Ultrasound in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy refers to routine examinations aimed at determining the functional state and development of the fetus. Screening is carried out at 30-32 weeks for all women, regardless of the presence or absence of complications during pregnancy.
The data obtained are very important for monitoring the course of pregnancy and choosing the method of birth of the child (natural birth, cesarean section).
The Miracle Doctor clinic employs qualified diagnosticians, specialists of the highest category, who are proficient in modern ultrasound research techniques. Experience and qualifications allow doctors to accurately interpret diagnostic results and timely detect abnormalities in the course of pregnancy.
Dates
An ultrasound in the third trimester of pregnancy should be done after consultation with your doctor during a routine examination. The referral is issued at 11-13, 20-22 and 30-32 weeks. At this time, it is possible to find out in sufficient detail the condition and characteristics of the development of the fetus, as well as the functional state of the cervix and uterine body, placenta and umbilical cord.
Depending on the condition of the pregnant woman, ultrasound can be prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist at various stages of pregnancy to exclude abnormalities in the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Consideration of the condition of the child’s internal organs
When performing an ultrasound in the third trimester of pregnancy, doctors must also diagnose the occurrence of malformations in the internal organs of a person. When viewed in this way, the most important internal organs are the child’s lungs and heart. If the diaphragm is underdeveloped, doctors can also diagnose underdeveloped lung tissue, which can lead to breathing problems in the future. When examining the heart, all possible functional capabilities of ultrasound technology are used to examine in detail the presence of valves, septa and vessels, their size and functionality.
The organs located in the baby's abdominal cavity are examined no less carefully. Any pathology that occurs during pregnancy can primarily affect the baby’s kidneys. Deviations in the size and shape of this organ always signal the presence of some disease. However, for the integrity of the picture, it is important to diagnose other abdominal organs - the stomach, liver, and intestines can also tell the doctor a lot.
Sometimes, when an ultrasound detects abnormal fetal development within one week, we can talk about an incorrect determination of the timing of pregnancy by a gynecologist. If with each subsequent study the deviation remains within the same limits, then this is not given much importance, since with a high degree of probability, this fact indicates that the due date was incorrect. But with a constant change in the deviation of indicators from the given period, doctors consider it necessary to sound the alarm and monitor the pregnancy in more detail.
What does an ultrasound scan include in the third trimester of pregnancy?
- Assessment of the condition of the pregnant woman's organs. Helps determine the risks of premature birth (shortening of the cervical canal, increased uterine tone, opening of the pharynx). If these abnormalities are detected, an ultrasound examination may be the basis for referral to a hospital for preservation.
- Study of the placenta. Its location and thickness are determined. Allows the doctor to decide how advisable a natural birth would be and whether there is a risk of bleeding or premature placental abruption.
- Determination of placenta maturity. The functional state of the umbilical cord blood vessels is assessed in order to promptly notice and take action due to premature aging, which can lead to negative consequences for the normal development of the fetus.
- Determination of the state of amniotic fluid. Evaluates the condition of amniotic fluid, helps to detect oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios in time.
- Assessment of blood flow using Doppler. Identifying the problem at this time reduces the risks for the mother and fetus during pregnancy and childbirth, and also allows you to bring the pregnancy to the natural terms of delivery.
Doppler testing helps to identify the following types of disorders:
- In the first degree, drugs are prescribed that improve blood circulation in the placenta, and periodic medical monitoring is also carried out.
- In the second degree, constant monitoring and drug support is carried out until birth.
- In the third degree, urgent delivery is indicated.
- Determination of the position of the fetus in the uterus (the protocol for the 3rd trimester allows you to determine the position of the fetus (fetuses in multiple pregnancies) and presentation (the position of the child in relation to the birth canal).
- Fetometry (correspondence between the size of the child and the gestational age, identifying the characteristics of the course of pregnancy, possible disorders or deviations in the development of the fetus).
