After cesarean section, leukocytes in the blood, urine and vaginal smear may increase due to physiological and pathological reasons. In the first case, this is a weakening of the immune system, tissue ruptures, and hormonal changes.
Pathologies with leukocytosis include sexually transmitted diseases, hepatitis, cystitis, adnexitis, endometritis, fibroids, oncology and other diseases. They are always accompanied by other symptoms, which makes diagnosis easier.
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor, the woman herself must adjust her diet, it is possible to use traditional methods, but only in consultation with specialists.
What will leukocytes tell you after a cesarean section?
An increased number of leukocytes in the blood after cesarean section is a frequently diagnosed condition that indicates some changes in the body. Leukocytes are part of the immune system, perform a protective function and are activated only when necessary to “silence” a developing disease. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish between two types of leukocytosis after cesarean section - physiological and pathological.
Physiological
It occurs during the period of bearing a child, when the body is actively restructuring its work and functioning in an enhanced mode. The doctor may prescribe control blood tests for the patient if the indicators are very high - if there is no increase in the number of leukocytes between two tests with a break of 3-5 days, then the pathological process is excluded.
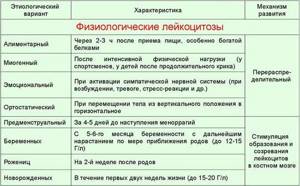
Gynecologists also consider such a concept as false leukocytosis of pregnant women, when the immune system actively protects the fetus. If the indicators remain unchanged, then there is no reason for additional examinations. The most important difference between physiological leukocytosis is the absence of other symptoms; the woman’s general well-being remains unchanged.
In theory, white blood cell levels should normalize after a cesarean section, but this does not happen immediately. Surgical childbirth means inevitable tissue damage, stress for the body and the immune system begins to protect it. Therefore, any positive changes should be expected only a week after the CS.
We recommend reading the article about discharge after cesarean section. From it you will learn about what lochia looks like after childbirth, its nature and duration, pathological discharge and the reasons for its appearance. And here is more information about why the suture hurts after a caesarean section.
Pathological
Leukocytosis after cesarean section with constantly increasing rates is evidence of a progressive pathological process in the body. And these can be inflammations, infectious diseases - an accurate diagnosis is made by a doctor after a thorough examination.
The main sign of a pathological increase in leukocytes is a constant increase in parameters and a general deterioration in well-being.

Normal after surgery
The norm of leukocytes after surgery is 4-9x10^9 cells per liter , and if there is a significant excess of this indicator, the doctor may suspect the development of internal pathology. It should be taken into account that during pregnancy the level of leukocytes increases by 20%, at the time of childbirth - by 30-40%. But already 2-3 days after cesarean section, the indicators should decrease and approach normal.
Why are high values dangerous?
Constantly high levels of leukocytes are dangerous for the development of:
- cervical erosion;
- mastopathy;
- uterine fibroids;
- adhesive disease;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- infertility;
- pathologies of the urinary system.
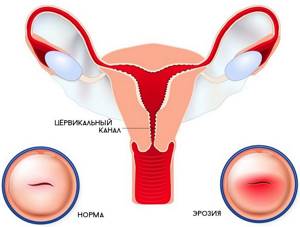
Most pathologies of internal organs in the postoperative period can be practically asymptomatic; a woman can ignore the signs (“the pain will go away”) or take targeted medications such as painkillers and antipyretics. In this case, only a blood, urine, or smear test can reveal to the doctor the true clinical picture.
Blood chemistry
A biochemical blood test during pregnancy, with determination of the level of transaminases, that is, liver enzymes, total and direct bilirubin, protein levels, urea and creatinine, amylase, glucose, cholesterol, is taken at the beginning of pregnancy, in the middle and in the late stages. The study allows us to judge the work of the most important internal organs:
- kidneys (urea and creatinine),
- liver (AST, ALT, total and direct bilirubin),
- pancreas (amylase).
