ATTENTION! Starting from October 2021, a new medical center will open for you at the address: Dmitrovskoye Shosse, 81 (5 min. walk from the Selegerskaya metro station), where you can receive a wide range of medical services, including CT (computer tomography).
- home
- Ultrasound
- Ultrasound of the chest
The medical doctor suggests undergoing an ultrasound examination of the chest and pleural cavity. The examination is carried out by qualified specialists using modern equipment at reasonable prices. We are within walking distance from the Bibirevo, Altufyevo, Medvedkovo metro stations.
Ultrasound of the chest organs is an ultrasound method for examining the pleural cavity, during which the condition of the tissues of the internal organs located in the thoracic region is assessed and pathological changes are identified.
How is a chest ultrasound done?
At KDS-Clinic, ultrasound diagnostics of the chest is performed by abdominal scanning. The patient will lie with his or her back on the couch and may need to sit or stand, depending on the area being examined. The ultrasound sensor is located in the subcostal space or parallel to the ribs.
During an ultrasound, sometimes the patient will need to hold their breath or take a deep breath, at the request of the doctor. This allows the device to increase the visibility of the peripheral parts of the lungs. At the end of the procedure, which lasts 15-20 minutes, the diagnostician issues the test result.
What equipment do we use to perform 3D ultrasound of the breast?
Breast cancer is aggressive. Even before it has time to settle in the breast tissue, the primary tumor can already send so-called wandering cells into the bloodstream, which will “wake up” and start the creation of secondary foci even after the destruction of the primary tumor.
Prevention and early diagnosis of breast cancer is one of the priorities of the Hadassah Medical Research Center. That's why we purchased the latest Siemens ACUSON S2000 ABVS ultrasound system with Automated Breast Volume Scanning capability.
ACUSON S2000 with ABVS module is a premium system for mammological examinations. It allows you to quickly and accurately acquire, analyze and document ultrasound volumetric (three-dimensional) data in an automated mode, and, if necessary, switches to manual ultrasound mode with expert characteristics.
The device received a bronze IDEA award (International Design Excellence Awards) in the “Medical and Scientific Objects” category. Clement Bommel and the famous international studio Frog Design, which has been involved in industrial design since 1969, worked on the ergonomics, functionality and design of the system commissioned by Siemens Medical.
In Moscow there are only 3 systems for 3D breast ultrasound and only 2 Siemens ACUSON S2000 ABVS devices - one of which is installed in our clinic.
When is the examination scheduled?
An ultrasound of the chest organs will be required if alarming symptoms appear:
- Labored breathing;
- Sudden production of sputum, without cold symptoms;
- Chest injuries;
- Pain and discomfort in the chest area at rest and when changing body position;
- Suspicions of cancer;
- The presence of foreign bodies in the lungs;
- Exclusion of focal pneumonia, etc.
If you experience any discomfort in the chest area, it is recommended to immediately seek qualified help.
Doctors' opinions on three-dimensional ultrasound of the breast
Olga Puchkova, mammologist, expert of the breast cancer screening program in Moscow and the Northwestern Federal District
The quality of breast ultrasound consists of several components. The class of the device is important - not all systems allow you to see formations of minimal sizes. The qualifications of the doctor are extremely important - he must have experience in diagnosing breast diseases in order to achieve maximum information content of the study. However, the expert level of the device and the doctor nevertheless does not solve the problem with the reproducibility of ultrasound research: no one other than the specialist performing the ultrasound will be able to see its data (as, for example, with mammography or MRI).
In the case of 3D ultrasound, absolutely all data coming from an expert-level device is stored on a special workstation. They are processed by an intelligent system, they are studied by the mammologist conducting the study ─ and they can also be reproduced in full at any time and reviewed again by the attending physician or any other specialist.
According to various international studies, the use of 3D ultrasound in patients with a dense x-ray background makes it possible to detect 30% more breast cancer. I believe that all women with dense x-ray background should be recommended to undergo three-dimensional automated ultrasound examination of the mammary glands.
Valery Khovrin, MD, PhD, Head of the Radiation Diagnostics Department, Hadassah Medical
A breakthrough in non-invasive diagnosis of breast diseases - this is how I would characterize the new method of volumetric ultrasound examination.
The ABVS (breast volumetric scanning) system based on the expert ultrasound device Acuson 2000 allows you to perform an ultrasound examination to the required tissue depth in an absolutely comfortable position for the patient with a three-dimensional reconstruction of the obtained ultrasound data. The high-performance workstation helps the physician identify and detect even the smallest changes in tissue structure and precisely coordinate the steps of the diagnostic process.