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Routine ultrasound of the 3rd trimester is indicated for all women and is mandatory. It not only helps to identify possible abnormalities and prescribe timely treatment, but also to decide on the method of delivery. If serious contraindications to natural childbirth are identified, the woman is prescribed a planned cesarean section.
An unscheduled additional ultrasound is indicated if a pathology is suspected and is carried out as prescribed by the doctor as often as necessary. Repeated ultrasound is often recommended for the following categories of patients:
- During pregnancy after 35 years. At this age, the risk of complications increases significantly.
- If the pregnancy was difficult, with gestosis and hypertonicity of the uterus, the woman felt unwell.
- With established fetoplacental insufficiency.
- If a woman has already had miscarriages, frozen pregnancy, or stillbirth.
- If a woman smokes, drinks alcohol or uses drugs during pregnancy.
An indication for an ultrasound may be a sharp deterioration in a woman’s well-being - increased pain in the lower abdomen, bloody discharge from the vagina of any intensity.
There are no contraindications to ultrasound examination. The procedure is considered completely safe, as no negative reactions have been identified so far. The only contraindication may be severe damage to the skin in the affected area. First, you will need to treat the wounds or rash, and only then go for examination.
What does it show
The third ultrasound during pregnancy allows you to confirm the sex of the child, multiple pregnancies and determine the approximate date of birth. The doctor pays special attention to the condition of the placenta, determines its presentation, on which the possibility of natural childbirth depends (for example, partial or complete presentation to the internal os is an indication for cesarean section).
During ultrasound screening of the 3rd trimester, the doctor observes:
- position and motor activity of the fetus;
- development of the child’s internal organs;
- condition of the blood vessels of the umbilical cord, fetus, uterine arteries;
- fetometric indicators;
- signs of fetal hypoxia;
- fetal heartbeat;
- fetal presentation;
- length of the cervical canal.
How to prepare for your third ultrasound
In order for the third ultrasound during pregnancy to go smoothly and without problems, you need to prepare for it in advance.
To prepare the body, experts recommend not eating foods that cause increased gas formation a day or two before the procedure.
It is also necessary to wash the genitals.

It is better to come to the clinic in advance so that the body is not overstimulated. If an ultrasound is performed on a paid basis, then, as a rule, you do not need to bring anything with you. If in a clinic, you may need a diaper, towel and shoe covers.

At the last scheduled ultrasound, the examination is carried out through the abdominal probe. A woman needs to take a comfortable position on the couch and listen to the recommendations of the diagnostician.
What pathologies does ultrasound reveal in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy?
The study is carried out at 30-34 obstetric weeks to identify potential complications that may interfere with the normal course of labor. During an ultrasound of the 3rd trimester, the doctor assesses how the size and weight of the fetus correspond to the duration of pregnancy, as well as:
- determines the location and thickness of the placenta, its degree of maturity,
- checks whether the umbilical cord is entangled around the neck and fetal hypoxia,
- measures the volume of blood flow,
- assesses the consistency of the uterine scar in case of repeat pregnancy after cesarean section.
Based on the results of the examination, the obstetrician-gynecologist specifies the preliminary date of birth and recommends the optimal method of delivery to the woman.
Using ultrasound in the third trimester of pregnancy, the following pathologies are diagnosed:
- risk of premature birth. It is indicated by an open internal or external pharynx, a shortened cervix, and increased tone of the uterine walls.
- umbilical cord entanglement. The study may reveal a situation of single or multiple entanglement of the umbilical cord in the shoulder girdle, neck or abdomen of the fetus.
- developmental defects. The most common malformations detected during ultrasound screening in the third trimester of pregnancy are the absence or abnormal structure of small parts of the body, for example, fingers, lips, jaw, palate. Organ pathologies are also diagnosed - defects of the heart, spine, brain, lungs and genitourinary system.
- incorrect presentation of the fetus. If the baby is not turned head down by the time of birth, breech presentation may require a cesarean section.