And also confirm the appearance of jaundice, Rh conflict, gestosis, renal failure, pancreatitis, the development of protein-free edema and other disorders that are dangerous during pregnancy.
A biochemical blood test, if necessary, can be expanded to determine protein fractions, acute inflammatory proteins and enzymes (C-reactive protein, creatine phosphokenase, MB fraction of creatine phosphokenase), triglycerides and lipoproteins, alkaline phosphatase, serum iron, ferritin, transferrin and other indicators. At the GMS medical clinic in Moscow you can undergo any modern biochemical test in the shortest possible time. And the experienced doctor with whom you make an appointment will tell you in detail about the identified indicators.
Elevated white blood cells after cesarean section: symptoms
If leukocytes are elevated after a cesarean section, the woman may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- high blood pressure;
- frequent or delayed urination;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting not associated with food intake;
- high body temperature;
- presence of blood in the urine;
- recurrent lower back pain;
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen.

A woman should pay special attention to:
- increase in body temperature - indicators can be critical and last for several hours even while taking specific medications;
- vaginal discharge - it may have light admixtures of blood and even “strings” of pus, and bleeding often occurs simply;
- burning during urination, accompanied by nagging pain in the lumbar region;
- unmotivated occurrence of headaches - there are no other symptoms, body temperature is normal.
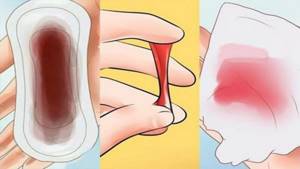
Vaginal discharge – it may contain light traces of blood and even “strings” of pus
HCG analysis
An hCG analysis during pregnancy, that is, an analysis for human chorionic gonadotropin, is an analysis that confirms the development of a new life in a woman’s womb.
From the very first days of conception, the membrane of the fertilized egg, the chorion, produces a special hormone - human chorionic gonadotropin. The fertilized egg grows into the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity, which is rich in blood vessels, so hCG enters the blood and is detected in a blood test even in the smallest concentrations. As a rule, hCG (free beta subunit) is usually tested at 11-13 weeks, and at 16-20 weeks as part of the so-called screening tests.
In individual cases, when a woman is planning a pregnancy and wants to know exactly about its occurrence, as well as after in vitro fertilization surgery, a blood test for hCG is taken from the very first days of the expected pregnancy. In early pregnancy, when ultrasound cannot visualize tiny embryos, only a blood test for hCG and some physiological changes in the woman's genitals can indicate pregnancy.
Leukocytes in the blood after cesarean section: why are they elevated, what to do
Elevated leukocytes in the blood after cesarean section may be due to the following reasons:
- excessive physical activity;
- eating food before donating blood for testing;
- stress, lack of sleep;
- breastfeeding;
- taking a very warm bath;
- the onset of menstruation after childbirth.
The listed reasons are classified as physiological and do not require intervention from health workers. But leukocytosis may also indicate pathologies:
- acute respiratory viral infections, sinusitis, sore throat;
- disturbances in blood circulation and oxygen supply to internal organs;
- cystitis, pyelonephritis of acute form and in the acute stage during chronic course;
- fluctuations in blood sugar levels (high or low);
- suppuration of the suture after cesarean section;
- lactostasis, mastitis associated with stagnation of milk in the breast;
- endometritis;
- growth of malignant neoplasms.
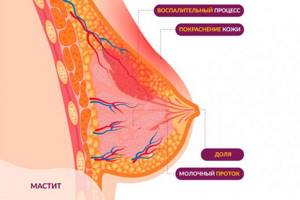
You cannot take any measures on your own; a full examination and an accurate diagnosis are required. It is the doctor who will be able to prescribe adequate treatment, which will help stop the pathological process and normalize the level of leukocytes.
As part of therapy, antihistamines and antiviral drugs may be prescribed, operations and radiation/chemical therapy for oncology, and antibiotics may be performed.
