If a gynecologist has diagnosed you with an ovarian cyst, do not be alarmed: as a rule, these formations are benign and do not pose a danger; surgery is not required. Often they do not need to be treated at all and disappear on their own within a few months. It is enough to periodically visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound examination.
- What types of ovarian cysts are there?
- When is laparoscopy performed?
- When is laparoscopy not performed?
- Benefits of laparoscopy
- Preparation
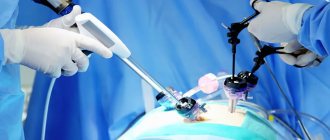
- How is laparoscopy performed?
- Postoperative period
- Complications
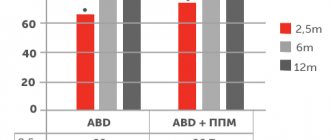
- Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
Sometimes ovarian cysts still have to be removed. Operations can be performed without an incision, through several punctures in the abdominal wall - laparoscopically. Euroonco employs expert-level gynecological surgeons who have extensive experience in performing such interventions. Come for a consultation with our specialist: he will tell you whether surgery is necessary in your case, and prescribe an examination that will help distinguish a benign neoplasm from a malignant one.
A cyst is not a specific disease. This term refers to any pathological cavity with fluid. The reasons for its formation are different. According to statistics, ovarian cysts are diagnosed in every tenth woman. They most often occur during puberty and menopause. Some girls have them from birth.
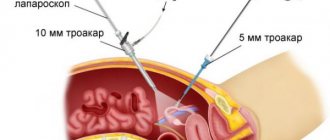
Main stages of laparoscopy
- General anesthesia is used to perform laparoscopy. Small incisions (about two centimeters long) are made on the skin, after which they are deepened using a blunt probe, thereby preventing damage to internal organs.
- One operation usually requires three or four holes. The introduction of sterile surgical instruments is carried out through special tubes inserted into the holes.
- To straighten the abdomen and provide maximum access to the internal organs, carbon dioxide is injected through one tube.
- A video camera and surgical instruments are inserted into other tubes.
- The video camera transmits the image of the operated organs to the monitor screen, which provides the doctor performing the operation with visual control over his actions.
- After all necessary actions have been completed, the instruments are removed and sutures are applied to the incision sites.
Menu (Power Mode)
The diet should consist of only 1/3 animal products, and 2/3 should be products of plant origin. It should be varied by including all kinds of vegetables and cereals. Breakfast can consist of cereals, salads, cottage cheese or eggs. Porridge should be consumed with the addition of seeds (pumpkin, sunflower, sesame, flax), raisins, dried apricots, and nuts.
Second breakfast - fresh fruit or cottage cheese. For lunch - vegetable soups, fresh vegetable salads, boiled fish, which is easier to digest than meat, so it is better to include it in the diet as often as possible. Legumes contain a large amount of fiber; in addition, they are a source of protein, so try to include them every other day.
Vegetable oils are added to prepared dishes. Make your diet healthy by excluding confectionery, chocolate, cakes; fruits and dried fruits can serve as sweets.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Benefits of laparoscopy
- Laparoscopy is characterized by minor tissue trauma, in contrast to conventional operations, for which large incisions are made.
- The rehabilitation period after laparoscopy is easier and shorter. Within a few hours after laparoscopy, the patient is allowed to get up and walk.
- The risk of complications (wound infection, adhesions, suture dehiscence) is significantly reduced.
- After laparoscopy there are no large scars or scars.
Types of laparoscopic operations
Laparoscopy is used to perform surgical interventions aimed at removing or restoring affected organs. Today, the following operations are performed using this method:
- remove the gallbladder (for patients with cholecystitis and cholelithiasis);
- the appendix is removed;
- remove the kidneys, bladder and ureter, or restore their functions;
- the fallopian tubes are removed or tied (sterilization);
- remove an ectopic pregnancy;
- treat endometriosis;
- treat PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome);
- treat hernias;
- perform surgical interventions on the liver, stomach and pancreas;
- examine and remove ovarian cysts;
- remove uterine fibroids;
- remove the adhesive process in the fallopian tubes;
- diagnose and stop internal bleeding.
Preoperative diet
Diet is an important component of both the preparatory and recovery periods for any surgical intervention.
Diet helps reduce the load on the cardiovascular system and reduces the risk of hypertensive surges during surgery.
