Author:
- Laricheva Larisa Alexandrovna
chief physician, gastroenterologist, therapist of the highest qualification category
5.00 (Votes: 1)
Have you been treated by an otolaryngologist , but the prescribed treatment did not help? You cannot understand why you are being referred to a gastroenterologist if you have a sore throat, a hoarse voice or even loss of voice, or a persistent cough that does not respond to standard therapy?
Often the cause of these complaints can be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, namely gastroesophageal reflux disease , or GERD .
FGDS - what is this procedure, preparation, indications and contraindications, complications after
FGDS - what kind of diagnostic procedure it is, preparation for the study with important medical recommendations, indications and contraindications, possible complications, consequences - we will describe all this on the website alter-zdrav.ru.
Such detailed information is often necessary for those patients who are prescribed fibrogastroscopy of the stomach and adjacent organs for the first time. In modern medicine, various diagnostic methods are used to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis. These include radiation diagnostic methods (fluorography, X-ray, angiography, computer, magnetic resonance and nuclear magnetic tomography), direct visual diagnostic methods (fibrogastroduodenoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, duodenal intubation, coproscopy, etc.).
Quite often, any visual examination of the stomach, based on the insertion of a probe through the oral cavity, is called gastroscopy - FGS (fibrogastroscopy).
Gastroscopy examines the gastric mucosa using a flexible tube (endoscope) inserted into the stomach through the mouth and a camera at its end.
Another type of visual examination - EGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) involves examining the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum with an endoscope.
Visual examination methods allow you to see the condition of the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small and large intestines, gall bladder, take gastric juice, bile, pieces of tissue for analysis, and deliver the medicine precisely. One of the visual inspection methods is the FGDS method.
What is FGDS
FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) is a method of examining the surfaces of the esophagus, stomach and the beginning of the duodenum using an endoscope. In gastroenterology it is considered the most informative method for making and clarifying the diagnosis.
The examination is carried out with a thin flexible probe 8-11 mm thick, which is inserted through the mouth and esophagus into the stomach. The image is projected onto the screen. There is a type of examination where a probe is inserted through the nose.
Advantages of the FGDS method:
- information content;
- safety;
- no pain;
- easy to carry.
The design of the device allows for diagnostics, taking tissue samples for analysis, and performing surgical manipulations at the time of the procedure.
Preparing for FGDS of the stomach - several important recommendations
The FGDS procedure requires certain preparation and it is advisable for the patient to familiarize himself in advance with the requirements that must be met in order for the procedure to be successful and with the greatest information content.
So how can you properly prepare for an FGDS? Can you drink water, what can you eat?
Preparation requirements:
- food that takes a long time to digest (nuts, seeds, fatty and fried meat), as well as products containing coloring substances (coffee, chocolate), carbonated drinks, alcohol, smoked foods should be excluded from the diet 2 days before the examination;
- Meals should be taken 12 hours before the procedure, i.e. you need to have dinner the night before at 18.00, excluding raw vegetables and heavy foods;
- do not smoke 3 hours before the test (smoking increases the volume of mucus in the stomach);
- do not take medications in capsules and tablets on the day of the examination; if this is not possible, notify the doctor conducting the examination;
- if you have an allergy, any disease or something is bothering you at the moment, tell your doctor about it;
- do not drink before the procedure (or at least three hours must pass and only clean water in small quantities);
- do not chew chewing gum;
- if the examination is not carried out in the first half of the day, then you need to consult a doctor about the possibility of eating breakfast;
- clothes should be loose so that unnecessary sensations do not interfere;
- you should not use perfume - it interferes with the doctor;
- bring a sheet (on the couch), a towel;
- immediately before the procedure, remove dentures, if any;
- Before the procedure, you need to calm down, set yourself in a positive mood (excessive anxiety can interfere with the examination) and be ready to do everything that the doctor advises.
Proper preparation of the patient and the right attitude will help you complete the examination without any difficulties.
