The level of hemoglobin in the blood is one of the most important indicators of health, on which the saturation of the body’s cells with oxygen, necessary for metabolic processes, depends. When hemoglobin decreases, weakness, loss of strength, regular headaches and dizziness occur, so it is very important to monitor its level at home.
The importance of determining hemoglobin levels
Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein found in red blood cells. It performs an extremely important function, ensuring the delivery of oxygen entering the blood to the tissues and cells of the internal organs.
When hemoglobin levels drop rapidly, cells do not receive enough oxygen, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire body.
The protein compound captures oxygen in the lung tissues and transports it to the body’s cells, ensuring their full functioning. Hemoglobin also captures and removes carbon dioxide from the body, which is a waste product.

Carbon dioxide accumulates in tissues, which leads to a deterioration in overall health and the development of such unpleasant symptoms as severe headaches, weakness, loss of strength, and pale skin. It is very important to promptly detect a decrease in hemoglobin and begin treatment. In its absence, complications such as a weakened immune system, tissue hypoxia, chronic insomnia, and heart failure may develop.
When choosing treatments for Covid, it is necessary to focus on the severity of the disease and the clinical situation. A well-designed therapeutic regimen can not only significantly speed up recovery, but also avoid the negative consequences of a dangerous infection. Read more in the article: “Covid treatment at home: drugs.”
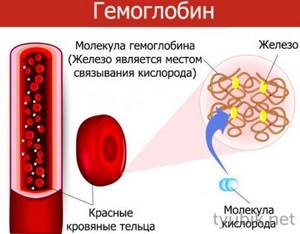
Hemoglobin test
- supply oxygen to body tissues;
- maintain acid-base balance;
- regulate metabolic rate.
Hemoglobin carries out gas exchange, supplying cells with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide from the lungs. Hemoglobin deficiency leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes, deterioration of brain and heart function, and weakened immunity.
Types of hemoglobin
Blood protein has 6 varieties, each with different properties and importance for human health. Among them:
- Oxyhemoglobin. The protein compound is bright scarlet in color. Responsible for binding oxygen molecules. It forms the basis of arterial blood cells.
- Glycated hemoglobin. A protein-carbohydrate compound that ensures the absorption of glucose. Serves as the main material for testing for diabetes mellitus.
- Carboxyhemoglobin. Associated with carbon molecules Regulates the excretion of carbon dioxide.
- Fetal hemoglobin. Present in the body of the intrauterine fetus and newborn child. As it grows, it turns into other types of hemoglobin. In adults it makes up 1% of the total blood protein. An increase in the level of fetal hemoglobin indicates the development of blood diseases or oncology.
- Methemoglobin. An abnormal type of hemoglobin that does not participate in gas exchange. An increase in methemoglobin volume causes oxygen starvation and death. Serves as a sign of intoxication of the body.
- Myoglobin. Protein related to hemoglobin. Part of the heart muscle and other muscle tissues. The gas exchange function is supported when oxygen levels drop.
During the analysis, each type of hemoglobin is examined. For a number of diseases, the volume of specific types of blood protein is measured.
Who is prescribed a hemoglobin test?
Chronic fatigue, decreased tone, and frequent headaches are good reasons to get tested. The study is also included in any preventive medical examination and medical examination. It helps to quickly identify disturbances in the functioning of the body.
It is recommended to check your hemoglobin level if sleep and appetite worsen, constant pallor, or vision or memory deterioration. In addition, doctors prescribe tests if the following diseases are suspected:
- diabetes;
- anemia;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- dystrophy.
Analysis is required before and after surgery, during pregnancy monitoring, and after large blood losses.
The study is carried out using a Sali hemometer, hemoglobin cyanide analysis or hemichrome method.
Hemoglobin norm depending on age
The normal level of iron-containing protein depends on several factors. It differs radically depending on the age and gender of a person. Before determining the amount of iron-containing protein in the blood, you need to familiarize yourself with the generally accepted reference values for this indicator.
