How do oxalate stones form? In the human body, calcium, among other important functions, performs astringent actions with oxalic acid salts. It prevents the introduction of oxalates into the body. When calcium appears at insufficient levels, and oxalic acid salts significantly exceed the norm, they bind and generate oxalate crystals. These crystals settle in the kidneys, where over time they turn into stones. Lack of calcium in the body leads to the formation of oxalate stones. The reasons for calcium deficiency can be completely different. Here are some of them:
Sedentary lifestyle. People who are engaged in sedentary office work are more prone to developing kidney stones. Such a sedentary sitting position often leads to disorganization of phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
Heredity. People whose close relatives have had or are suffering from urolithiasis and are deficient in calcium are much more likely to develop kidney stones.
Improper and unbalanced nutrition. Insufficient use of foods containing calcium and eating large amounts of meat can lead to stone disease.
The formation of oxalate stones may be preceded by a chronic infection of the genitourinary system. Due to infection, an increased percentage of proteins is present in the urine. So salt crystals settle on them and gradually grow to the size of stones. At the first suspicion, it is recommended to immediately consult a urologist.
General rules
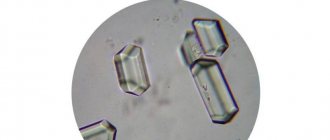
In the structure of deposited stones in ICD, oxalates ( calcium oxalate ) occupy a leading place.
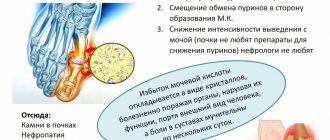
The main predisposing factor for the formation of calcium oxalate stones is hyperoxaluria , which refers to high urinary excretion (more than 40 mg per day) of oxalic acid . The oxalic acid anion combines with a calcium cation to form a soluble salt calcium oxalate , most often in the form of a monohydrate - wewellite (calcium oxalate monohydrate) and a dihydrate - weddelite (calcium oxalate dihydrate).
One of the reasons for the formation of oxalate stones in the kidneys is excessive intake of oxalates from food or increased intestinal permeability, which increases the penetration of oxalic acetic acid through the intestinal mucosa and its entry through the kidneys into the urine.
This is due to a deficiency of calcium, which binds oxalates in the intestines. High absorption of oxalates in the intestines is mainly associated with impaired fat digestion. Increased formation of oxalates can also be caused by the consumption of excessive amounts of ascorbic acid , including synthetic, which is metabolized in the body into oxalic acid , insufficient magnesium and vitamin B6 . In this regard, diet therapy predominates in the complex treatment of oxalate urolithiasis .
The hypooxalate diet aims to:
- exclusion/restriction of foods high in oxalic acid from the diet;
- normalization of oxalate metabolism;
- decreased synthesis of oxalates in the body;
- decreased absorption of oxalates in the intestine;
- active excretion of oxalates in the urine;
- elimination of vitamin B6 and magnesium deficiency.
The diet for oxalate kidney stones involves the complete exclusion from the diet of foods containing large quantities of oxalic acid - offal (kidneys, tongue, brains, liver), meat and fish broth, salted fish, sharp salted cheese, jellied meat, spinach, sorrel, chocolate , gelatin, rhubarb, tomatoes, celery.
As a guide to the amount of oxalic acid, 4 groups of products can be distinguished:
- large amounts (> 1 g/kg) - in spinach, parsley, cocoa beans, rhubarb, chocolate, sorrel, celery;
- moderate amount (0.3–1.0 g/kg) - in chicory, tea, carrots, green beans, beets, onions, tomatoes;
- a small amount (0.05–0.3 g/kg) - in apricots, fresh cabbage, Brussels sprouts, bananas, currants, potatoes.
Roasted Cauliflower
Cucumbers, eggplants, pumpkin, lettuce, mushrooms, cauliflower, and peas have a minimum amount of oxalic acid However, the content of oxalic acid in products is largely determined by the type of soil and the technology of their cultivation.
If a kidney stone is detected and an inflammatory process develops in the kidneys or urinary tract, the following are prohibited: spicy foods, seasonings, pickles, smoked meats, marinades, horseradish, mustard, vinegar, fish roe, onions, garlic, eggs (1 egg per day), alcoholic beverages .
In case of oxalates in the kidneys, to reduce absorption due to intestinal pathology, fat intake in the diet should be limited to 60 g and include foods with sufficient calcium content. It is also recommended to reduce the amount of carbohydrates in the daily diet to 300 g, since it is possible to synthesize oxalic acid in the intestines from carbohydrates under the influence of intestinal bacteria.
