Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis based on test results and prescribe appropriate treatment. Don't self-medicate!
Preventive medical examination of children necessarily includes a general urine test. Detection of salts in a child’s urine becomes a reason for further examination of the child by a pediatrician. There are many reasons for the accumulation of salts, and the result is the formation of urolithiasis.
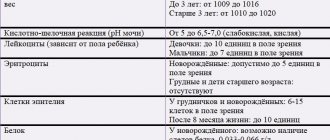
Table of daily indicators of protein and salt content in urine in infants and older children.
| Index | Normal for a child |
| Oxalates | 0.14-0.42 mmol |
| Uric acid | 1.2-5.9 mmol |
| Phosphorus | 13-42 mmol |
| Protein | Protein in the child’s urine is not detectable or there are only trace amounts |
A small amount of mucus is acceptable; it is usually associated with insufficient hygiene of the baby before collecting biomaterial.
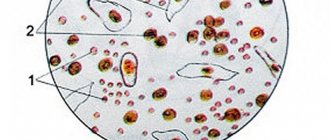
Types of salts in urine
There are three main types of salts that are found in the urine of children:
- oxalates, derivatives of oxalic acid - the most common type;
- urates, or derivatives of uric acid;
- phosphate salts, derivatives of phosphoric acid.
Calcium and hippuric salts are less commonly found.
Oxalates
The accumulation of oxalate salts in the urine of a child is associated with a violation of oxalic acid metabolism. The physiological reason is the excessive content of sorrel, rhubarb, spinach, and beets in the diet. Oxalates accumulate in diseases: pyelonephritis, diabetes, urolithiasis, poisoning.
Phosphates
The appearance of phosphate salts in the urine of a child is associated with a change in the urine reaction towards the alkaline side. The physiological reason is excessive consumption of sea fish, as well as long-term storage of biomaterial before examination. Diseases with accumulation of phosphates: cystitis, febrile conditions, increased function of the parathyroid glands.
Urats
The accumulation of urate salts in a child’s urine gives it a reddish color. Urates are formed when there is excess uric acid in the urine. The physiological reason is excessive consumption of meat, offal, and fish. Pathological causes of urate accumulation are dehydration, feverish conditions.
What symptoms of VUR can a child have?
In the early stages, the disease may be asymptomatic. The first signs appear in the absence of treatment or infection.
With congenital or acquired reflux at an early age, children are characterized by :
- sickly appearance;
- pale skin;
- reduced weight;
- level of development and growth that is not appropriate for age;
- pain in the lower back, stomach;
- restless behavior.
As the condition worsens, urinary retention develops and body temperature rises. These are signs that an infection has set in. In infants, signs of infection include lack of appetite, diarrhea, irritability, and fever. Source: N.A. Pekareva, E.Yu. Panteleeva, S.A. Loskutova Features of the course and diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux in children // Pediatrics. Journal named after G.N. Speransky, 2008, t.87, no.3, p.31-36
The older the child, the more severe the reflux , if there is no treatment:
- nocturnal enuresis;
- renal failure;
- protein in urine;
- high blood pressure.
Effective treatments
In order to prescribe treatment, the doctor needs to determine why there are a lot of minerals in the urine. Treatment consists of selecting a diet and medications based on the type of salt deposit.
Basic actions during treatment
Initially, the doctor determines whether the appearance of sediment is due to errors in nutrition. If this is the case, the pediatrician recommends that the mother properly baby. If the problem occurs in an infant, the mother's diet should be reconsidered.
Often the appearance of salts in a child’s urine depends on the diet of the mother or the child himself.
If the examination reveals a disease, medications are prescribed in addition to the diet.
Diet
The therapeutic diet directly depends on the type of sediment.
- Urats. You should limit your consumption of meat, fatty fish, and strong broths. Eliminate coffee and chocolate. It is useful to drink clean water, eat cereals, fruits and vegetables.
