Why are leukocytes in a child’s blood low: possible reasons
In order to monitor the condition of the body, it is necessary to test the blood from time to time.
Deviations and changes in its composition will indicate emerging problems. Prompt information about possible pathologies will help to eliminate them in time.
This is especially true for a child’s body, which is growing and needs timely protection. An important mission in this process is assigned to leukocytes - the formed elements of blood. The purpose of these white cells is to provide the body with protection from pathogenic bacteria and foreign proteins. Leukocytes have developed a special sensitivity to them.
What it is?
Leukocytes are white blood cells whose main task is to maintain immunity and protect the body from foreign agents. Unlike red blood cells (red cells), their content is approximately 1000 times less, so the blood itself is red. There are so many types of white blood cells that perform specific functions and are contained in different percentages.
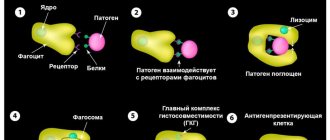
When a foreign cell enters the body, leukocytes rush to it and completely block it. There are several subtypes of white blood cells:
- Basophils contain heparin and histamine. This helps them be a catalyst for the process of lipolysis of fats in the blood. Histamine has an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulates phagocytosis. Basophils perform the function of preventing the formation of blood clots.
- Neutrophils are “suicide” cells. They absorb and break down the harmful cell. In this case, the neutrophil itself dies. The accumulation of dead neutrophils is called pus. Their main function is to fight bacteria and toxic substances. They can exist in tissues with poor oxygen supply. Active against virus attacks.
- Lymphocytes are the largest group of white blood cells. They make up approximately 40% of the total. Lymphocytes fight antigen proteins and bacteria. Some of them synthesize groups of immunoglobulins.
- Monocytes are macrophages that are the main catalysts of phagocytosis. These cells are designed to fight parasitic attacks. Actively block tumor tissues and stimulate normal levels of cell regeneration.
- Eosinophils perform an antibacterial function. They penetrate the membrane of the infectious cell and destroy it from the inside with the help of secreted enzymes. An active process of accumulation of eosinophils also occurs at the site of an allergic reaction.
In total, human blood contains 4000–9000 μl of leukocytes. Their number is constantly fluctuating. Red blood cells are more permanent. They have a fixed level.
Normal levels of leukocytes in the blood of children
The norm of leukocytes in the blood of children exceeds their normal content in the blood of adults. This is based on the physiological characteristics of the child’s body, whose immunity is still imperfect, therefore, increased protection of his body from possible infection is necessary.
Below is a table showing leukocytes in the blood of children depending on age:
| Age | Normal value, /l |
| Newborns | 9-30×109 |
| 1 month | 8-21×109 |
| 6 months | 7-18×109 |
| 1 year | 6-15×109 |
| 1-2 years | 6-14×109 |
| 3-4 years | 5-12×109 |
| 5-7 years | 5-10×109 |
The normal white blood cell count in children depends on their age. The number of leukocytes in children under one year of age significantly exceeds that of adults. As the child grows older, the number of white blood cells in the blood decreases. The age-related dynamics of the content of leukocytes in the blood is reflected in the table.
Diagnostic measures
It is possible to detect leukopenia in a baby using a number of standard studies:
- physical examination and history;
- clinical, biochemical, serological blood tests;
- sternal puncture;
- immunological tests;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- MRI (if indicated).
To make an accurate diagnosis, the number of all types of leukocytes is counted. In the interval between six months and six years, the proportion of granulocytes/lymphocytes physiologically changes in children; these changes can be mistakenly attributed to pathologies.
What is the danger of leukopenia?
Many people have no idea what the dangers of a sharp decrease in the level of white blood cells in the blood are. They believe that this happens after they have suffered from an illness. This may be so, since many pathological conditions can cause leukopenia. However, it also happens the other way around - many diseases can be caused by leukopenia. This happens due to a decrease in the body’s defenses when access to various bacterial and viral infections opens.
In people with an altered leukocyte formula and a reduced number of leukocytes in the blood, the risk of cancer, viral hepatitis, AIDS and other infections doubles. For children, this syndrome is dangerous because if the child is not examined and treated, then a serious blood disease - leukemia - can be missed, since its onset can manifest itself as both leukocytosis and leukopenia.
Drug therapy (especially cytostatics) can also cause neutropenia in children.
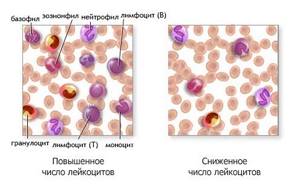
Development mechanisms
Leukopenia has several development mechanisms, the main ones include:
- Impaired formation of leukocytes;
- Active destruction of white blood cells (rarely observed in young patients);
- Redistribution of leukocytes (during some processes they do not disappear from the hematocirculatory bed, but only leave it for a while, being in the small vessels of the lungs, kidneys, muscle tissue);
- Increased loss of white blood cells (with large plasma, lymph or blood loss);
- Hemodilution (a consequence of excessive intravenous replacement treatment, extremely rare).
Due to damage to the cell membrane, granulocytes are released into the blood from the bone marrow in a slower manner.
- The norm of leukocytes in the blood of women after 40–50 years - table with explanation
What do low leukocytes in a child’s blood indicate?