Indications for gastroscopy (FGDS)
Tests and x-rays do not always make it possible to make a diagnosis, but performing an FGDS allows you to see the picture of the disease from the inside, clarify or make a final diagnosis. The examination is mainly carried out to diagnose diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially its upper part.
When is FGDS performed:
- in the presence of nausea, heartburn, belching;
- cough for no apparent reason;
- pain when swallowing;
- swallowing dysfunction;
- bloating, gas formation;
- noticeable weight loss;
- abdominal pain, especially in the epigastric region;
- blood in stool;
- vomiting, blood in vomit;
- B12 deficiency anemia;
- with stomach bleeding;
- to deliver a medicinal product;
- remove polyps;
- take tissues, gastric juice for analysis, samples for gastrobacteria, for example, they often jointly perform a urease test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori (Helicobacter pylori);
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
FGDS reveals the following diseases: gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, stomach and esophageal cancer, inflammatory processes in the esophagus, reflux disease, polyps, duodenitis and other diseases.
A timely EGD of the stomach will help diagnose the disease at an early stage, which makes it possible to start treatment on time.
For chronic diseases, FGDS is performed once a year, in other cases - according to the indications and direction of the attending physician.
Lump in the throat
The appearance of a lump in the throat
is a very common problem. Many patients browse the Internet every day to understand why they have a lump in their throat and what to do in such a case. In the practice of an endocrinologist, patients who seek consultation regarding a lump in the throat are encountered almost every day.
What diseases can cause such sensations? A lump in the throat occurs with diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland, the appearance of thyroid nodules, thyroid tumors, inflammation of the thyroid gland (thyroiditis), tumors of the anterior surface of the neck, tumors of the esophagus, neck abscesses, osteochondrosis, neurosis.
Contraindications for FGDS
Although the FGDS procedure is informative and without it it is sometimes difficult to make a diagnosis, it cannot always be carried out. There are conditions when research is contraindicated:
- narrowing of the esophagus due to neoplasms and physiological reasons;
- narrowing of the stomach;
- signs of intestinal obstruction;
- severe stomach bleeding;
- mental illness in the acute stage;
- protrusion of the walls of the esophagus;
- aortic aneurysm;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart;
- immediately after a hypertensive crisis;
- bronchial asthma;
- strong gag reflex;
- enlarged thyroid gland;
- severe upper respiratory tract diseases;
- severe anemia, obesity;
- blood clotting disorder;
- colds when the procedure is impossible (nasal congestion, cough, laryngeal swelling, high temperature).
Recommendations
Most often, people are interested in what to do if their stomach hurts after gastroscopy. The following recommendations have been developed on this issue:
- In almost all cases, discomfort does not require any drug treatment;
- If the pain does not relieve itself on its own, it intensifies or becomes cramping in nature, you should immediately consult a doctor;
- Minor pain can be relieved with a gentle diet for the first few days after FGDS;
- In case of inflammatory changes in the oral cavity, antiseptics are first prescribed:
- "Chlorhexidine";
- "Furacilin";
- "Miramistin";
- Saline solutions;
- An increase in body temperature, the development of intoxication, the appearance of cough and shortness of breath indicates an inflammatory process of the upper respiratory tract (pneumonia, bronchitis, tracheitis). In this case, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial drugs or even hospitalize the patient.
If pain persists, self-medication is strictly prohibited. In order not to miss a serious complication that requires timely surgical intervention, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Description of the procedure, what FGDS shows
FGDS is carried out in special diagnostic rooms as planned or urgently, strictly on an empty stomach.
Before the procedure, the patient is introduced to the examination technique, and written permission to conduct it is taken.
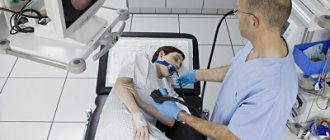
FGDS procedure
A nurse or doctor irrigates the throat with lidocaine spray if there is no allergy to it (this issue must be clarified in advance).