- Phosphates. You should limit your consumption of fish and dairy products.
- Oxalates. The consumption of beets, spinach, sorrel, and strong broths is limited. It is useful to drink clean water, eat seafood, vegetables, and cereals.
For any type of sediment, it is helpful to drink more clean water. It flushes mineral crystals from the kidneys and urinary tract and prevents their deposition.
Drug treatment
The selection of medications is carried out only by a doctor based on test results.
- If urates are detected, medications are prescribed to reduce the acidity of urine. Additionally, diuretics and herbal medicine are recommended.
- If oxalates are detected, vitamins are indicated - retinol, tocopherol, pyridoxine.
- Phosphate deficiency is treated with vitamin D.
The accumulation of salts in the urine is not a harmless condition. Deposited on the walls of the bladder and ureters, crystals scratch the mucous membrane and contribute to chronic inflammation. Subsequently, the sediment turns into stones, and the child develops urolithiasis.
Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor! Be healthy.
Causes of development of vesicoureteral reflux
PMR is usually divided into primary and secondary. The cause of the primary disease is a violation of the location of the ureteric orifice, a congenital valve defect that prevents the reverse flow of urine Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31692745 Oukhouya MA, Andaloussi S, Tazi M, Mahmoudi A, Khattala K, Bouabdallah Y Long-term evolution of vesicoureteral reflux in children // Pan Afr Med J. 2021 Aug 19;33:304. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2019.33.304.18966. eCollection 2021. Secondary VUR develops against the background of a neurogenic bladder, that is, a violation of its innervation, which causes a number of diseases of the urinary system, as well as due to infection.
Common causes of vesicoureteral reflux:
- Disturbance in the development of the urinary system.
- Increased urine pressure inside the bladder.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Previous operations on the excretory system.
Newborn urine
The urine of a newborn becomes cloudy on the 3rd - 4th day after birth, in particular on the days of greatest weight loss. A large amount of urate salts is excreted in the urine. This is the so-called infarction urine. Such urine is released as a result of the formation of uric acid infarction of the kidneys, which occurs in more than half of newborn children.
Macroscopically, the kidney (with a heart attack) on a section appears to be riddled with golden-yellow or brownish-red stripes; these stripes are located radially from the cortex at the apex of the papillae (in the region of the pyramids).
Microscopically, salts of ammonium urate, uric acid, sodium urate, and oxalate of lime are found in the collecting ducts and in the ducti papillari.
The formation of uric acid infarction is explained by the fact that the epithelium of the urinary tubules secretes hyaline, which forms hyaline casts, and in the hyaline casts the deposition of uric acid salts occurs. The latter is facilitated by thickening of the blood and a small amount of urine, which in the first days of life is very concentrated
Uric acid infarction occurs in completely healthy newborns; gradually, with an increase in the amount of liquid the child drinks and with an increase in the amount of urine excreted, the salts are washed out of the urinary tubules, and the heart attack goes away without a trace within about the first 2 weeks.
Uric acid infarction is easily diagnosed based on the characteristic intense reddish-brown color of the urine, leaving a characteristic sediment with the formation of reddish-brown spots on the diapers.
The amount of urine in newborns varies within extremely wide limits. The urine reaction, sharply acidic in the first days, subsequently becomes slightly acidic. The average specific gravity is 1008 - 1013; During the period of maximum weight loss, the specific gravity of urine increases and subsequently decreases to 1002 - 1004.
The actual acidity (AA) of urine in full-term newborns in the first days of life ranges from 5.4 to 5.9; in premature infants the actual acidity is higher. Subsequently, by the end of the neonatal period, AK is equal to 6.9 - 7.8 (with breastfeeding).
Protein (so-called acetic acid protein bodies) is often found in the urine of newborns; This is physiological albuminuria: fasting and insufficient fluid intake by the newborn increases its degree. The number of urinations per day in the first days of life is small - 4 - 5 times in the first 2 days. From the 3rd day the number of urinations increases and on the 8th - 12th day it reaches 20 - 25 per day.