Features of the anatomy of the female body include the close proximity of the ovaries and intestines. In this regard, any dysfunctions caused by disturbances in the functioning of the latter affect the ovaries before and after surgery
The diet before laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is aimed at normalizing stool, intestinal functions and maximizing its unloading and involves the consumption of easily digestible foods. Recommendations for preoperative nutrition also include small and frequent meals without overeating. A few days before the operation, it will be easier for the body to adjust to the fasting menu, because the diet before gynecological laparoscopy surgery brings the caloric content of the diet to the required physiological level. Before surgery, it is recommended to eat before 18:00.
Preparation for laparoscopy
Preparation for laparoscopic surgery is discussed between the doctor and the patient individually. The following actions are recommended:
- refusal to eat food 8 hours before the intervention;
- administering a cleansing enema several hours before the operation;
- epilation of the abdomen (if laparoscopy is performed on men).
Before the operation, the patient must inform the doctor about the medications he is taking. Due to the effect of some medications (aspirin, contraceptives) on hemocoagulation, their use before laparoscopy is strictly contraindicated.
Fully or partially limited products
- Products with stabilizers, emulsifiers, dyes and sweeteners - all of these substances are highly carcinogenic.
- Animal fats, fatty meats, red meats, shelf-stable foods with additives, margarine, cooking fats, fried foods, mayonnaise.
- Baked goods made from refined flour, pastries, pastries, cakes.
- Any canned food, pickles, sauces, marinades, smoked meats, sausages due to the content of dyes and preservatives.
- Strong coffee, black tea, chocolate, sugar and simple carbohydrates, which stimulate the growth of cancer cells.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| Kurabye cookies | 6,7 | 25,8 | 64,6 | 516 |
| butter cookies | 10,4 | 5,2 | 76,8 | 458 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Possible development of complications after laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a method characterized by a minimal risk of developing dangerous complications. As a rule, this operation is easily tolerated, and recovery after laparoscopy is quick.
You should consult a doctor after discharge from the hospital as soon as possible if the following symptoms appear:
- high temperature, chills;
- fainting (loss of consciousness);
- increased pain in the abdominal area, nausea, vomiting that does not stop for several hours;
- swelling, suppuration or redness in the suture area;
- bleeding from wounds;
- urinary disorders
Recovery period after laparoscopy
Most often, the patient recovers within a few days after laparoscopy, and sometimes can even be discharged on the day of the operation.
After laparoscopy, the patient may complain of intense pain in the abdomen and in the area of postoperative wounds, which intensifies with movement. This is considered normal. To relieve pain, painkillers may be prescribed.
In some cases, bloating, nausea, and general weakness may occur. To eliminate severe bloating, medications that include simethicone are prescribed.
Feelings of weakness, nausea, loss of appetite and increased urge to urinate go away on their own within 2-3 days after laparoscopy.
Authorized Products
Diet for ovarian cysts includes:
- Vegetables without nitrates. The diet includes all green leafy salads, broccoli, cauliflower, cucumbers, eggplants, potatoes, tomatoes, pumpkin, beets, carrots, zucchini, peppers, ginger, legumes, Jerusalem artichoke, garlic, greens in salads and soups. Vegetables with red and yellow colors (red peppers, carrots, yellow peppers, pumpkin) contain carotenoids with antitumor effects. The development of cancer cells is stopped by anthocyanins, which are found in eggplants, red cabbage and beets.
- It is useful to include fresh onions and garlic in your diet if there are no contraindications from the gastrointestinal tract. All salads and other dishes should include seaweed as a source of iodine, zinc and fiber. Vegetables, whenever possible, are consumed raw, and if tolerated poorly, they are consumed in processed form.
- Fruits and berries - 200 g per day or more. This can be any fruit that you prefer and is well tolerated.
- Whole grain bread, bran, bread with bran, nuts, flax seeds, apricot kernels, seeds contain fiber, so they should be present in the diet daily.
- Dietary meat (chicken and turkey) is consumed limitedly in the form of cutlets or in pieces. The meat is boiled or baked. It is better to give preference to fish and seafood, as these proteins are easier to digest.
- Soups are prepared with vegetable broth; you can use recycled meat broth. You can prepare vegetable or cereal soups, you can eat borscht, cabbage soup and pickles (not very salty).
- First courses are not allowed to be fried in order to minimize the consumption of thermally processed fats.
- Any crumbly porridge (for constipation, rice is excluded; for concomitant intestinal pathology, millet and pearl barley are excluded). Preference is given to buckwheat. Porridge is boiled in water, you can add milk, prepare cereal pancakes, puddings or casseroles.
