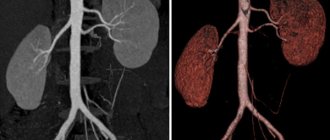
July 9, 2021 If, based on the patient’s complaints, the doctor suspects a urological disease, then he may prescribe urography. This is a type of x-ray examination, essentially an x-ray of the kidneys and urinary tract. Depending on the indications, one of the following types of research is used:
- Survey general urography. Safe and simple examination without the introduction of a contrast agent. Gives a general picture of the condition of the abdominal cavity, including the organs and bones located in it.
- Intravenous (excretory) urography of the kidneys using a contrast agent. It is administered intravenously, after which X-rays are also taken. The contrast agent moves through the urinary system and helps to better see individual structures.
Indications for use
Indications for urography are the following symptoms:
- the presence of blood impurities in the urine;
- pain in the lumbar region, in the projection of the kidneys;
- frequently occurring infectious and inflammatory processes in the urinary tract;
- suspicion of kidney cancer;
- diuresis disorders caused by urinary tract obstruction.
Urography is not painful and safe, so the method can be used to examine children.
An allergic reaction to iodine is an absolute contraindication for excretory urography. The procedure is contraindicated for severe diseases of the heart and blood vessels in the stage of decompensation, or heart disease. Also, the examination cannot be carried out in the presence of the following pathological conditions:
- liver and kidney failure;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- potential allergy to the administration of a contrast agent;
- severe pulmonary pathologies in the stage of decompensation;
- radiation sickness.
Urography is not performed on women expecting a child, since the fetus can be damaged by both exposure to radiation, even in small doses, and the administration of a contrast agent.
Diseases that excretory urography helps to diagnose
Excretory urography is used to diagnose diseases and pathologies such as:
- urolithiasis, especially if it is necessary to visualize stones in the ureter;
- kidney tumors and cysts;
- kidney development abnormalities;
- obstruction of the upper urinary tract (for example, compression of the ureter by other organs);
- kidney prolapse.
Objectives of the study
Excretory urography allows you to evaluate the efficiency of the kidneys, as well as the entire excretory system. The contrast solution, passing through the filtration system of the renal tubules, remains unchanged and is clearly visible on an x-ray. Based on where the contrast is located a certain time after administration, the excretory function of the kidneys is judged.
The purpose of the study is to identify the following pathologies:
- kidney stone disease;
- hydronephrosis;
- kidney injuries;
- tumor processes in the kidneys, both benign and malignant;
- diverticulosis, bladder deformities;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- congenital pathologies of the kidneys and excretory system organs.
What is CT urography?
CT urography is a test that uses a CT scan and a special contrast material or dye that a doctor injects into a vein. The contrast dye provides high-quality images that allow doctors to examine the urinary system and make a diagnosis.
A CT scan is a form of medical imaging that allows doctors to see images of the inside of the body without surgery.
A CT scanner is a short tunnel containing a rotating X-ray machine. The patient lies in the scanner and the outside of the scanner rotates and takes a series of X-rays from different angles.
The computer then combines these images so the doctor can visualize cross-sections, or 3-D images, of a specific area of the body. Unlike traditional X-rays, which show bones, these images also show details of soft tissue and blood vessels.
In general, during CT urography:
- The doctor will first do a non-contrast scan. This may show kidney stones and any serious structural abnormalities.
- He will then administer contrast and a second scan will show the soft tissue of the kidneys, bladder and adrenal glands in more detail.
- He will then perform a third scan in just a few minutes. This will show how contrast drains into the bladder, which will provide information about the collecting systems of the kidneys and bladder.
Is preparation necessary?
To obtain complete and reliable data on the functioning of the kidneys and excretory system, the patient must adhere to a diet and undergo a series of cleansing procedures. Preparation for the study using excretory urography begins several days in advance. The patient is given recommendations following which he should prepare for the examination.
The algorithm is as follows:
- for 3-4 days, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that contribute to the formation of intestinal gases (legumes, cabbage, fruits and vegetables, fresh bread), potentially allergenic foods (citrus fruits, chocolate, seafood), and also stop drinking alcohol;
- on the eve of the procedure, the dinner should be light, food should be eaten no later than 18 hours;
- on the evening before the examination, a cleansing enema is performed, after taking a laxative; if necessary, this procedure is repeated in the morning;
- the day before the examination, the patient should reduce fluid intake so that the urine is more concentrated;
- on the day of the examination you should not drink; if you are thirsty, you can take a small sip of clean water;
- It is better to abstain from breakfast before the procedure.
To exclude possible negative reactions to the administration of contrast, the patient is given a test before the procedure: a small amount of contrast agent is injected.
In some cases, a person needs urgent medical care, for better provision of which the results of intravenous urography are needed. When there is no time to prepare for the procedure, the patient is given a series of cleansing enemas.
It is quite difficult to properly prepare a small child under 4-5 months for urography, since children, due to their physiological characteristics, have a lot of intestinal gases. Therefore, this method of examination in young children does not always give reliable results.