The processes of comparative exicosis and dehydration that take place in the body of a newborn in the first days of life due to initial weight loss and insufficient supply of nutrients can lead to the appearance of formed elements in the urine, as well as sugar, acetone, indican, and glycuronic acid.
There are indications (E. Ya. Poyurovskaya) that the urine of newborns contains enzymes (pepsin, amylase) and that their content, falling during the first days, subsequently increases. There are also indications that the urine of newborns is toxic (L. L. Kocherovsky).
Dependence of temperature and weight on each other
If you place the weight curve and the temperature curve side by side (see the figure below), it turns out that they resemble open scissors, where the top of one jaw is the temperature, and the bottom point of the other is the weight (inverse relationships can be obtained when the weight is equalized and the temperature drops). The relationship between a drop in weight of a newborn and transient fever (own observation) In this case, the child ...
Newborn body temperature
Heat formation and thermoregulation in newborns differ in some features. The fetal temperature is higher than the mother's body temperature at the time of birth; its temperature, measured per rectum, is 0.1 - 0.6° higher than the mother's rectal temperature and amounts to 37.7 - 38.2°. When a child transitions to new environmental conditions with a lower temperature, his body temperature during the first 30 -...
Causes of weight loss
The magnitude of the initial weight loss is influenced by the following factors: The nature of the child's feeding: the timing of the first feeding (for children with signs of trauma to the central nervous system during childbirth, for whom the first feeding is often delayed); the state of lactation in the mother (lactation in multiparous women is better expressed than in primiparous women). Features of the birth act, in particular, the intensity of birth trauma in newborns, the duration of labor, the timeliness of birth...
Physiological weight loss in newborns
Starting from the first day of life, a newborn experiences a drop in weight, usually lasting until the 3rd or 4th day. This weight loss is due to certain physiological patterns characteristic of this age, which is why it is called physiological. The limit of physiological weight loss is from 1 to 7 - 8% of the initial weight. Weight loss greater than 10% should be prompted by your attending physician...
Swelling of the mammary glands
Most full-term newborns, both girls and boys, experience swelling of the mammary glands soon after birth; There is usually no redness of the skin. This swelling reaches its maximum by the 8th - 10th day, less often by the 5th - 7th day. A secretion resembling colostrum in composition is squeezed out of the enlarged glands. By the end of the first month of life, the swelling of the glands usually goes away, ...
Causes of diseases
Doctors have not identified a clear cause for the appearance of a pathological condition called nephropathy (functional and structural changes in the kidneys, which are formed on the basis of metabolic disorders, accompanied by crystalluria). Experts consider the pathology to be a hereditary disease that develops against the background of a genetic predisposition to diseases of the kidneys and excretory system.
The baby inherits metabolic features that contribute to increased absorption of salts in the intestines and various defects in the anatomical structure of the kidneys. A combination of negative factors leads to excessive excretion of salts in the urine.
The pathological condition is affected by:
- infections, severe toxicosis during pregnancy,
- poor quality of consumed water, unfavorable living conditions (polluted environment),
- consumption of foods rich in chemical elements.
Nephropathy in children can develop due to a lack of vitamins in the body, severe infectious diseases, or surgical interventions. Young patients have a high risk of developing urolithiasis, which should alert parents and begin treating their child at the beginning of the development of the pathological condition.
Rehabilitation and prevention of nephropathy in children
During inpatient treatment, upon discharge, the doctor prescribes various types of rehabilitation - exercise therapy, special gymnastics courses, drinking regimen and diet. But the recovery process will be monitored by a local doctor.
Prevention of dysmetabolic disorders includes strict adherence to the prescribed diet, provision of an increased drinking regime (especially in summer), courses of mineral waters (preferably in a specialized sanatorium), the use of a course of vitamins and metabolic therapy, active prevention of urinary tract infections and acute respiratory viral infections, which negatively affect on the course of nephropathy.