- middle-aged men - 120-160 g/l;
- middle-aged women - 110-140 g/l;
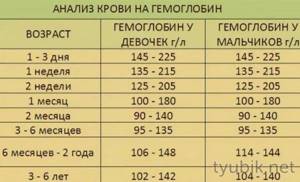
- children under 6 months - 140-220 g/l;
- children from 6 months to 18 years - 95-140 g/l.
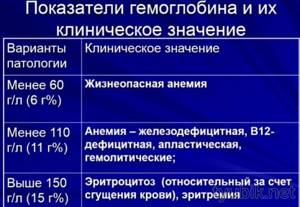
A decrease in hemoglobin levels below critical levels is called iron deficiency anemia and requires treatment. Correction of healthy protein levels can be carried out using medications containing iron or following a special diet.
To verify the reduced value, it is advisable to repeat the home measurement several times.
If all the results indicate a pathologically low level of hemoglobin, you should definitely consult a physician, since anemia can have dangerous consequences for the human body.
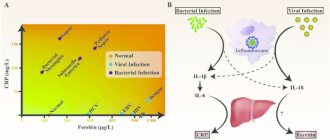
If a patient shows signs of an infectious-inflammatory process, it is necessary to find out the cause in a timely manner in order to begin treatment. Laboratory and instrumental tests are carried out to identify the pathogen and the state of the body. Read more in the article: “how to find out if there is an infection in the body.”
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin
Hemoglobin in the blood can decrease for various reasons. Among the main factors that can provoke a lack of iron-containing protein, doctors identify:
- unbalanced diet with insufficient amounts of foods containing iron;
- excessively heavy or prolonged periods;
- abortion, childbirth or surgery accompanied by significant blood loss;
- hemorrhoids with bleeding;

- following a strict diet or fasting;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- disruption of the absorption of iron in the intestinal cavity;
- lack of vitamin B12, necessary for the formation of hemoglobin in the body.
Common causes of iron deficiency anemia are diseases of the digestive system - chronic enteritis or atrophic gastritis, leukemia, benign or malignant neoplasms in the body.
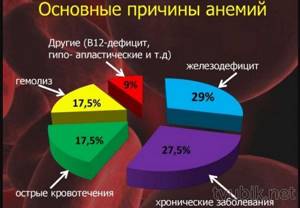
The causes of a rapid decrease in hemoglobin levels can also be autoimmune and long-term infectious diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, tuberculosis, pneumonia, hepatitis. Many factors can cause the development of anemia; the exact cause can only be determined after a medical examination.
Norms
The amount of hemoglobin is inextricably linked with the number of red blood cells, therefore, the norms of red blood cells are:
- for men 4.5-5.5*1012 / liter,
- for women – 3.7-4.6*1012/liter.
The amount of hemoglobin is:
- in men 125-145 g/l,
- in women 115-135 g/l.
There are also special indicators that reflect the hemoglobin content in the body, necessary for normal life - color indicator , that is, the degree of saturation of red blood cells with hemoglobin, it is normally 0.8-1.1 units. The degree of saturation of each red blood cell with hemoglobin is also determined - on average this is 28-32 picograms.
Hemoglobin in children
In adults, only the adult form of hemoglobin circulates in the blood. In fetuses and newborns, due to the characteristics of blood circulation, there is a special form of hemoglobin - fetal. After the birth of a child, it is quickly destroyed and replaced with normal, adult hemoglobin. Normally, fetal hemoglobin is allowed in the blood no more than 0.5-1%.
The average lifespan of an erythrocyte is about 120 days; if the viability of an erythrocyte decreases, this leads to the development of various anomalies in the form of hemolytic anemia.
Disturbances in the structure of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin, as a result of congenital or acquired abnormalities, may acquire irregular shapes or structure, which affects the ability of the red blood cell to carry oxygen. Violations such as:
- abnormal hemoglobins (about 300 forms are known, one of the most famous is hemoglobin in thalassemia),
- carbon monoxide poisoning produces carbohemoglobin, a stable compound that is unable to carry oxygen,
- When poisoned by many poisons, methemoglobin is formed, which is also unable to carry oxygen.