- Fermented milk products and freshly prepared cottage cheese are included in the diet daily.
- Preference should be given to “live” kefir and yogurt, which normalize the microflora. Well-functioning flora has an anti-carcinogenic effect.
- Two eggs a day (soft-boiled or scrambled eggs).
- Unrefined vegetable oils added to prepared dishes.
- Green tea, a variety of freshly squeezed juices (limit cabbage and grape juices, which can cause bloating).
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| green beans | 2,8 | 0,4 | 8,4 | 47 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
| dried pears | 2,3 | 0,6 | 62,6 | 249 |
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| brown rice | 7,4 | 1,8 | 72,9 | 337 |
| brown rice | 6,3 | 4,4 | 65,1 | 331 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Bakery products | ||||
| vysivkovy bread | 9,0 | 2,2 | 36,0 | 217 |
| Old Russian grain bread | 9,6 | 2,7 | 47,1 | 252 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
| doctor's bread | 8,2 | 2,6 | 46,3 | 242 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| vegetable oil | 0,0 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 899 |
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| Cherry juice | 0,7 | 0,0 | 10,2 | 47 |
| tangerine juice | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,1 | 36 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Menstruation and discharge after laparoscopy
After a laparoscopic operation aimed at treating or diagnosing gynecological diseases, scanty mucous or bloody vaginal discharge may be observed, which can last 10-14 days. This is not a cause for concern.
Severe bloody vaginal discharge may be a concern, as it may indicate internal bleeding.
After laparoscopy, menstrual irregularities may occur: menstruation may not occur on time and may be delayed for several days or weeks. This is also considered normal.
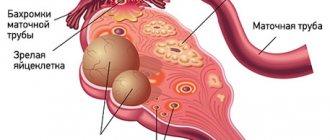
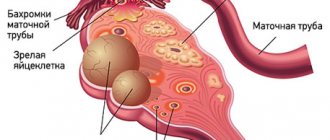
What types of ovarian cysts are there?
All ovarian cysts are divided into two large groups: functional , which occur in most cases, and pathological , which doctors have to deal with much less frequently.
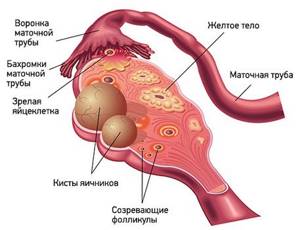
Functional cysts are the result of disturbances during the menstrual cycle. Usually they do not cause complications and disappear on their own. They come in three types:
- Follicular . follicle matures in a woman’s ovaries . Normally, it should open and release the oocyte. If this does not happen and the follicle continues to grow, it turns into a cyst.
- Corpus luteum cysts . After the follicle releases the egg, it turns into a special gland - the corpus luteum . It produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum atrophies. And if fluid accumulates in it, it turns into a cyst.
- Theca-luteal cysts often develop as a side effect of infertility treatment with hormonal drugs.
Pathological ovarian cysts are not associated with the menstrual cycle. They are always characterized by the appearance of “wrong” cells that should not be present normally. The most common types of pathological cysts:
- Endometrioid . This is a form of endometriosis, a condition in which endometrial tissue (the lining of the uterus) gets into unusual places and grows there. In the ovaries, it can form cavities with fluid. They often appear as “chocolate” cysts filled with dark blood.
- Dermoid cysts , or teratomas , are a special type of benign tumors made from embryonic cells. There may be different tissues inside them, for example, skin, hair, nails. Dermoid cysts become malignant very rarely.
- Cystadenomas are benign neoplasms of epithelial cells. Usually they are filled with contents of a mucous or watery nature.
For more information about malignant cysts, please visit the ovarian cancer page on our website.
When to plan a pregnancy after laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is often prescribed as a diagnostic and therapeutic method for diseases that are accompanied by infertility (endometriosis, fibroids, adhesions, ovarian cysts, polycystic ovary syndrome, reconstruction of the fallopian tubes, etc.). If the operation was successful, you can plan a pregnancy a few months after the operation.
Due to the fact that not only surgery is used to treat infertility, but also conservative therapy, which involves taking medications that affect female reproductive function, pregnancy planning should be discussed with the attending physician who has studied the patient’s medical history.
Successful pregnancy depends on what factors caused infertility before treatment, as well as on how effective the treatment was.
laparoscopy