Anti-relapse (aimed at eliminating exacerbations, preventing complications) treatment should be carried out 2-3 times a year, and it is necessary to alternate courses of treatment with various drugs so that the body does not get used to them. Phytotherapy courses have proven themselves to be especially effective - taking herbal teas that have a diuretic, salt-removing and restorative, tonic effect. Active activities with the baby are recommended, providing him with a sufficient range of movements.
With proper nutrition and following the doctor’s recommendations, the risk of developing complications if a child has dysmetabolic nephropathy can be minimized, and in many children, metabolic disorders disappear completely with age. It is important to develop the habit of eating right from childhood and leading a certain lifestyle while suffering from this disease. And then, already in adulthood, the child will be able to avoid problems with the urinary system.
How are children with nephropathy monitored?
Children with all types of nephropathies are monitored in the clinic by a pediatrician and a nephrologist. Hospitalization in a hospital is required only in case of complications - pyelonephritis, urinary tract infection, stone formation, or in case of a detailed examination to determine the cause and clarify the diagnosis.
Children with dysmetabolic nephropathy, depending on the condition, are assigned health groups from IIb to IV. Such babies are examined by a pediatrician monthly during the first year of observation, then once every three months, and by a nephrologist - once every six months.
Children take the necessary tests and undergo examinations - urine analysis is monitored monthly. Moreover, it is desirable to determine the nature of the urinary sediment and the size of salt crystals. A Zimnitsky test is performed, which gives an idea of the concentrating ability of the kidneys, and an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is performed. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe an X-ray examination using contrast agents.
Sometimes the doctor asks parents to monitor urine pH at home with special test strips and record the results. These data make it possible to adjust the diet and dosage of medications.
Dispensary observation is carried out before the child is transferred to an adult clinic.
Advertising
Diagnosis of the disease in children
The diagnosis is made by a pediatric urologist. Usually, interviewing the patient and examining him is sufficient. Additional diagnostic methods allow you to determine the cause and severity of the pathology:
- Ultrasound of the bladder, urethra, and prostate makes it possible to determine the cause of the disease, detect adenoma, stricture, inflammatory edema, and tumors.
- Neurological examination, that is, consultation with a pediatric neurologist. It may be required if a neurogenic origin of VUR is suspected.
- X-ray with contrast and endoscopic techniques (cystoscopy). They help determine the cause of urinary retention - strictures, blood clots, stones. Source: V.A. Sharifullin New approaches to the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux in children. Literature review // Bulletin of the Russian Scientific Center of X-ray Radiology of the Ministry of Health of Russia, 2010
Norm and deviations of indicators
A general urine test informs the doctor about the presence of salts in urine with pluses (+) opposite the detected element in the urine. The specific amount of salts is indicated on a scale that includes four pluses. The presence of “,+” or “,++” marks opposite any type of salt is considered the norm if the situation was isolated. With the constant repetition of the presence of salts in the urine of a small patient, the physician begins to look for the cause of the pathology.
Learn about the symptoms of bladder cancer in women and the treatment of cancer.
Effective methods for treating postcoital cystitis in women are collected in this article.
For infants, the rules change: the presence of elevated salt levels obliges the doctor to find out the cause of this phenomenon. A baby's indicators may change due to the mother's consumption of certain foods (beans, mushrooms, chocolate). A common cause of such changes are kidney pathologies and inflammation of the bladder. The baby is sent for an ultrasound of the components of the excretory system to identify the cause of the increase in salts in the urine.
The formation of crystals occurs in the kidneys of a small patient, after a few minutes they enter the pelvis, then into the bladder, where they remain for up to six hours. If the residence time of the crystals exceeds the specified time frame, the crystals begin to accumulate, increasing in size. The pH of urine plays an important role in this process. Normally, urine should have a slightly acidic pH; any deviations from the norm lead to the development of pathological conditions.