Increased hemoglobin is a rather dangerous condition, which in 90% of cases indicates disruptions in the metabolic processes occurring in the body.
This may also mean that tissues and organs experience oxygen starvation, and increased hemoglobin is the body’s protective reaction to a decrease in the amount of micronutrients received.
In any case, according to research , it is possible, in most cases, to lower hemoglobin levels in men and women with the help of a specialized diet. What products best reduce it? And which ones, on the contrary, should not be consumed?
When should hemoglobin be reduced?
In most cases, an increase in hemoglobin levels in adults is complemented by an increase in blood viscosity due to impaired water-salt metabolism. And thick blood leads to an increased risk of blood clots and plaques, and coagulation also increases. All this can be supplemented:
- hypertension (increased blood pressure to a critical level);
- thrombosis (if the blood flow slows down to the point where the blood literally coagulates in some vessels);
- heart attack (if thrombosis affects the heart muscle or the blood vessels that supply it);
- stroke (if thrombosis affects the circulatory system of the brain);
- atherosclerosis (when cholesterol plaques form on the walls of blood vessels, thereby impeding normal blood flow).
At the same time, an increase in hemoglobin may indicate pathologies in metabolic processes when the body receives insufficient amounts of oxygen and other micronutrients.
In some cases, elevated hemoglobin is normal. This happens, for example, among residents of mountainous regions, where the oxygen content in the air is significantly lower.
Also, hemoglobin and red blood cells naturally increase in smokers, since they inhale fumes while smoking. It, in turn, creates inseparable compounds with hemoglobin, thereby deactivating the molecule. In these cases, the hemoglobin level should not be reduced, since the body will experience constant oxygen starvation.
Hemoglobin also often increases in the summer or during regular physical activity, when the body actively loses water and minerals (along with sweat). But normalizing hemoglobin concentration in this case is quite simple - you need to drink as much water as possible (in summer - from 3 liters or more).
Hidden iron deficiency - how to deal with it?
I feel bad, constant weakness. I took a blood test and the doctor said it was normal. Tell me what to do...
If you get tired quickly, often suffer from acute respiratory viral infections, if you are worried about hair loss, brittle nails, dry skin, if “everything hurts, nothing helps” - it’s time to rule out iron deficiency, says OKDC doctor-therapist Tatyana Abramova
There are more and more “iron deficient” people...
Today, iron deficiency is the most common pathology. According to some reports, more than 1.5 billion people on our planet have iron deficiency. Iron deficiency anemia itself is not a disease, but it can become a symptom of a serious pathology.
The biological role of iron in the body is great - it is involved in redox processes, tissue growth and aging, immunity mechanisms, hematopoiesis, oxygen supply to organs and tissues, and the functioning of a number of enzymes.
Lack of iron and subsequent tissue and hemic hypoxia lead to significant trophic changes in hair, thinning, increased hair loss and even early greying. Along with this, brittleness of the nails, their transverse striations, jagged edges of the nails, curvature of the nail plate, flattening or concavity of the nails up to spoon-shaped appear. In this case, urinary incontinence is often observed. A perversion of taste occurs in the form of an addiction to raw meat, dough, chalk, tooth powder, etc. Patients are attracted to the smells of mold, gasoline, kerosene or acetone.
Sometimes iron deficiency leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane of the tongue, angular stomatitis, glossitis, dental caries and muscle weakness. An increase in temperature to subfebrile levels can also be a manifestation of iron deficiency.
Everything hurts...
What could be the connection between iron deficiency anemia and back pain? Imagine not getting enough sleep for several nights in a row. The body then seems sluggish, disobedient, heavy, pain appears or intensifies in those places of the spine in which it was previously felt. People suffering from chronic iron deficiency anemia experience something similar. In addition to general weakness, malaise, brittle nails and hair loss, they may also experience persistent back pain. And some complain that “everything hurts.” To understand why this happens, remember that iron deficiency anemia is characterized by a low level of hemoglobin in the blood, which is a transporter for oxygen. A person with a low hemoglobin content can breathe the purest air in a pine forest, but oxygen in the required quantity will not enter the body’s cells, because there is not enough transport - hemoglobin. In turn, oxygen is an oxidizing agent, thanks to which metabolic processes occur in cells. Not enough - they accumulate under-oxidized metabolic products, essentially poison, poisoning the body and disrupting its functioning.