Leukopenia, although widespread and well known, still occurs much less frequently than leukocytosis. The etiology and pathogenesis of the syndrome are very extensive. The most common factors that lead to a decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood are:
A decrease in the level of leukocytes in children is due to inhibition of their formation in the hematopoietic organs, which is caused by the following reasons:
- Hypothyroidism.
- Autoimmune problems.
- Anaphylactic shock.
- Metastases of various tumors to bone marrow tissue.
- Aleukemic variant of leukemia.
- Enlargement of the spleen, which is accompanied by the development of hypersplenism.
- Any generalized infectious condition - miliary tuberculosis, septicemia, etc.
- Some types of bacterial diseases (paratyphoid, typhus, brucellosis), protozoal (malaria) and rickettsial (typhus) infections.
- Damage to the bone marrow, accompanied by its hypoor aplasia. In this case, a decrease in the level of leukocytes will be accompanied by a decrease in the number of red blood cells and platelets.
- Various viral diseases (rubella, influenza, HIV infection, viral hepatitis, etc.) that have a depressing effect on the process of formation and specialization of leukocytes.
- As a result of exposure to the body of certain medications (sulfonamides, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, thyreostatics, etc.).
To answer the question of what is the real cause of low white blood cells, it is necessary to undergo a full examination. The fact is that the leukocyte count depends on many reasons. The most trivial of them are ambient temperature and diet.
Symptoms of the disease
Sometimes at the initial stage leukopenia occurs unnoticed. Symptoms of the disease depend on the nature of the causes that caused it; general symptoms include:
- increased heart rate;
- hypothermia;
- chills;
- headache;
- severe weakness;
- increased sweating;
- shortness of breath.
As the pathology develops, the following may appear:
- skin rashes;
- ulcers in the mouth;
- signs of sore throat, pneumonia.
An enlargement of the spleen and lymph nodes is often observed.
How to treat?
First of all, in order to increase the level of leukocytes, you need to clarify the exact reason for their decrease. Often additional examination methods may be required. When an accurate diagnosis is established, etiotropic therapy is prescribed, which is aimed at eliminating the very cause of the pathology, for example:
- If these are signs of group B vitamin deficiency, medications containing these substances are prescribed and the diet is adjusted.
- If leukopenia is caused by diabetes, then medications are used to maintain blood sugar levels and normalize the functioning of the pancreas.
- For HIV infection, lifelong ART therapy is prescribed. The viral load (the number of copies of the virus) drops, and the immune system recovers on its own.
Among the common medications, immunostimulants, immunomodulators (restore the functioning of the immune system) and immunocorrectors (remove damaged parts of the immune system) are used:
- recombinant – interferons alpha, beta, gamma;
- colony-stimulating factors – Filgrastil, Lenograstim;
- fungal and microbial origin - Bronchomunal, IRS-19, Likopid;
- animal origin – Myelopid, Thymogen, Timalin;
- interleukins – interleukocyte mediators (Roncoleukin);
- other active substances - vitamins, adaptogens (eleutherococcus, ginseng, etc.);
- of plant origin - products containing echinacea (Immunal, Ikhinacin, Ikhingin).
In addition, you need to independently help the body increase white blood cells; to do this, you should eat a balanced diet: eat more vegetables and fruits, protein foods, and reduce fat intake. The diet should contain meat, legumes, dairy products, cereals, and walnuts. It is not recommended to eat fatty fish and meat. Do not use spices and seasonings when preparing dishes.
In addition to drug treatment, you can increase your white blood cell level at home. Traditional recipes for leukopenia should be used as an auxiliary therapy, but not as the main one.
Symptoms
Leukopenia, as a rule, is determined accidentally during a preventive study, since it does not have specific clinical symptoms.
The first signs of a decrease in leukocytes may appear when bacterial, viral or infectious complications are involved in the pathological process.
What this entails:
- Increased body temperature;
- The appearance of aphthae on the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- Increased gum bleeding;
- Pustular infections;
- Tachycardia;
- Headache;
- Anxiety;
- Pain in the left hypochondrium (associated with an enlarged spleen).
All symptoms of leukopenia must be carefully examined, so in this case, consultation with a doctor is mandatory.
Which doctor should I contact?
In the event that the test results show a reduced level of leukocytes, the pediatrician prescribes a repeat test. If the second analysis shows deviations from the norm, the pediatrician prescribes a full examination of the child, first collecting anamnesis from the parents. You may need to consult a geneticist and hematologist to eliminate the risk of leukopenia in the case of autoimmune and genetic abnormalities.
Treatment depends entirely on what caused the pathology. If it is a disease, it needs to be eliminated; if it is nonspecific factors (prolonged fasting, psycho-emotional disorders), the increase in the level of leukocytes depends entirely on their elimination.
Reasons for the development of pathology in children
The reasons for the progression of leukopenia in young patients are divided into two groups:
- Infectious:
- sepsis;
- sixth and seventh types of herpes;
- typhus, paratyphoid;
- flu;
- brucellosis;
- rubella;
- measles;
- AIDS and HIV;
- Non-infectious:
- leukemia;
- plasmacytoma;
- ion irradiation;
- diffuse connective tissue pathologies;
- autoimmune diseases;
- anaphylaxis;
- hypersplenism;
- Addison-Beermer anemia;
- metastasis of neoplasms to the bone marrow;
- autoimmune diseases;
- endocrine pathologies (hypothyroidism, diabetes).
The development of leukopenia in newborns can be provoked by intrauterine inflammatory processes.