- pathology of the placenta. Special attention is paid to this organ during ultrasound of the third trimester of pregnancy. The most dangerous condition is its presentation - location in the lower part of the uterus, partial or complete overlap of the area of the internal pharynx, which complicates natural delivery. Placental hypoplasia is diagnosed at 32 weeks when its thickness is less than 23.5 mm, hyperplasia - when it is more than 41.6 mm.
- premature aging of the placenta. It is determined by the appearance of lobules in its structure before 36 weeks.
If there is a threat of miscarriage or serious complications for the mother and child, the specialist may prescribe additional tests. Our clinic specialists take good care of the health of the expectant mother and carefully check the key parameters of fetal development. Here you can undergo an ultrasound scan of the third trimester of pregnancy at an affordable cost from leading doctors in Moscow.
How is the examination carried out?
Ultrasound in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy is performed using the transabdominal method through the anterior wall of the abdomen. The woman takes off her clothes to expose her stomach and pubic area and lies down on the couch. The doctor applies a water-based gel to the skin, which is necessary for better ultrasound conductivity.
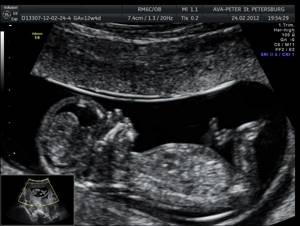
An ultrasound probe is applied to the abdomen. The device emits high-frequency ultrasound, which is repelled from body tissues at different frequencies and strengths. The result is captured by the sensor and transmitted to the computer, where it is converted into an image. The doctor sees the child and his organs on a computer monitor.
During the ultrasound, the doctor records all the necessary data in the study protocol, which is given to the patient. The whole procedure takes 15-20 minutes, after which the woman can get dressed and return to her usual activities.
Decoding
Screening ultrasound allows you to obtain data on the development of the fetus, as well as show the individual characteristics of skeletal development, insufficiency or excess of body weight and size of the child. There are the following fetometric standards with which current indicators are compared during a routine ultrasound:
- The biparietal head size (BSD) in the period from the 32nd to the 34th week is 78–82 ± 7 mm, increasing in proportion to the period.
- Fronto-occipital head size – indicators for this period are 104–110 ± 9 mm.
- Head circumference is normally 304–317 ± 21–22 mm.
- Abdominal circumference – 286–306 ± 28–30 mm.
- The length of the femur is 61–65 ± 5 mm.
- The length of the tibia bones is 56–60 ± 4 mm.
- The length of the humerus is 56–59 ± 4 mm.
- The length of the forearm bones is 49–52 ± 4 mm.
Also, during an ultrasound, it is important to set the following parameters and compare them with the norms for a given gestation period:
- volume of amniotic fluid (the amount of amniotic fluid should not be more than 1700 ml);
- condition of the placenta (its thickness should be in the range of 23.5-41.6 mm and not older than 2 degrees of maturity);
- condition of the uterus and cervical canal (the length of the cervical canal must be at least 30 mm.).
The placenta is the organ that is the focus of the third ultrasound
The placenta, also called the “baby place,” is a completely unique, important organ that develops and is present only during pregnancy. Normally, it is located in the uterine cavity on the back or front wall. The formation of the placenta is finally completed by the 15th - 16th week of gestation; after the 20th week, the intensive functioning of the “baby place” and blood exchange through the placental vessels begin.
At the 22nd – 36th week, the weight of the placenta noticeably increases, and by the 36th week it becomes functionally mature. In appearance, the placenta resembles a flattened round disk at the time of birth with a diameter of 15–18 cm, a thickness of 2–3 cm and a weight of 500–600 grams.
Functions of the "children's place":
- gas exchange - transporting oxygen from the mother’s blood to the fetus, and carbon dioxide from the fetus to the maternal bloodstream;
- trophic – the fetus receives nutrition thanks to the placenta;
- immunological - the “baby place” prevents the mother’s immune cells from reaching the fetus (they perceive the embryo as a foreign object and are capable of destroying it), but allows maternal antibodies to pass through, protecting the baby from various infections;
- secretory - the placenta produces chorionic hormone (hCG), placental lactogen, prolactin, etc., which guarantee the preservation, successful course of pregnancy and the proper development of the fetus.