The amount of proteins is at the level of 100 g. At the same time, meat, poultry fish, and boiled sausages are consumed only in moderate quantities (up to 150 g/day), preferably boiled. It is also necessary to limit the consumption of milk, cottage cheese and cheese, but there is no need to completely abandon them. Preference should be given to fermented milk and low-fat dairy products and it is recommended to consume them in the first half of the day.
Since oxalates in KSD are often formed due to a lack of magnesium and vitamin B6, it is necessary to include foods rich in magnesium in the diet: wheat bran, oatmeal, buckwheat, pearl barley, wholemeal bread, dried apricots, oatmeal, peas, soybeans, seaweed, beans, radish. This can form magnesium oxalates , which, compared to calcium oxalates, are highly soluble in water.
Limit the consumption of foods high in vitamin C - gooseberries, currants, rose hips, cranberries, oranges, tangerines, rowan berries, strawberries, grapefruit, strawberries, lemon, wild garlic, sweet red peppers, dill, horseradish.
To prevent the precipitation of calcium oxalates and reduce the concentration of oxalic acid in the urine, it is necessary to ensure high diuresis (in the absence of contraindications) by increasing the consumption of free fluid - up to 3.0 liters per day and limiting the consumption of sodium chloride, which retains fluid in the body. At the same time, it is necessary to drink liquid not just in the form of water, but alternating with juices, fruit teas, compotes, decoctions (vegetable and fruit), since weak organic acids (malic, citric, lactic, benzoic, formic, fumaric) contained in these drinks dissolves oxalate stones.
Healing mineral water Essentuki No. 4
A diet for oxalate in the urine involves consuming drinks and foods that help change the pH of the urine. To alkalize urine, it is recommended to include in the volume of free liquid the mineral waters Naftusya , Truskavetskaya , Berezovskaya , Essentuki No. 4 and No. 20 , Luzhanskaya , Morshynskaya , as well as cucumber and other vegetable juices.
The presence of oxalate salts in the urine also occurs in children of different ages. At the same time, the appearance of oxalates in a child’s urine may also be a sign of the presence of another pathology, which will be discussed in the corresponding section below.
A few words about oxalaturia . Oxalaturia (oxalic acid diathesis) is, in fact, a harbinger of urolithiasis . Against this background, the threat of formation of “sand” or stones in the kidneys sharply increases. However, with oxalaturia there is no urgent need to follow a very strict dairy-vegetable (“alkaline”) diet. It is enough to exclude foods rich in oxalic acid from the diet, and also limit foods containing carbohydrates, table salt, strong broths, fried meat and fish. It is important to monitor the pH of urine, given that a pH in the range of 5.5–6.5 is optimal for the precipitation of oxalic acid salts.
There are no special requirements for culinary processing of products, but at the same time it is preferable to boil or stew the products.
What to eat to dissolve oxalate kidney stones
It is impossible to dissolve mineral stones with products. But proper nutrition restores the pH of urine, which prevents further stone formation. Therefore, the diet includes products with the following important components:
- pyridoxine – rice flour, oregano, mint, corn, millet, flax seeds;
- retinol – carrots, chicken eggs, fish oil, baked zucchini, apricots, dried apricots;
- magnesium – pine nuts, hazelnuts, rice, pearl barley, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds.
Pyridoxine and magnesium accelerate the excretion of ethanedioic acid. Due to this, the risk of stone formation in the renal pelvis is reduced.
When following a diet, special attention is paid to folk remedies. To restore metabolism, you need to use decoctions of the following herbs:
- Linden;
- peppermint;
- elderberry inflorescences;
- violet roots;
- bearberry;
- Birch buds;
- nettle.
Every day, between main meals, drink 150-250 ml of decoction. For oxalate stones, diuretic herbs are no less effective - juniper, bird knotweed, horsetail.
Decoctions of diuretic action are used only in the absence of concomitant diseases - ureteral obstruction, renal failure, obstructive urethritis.
Authorized Products
It is allowed to consume fish, meat and low-fat poultry in baked/boiled form in small quantities, wheat and rye bread made from second-grade flour, vegetable oil, porridge, almost all cereals (buckwheat, pearl barley, oatmeal, wheat), dairy products (sour cream , fermented milk products, butter (in the first half of the day).
Vegetables and fruits in the diet include cauliflower and white cabbage, boiled potatoes, eggplant and squash caviar, carrots, eggplants (in moderation), pumpkin, cucumbers, apricots, bananas, grapes, pears, prunes, apricots, cilantro, sour apples, watermelons, melon, peaches, dogwood, quince, rowan.