- When there is an excess of blood glucose in diabetes mellitus, glycated hemoglobin is formed, which is also unable to fully perform its functions.
There may also be quantitative violations:
- an increase in the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells during erythrocytosis and dehydration (blood thickening),
- decrease in hemoglobin in various types of anemia.
Determination of hemoglobin using the device
Today in the pharmacy chain you can find a wide selection of special devices designed to measure hemoglobin levels at home. Such a device is called a hemoglobinometer and is produced by several pharmacological companies.

Some of the most popular devices are MiniGem 540 and Easy Touch. Such hemoglobinometers allow you to determine protein levels in 10 seconds. Technique for performing home analysis:
- using a special needle from the set, pierce your finger;
- drop a few drops of blood into a test tube;
- add hydrochloric acid (included with the device);
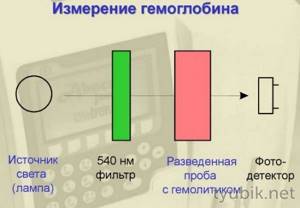
- pour distilled water into the device - the liquid should take on the scarlet hue of blood;
- evaluate the result obtained on a special scale and compare it with the presented age norms.
The results of the study will be reliable only if you properly prepare for the procedure yourself. To do this, you must avoid any food or drink for at least 12 hours, and also stop taking any medications.

Hemoglobin measurement with portable rapid tests
To measure hemoglobin levels at home, you can use simple and convenient test strips. Many manufacturers offer functional portable blood analyzers that measure not only iron protein levels, but also blood sugar and cholesterol. To do this you need to follow a few simple steps:
- wash your hands thoroughly;
- sit down and try to relax;
- Shake your hand for 2-3 seconds to activate blood circulation in your hand;
- lubricate your finger with alcohol;
- install the test strip with a connector specially designated for it - the device turns on in automatic mode;
- The device comes with a special pen with a needle, with which you need to puncture the treated finger;
- Apply a drop of blood from your finger to the control field of the strip.
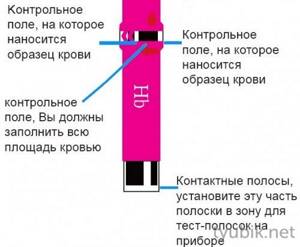
Within a few seconds, information about the level of hemoglobin in the blood will appear on the device monitor. Many such devices are equipped with an electronic memory function, which allows them to record the obtained analysis result.
Detecting anemia and assessing hemoglobin levels using a smartphone camera
Anemia - a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood - is a widespread pathology, affecting more than a quarter of the world's population. Anemia is a significant risk factor for morbidity and mortality, especially among vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and patients with chronic diseases. The gold standard for diagnosing anemia is a complete blood count, which requires venipuncture, specialist laboratory diagnostics, special equipment and chemical reagents. As is known, on physical examination, pallor of the conjunctiva can be a sign of severe anemia. However, the sensitivity of this subjective method is highly dependent on the experience of the clinician. The use of non-invasive methods to detect anemia opens the door to widespread screening, early diagnosis and treatment, especially in resource-poor countries where access to healthcare is limited.
Non-invasive assessment of hemoglobin concentration is quite possible due to its biochemical structure. Hemoglobin is a chromophore, which allows its level to be assessed using spectroscopic methods. This property has led to the development of various devices capable of measuring hemoglobin levels using transcutaneous, retinal and mucosal spectroscopy or photofixation. The conjunctiva of the eyelids is a mucocutaneous surface with a rich blood supply and a minimal amount of connective tissue. In addition to the absence of other chromophores such as bilirubin, melanin, and melanin, this anatomical region lacks epidermis and subcutaneous fat that could block the passage of light. This study is developing a non-invasive method for measuring hemoglobin concentration using digital images of the conjunctiva obtained using a smartphone. This procedure does not require specific skills; the user only needs high-quality photographic recording of the inside of the lower eyelid with a minimum amount of shadows, highlights and movements. Subsequent fast calculations in real time provide a numerical value for the hemoglobin concentration.