Hepatitis test
Testing for hepatitis during pregnancy is mandatory and is carried out upon registration and at the 32nd week of pregnancy.
During the initial examination for hepatitis B and C, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of venous blood is performed. In this case, antibodies to the hepatitis virus are determined, and not the virus itself, which makes it impossible to judge the presence of infection in the blood and its activity. But, most often, this is an indirect sign of a disease - chronic viral hepatitis. If positive ELISA results are obtained for hepatitis, additional tests are required, such as PCR and determination of the genotype of the virus.
Pregnant women, due to weakened immunity, are more susceptible to infection with viral hepatitis, and their disease occurs with pronounced symptoms and can lead to the death of the fetus or newborn.
You can get a complete examination for viral hepatitis in the shortest possible time at the Moscow GMS Medical Center. Modern equipment for diagnosing viral infections makes it possible to judge the presence, genotype and activity of the hepatitis virus. And experienced and qualified doctors will help cope with a chronic disease and prevent its progression.
If leukocytes are found in a smear after a cesarean section
If too many white blood cells are found in a vaginal smear after a cesarean section, this may indicate the development of:
- sexually transmitted infections - syphilis, chlamydia, herpes, candidiasis, HIV, cytomegalovirus, gonorrhea and others;
- vaginal dysbiosis - affects the decrease in general immunity in the postoperative period, changes in hormonal levels;
- allergic reaction to intimate gels, lubricants for sexual intercourse;
- cancer of the female reproductive system.
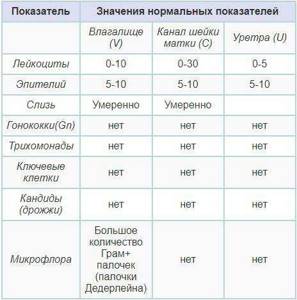
The same results can “speak” about urethritis, colpitis, adnexitis - it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the patient, analyze the accompanying symptoms in order to make an accurate diagnosis.
Antibody test
An antibody test during pregnancy has several purposes:
- prevention of Rh conflict and prevention of hemolytic disease of the fetus by identifying autoantibodies in the Rh-negative mother, which could potentially harm the Rh-positive fetus;
- conflict prevention using the AB0 system;
- detection of antibodies to various infectious agents that pose a danger to the mother and fetus (antibodies to HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, chlamydial infection, rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasma).
If preventive measures were not taken (specific immunoglobulin was not administered), then in the later stages of pregnancy, Rh conflict in Rh-negative mothers with repeated pregnancies occurs, according to some studies, in up to 70% of cases.
In general, a Rh-negative woman during pregnancy needs to have a blood test regularly - once a month until the 30th week of pregnancy, and after that - once every one to two weeks. In the absence of an antibody titer in a pregnant woman in the seventh month of pregnancy (at 28 weeks), anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is administered, which is the most important measure for the prevention of Rh conflict. The same drug is administered in the first 72 hours after birth, if a Rh-positive baby is born. Determining the titer of antibodies to various infections makes it possible to judge the strength of the immune system and the presence of infection in the body. Infections that are normally hidden can manifest themselves during pregnancy, since the woman’s immune system in this state is somewhat reduced. As a rule, such tests are taken upon registration and during pregnancy.
You can take tests for antibodies to various infections, determine the presence or exclude Rh conflict at the Moscow GMS medical clinic. Modern laboratory equipment and the absence of queues speed up the completion of antibody tests.
Reasons for detecting leukocytes in urine after cesarean section
Most often, the detection of leukocytes in urine after cesarean section is associated with:
- cystitis - inflammation of the walls of the bladder, which is caused by pathogenic bacteria;
- worms – when treatment for helminthiasis has not been carried out and the disease has reached a severe stage of development;
- pyelonephritis - inflammation of the tissues of the renal pelvis caused by a bacterial infection or physiological factors such as hypothermia;
- problems in the functioning of the endocrine system - after a cesarean section, for example, women often have metabolic disorders;
- urolithiasis;
- renal failure.
