 points) from the uterine walls to the developing fetus. The values can fluctuate within the normal range of 70-300 mm, and any deviations from these numbers threaten the child and require urgent medical intervention. Amniotic fluid index (week – minimum and maximum value):
- 16 – from 73 to 201;
- 17 – from 77 to 211;
- 18 – from 80 to 220;
- 19 – from 83 to 225;
- 20 – from 86 to 230.
The standards for ultrasound examination at the first and second screening are the same, and three new important indicators appear in blood biochemistry. If the blood is also tested for inhibin A, then the test is called a quadruple test. The hCG level initially increases greatly, but after 7-8 weeks it also begins to actively decrease. Estriol (E3) is a hormone responsible for the development of the placenta.
Normally, immediately at the beginning of its formation, active growth of the substance is observed. A critical decrease in hormone levels is from 40 percent of the accepted values. AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) is a protein that is produced in the fetus in the gastrointestinal tract and liver from 5-1 weeks of existence. The level of the substance begins to actively increase from the 10th week. The norms for different periods are shown in the table.
| Duration in weeks | hCG | Duration in weeks | EZ in nmol/l | AFP in IU/IU | |
| 1-2 | 150 | 16 | from 4.9 to 22.75 | 34,4 | |
| 6-7 | 50000-20000 | 17 | from 5.25 to 23.1 | 39 | |
| 11-12 | 20000-90000 | 18 | from 5.6 to 29.75 | 44,2 | |
| 13-14 | 15000-60000 | 19 | from 6.65 to 38.5 | 50,2 | |
| 15-25 | 10000-35000 | 20 | from 7.35 to 45.5 | 57 |
Deciphering the 2nd screening without the specified parameters is impossible. The results of the first ultrasound are also taken into account. This helps to identify gene diseases, the risk level of which is calculated using the MoM coefficient. It takes into account the age, weight, and pathologies that the pregnant woman has suffered from. All this ultimately leads to the digital value of the limits:
- low – 0.5;
- optimal – 1;
- top – 2.5.
Based on these values, the possibility of abnormalities occurring in the fetus is calculated. If it is 1:380, then the indicator is normal. However, if the second figure begins to decrease, then the chances of having a healthy child also decrease.
When a high risk of 1:250 (360) is detected, the woman is referred to a geneticist for consultation. If the value reaches the limit level of 1:100, then additional diagnostic methods are required to confirm or refute possible anomalies.
If the umbilical cord is attached to the middle of the placenta and the anterior wall of the peritoneum, then this is normal. Abnormal - shell-like, marginal or split, leading to fetal hypoxia, problematic childbirth, and death of the baby.
The placenta is often attached to the back of the uterus, which is the best location due to the full blood supply. It is also good at the uterine fundus. When the placenta is attached to the anterior wall of the uterus, this does not refer to a violation, but creates certain risks - severe stretching, detachment due to active movement of the fetus, presentation.
The edge of the canal connecting mother and child should be located at least 6 cm above the pharynx. The location of the placenta is considered abnormal when it is located at the bottom of the uterus or in the pharynx, blocking the exit. The thickness of the connecting canal is measured after the 20th week of gestation; before that, only the homogeneity of the structure is checked (ideally, it is solid, without inclusions).
A normal umbilical cord has two arteries and a vein. Violation is the absence of at least one vessel. However, pregnancy is considered normal if the missing artery is replaced by a functioning one 100 percent. At the same time, all indicators are normal and no defects are observed.
The normal length of the uterine cervix is at least 3 cm. When shortening or lengthening, sutures are applied or a pessary is installed. This allows you to complete the pregnancy and keep a healthy baby.
Uterus, cervix
The tone of the uterus, the presence of myomatous nodes, and the condition of scars are checked if operations have been previously performed.
The cervix is examined to exclude pathologies such as isthmic-cervical insufficiency and premature opening of the internal os. The normal length of this organ at this stage is 35 millimeters, the lower limit for the first pregnancy is 33 and for repeat pregnancies – 22 millimeters.