Drinks include juice from dried apricots, pears, prunes, birch, cucumber juice, compotes, jelly, slightly alkaline mineral waters.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 1% | 3,3 | 1,0 | 4,8 | 41 |
| kefir 1% | 2,8 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
| sour cream 10% (low-fat) | 3,0 | 10,0 | 2,9 | 115 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
Bird | ||||
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| boiled fish | 17,3 | 5,0 | 0,0 | 116 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot compote | 0,5 | 0,0 | 21,0 | 85 |
| Birch juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 5,8 | 24 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| dried apricot jelly | 0,4 | 0,0 | 12,9 | 54 |
| cucumber juice | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,5 | 14 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fully or partially limited products
The diet completely excludes foods rich in oxalic acid, such as strong tea, sorrel, spinach, offal (kidneys, tongue, brains, liver), fatty meats and fish, bread kvass, jelly, gelatin-containing dishes, cocoa, coffee, chocolate, rhubarb , mushrooms, pickled vegetables. During the period of exacerbation, the consumption of potatoes, beets, tomatoes, onions, and carrots is also limited. Salted cheeses, canned food, smoked meats, fish caviar, as well as soups prepared in strong broths (meat, fish and mushroom) and containing legumes, spinach, sorrel, and vegetable caviar are excluded.
The consumption of milk (up to 250-300 g per day), fermented milk products and lean meat (no more than 150 g / day), fatty sausages, pork, beef and cooking fat, and pasta is limited. The diet is limited to foods containing a lot of vitamin C - lemon, grapefruit, oranges, currants, rose hips, rowan berries, Antonov apples, strawberries, gooseberries, cranberries, tangerines, sweet peppers, horseradish, dill, wild garlic. The restriction also applies to sodium chloride (up to 3-4 g/day), pepper, spices, eggs (no more than 2 per day), sugar (no more than 30 grams).
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| rhubarb | 0,7 | 0,1 | 2,5 | 13 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| strawberries | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| cranberry | 0,5 | 0,0 | 6,8 | 26 |
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Rowan | 1,5 | 0,1 | 10,9 | 50 |
| currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 43 |
| rose hip | 1,6 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 51 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0,0 | 360 |
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| cod roe | 24,0 | 0,2 | 0,0 | 115 |
| pike caviar | 17,3 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 87 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| sturgeon | 16,4 | 10,9 | 0,0 | 163 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| sardine | 20,6 | 9,6 | — | 169 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| rendered beef fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Oxalic acid in products: what is prohibited
The diet for mineral stones excludes foods with ethanedioic acid. Therefore, pickles, marinades, smoked meats, rich broths, canned meat, and dried fish are removed from the menu. To avoid the formation of stones in the urinary system, limit fruits with vitamin C - gooseberries, all citrus fruits, sour apples. According to diet No. 5, reduce the consumption of table salt to 3 g/day.
What not to eat if you have calcium oxalate stones
| Product groups | Examples |
| fermented milk | suluguni, fat sour cream and cottage cheese |
| greens, vegetables | celery, salad pepper, horseradish, sauerkraut, spinach, radish, canned cucumbers, tomatoes, sorrel |
| fruits, berries | raspberries, lemons, grapefruits, pomegranate, currants, strawberries, tangerines, gooseberries |
| nuts, dried fruits | cashews, walnuts |
| confectionery | pastries, chocolates, cakes |
| sauces, oils and fats | ketchup, mustard, cooking oil, refined oil, margarine, mayonnaise, adjika |
| meat products | pork, dried meat, sausage, goose, sausages, smoked chicken, bacon |
| fish, seafood | red and black caviar, cod liver, canned fish, silver carp, sturgeon, salmon |
| beverages | alcohol, cocoa, strong tea, carbonated drinks, natural coffee, citrus juices, hot chocolate |
| other products | lard, offal, marmalade, corned beef, mushrooms |
To prevent stones in the renal pelvis, dishes with gelatin are removed from the diet.

Strong herbal teas disrupt phosphorus-calcium metabolism, so they are completely excluded.
If urolithiasis is diagnosed, it is undesirable to consume prohibited foods even outside of exacerbations. Neglect of diet is dangerous due to the deposition of stones in the urinary ducts, bladder, and urethral canal.