During an ultrasound examination, the structural features of the placenta are studied, its width at the point of attachment to the umbilical cord (for example, its thinning indicates placental insufficiency), localization in the uterus (required to exclude a pathology such as presentation, which can complicate bleeding in the last weeks of gestation and childbirth) , blood flow intensity and other parameters.
There are also 4 degrees of maturity of the “baby place” (at 27 - 34 weeks, 2nd stage - from 34 to 39 weeks, and 4th stage - from the 37th week).
Advantages of the center
The Miracle Doctor clinic has a staff of experienced obstetricians and gynecologists who you can safely trust with the health of your mother and unborn child:
- The best diagnostic doctors are specialists of the highest category who are fluent in modern diagnostic equipment in obstetrics and gynecology.
- Adequate prices for diagnostics (ultrasound and interpretation).
- Convenient location of the clinic (Southeastern Administrative District of Moscow, next to the metro station “Rimskaya”, “Pl. Ilyich”);
- Modern medical equipment (ultrasound machines Hitachi Hi Vision Ascendus, Samsung WS80A, Toshiba Aplio), providing three-dimensional visualization.
- Accurate and reliable results and correct interpretation of readings.
Now you know where to get an ultrasound in the 3rd trimester! Make an appointment with the clinic doctor by calling the reception desk or fill out the registration form on the website.
What indicators of baby development are studied using ultrasound at 30–34 gestational weeks?
The biophysical profile of the fetus is assessed - the number of its movements (at least three during the 30-minute examination period), its position in the uterine cavity, and the movements of its lungs. The third ultrasound normally shows that the baby is active, he moves his limbs, which are in a semi-bent state, his fingers are tightly clenched (into fists). Hypotension indicates oxygen starvation.
The main organs and systems of the fetus can be easily studied using an ultrasound device at 30 - 34 weeks, and therefore at the third ultrasound the following are carefully examined in the baby:
- brain;
- spine;
- face (particular attention is paid to the upper lip);
- respiratory organs - lungs;
- anatomical structures of the abdominal cavity;
- reproductive apparatus (sex establishment).
The weight of the fetus, the fronto-occipital and biparietal dimensions, the length of the femur and tibia, the shoulder and forearm, the nose, the circumference of the head and abdomen are measured. Only if the size of the fetus turns out to be much smaller than normal, the doctor has the right to indicate intrauterine growth retardation in the conclusion. In such cases, auxiliary diagnostic methods and appropriate therapeutic measures are certainly prescribed.
At the request of the future parents, the doctor will provide them with a photograph of the baby in the mother’s womb. At this stage of gestation, the fetus already has clear outlines of body parts.
To summarize, it should be recalled that independent unqualified interpretation of the results of the third planned ultrasound (as well as all previously obtained conclusions) is unacceptable! If significant discrepancies between the actual data and generally accepted standards are detected, a repeat study is ordered. An experienced obstetrician-gynecologist can adequately interpret the result. The doctor will answer all the woman’s questions competently, help get rid of far-fetched fears, or provide medical assistance if necessary.
Amniotic fluid index
| Week of pregnancy | Normal value, mm |
| 28 | 168±81 |
| 29 | 164±85 |
| 30 | 170±88 |
| 31 | 171±92 |
| 32 | 174±95 |
| 33 | 174±100 |
| 34 | 173±103 |
| 35 | 174±105 |
| 36 | 173±106 |
| 37 | 170±105 |
| 38 | 153±102 |
| 39 | 164,5±95,5 |
| 40 | 151,5±88,5 |
The doctor also assesses the condition of the umbilical cord using Doppler ultrasound. A normal umbilical cord should have two arteries and only one vein. During the examination, it is possible to detect a twisted umbilical cord or entwined around the child’s neck, which poses a particular danger.