Fetal dimensions, facial structures, internal organs of the fetus
Fetometric data of the fetus such as head circumference, length of hip bones, elbows, chest diameter, spine size, abdominal girth, body weight and overall height make it possible to determine whether its size meets the norms of this period. A specialist can assess the pace of his development and diagnose his intrauterine retardation. The results obtained provide grounds for recording pathologies and congenital defects.
The doctor examines the child’s face for indicators indicating Down syndrome: an open mouth and protruding tongue, a large gap between the eye sockets. In addition, examination of the orbits reveals cyclopia or anophthalmia, lips and palate - “cleft palate” or “cleft lip”.
The study of the forms and structures of the internal organs of an already fully developed fetus is aimed at identifying various anomalies:
- A transverse section of the head is examined for its double contour, oval, oblong or pear-shaped shape, as well as the integral structure of the cranial bones.
- The brain is measured by the size of the ventricle - if they increase, ventriculomegaly is stated; The presence of cysts and similar formations inside and outside the skull, and pathologies of the socket are examined.
- The degree of maturity of the lungs is considered.
- The normal structure of the heart should be four-chambered; the characteristics of the blood vessels are studied. His work is also measured by the number of beats per minute.
The liver, digestive organs, kidneys, bladder and diaphragm are examined for abnormalities.
Explanation of possible deviations
When deciphering the results, the normal size is taken to be the size of the fetus corresponding to the accepted values, the absence of abnormal growths or clefts on the face or body. The eyeballs must be well developed, the proportions of the nose must be respected, and the internal organs must develop correctly. The level of amniotic fluid and the condition of the placenta must be checked. Examples of what detected deviations from the norm may indicate:
- high hCG indicates Down or Klinefelter disease, low hCG indicates Edwards pathology;
- deviations from normal indicators of BPR and LZR may indicate serious deformities of the child (for example, cerebral hydrocele, anecephaly);
- decreased AFP - possible fetal death or incorrect determination of the timing of pregnancy; increased AFP is detected in Meckel's syndrome, central nervous system defects, umbilical hernia, death of liver cells;
- low blood counts are characteristic of Edwards syndrome;
- a high EZ may indicate multiple pregnancies, a decrease in the level may indicate placental insufficiency, the possibility of miscarriage, infection, Down's disease, or a disorder in the development of the adrenal glands;
- with severe oligohydramnios, limbs may develop incorrectly, deformation of the spinal column may occur, the central nervous system also has a negative effect, the fetus weighs little;
- with normal hCG, but high AFP and EZ - damage to the neural tube;
- the absence of even one vessel leads to developmental pathologies - cardiac, the appearance of fistulas, the development of esophageal atresia, central nervous system disorders, hypoxia;
- changes in the structure of the placenta impair fetal nutrition, resulting in hypoxia and developmental inhibition.
The second examination is carried out almost in the middle of gestation, when it is no longer possible to have an abortion. Then, if necessary, premature birth is induced.
Detailed transcript, norms and pathologies: transcript of ultrasound of the second trimester of pregnancy
The ultrasound report of this period contains the following abbreviations and abbreviations:
- BPR – biparietal size of the fetal head;
- LZR – fronto-occipital size;
- BPR/LZR – cephalic index;
- OG – head circumference;
- AB – abdominal circumference;
- RS – heart size;
- DP – shoulder length;
- DB – thigh length;
- OG – head circumference;
- s/b or heart rate - heartbeat;
- IUGR – intrauterine growth restriction;
- DgRK – chest diameter;
- AFI - amniotic fluid index - an indicator of the amount of amniotic fluid;
- ICI - isthmic-cervical insufficiency - the cervix with this pathology is not long enough for full gestation.
Size is indicated in millimeters, weight in grams.
What influences the results of the second survey?