For children
Since the urinary system of children is physiologically immature, the kidneys, in some cases, are not yet able to fully maintain salts in dissolved form. First of all, a non-episodic increased content of oxalates in a child’s urine should be a serious reason for his in-depth examination and the exclusion of pathologies of the urinary system and diseases (intestinal infections, kidney diseases, endocrine diseases). However, most often, the presence of oxalates in a child’s urine is caused by an unbalanced diet with the consumption of foods rich in oxalic acid, insufficient fluid intake or intense sweating (during intense physical activity, hot weather). An acceptable norm is the occasional presence of calcium oxalate salts in the urine at the end.
The diet for oxaluria (diet for children) has some features that determine the nature of the diet and drinking regime. Despite the general approaches to permitted and prohibited foods, the hypooxalate diet should not simply copy the diet of adults, but take into account that the growing body of a child needs a sufficient supply of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins . Therefore, only products containing oxalic acid more than 50 mg/100 g should be excluded from the diet and products containing oxalic acid should be limited to 5 to 50 mg/100 g.
It is also unacceptable to deprive a child of dairy products - at this age the skeleton is actively developing and insufficient calcium in the diet can lead to negative consequences. It is important to monitor the amount of daily intake of vitamins , both with products - black currants, rose hips, Antonovka, radishes and others, and with medications, since the formation of oxalic acid in the body increases with its consumption of more than 150-200 m3 / day.
The child's drinking regime requires special attention. It is recommended to increase the daily volume by 50% of the required age volume. At the same time, it is especially important not to limit fluid intake before bedtime, but on the contrary, in the evening the amount of fluid you drink should be increased. It is recommended to drink slightly alkaline mineral waters, lingonberry or cranberry fruit drinks, cherry and pear leaf tea, and flax seed decoction before meals.
Sample menu for the week
A diet with oxalates in the kidneys has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the digestive system and prevents cardiovascular diseases. If you follow the doctor’s recommendations, your stool will normalize, your body weight will decrease, and your overall well-being will improve.

Failure to diet for stones in the urinary system leads to complications - renal colic, sluggish pyelonephritis, renal failure.
To increase the effectiveness of diet therapy, the menu includes a variety of dishes. This prevents vitamin and mineral deficiency, anemia and other undesirable effects. When following a diet, it is better to create a menu of healthy foods at least 4-7 days in advance.
Sample diet menu for oxaluria
| Days of the week | 1 breakfast | 2 breakfast | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Monday | muesli with milk, toast bread with butter, tea | carrot pancakes, tea | dietary soup, boiled beef, jelly | drinking yogurt | casserole with zucchini, carrots and hake, juice |
| Tuesday | egg white omelette, toast with jam, tea | baked pear with honey | cabbage soup without meat, boiled chicken, vegetables, compote | cottage cheese casserole, kefir | noodle soup, mashed fish cutlets, compote |
| Wednesday | oatmeal, drinking yogurt | 2 wedges of melon | baked pollock, broccoli soup, vegetable salad, herbal decoction | 100 g dates, kefir | diet soup, stewed cabbage, tea |
| Thursday | cottage cheese with dried apricots, compote | fruit salad, juice | soup with barley and potatoes, boiled veal, sliced vegetables, jelly | cucumber and carrot salad | chicken soufflé, vegetable stew, tea |
| Friday | cottage cheese with dried fruits, weak coffee | 100 g raisins, vegetable juice | lean borscht, vinaigrette, boiled fish, tea | oatmeal with dates | vinaigrette, carrot pancakes, tea |
| Saturday | muesli with milk, sweet apple | rye bread with jam, tea | noodle soup with meatballs, vegetable salad, herbal tea | 100 g raisins | cream soup with potatoes and broccoli, meat soufflé, tea |
| Sunday | buckwheat, toast bread with jam, drinking yoghurt | cottage cheese with dried apricots | vegetarian borscht, baked fish with boiled green beans, lingonberry juice | pumpkin casserole, compote | millet soup, cutlets, stewed cabbage, tea |

During periods of relapse of urolithiasis, it is better to abandon cereals and cereals in favor of boiled meat and vegetables.
Reviews and results
Reviews about dietary nutrition for urolithiasis vary significantly. Obviously, this is how it should be, since dietary nutrition in the presence of already large formed conglomerates of oxalate etiology is weakly effective. Conversely, with oxaluria, prescribing a diet can prevent the process of stone formation.
- “...I have had urolithiasis for 5 years now. I went on a diet periodically, but the stones did not decrease in size. And after frequent occurrence of colic, he underwent surgery”;
- “... When analyzing urine for an infectious disease, a high content of oxalic acid was found. They prescribed a diet. I ate with restrictions for almost 6 months. I had my urine tested again and everything returned to normal.”