Normal placental thickness
| Week of pregnancy | Thickness, mm |
| 28 | 29,9±7,5 |
| 29 | 31±7,4 |
| 30 | 31,5±7,8 |
| 31 | 32,6±8 |
| 32 | 33,6±8,1 |
| 33 | 32,6±8 |
| 34 | 33,2±8,3 |
| 35 | 34,3±8,3 |
| 36 | 37±9 |
| 37 | 36,8±8,9 |
| 38 | 37,3±9 |
| 39 | 36,1±9,1 |
| 40 | 35,7±9,2 |
When the thickness of the placenta exceeds the average, there is a possibility that it is inflamed (placentitis). If there is a suspicion of placentitis, the doctor prescribes a Doppler ultrasound examination.
It is considered normal when the placenta is attached to the posterior wall of the uterus, 6 cm from the internal os. Central presentation, marginal and low attachment of the placenta are extremely dangerous pathologies; they threaten the child and mother. If these diagnoses are present, the woman is transferred to a hospital or, if it is possible to ensure complete rest, to home.
In case of complete placenta previa, a cesarean section is prescribed, since it blocks the exit from the uterus and prevents the baby from being born naturally. If the placenta is low, then natural delivery is possible, but there is a high risk of bleeding during childbirth.
When the thickness of the placenta exceeds 45 mm, this may indicate the following disorders:
- Rhesus conflict;
- dropsy;
- infectious process;
- diabetes.
Examination of the condition of the placenta and uterus on ultrasound
Specialists pay great attention to ultrasound and the condition of the placenta and uterus, since the health and proper development of these organs is the key to the success of a successful birth. Normally, the absence of deviations here is characterized by:
- establishment of a cephalic intrauterine presentation in a child;
- the first stage of placental maturity;
- absence of death of areas inside the placenta (placental infarction);
- absence of hematomas (otherwise the woman in labor is admitted to the hospital);
- absence of tissue detachments, which may mean the onset of premature birth;
- normal amount of amniotic fluid with epithelial cells present in it;
- closing both the external and internal pharynx;
- the size of the cervix is at least 30 centimeters.
It happens that doctors classify some deviations as normal. In such cases, no additional tests are prescribed for the pregnant woman. If the normal range of deviations is exceeded, the woman in labor can be sent both to a hospital for treatment and for additional examinations in order to identify and eliminate all emerging pathologies.
Fetal size depending on week of pregnancy
| Week of pregnancy | Weight, g | Height, cm |
| 28 | 1004±75 | 37,7±0,7 |
| 29 | 1152±75 | 38,6±0,7 |
| 30 | 1320±75 | 40±0,5 |
| 31 | 1502±75 | 41,1±0,7 |
| 32 | 1702±75 | 42,3±0,5 |
| 33 | 1918±75 | 43,7±0,5 |
| 34 | 2146±75 | 45±0,5 |
| 35 | 2384±125 | 46,1±0,5 |
| 36 | 2622±50 | 47,4±0,7 |
| 37 | 2858±100 | 48,6±0,5 |
| 38 | 3084±100 | 49,9±0,5 |
| 39 | 3288±100 | 50,7±0,5 |
| 40 | 3462±150 | 51,2±1,5 |
| 41 | 3598±125 | 51,7±0,7 |
| 42 | 3684±125 | 51,5±0,7 |
Exceeding the norm indicates that the fetus is large for the gestational age. This is not a pathology if the woman does not have diabetes. Typically, with this disease, delivery is necessary at 37-38 weeks due to increasing complications. The decisive factor in decision making is the weight of the fetus at 38 weeks:
- more than 3900 g – induction of labor;
- 2500-3800 g – prolongation of pregnancy.
A large fetus also poses a problem for a woman with an anatomically narrow pelvis. In this case, a caesarean section is indicated.
When is the third ultrasound performed?
The third trimester is considered to be the period from 28 weeks until the birth of the child. By decree of the Ministry of Health, routine ultrasound is performed at 30-34 weeks of pregnancy. Doppler ultrasound is mandatory, which allows you to accurately assess the functioning of blood vessels and find out the amount of oxygen supplied to the child.