What does ultrasound reveal and what diseases does it diagnose?
When going for a chest ultrasound, you should know what the diagnostics shows and reveals. During the examination, the doctor examines the location of organs, their structure and size. The technique allows you to thoroughly scan the bone skeleton, intercostal area, soft tissues of organs, pleura and air lung tissues, among others.
During an ultrasound scan, the functionality and condition of internal organs and blood vessels are assessed, the presence or absence of tumor processes, foreign objects, fluids inside the pleura, as well as the dynamics of the heart muscle are determined.
During the examination, the diagnostician can identify the development of diseases and abnormalities such as:
- Hematomas;
- Infiltrate;
- Lipoma;
- Tumors of various etiologies;
- Metastases;
- Heart disorders;
- Fluid in the lungs and stuff.
Based on the examination results, an accurate diagnosis will be established and the correct treatment will be prescribed. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostics, for example, puncture of tissue affected by the tumor.
At KDS-Clinic you can do a full examination of the chest organs near Bibirevo, Altufyevo, Medvedkovo metro stations. We offer innovative methods of diagnostic therapy, modern equipment, as well as qualified specialists.
You can find out the exact prices for ultrasound of the chest organs, as well as make an appointment by calling the contact phone numbers at any convenient time.
Why does every second woman over 40 need not only a mammogram, but also an ultrasound of the breast?
There is a concept of x-ray structure density ─ this is an individual for each patient ratio of the three types of tissues that form the gland on an x-ray image: fatty, glandular and fibrous.
At the age of up to 35 years, glandular tissue predominates in the structure of the mammary gland. On mammography it looks like cotton ─ white. The radiologist classifies all white areas of the image as dense. The tumor is also dense, which means it is also white. Some tumors, due to their structural features, are visible on mammography even against the background of pronounced glandular tissue, but in most such cases at a young age, tumors can only be seen on other types of studies - ultrasound and MRI.
After 35 years, the proportion of adipose tissue in the mammary gland begins to increase, a natural physiological process that ends around 55 years. WHO believes that the average 40-year-old woman already has a high enough proportion of adipose tissue for mammography to be informative.
However, mammography is not informative enough in all cases where, due to the individual characteristics of the patient, the replacement of glandular and fibrous tissue with adipose tissue is slower than the statistical norm or does not occur at all.
In addition to mammography, women of all ages with a dense X-ray background should be prescribed breast ultrasound. This is a mandatory part of the preventive protocol.
How can you tell if you have a dense x-ray background?
It’s quite simple: ask the doctor describing the mammography, or independently find in the study protocol the letters ACR, next to which will be indicated either the numbers from 1 to 4, or the letters A, B, C or D, or the percentage value: “up to 25%” , “up to 50%”, “up to 75%” or “more than 75%”.
The numbers 3, 4 or the letters C, D are an indication of a dense x-ray background. If the protocol indicates percentages, then the values “up to 75%” or “more than 75%” also indicate a dense x-ray background. If these marks appear on your mammogram, then you are advised to have a breast ultrasound in addition to your mammogram.
How is an ultrasound performed?
Ultrasound examination is a procedure well known to many. It is necessary to free the part of the body where the problem occurred from clothing and sit on the couch. The patient lies or sits while the doctor moves the device's sensor over a thin layer of a special gel.
The image on the screen in real time shows the structure of the internal tissues and the progress of manipulations (during a biopsy). All sizes, anatomical features of tissues, organs and detected pathologies are immediately recorded, and photos can be saved. The process will take no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient can get dressed and receive a conclusion. Based on the findings of this and other examinations, the attending physician can make or clarify the diagnosis.
Preparing for a chest MRI
Native magnetic resonance imaging does not require specific preparation. If contrast is required, you should have a light snack 45 minutes before the scan.
At the Magnit diagnostic clinic, the procedure is carried out by appointment. The patient should arrive 5-10 minutes earlier than the appointed time in order to fill out the documents without haste.
Preparation involves consultation with a radiologist. The doctor asks questions regarding the purpose of the study and whether the patient has any contraindications. If none are identified, the person is taken to the locker room. Here he must remove jewelry (hairpins, glasses, rings, earrings, chains, piercings), clothes with metal inserts or fittings, and leave electronic devices (phone, watch, player, etc.).
Anxious patients may experience fear or discomfort during the test or feel unwell after the procedure is completed. To avoid unpleasant phenomena, they practice the use of sedatives before the study, but only on the recommendation and prescription of a doctor. The patient should inform the radiologist about anxiety in advance.