The purpose of this study was to develop a special algorithm for determining hemoglobin concentration using photographic recording of the conjunctiva of the eye on a smartphone.
Materials and methods. This randomized prospective study was conducted among patients in the emergency department of a university teaching hospital. As part of the phase 1 study, images of the conjunctiva of 142 patients were obtained using a smartphone to develop the algorithm. In each photograph, an area of high interest was selected, which was the conjunctiva of the lower eyelid. The parameters obtained from the images were further used in stepwise regression analysis to develop a model of estimated hemoglobin levels. As part of the 2nd phase of the study, the previously constructed model was tested on new 202 patients from the emergency department. The final model, based on data from all 344 patients, was tested for accuracy in determining thresholds for assessing the severity of anemia and the need for blood transfusion. Study participants' hemoglobin levels ranged from 4.7 to 19.6 g/dL (mean 12.5 g/dL).

Results. In the Phase 1 study, the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of algorithm-calculated hemoglobin levels for assessing anemia severity were 82.9 [79.3, 86.4], 90.7 [87.0, 94.4], and 73.3 [67.1, 79.5], respectively. . In phase 2, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity decreased to 72.6 [71.4, 73.8], 72.8 [71, 74.6], and 72.5 [70.8, 74.1], respectively. The accuracy for low (<7 g/dL) and high (<9 g/dL) cutoff values for determining the need for blood transfusion was 94.4 [93.7, 95] and 86 [85, 86.9], respectively.
Conclusion. The authors invented a method for estimating hemoglobin concentration using images of the conjunctiva obtained using a smartphone. The study results demonstrated that estimating hemoglobin levels using this method can be used as a screening tool for anemia and assessing thresholds for blood transfusion. In addition, image quality enhancements and computational corrections may improve hemoglobin level estimation. In the future, it is necessary to create a stand-alone application on a smartphone for both ordinary users and medical personnel.
Source
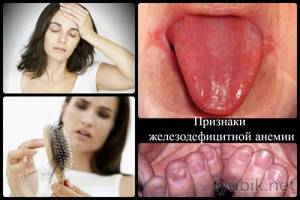
Main symptoms of iron deficiency anemia
You can determine a low hemoglobin level yourself, without special equipment. To do this, you need to pay attention to the characteristic signs that may indicate the development of iron deficiency anemia. The main manifestations of low hemoglobin:
- headaches accompanied by dizziness or fainting;
- noise in ears;
- pale or yellowing of the skin of the face and body;
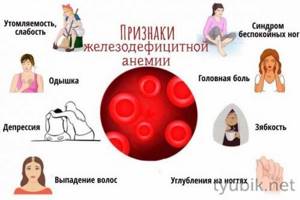
- lethargy, weakness, loss of strength;
- loss of appetite;
- muscle pain;
- decreased immunity and frequent colds;
- cold extremities;
- change in taste preferences - the desire to eat chalk, raw dough, eggshells.

Iron deficiency anemia is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, constant shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and heart rhythm disturbances. Also, a decrease in iron-containing protein in the blood leads to indigestion, changes in the color and consistency of stool. A lack of hemoglobin can also be detected by a person’s appearance. His skin becomes dry, acquires a jaundiced or pale tint, the conjunctiva of the eyes turns red, hair and nails become brittle, and their growth slows down.
Proper nutrition to increase hemoglobin
If your hemoglobin level is low, you should include as many iron-containing foods as possible in your diet.
| Healthy foods | Variety |
| Meat and offal | Beef, chicken, beef liver, tongue |
| Cereals | Buckwheat |
| Fish and seafood | Red fish, red caviar, shrimp, crabs, mussels, oysters, kelp |
| Eggs | Egg yolk |
| Fruits | Pomegranate, feijoa, plum, persimmon, apples, bananas, apricots, peaches |
| Berries | Cranberries, wild strawberries, raspberries, strawberries, blueberries, black currants, rose hips |
| Vegetables | Beets, carrots, beans, lentils, peas, pumpkin, tomatoes, potatoes, onions |
Various dried fruits can be an effective way to quickly increase hemoglobin at home. Raisins, apricots, and dried apricots contain a significantly higher concentration of iron than fresh fruits.