Even with normal values, there is a possibility of some errors. And vice versa - even bad results do not always indicate pathological processes. There are a number of factors that can negatively affect pregnancy:
- chronic pathologies in a pregnant woman (for example, diabetes, etc.);
- multiple births;
- obesity (indicators always increase);
- pregnancy caused by IVF;
- bad habits (drug addiction, smoking, frequent and excessive drinking).
If during the second screening a disease is detected that leads to serious developmental problems or deformity of the unborn baby, then the woman is sent for additional examinations (for example, cordo- or amyocentesis) and a repeat ultrasound scan. This is necessary to accurately determine developmental disabilities and determine whether to keep the child.
Despite the importance of the second ultrasound, a woman has the right to refuse to have it performed. However, this may further negatively affect not only the child, but also the health of the mother herself. If abnormalities are detected in time, it is possible to terminate the pregnancy in time and decide how the birth will proceed (naturally or by caesarean section).
Related articles:
- The test is positive, but the ultrasound does not show pregnancy
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- Mammography or breast ultrasound: which is better?
- Pregnancy after hysteroscopy
- Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages. How does it go and what will it show?
What to do if pathologies are detected
If pathologies of the pregnant woman's organs are detected - uterine tone, placental expulsion, low or polyhydramnios, drug therapy is carried out to eliminate the problem, under the supervision of specialists. In case of ICI (cervical insufficiency), it is possible to apply sutures to the cervix and prescribe a gynecological pessary.
Fetal growth retardation can also be corrected with proper therapy. If serious pathologies of the fetus are detected, doctors talk about options for the development of events, taking into account all the risks. The final decision is made by the future parents - no one will force you to do anything.
The second trimester is a period when it is still possible to terminate a pregnancy in the later stages, so you cannot delay the ultrasound.
The value of 4D ultrasound in perinatal diagnosis: advantages and features
In modern practice of medical management of pregnancy, such a procedure as 4D ultrasound has become basic, both for a specialist monitoring the course of gestation and for impatient parents who are waiting to meet their child. This technique has several significant advantages over classical two-dimensional screening and is very often used as an addition to the basic course of mandatory research.
4D ultrasound will provide an opportunity not only to fully assess the health and development of the baby, but will also give parents the joy of first visual contact with the child, who will be in the natural intrauterine environment.
4D ultrasound - capabilities and advantages
The capabilities of the 4D ultrasound procedure are somewhat expanded in comparison with the usual two-dimensional echography. This is ensured by the fact that the examination (also called color ultrasound) allows you to evaluate the external manifestations of the fetus using four dimensions simultaneously: depth, height, length and time. As a result of the procedure, the image displayed on the dashboard monitor will resemble a video that in real time demonstrates not only the appearance and main morphological features of the baby, but also his movements, facial expressions, gestures and smile.
If the baby has not turned his back to the ultrasound scanner, such a sight evokes a lot of positive emotions among parents and provides certain diagnostic information to the specialist.
Positive aspects of 4D ultrasound for a pregnancy specialist
In addition to data that is standard for all ultrasound methods regarding the age, size and position of the fetus, 4D ultrasound gives the specialist the opportunity to determine the presence of the following anomalies in the baby’s development:
- Facial defects (facial clefts)
- Skeletal malformations (non-fusion of the spinal cord)
- Anomalies of the hands (quantitative pathologies of the fingers)
- Presence of space-occupying formations in the fetus
- Pathological changes in the placenta
- Defects of the anterior abdominal wall
- Abnormal development of the external genitalia
4D ultrasound makes it possible to track the natural movements of the fetus. This can also become important information in the process of confirming a particular developmental pathology. Thanks to the expanded review that this option of ultrasound screening implies, it is also possible to visually assess the structure of all external signs. This is especially true for facial structures (nasolabial triangle, lips, ears, chin, nose, etc.).
It should also be noted that the 4D technique provides more accurate information regarding the baby’s gender. This information is of interest to the doctor due to the presence of a hereditary pathology factor or genetic abnormalities linked to sex. And this is one of the main tasks of perinatal screening.
Positive aspects of 4D ultrasound for expectant parents:
- The opportunity to see the baby long before his birth, establish a certain psychological contact with him, and also prepare for the external characteristics of the baby.