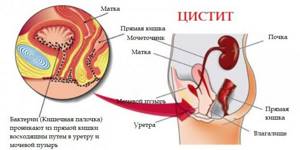
In addition, it is necessary to exclude or confirm viral pathologies (rubella, hepatitis), neoplasms (malignant, benign), trichomoniasis, candidiasis (thrush).
Risk factors
As you know, inflammation is the result of the activity of bacterial microorganisms. As a rule, these are opportunistic bacteria, in particular, staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, etc. They are always present in the body, but their reproduction processes are activated against the background of stress, which is the birth process, as well as when the immune system is weakened. Risk factors include:
- loss of blood, which, alas, is inevitable during childbirth;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- anemia (decreased number of red blood cells);
- disturbances in blood clotting processes (fraught with additional blood loss);
- the presence of remnants of membranes and/or placental tissue in the uterus;
- cracks in the nipple area;
- surgical interventions during childbirth;
- severe pregnancy;
- birth process with complications;
- Constant stress, overwork and lack of sleep also affect hormonal levels and the immune system, weakening the body.
How to influence indicators without medications
If the increase in leukocytes is associated with physiological reasons, then drug therapy is not advisable. You can solve the problem yourself by correcting your diet and using folk methods. They will also help with pathologies, but it is necessary to coordinate their use with your doctor.
Diet
A woman’s menu should include foods high in B vitamins and ascorbic acid:
- persimmons, lemons, oranges, apples, apricots;
- rosehip, sea buckthorn, black currant;
- sweet pepper (Bulgarian);
- broccoli, Brussels sprouts, red cabbage;
- whole milk;
- dairy products;
- chicken/quail eggs;
- low-fat fish;
- pine nuts, hazelnuts;
- buckwheat, pearl barley, barley, wheat porridge.

If a woman is breastfeeding, then the list of healthy foods for leukocytosis should be agreed upon with the pediatrician - the baby may develop a strong allergic reaction to most of those listed. It is imperative to exclude canned foods, hot/spicy spices, semi-finished and smoked foods, mayonnaise, too fatty foods, and sweets from your diet.
It is important to maintain a drinking regime - at least 2 liters of liquid per day, this can be clean water, natural fruit drinks, tea without sugar, and herbal infusions.
Traditional methods
If elevated white blood cells are detected in a vaginal smear, then you need to douche with a soda solution (1 teaspoon per 300 ml of warm water). You can combine aloe juice and honey in equal proportions in a bowl, soak a tampon with the mixture and insert it into the vagina overnight.
Combine aloe juice and honey in equal proportions in a bowl and soak a tampon with the mixture. Insert the tampon into the vagina overnight
Typically, on days 5-7 of such procedures, test results return to normal. In parallel with this, it is recommended to take a decoction of St. John's wort internally - 1 teaspoon of raw material per glass of water, simmer in a water bath for 10 minutes, drink 3 times during the day.
All traditional methods must be agreed with a doctor. Douching and tampons should not be used earlier than 30 days after a cesarean section; a herbal decoction can negatively affect lactation.
We recommend reading the article about temperature after cesarean section. From it you will learn about when you need to visit a doctor if you have a fever after a caesarean section and how to lower your temperature at home. And here is more information about how long after a cesarean section you can play sports and what kind of sports.
An increase in white blood cells after a cesarean section does not always indicate the development of a pathological process. Only a doctor can read the analysis, and he will prescribe further examinations if necessary, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe therapy. More often, deviations from the norm are observed solely for physiological reasons.
What to do if the level of leukocytes increases?
Under no circumstances should such a problem be ignored. If you notice the symptoms described above, you should definitely consult a doctor. The success of therapy largely depends on how quickly the disease is diagnosed.
The treatment regimen depends on the type and location of the inflammatory process and the nature of the pathogen. Treatment almost always involves taking antibiotics. During laboratory tests, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a particular drug. In addition, patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antihistamine medications, vitamins, and other drugs.