Ultrasound diagnosis of rib fractures (clinical observations)
Ultrasound scanner WS80
An ideal tool for prenatal research.
Unique image quality and a full range of diagnostic programs for an expert assessment of a woman’s health.
Introduction
In modern society there is a high level of injuries, and the number of injuries is not decreasing. Most injuries are easily diagnosed both clinically and with the help of x-ray examination, but some - minor injuries, non-displaced rib fractures in the inferolateral parts of the chest - are much more difficult to diagnose. Primarily due to the abdominal organs, which “layer” on the lower ribs. It is difficult to diagnose such fractures radiologically and the doctor often diagnoses “chest contusion” instead of a rib fracture, which is not confirmed by instrumental research methods [1-3].
However, unrecognized fractures of the lower thoracic ribs cause a lot of discomfort and pain for patients who want to know the clear origin of the pain and make sure that they have “nothing serious.” Of course, all this can lead to conflict situations and misunderstandings between the doctor and the patient. The article presents the author's own observations, confirming the need for ultrasound in patients with chest trauma.
Material and methods
Over 11 months of 2015, 5 patients independently applied to the clinic’s ultrasound room with complaints of incessant pain in the inferolateral parts of the chest after injuries. The time elapsed since the injury ranged from 5 to 14 days. Three of them were undergoing outpatient treatment, were examined by a surgeon and listened to by auscultation; an X-ray examination of the chest revealed no rib fractures; urine tests showed no pathology. One of the patients suffered from epilepsy; pain in the lower parts of the chest appeared after another attack, during which he was injured. All patients were bothered by incessant pain in the lower lateral parts of the chest, intensifying with deep inspiration, coughing, turning the body and changing body position. It was characteristic that patients clearly indicated the pain point on the surface of the chest.
Results and discussion
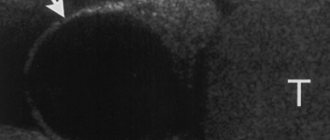
The study was carried out on SonoAce-8000, SonoAce-X8 and Accuvix-V10 devices (Medison company) with linear sensors 5-9 and 5-12 MHz in B-mode with the patient standing, without special preparation. The examination began with an examination of the pain point indicated by the patient, which is an undoubted advantage of the method, ensuring accuracy and a short examination time. In all cases, fractures of the VII, VIII or IX ribs of the chest were detected on both sides along the anterior, middle and posterior axillary lines. One of the patients had a fracture of two ribs (Fig. 1, 2). All fractures were incomplete and without displacement. In five cases, a fracture with a sharp end of a bone fragment was observed (Fig. 2-6), in one case, a double “fennel” fracture was observed in a patient with a fracture of two ribs (see Fig. 1). In three cases, local hemorrhage into the soft tissue was observed at the site of fractures (see Fig. 1, 2, 4), which was visualized as a small hypoechoic zone.
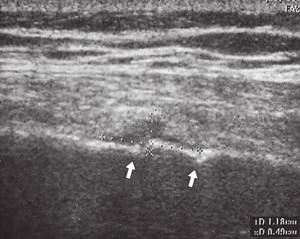
Rice. 1.
Double “fenestrated” fracture of the VII rib of the right half of the chest (indicated by arrows).
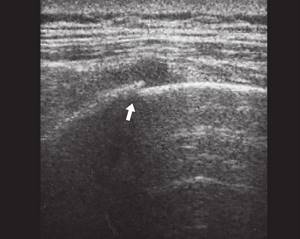
Rice. 2.
Oblique fracture of the VIII rib of the right half of the chest (indicated by an arrow).
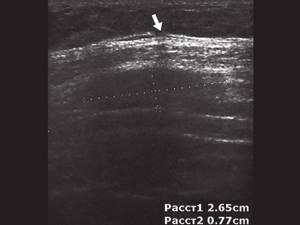
Rice. 3.
Oblique fracture of the ribs of the inferolateral sections of the chest (indicated by an arrow).
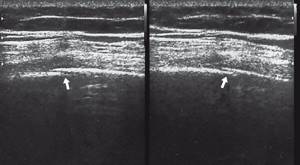
Rice. 4.
Oblique fracture of the ribs of the inferolateral sections of the chest (indicated by an arrow).
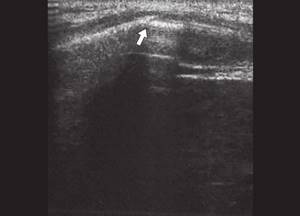
Rice. 5.
Oblique fracture of the ribs of the inferolateral sections of the chest (indicated by an arrow).