- You can find out exactly the gender and even see the confirmation in person, on the monitor screen. This aspect almost always worries parents, as well as the developmental characteristics of the child.
- Parents can receive a video that will remain an unusual memory of such an important period in the life of every family as pregnancy. We are giving a CD with the recording as a gift!
How does 4D ultrasound work?
The procedure is practically no different from standard ultrasound screening. However, four-dimensional echography takes almost three times longer than black-and-white ultrasound (about 45 minutes). At the same time, a pregnant woman should know that filling the bladder does not affect the results obtained. In addition, it is worth understanding that the 4D technique has a maximum level of information content in the period from 22 to 33 weeks, which is due to the development and size of the fetus.
Patients suffering from severe forms of obesity or having scars on the abdomen, as well as when diagnosing a condition such as oligohydramnios, should be prepared for the fact that the picture may not be clear enough. In almost all other cases, 4D ultrasound will be an excellent way to get to know the baby and get a guarantee of its normal intrauterine development. The Diana Clinic offers its patients a 4D ultrasound procedure, guaranteeing information content and safety for the baby and the expectant mother.
Analysis for hCG β - unit for perinatal diagnosis
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is a hormone whose concentration increases sharply during pregnancy. Its increase indicates that conception has occurred, which is extremely important during pregnancy resulting from infertility treatment. HCG is not strictly a “female” hormone. This substance is specifically administered to men in order to improve sperm count in cases of suspected male infertility.
What is hCG and β – hCG
This substance consists of two components:
- α-unit similar to other hormones;
- β is a unit unique to hCG, distinguishing it from other hormonal substances.
That is why it is the β - unit that is analyzed, and the analysis itself is often called β - hCG.
The hormone is produced by the cells of the embryonic membrane to stimulate hormones that support pregnancy - progesterone and estrogen. This prevents the onset of menstruation and allows the embryo to “take root.” That is why, in case of infertility, doctors analyze the level of hCG in the patient’s body. If its content drops or lags behind the norm, the woman is prescribed hormonal drugs to support pregnancy. Monitoring the level of the hormone is necessary for women who are prone to recurrent miscarriage and have had frozen pregnancies.
The concentration of hCG increases rapidly until the placenta is formed, which later takes over the hormonal function. A rapid increase in hormone levels indicates that the pregnancy has continued and the embryo is developing. Subsequently, the hormone content decreases, remaining elevated before childbirth and somewhat after it.
Normal hCG levels vary greatly between women. The doctor determines whether everything is normal by the dynamics of changes in the indicator in a particular patient.
Approximate hormone concentrations during pregnancy are given in the table
| Duration, weeks | Concentration, honey/ml |
| 1 | 20-155 |
| 2 | 100-4850 |
| 3-4 | Up to 82,000 |
| 5-6 | Up to 151,000 |
| 7-8 | Up to 230,000 |
| 9-10 | Up to 290,000 |
| 11-16 | Decreases from 290,000 to 245,000 or less |
| 17-25 | Reduces to 50,000-80,000 |
| 25-37 | gradually decreases to 40,000 or less |
Inconsistency between the level of hCG and the period is observed in pathologies of pregnancy and abnormal development of the fetus
| promotion | demotion |
| hydatidiform mole | frozen pregnancy, embryo death |
| multiple pregnancy | risk of miscarriage |
| toxicosis | fetal underdevelopment |
| congenital hereditary diseases and fetal malformations | ectopic embryo implantation |
| hormonal pathologies in the mother | in the later stages indicates post-maturity |
Unlike pregnancy, in diseases that cause an increase in hCG levels (ovarian, stomach and breast cancer), the level of the hormone increases gradually and does not decrease. Therefore, a woman is prescribed such an analysis several times during pregnancy.
How is the β-hCG screening test performed?
For this study, blood from a vein or urine is donated, but the hormone is determined in urine later, and the result is not so accurate. Therefore, it is better to rely on a blood test showing the presence of the hormone and its concentration.