The date of the examination is determined by the doctor. It will depend on the available information about the mother’s health and the data obtained from past examinations. Therefore, it is extremely important to tell your doctor about any problems or problems in your health and well-being. If various pathologies are detected, the number of ultrasound examinations prescribed may be more than three.
The doctor may recommend an additional ultrasound immediately before birth (38-40 weeks). This examination is designed to determine the location of the baby in the uterus, its weight and the location of the umbilical cord. This information will help determine whether the birth will take place naturally or whether a caesarean section will have to be used.
Fetal head size
| Week of pregnancy | Fronto-occipital size, mm | Biparietal size, mm |
| 28 | 91±8 | 73±6 |
| 29 | 94±8 | 76±6 |
| 30 | 97±8 | 78±7 |
| 31 | 101±8 | 80±7 |
| 32 | 104±9 | 82±7 |
| 33 | 107±9 | 84±7 |
| 34 | 110±9 | 86±7 |
| 35 | 112±9 | 88±7 |
| 36 | 114±10 | 90±7 |
| 37 | 116±10 | 92±6,5 |
| 38 | 118±10 | 94±7 |
| 39 | 119±10 | 95±7 |
| 40 | 120±10 | 96±7 |
An enlarged fetal head often indicates hydrocephalus. Modern medicine, subject to timely diagnosis, can cure this. After the birth of the child, the pathological fluid from the skull is removed through puncture, which gives a quick effect.
In rare cases, the reason for exceeding the norm is brain tumors (cysts, tumors).
If the fetus has a small head, you should only worry if there is a repeated and significant lag from the norm.
The appearance of a double outline of the head on an ultrasound indicates swelling of the subcutaneous fatty tissue.
Degree of maturity of the placenta
| Week of pregnancy | Maturity level |
| Up to 30 | 0 |
| From 30 to 34 | 1 |
| From 35 to 39 | 2 |
| After 40 | 3 |
A change in the structure of the placenta ahead of schedule indicates its premature aging. The cause may be a violation of blood flow caused by gestosis (a complication in which blood pressure increases, protein appears in the urine, swelling) or anemia (decreased hemoglobin). Sometimes this is simply a consequence of the individual characteristics of the expectant mother.
If such a deviation is detected, Doppler and cardiac monitoring studies are prescribed.
During an ultrasound, the amniotic fluid is necessarily assessed - its quantity and quality. It must be transparent and free of any foreign impurities. The presence of mucus, flakes, or cloudy water may suggest an infection.
The amniotic fluid index is used to determine its quantity. A lag from the norm is a sign of oligohydramnios, an excess is a sign of polyhydramnios.
Ultrasound diagnostics
Ultrasound in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy refers to routine examinations aimed at determining the functional state and development of the fetus. Screening is carried out at 30-32 weeks for all women, regardless of the presence or absence of complications during pregnancy.
The data obtained are very important for monitoring the course of pregnancy and choosing the method of birth of the child (natural birth, cesarean section).
The Gamma Med clinic employs qualified diagnostic doctors, specialists of the highest category, who are proficient in modern ultrasound research techniques. Experience and qualifications allow doctors to accurately interpret diagnostic results and timely detect abnormalities in the course of pregnancy.
Dates
An ultrasound in the third trimester of pregnancy should be done after consultation with your doctor during a routine examination. The referral is issued at 11-13, 20-22 and 30-32 weeks. At this time, it is possible to find out in sufficient detail the condition and characteristics of the development of the fetus, as well as the functional state of the cervix and uterine body, placenta and umbilical cord.
Depending on the condition of the pregnant woman, ultrasound can be prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist at various stages of pregnancy to exclude abnormalities in the intrauterine development of the fetus.
What does it include
- Assessment of the condition of the pregnant woman's organs. Helps determine the risks of premature birth (shortening of the cervical canal, increased uterine tone, opening of the pharynx). If these abnormalities are detected, an ultrasound examination may be the basis for referral to a hospital for preservation.