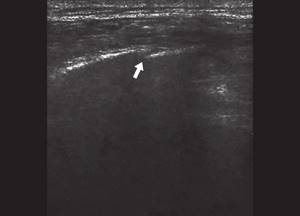
Rice. 6.
Oblique fracture of the ribs of the inferolateral sections of the chest (indicated by an arrow).
It should be recalled that we are talking about the diagnosis of small fractures without displacement of fragments, which caused pain in patients, but did not limit movement.
Conclusion
In conditions of large outpatient visits, the actions of surgeons and traumatologists, their methods of work and diagnosis are often standardized and the introduction of ultrasound into a doctor’s daily practice when diagnosing rib fractures is difficult, and more often, as the author of the article is convinced, causes bewilderment and wariness of doctors. Continued complaints in patients of pain in the lower parts of the chest after injury (with chest pathology not recognized by x-ray) should alert the doctor, and he must prescribe an ultrasound of the chest at the site of greatest pain to exclude bone pathology and correct diagnosis. I would especially like to emphasize that none of the five patients examined was referred for an ultrasound scan by a doctor. All patients consulted an ultrasound specialist independently. Ultrasound is available in almost all hospitals and is becoming routine in the examination of many organs, and the presented cases indicate that the possibilities of ultrasound have not yet been exhausted and it should be actively introduced into the work of ultrasound diagnostic doctors.
Literature
- Pasynkov D.V. Sonography in modern radiodiagnosis of bone fractures and control over their repair: Abstract of thesis. diss. ...cand. honey. Sci. M., 2005.
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of December 20, 2012 No. 1110N “On approval of the standard of primary health care for fractures of the rib (ribs) and sternum.”
- Klyushkina Yu.A., Klyushkin I.V., Gazizyanova R.M. Sonography in the diagnosis of “unrecognized” rib fractures // Bulletin of modern clinical medicine. 2014; T. 7, Appendix 2: 92-97.
Ultrasound scanner WS80
An ideal tool for prenatal research.
Unique image quality and a full range of diagnostic programs for an expert assessment of a woman’s health.
Indications for ultrasound
- A tumor-like neoplasm detected by palpation or mammography.
- Diagnosis of pathological conditions of the mammary gland.
- Pain, swelling or hyperemia in the breast area.
- Acute chest injury.
- Change in the shape of the nipple (retraction or thickening), discharge from the breast.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Selection of hormonal contraception.
- Assessment of gland function during pregnancy.
- Lactation monitoring.
- Pregnancy planning.
- Preventive examination of women under 45 years of age.
- Preparation for breast surgery.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
- Monitoring the condition of silicone implants.
- Preparation for the IVF protocol.
Indications
Ultrasound examination of soft tissues is prescribed when
- Injuries, severe bruises that led to hematomas, ruptures and tears of ligaments.
- Atheroma (a sebaceous gland cyst with an accumulation of secretion produced by the gland under the skin).
- Lipomas are benign tumors of subcutaneous fat.
- Chondromas are neoplasms of benign cartilage tissue.
- Cellulitis, abscesses - bacterial infection or purulent inflammation of subcutaneous tissues.
- Myositis, spasms and other muscle pathologies in different areas of the body.
- Hernia is a protrusion of an organ, a large blood vessel in the abdomen or groin.
- Fistulas and poorly healing scars after surgery.
Symptoms of these and other pathologies are:
- Noticeable or palpable mass formations under the skin (painful or not).
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
- Subcutaneous bleeding, bruises on the body.
- Pain in different parts of the body (usually arms and legs), deterioration of sensitivity due to impaired innervation due to pinching of nerve endings by muscles.
An ultrasound of soft tissues is also necessary to assess the development of the disease and the effectiveness of the treatment. Under ultrasound control, puncture (taking a tissue sample for biopsy) of neoplasms of unknown nature is also performed.
Ultrasound of soft tissues will show accumulations of fluid or pus, inflammation and other types of pathologies in the early stages.
How is it carried out?
All parts of the gland are subject to examination from the border with the soft tissues of the chest wall in front to the area near the nipple. To obtain accurate results, small high-frequency sensors of 5-7 MHz, 5-13 MHz with a field width of 5 * 5 cm and dynamic focusing (focal length - 0.5-2.5 cm) are used.
During the examination, the woman must be undressed to the waist. To avoid inconvenience, check in advance which gender of the doctor will perform the procedure. If you feel uncomfortable seeing a male doctor, Hemotest will suggest you undergo an ultrasound with another specialist or tell you in which department a female doctor can see the patient.