The material is collected in the morning on an empty stomach; if you need to take tests urgently, you need to fast for 4-6 hours. It is advisable not to take medications at this time. If the level of hCG in the early stages begins to rapidly decrease or increase, you need to consult a doctor and identify the cause.
Negative results: what to do?
The period of the second screening occurs in the middle of pregnancy, so doctors no longer talk about terminating it for medical reasons. Sometimes there are cases when fetal pathology can be corrected by medical methods - in this case there is hope, and doctors will offer the pregnant woman a choice of possible manipulations and interventions. If the negative results of the second screening show a high risk of developing anomalies (in a ratio of 1:360) without hope of reversing the process, then the woman is asked to decide on an artificial birth.
In any case, both parents will have to make the difficult decision to continue or terminate the pregnancy. When there is a chance to correct the pathology, the expectant mother is explained in detail: what modern methods exist to correct the situation, how risky they are, whether complications are possible during the intervention process, and what are the overall chances of having a healthy baby.
Where to do perinatal screening in St. Petersburg
The Diana Clinic in St. Petersburg offers all stages of perinatal screening, guaranteeing an individual approach to each woman and maximum reliability of the results obtained. Our specialists have extensive experience in the field of diagnostics during pregnancy. The medical center’s hardware makes it possible to carry out both basic and additional stages of screening.
<
p style=”text-align: justify;”>
CLICK TO SIGN UP
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
The role of 3D ultrasound in perinatal screening: 3D or 2D?
Today, no one doubts that ultrasound diagnostic techniques are the most important aspect of monitoring intrauterine development, age and position of the fetus. At the same time, the technical base of medicine does not stand still, and in addition to the classic, two-dimensional ultrasound, such a useful diagnostic practice as 3D ultrasound or three-dimensional echography has come. The advantages of this research method lie in the possibility of obtaining a three-dimensional image, which in all colors demonstrates to the specialist and future parents all aspects of the external manifestations and organs of the baby.
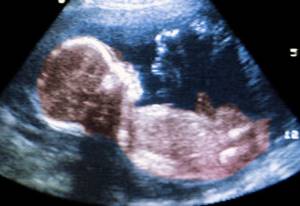
Differences between 3D ultrasound and classical ultrasound
All ultrasonic research methods have a common principle, which is based on the use of ultrasonic radiation, the wave frequency of which does not exceed 20 kHz. Applying such a wave load in a pulsed mode makes it possible to assess the functional normality and morphological structure of tissues, organs and systems of the fetus. At the same time, the traditional two-dimensional method displays a flat image on the dashboard monitor, which is understandable to doctors, but is not informative for non-professionals, namely for the child’s parents who are looking forward to meeting the baby for the first time. It should be noted that this method of diagnostic monitoring is important for medical specialists managing pregnancy, as it makes it possible to fully assess the structure of the internal organs of the fetus, which is incredibly important when organizing comprehensive monitoring.
Three-dimensional echography produces a full-fledged three-dimensional image that does not require decoding and clearly reflects the external features and position of the baby in the womb.
Advantages of 3D ultrasound in perinatal screening
3D ultrasound provides doctors with a number of obvious advantages:
- A clearer image
makes it possible to identify a number of defects that cannot be identified during classical ultrasound screening: hand anomalies, facial clefts, skeletal malformations, disturbances in the formation of the anterior abdominal wall, placenta anomalies, structural features of the external genitalia, non-fusion of the spinal cord, etc. . Identification of all of these abnormalities requires a change in the strategy for managing such a pregnancy. - 3D ultrasound allows you to determine the sex of the baby
more accurately in the early stages of pregnancy, which may be necessary not only to satisfy the curiosity of future parents, but also from the point of view of eliminating the likelihood of hereditary pathologies associated with gender. - The psychological readiness of the mother and father
for the birth of the long-awaited child, of course, increases after the initial acquaintance with the baby, even through a monitor and a photograph, which, at the request of the parents, can be provided after this manipulation.