Increase in hemoglobin
Normally, the level of hemoglobin is increased in athletes and climbers, pilots and people who spend a long time in the fresh air. Mountain residents also have physiologically increased hemoglobin.
With pathology, hemoglobin increases:
- with erythrocytosis, pathological increase in the number of red blood cells in oncology,
- with pathological thickening of the blood due to dehydration and increased viscosity,
- for heart defects,
- for burns,
- with the development of pulmonary heart failure,
- with intestinal obstruction.
Consequences of low hemoglobin
Decreased immunity is a dangerous condition that cannot be ignored. It is accompanied by a serious deterioration in general well-being - a person is bothered by regular headaches, weakness, lethargy and loss of strength. In severe forms of iron deficiency anemia, severe dizziness and fainting may occur, attention disturbances, increased fatigue and muscle relaxation are often observed, which at an advanced stage can lead to urinary incontinence.
A decrease in hemoglobin below critical levels negatively affects not only a person’s well-being, but also his appearance.
As a result of lack of oxygen, skin, hair and nails dry out and become thinner, becoming dull and faded.
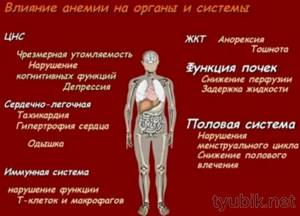
If iron-containing protein falls below normal, this negatively affects the immune system. As a result, a person is bothered by regular colds, as well as exacerbations of chronic diseases.
Decreased hemoglobin
A physiological decrease in hemoglobin can occur during pregnancy due to an increase in circulating blood volume and dilution of blood with plasma.
Typically, a pathological decrease in the amount of hemoglobin is called anemia. It may occur:
- due to acute blood loss during bleeding,
- as a result of chronic microbleeding and blood loss due to hemorrhoids, intestinal, uterine, and gingival bleeding.
- during plasma transfusion, infusion of large amounts of liquids,
- with increased destruction of red blood cells due to hemolysis,
- with deficiency of iron, folic acid, vitamin B12,
- in case of chronic pathology of the body,
- with damage to the bone marrow with inhibition of its functions.
About how to eat properly in order to increase hemoglobin - in our separate article.
A few words about the role of hemoglobin
The hemoglobin level plays a very important role in the full functioning of the human body. This iron-containing protein supplies oxygen to the cells and tissues of internal organs, ensuring their normal functioning.

You can increase your hemoglobin level if it decreases with the help of a proper, balanced diet. Additionally, you can take pharmaceutical iron supplements, which will be prescribed by your doctor based on the results of a blood test.
Protein functions
Hemoglobin contains two components:
- globin protein, which is the basis for hemoglobin,
- iron in the form of heme, attached to certain areas of the protein.
Only in this form is hemoglobin able to transport oxygen into tissues in the form of oxyhemoglobin, and remove carbon dioxide from them in the form of carboxyhemoglobin. These are colored pigments, oxyhemoglobin has a bright scarlet color, and carboxyhemoglobin is cherry. This is the reason for the difference in the color of arterial and venous blood; arterial blood is rich in oxygen, venous blood is rich in carbon dioxide.
The exchange of gases occurs continuously in the body; even the slightest disturbance in the respiratory system or gas exchange immediately leads to malfunctions in the functioning of the entire body and the development of hypoxia (lack of oxygen).
Hemoglobin is found inside erythrocytes (red blood cells), which are found in the blood in strictly defined quantities. As the number of red blood cells decreases, the amount of hemoglobin in them naturally decreases.
The bone marrow, where they are formed, as well as the spleen and liver, where old red blood cells are destroyed and the hemoglobin from them is utilized, are responsible for maintaining a stable number of red blood cells in the human body.