The patient is placed on the couch on his left side. The position should be convenient and comfortable for the patient, otherwise he will be tense, and this interferes with the insertion of the probe.
A mouthpiece is inserted into the mouth for ease of insertion of the endoscope (sometimes the device for FGS is called a gastroscope) and so as not to injure the mucous membranes of the lips and mouth.
The doctor begins to insert the endoscope, the patient, at the doctor’s command, performs a swallowing movement. At the time of administration, a gag reflex may appear, but if you breathe deeply and calmly, this condition goes away. After insertion of the endoscope, you should not swallow; saliva is collected by suction.
When the probe is inserted, air is introduced into the stomach (to straighten the folds) so that the mucous membrane can be better examined.
The duration of the procedure is 5-10 minutes and, if the doctor’s requirements are met, does not cause much discomfort to the patient.
If any therapeutic measures are carried out, then the time of its implementation reaches 30 minutes.
In some cases, the study is performed under general anesthesia (children, the patient’s agitated state, complete pain intolerance).
With FGDS you can see:
- what is the condition of the mucous membrane and walls of the stomach and esophagus;
- scar formation;
- narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- degree of reflux (reflux - stomach contents enter the esophagus);
- various neoplasms.
After the procedure, the endoscopist issues an FGDS conclusion - the result of the examination, a description of the consistently seen picture of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach, pylorus, and duodenal bulb. The presence of free patency, peristalsis, the amount of gastric secretion/bile reflux, varicose veins, plaque, closure/insufficiency of the cardiac rosette, inflammation (hyperemia, swelling), folds, and damage are indicated.
Quite often, a biopsy is taken - a microscopic piece of the mucosa to check for the presence of malignant cells.
What to do when your throat or stomach hurts
If, a day after the procedure, the patient continues to complain that it hurts to swallow, feels severe pain in the stomach, and his health does not improve, it is time to see a doctor. In such cases, the doctor is asked to wait a little, since the unpleasant sensations are the consequences of FGDS. Frequently used methods of treating pain are gargling and a special diet.
How to gargle
Rinsing helps relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx, disinfect and anesthetize the tracheal microtraumas received during the procedure. Doctors recommend using one of the following rinsing methods:
- Inhalipt spray is used for pain relief.
- Chlorophyllipt spray helps reduce pain and has an antiseptic effect.
- Miramistin relieves inflammation well.
- Furacilin solution helps relieve discomfort and accelerates healing.
- A solution of salt, soda and iodine, applied once every two hours, will also relieve pain.
- Chamomile solution has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect; it is recommended to use it a couple of times a day.
- Antiseptic tablets.
It is important to consult with your doctor regarding the choice of rinse and frequency of use. To achieve a better effect it is possible to combine.
In addition to rinsing solutions, doctors recommend drinking herbal teas, in particular chamomile. Drinking warm water with honey has a good effect on the throat. You can simply eat honey, even without water. The product has a rapid anti-inflammatory and soothing effect on the mucous membrane.
Complications after FGDS
A correctly performed FGDS procedure and the patient's compliance with the doctor's recommendations practically do not result in complications. The most serious complication is a violation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus or stomach, infection.
To avoid unwanted reactions of the body, any complications, the doctor always asks about the presence of diseases, and the patient must tell about his individual characteristics, about his condition before the examination (if he does not like something about his feelings).
Complications after FGDS:
- body temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- black color of stool;
- gag reflex and blood in vomit;
- pain in the abdominal area.
If you have any undesirable symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Stage 3. After.
A drunk-like state is normal and may last for several hours until the effects of the sedatives wear off. Be also prepared for bloating due to gas remaining in the stomach, which was used to inflate the walls of the organ for a full view. The throat will experience soreness, dryness, slight inflammation, hoarseness, tickling - not necessarily all at once, but such sensations are also allowed and can persist for several days.
To reduce their manifestation, gargle with soda or herbal solution, buy softening lozenges. And remember: if you have any doubts about your condition, forget about all the rules and consult a doctor.