Features of three-dimensional echography
According to the results of numerous medical studies, 3D ultrasound is an absolutely safe diagnostic method that is used for medical reasons. The features of 3D ultrasound during screenings during pregnancy include the following factors:
- Three-dimensional echography is most informative at 22-33 weeks of pregnancy, since during this period the external signs of the fetus are already sufficiently formed, and its size does not interfere with visual inspection.
- The duration of a three-dimensional ultrasound is about 40 minutes, which is much longer than the time required for classical two-dimensional screening.
- The bladder does not have to be full before performing a 3D ultrasound.
- The diagnostic capabilities of the technique drop significantly in the presence of such characteristics of the patient or the course of pregnancy as severe obesity of the expectant mother, oligohydramnios, the presence of scars on the woman’s abdominal wall, or uncomfortable position of the fetus.
Three-dimensional echography is a diagnostic practice that has earned the trust of doctors and patients around the world, confirming its exceptional effectiveness and safety for both women and babies. At the same time, today, 3D ultrasound remains the “gold standard” for intrauterine study of the structure of facial structures, limbs, sexual characteristics and space-occupying formations in the fetus, as well as a backup method for identifying such chromosomal abnormalities as Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, etc.
How to prepare
Preparation for the second study is somewhat different from the previous one, since this time you do not need to follow a strict diet and drinking regime. There are no dietary restrictions, but experts still do not recommend overeating or drinking a lot before the procedure, so that nothing distracts the mother from admiring her baby, and the doctor from the scrupulous work of assessing his development.
You need to take a diaper, towel and shoe covers with you. You should check in advance whether they are included in the cost of the ultrasound. Many paid clinics do not require you to carry these items with you.
Stage II of perinatal screening (16-18 weeks)
At this stage, it is quite possible to conduct a 3D or 4D ultrasound, which makes it possible to evaluate all the external aspects of the baby, and also, in the case of four-dimensional echography, determine the mobility of the fetus and its gender.
The biochemical component of the second stage is a “triple” test, which involves identifying and measuring the following protein components in the blood of the expectant mother:
- Free β subunits of hCG.
- Alphafetoprotein.
- Free estradiol.
ACE (Alpha Fetoprotein)
- a specific protein that is produced directly by the fetus and enters the mother’s blood through the placenta. Its increased content may indicate defects of the fetal neural tube and defects of other vital organs. A decrease in ACE can be recorded in chromosomal diseases such as Down syndrome.
Free estradiol
is a female steroid hormone that must be produced by the placenta during pregnancy. A decrease in the level of estradiol in a woman’s blood may indicate a violation of fetal development.
Goals and objectives of the study
In addition to ultrasound diagnostics, the second trimester of pregnancy also involves taking blood from a vein and testing for certain hormones. These two studies are complementary and are carried out in order to identify possible disorders in the body of the fetus or mother as early as possible. The examination, performed in a timely manner, allows the woman to determine the choice of subsequent actions.
Leading goals 2 of screening during pregnancy:
- clarification of the degree of probable risk of genetic abnormalities;
- assessment of the threat of development of defects of the nervous and other systems;
- analysis of the child’s current condition (body size, how proportions and gestational age relate);
- identifying possible disorders in the placenta, the uterus of the expectant mother, amniotic fluid, as well as in the cervical canal, preventing possible complications.
Contraindications for examination
All women, without exception, need to undergo a fetal ultrasound during pregnancy from 11 to 22 weeks. There are no contraindications to the examination. There is no need to be afraid of screening; already at the very beginning of expecting a baby, the doctor will tell you how an ultrasound is done, in which week a consultation is required and what tests will need to be taken.
All procedures are carried out with the written consent of the woman, but you should not refuse screening in the 2nd trimester. Ultrasound is completely safe for the health of the mother and baby, but gives a very informative picture of the condition of the fetus and reproductive organs, which allows you to avoid unnecessary risks, endure pregnancy and give birth to a healthy child.