Side effects of kidney urography
During the administration of contrast, the patient may experience nausea, a burning sensation in the vein and heat throughout the body, and dizziness. These are normal reactions of the body that go away on their own over time. Since a sensitivity test is performed before a full dose of contrast is administered, allergies develop in rare cases.
To speed up the process of removing the contrast agent and reduce the resulting radiation dose, you should consume more fluid on the first day after the procedure. Fruit juices and milk are best for this.
With proper preliminary examination, exclusion of contraindications and compliance with preparatory measures, urography allows you to identify possible disorders with maximum accuracy and select appropriate treatment.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 7345 Date of publication: 11/16/2017
Urologists - search service and appointment with urologists in Moscow
How is it carried out?
The procedure takes place in a specially equipped room where an X-ray machine is located. The patient is placed on the couch in a supine position. A contrast agent (as a rule, iodine-containing solutions are used) is injected into the vein in a stream and gradually, over several minutes. During this time, the doctor closely monitors the patient's condition. He evaluates his blood pressure, pulse and respiration rates, and the condition of his skin.
After the contrast is introduced, the first picture is taken after 5-7 minutes. Then another series of radiographs is taken, usually at 12-15 minutes and at 20-25 minutes. If the patient has a disease accompanied by a slowdown in excretory function, then images taken at 40-45 and 60 minutes are required.
If the patient strictly followed the doctor’s recommendations, and the technique of the procedure was not violated during the process, then urography takes place without complications. The dose of radiation received does not exceed permissible values, the contrast does not harm the body. Like other radiographic studies where the patient is exposed to radiation, such studies should not be performed more than 2-3 times a year.
X-ray with contrast agent
An X-ray of the kidneys with a contrast agent is performed when there is a pronounced symptomatic picture of certain diseases or confirmation of suspicions after previous examinations. The essence of the method, like the previous one, is the ability of x-ray waves to linger in denser structures. However, when X-raying the kidneys with a contrast agent, a drug that has X-ray contrast properties is specially injected into the bloodstream. Since the kidneys are continuously involved in filtering the blood, the administered drug ends up in the urinary tract over time, which makes it possible to assess the functional abilities of the kidneys, as well as the condition of the urinary organs and structures.
Advantages
The advantages of kidney urography using a contrast agent are its high informativeness and revealing nature. X-ray of the kidneys with contrast makes it possible to identify many diseases of the urinary system, assess the quality and intensity of kidney function, and accurately determine the localization of the pathological process. This will allow the specialist to choose the most rational treatment.
Side effects from contrast
In some cases, side effects of X-ray contrast agents may occur. The negative effects of water-soluble substances are associated with the chemotoxic effect of iodine and the phenomenon of osmotic toxicity. This phenomenon is characterized by an increase in osmotic pressure at the site of drug administration, which entails damage to the vascular endothelium and blood cells. There are several types of side effects from RHS:
- anaphylactoid (anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, etc.);
- local manifestation (phlebitis, soft tissue necrosis);
- toxic effects (nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, etc.).
It is worth noting that these adverse reactions occur extremely rarely, but the risk of their development still exists. That is why this study is carried out under the strict supervision of medical personnel who can provide emergency care.
Decoding the results
Interpretation of urography results is carried out by a urologist. Based on the study of the images, he gives a conclusion about the condition of the kidneys and other organs of the excretory system, in which he describes the identified deviations from the norm. Excretory urography shows:
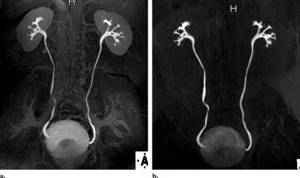
- anatomical position, structure of the kidneys;
- the condition of the renal collecting apparatus, its structure, shape;
- the condition of the ureters individually and in comparison, their sizes, anatomical position, deformations, the speed of movement of the contrast agent through them;
- condition of the bladder, its size, location, characteristics of the walls.
In Moscow, excretory urography is performed in various medical centers. You can find out how much the procedure will cost at your chosen clinic by phone. The price ranges from 4500-12500 rubles. The cost of the procedure is determined by the level of the medical institution and the qualifications of the specialist.
How to prepare for a kidney x-ray
To obtain reliable diagnostic results, radiography requires preliminary preparation, which consists of following dietary nutrition and a number of recommendations.
The diet before a kidney x-ray is followed for 2-3 days on the eve of the study. Foods that increase flatulence (butter and dairy products, brown bread, carbonated drinks, fresh fruit, cabbage, legumes, potatoes, etc.) should be excluded from the daily diet.
Some types of x-ray diagnostics are performed on an empty stomach. Patients who suffer from constipation and cannot empty their bowels naturally are prescribed laxatives. A cleansing enema may also be prescribed, which is performed in the evening and morning before the x-ray.
The last meal before the upcoming procedure should be no later than six o'clock in the evening. At the same time, food should be easily digestible and low-fat. On the day of the test, you should not drink anything except water. Immediately before the x-ray, the bladder is emptied.