- Study of the placenta. Its location and thickness are determined. Allows the doctor to decide how advisable a natural birth would be and whether there is a risk of bleeding or premature placental abruption.
- Determination of placenta maturity. The functional state of the umbilical cord blood vessels is assessed in order to promptly notice and take action due to premature aging, which can lead to negative consequences for the normal development of the fetus.
- Determination of the state of amniotic fluid. Evaluates the condition of amniotic fluid, helps to detect oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios in time.
- Assessment of blood flow using Doppler. Identifying the problem at this time reduces the risks for the mother and fetus during pregnancy and childbirth, and also allows you to bring the pregnancy to the natural terms of delivery.
Doppler testing helps to identify the following types of disorders:
- In the first degree , drugs are prescribed that improve blood circulation in the placenta, and periodic medical monitoring is also carried out.
- In the second degree, constant monitoring and drug support is carried out until birth.
- In the third degree, urgent delivery is indicated.
- Determination of the position of the fetus in the uterus (the protocol for the 3rd trimester allows you to determine the position of the fetus (fetuses in multiple pregnancies) and presentation (the position of the child in relation to the birth canal).
- Fetometry (correspondence between the size of the child and the gestational age, identifying the characteristics of the course of pregnancy, possible disorders or deviations in the development of the fetus).
Preparation
There is no need to prepare for an ultrasound in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy - follow a diet, cleanse the intestines, or refuse to take certain medications. It is advisable for the patient to be well rested before the ultrasound, as stress can adversely affect the procedure and may show signs of risk of preterm labor. The expectant mother should not come to the ultrasound hungry; you can take sweets (sweets, chocolate) with you so that the baby is active.
What does it show
The third ultrasound during pregnancy allows you to confirm the sex of the child, multiple pregnancies and determine the approximate date of birth. The doctor pays special attention to the condition of the placenta, determines its presentation, on which the possibility of natural childbirth depends (for example, partial or complete presentation to the internal os is an indication for cesarean section).
During ultrasound screening of the 3rd trimester, the doctor observes:
position and motor activity of the fetus; development of the child’s internal organs; condition of the blood vessels of the umbilical cord, fetus, uterine arteries; fetometric indicators; signs of fetal hypoxia; fetal heartbeat; fetal presentation; length of the cervical canal.
Decoding
Screening ultrasound allows you to obtain data on the development of the fetus, as well as show the individual characteristics of skeletal development, insufficiency or excess of body weight and size of the child. There are the following fetometric standards with which current indicators are compared during a routine ultrasound:
- The biparietal head size (BSD) in the period from the 32nd to the 34th week is 78–82 ± 7 mm, increasing in proportion to the period.
- Fronto-occipital head size – indicators for this period are 104–110 ± 9 mm.
- Head circumference is normally 304–317 ± 21–22 mm.
- Abdominal circumference – 286–306 ± 28–30 mm.
- The length of the femur is 61–65 ± 5 mm.
- The length of the tibia bones is 56–60 ± 4 mm.
- The length of the humerus is 56–59 ± 4 mm.
- The length of the forearm bones is 49–52 ± 4 mm.
Also, during an ultrasound, it is important to set the following parameters and compare them with the norms for a given gestation period:
- volume of amniotic fluid (the amount of amniotic fluid should not be more than 1700 ml);
- condition of the placenta (its thickness should be in the range of 23.5-41.6 mm and not older than 2 degrees of maturity);
- condition of the uterus and cervical canal (the length of the cervical canal must be at least 30 mm.).
Advantages of the center
- The best diagnostic doctors are specialists of the highest category who are fluent in modern diagnostic equipment in obstetrics and gynecology.
- Adequate prices for diagnostics (ultrasound and interpretation).
- Modern medical equipment (ultrasound machine ALPINION E-CUBE 15 EX), providing three-dimensional visualization.
- Accurate and reliable results and correct interpretation of readings.
Now you know where to get an ultrasound in the 3rd trimester! Make an appointment with the clinic doctor by calling the reception desk or fill out the registration form on the website.