Hence the weakness and lethargy, as in case of poisoning, and increased muscle fatigue. And if we take into account that nervous tissue is most sensitive to hypoxia, then the strange at first glance complaint of patients that “everything hurts” also finds an explanation.
Patients go to a neurologist, gastroenterologist or cardiologist; they have disorders of the cardiovascular system, myocardial dystrophy; vegetative-vascular and vestibular disorders occur. People suffer from frequent colds and acute respiratory infections, problems with the digestive system and kidneys. They undergo treatment for a long time, follow the instructions of specialists, but find that the expected recovery and improvement in quality of life does not exist, or they are short-lived. And all this is only because they overlooked an important one - iron deficiency. In such cases, the therapist had to conduct all the necessary research and identify the true causes of the ailment.
And there can be a lot of reasons for iron deficiency, and they are very different:
- chronic blood loss of various locations: gastrointestinal (gastroesophageal reflux disease, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach, tumors of the stomach and colon, terminal ileitis, ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, bleeding hemorrhoids);
- menstrual blood loss (menorrhagia of various etiologies, fibroids, endometrosis);
- nasal (hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and other hemorrhagic diathesis);
- iron absorption disorders
- resection of the small intestine, stomach with exclusion of the duodenum;
- increased need for iron: pregnancy, lactation, intensive growth and puberty;
- impaired iron transport (hypoproteinemia of various origins);
- nutritional deficiency.
Hidden threat
The most unpleasant thing is that latent (hidden) iron deficiency is widespread among the population, when hemoglobin levels are still normal, but transport and organ reserves of iron are already depleted. This “disguised” deficit ranges from 19.5 to 30%. In addition, 50 to 86% of women in various populations have risk factors for anemia. Therefore, the Regional Consultative and Diagnostic Center has introduced the most modern methods for identifying hidden processes of changes in blood composition and early diagnosis of iron deficiency conditions.
Therapists from the OKDC will always help you to clarify the causes of the development of anemia and iron deficiency, select the right set of diagnostic laboratory tests, and understand the causes of the pathology.
share information
0
Social buttons for Joomla
General nutrition rules
With elevated hemoglobin, nutritionists recommend following the following tips and recommendations:
- Consume foods and dishes rich in calcium. This element reduces the bioavailability of iron. That is, it slows down its absorption. Namely, iron is the main component of hemoglobin and it is with its help that oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported to/from the lungs.
- Eliminate foods rich in vitamins B12 and B9 from your diet. This will also help reduce the bioavailability of iron and slow down the processes of generating new hemoglobin molecules.
- Eliminate iron-rich foods from your diet. These include apples, greens, beef, pork, meat by-products (liver, lungs, heart), fish. Preference should be given to porridge (with the exception of buckwheat), dairy products, and pasta. The diet for each patient must be prepared individually by a nutritionist.
If we are talking about infants, then breast milk helps them normalize hemoglobin. If artificial feeding (formulas) is used, then you should consult a pediatrician about this - he will recommend formulas that contain a minimum of iron and B vitamins.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
What should be excluded from the diet?
For greater effectiveness, when following a diet, be sure to exclude from the diet foods that cannot be eaten with increased hemoglobin:
- Fat meat. Particularly “dangerous” are beef, pork, as well as meat by-products (liver, lungs, heart, kidneys, and so on). Meat is rich in iron, as well as B-group vitamins (therefore, iron from such products is easily absorbed).
- Pomegranate and pomegranate juice. Pomegranate increases hemoglobin and blood pressure. For hypotension, it is extremely useful to include in the diet, but with increased blood viscosity, it should be completely excluded.
- Fatty fish. Rich in omega-3 acids, which accelerate most intercellular metabolic processes. Their use should be minimized. You can also include other seafood here, including oysters, shrimp, red and black sparkle, and seaweed.
- Chicken eggs. More precisely, it is the yolks (but the whites – slightly, but still reduce hemoglobin). It is also better to exclude quail from the diet.
- Spices. Turmeric especially strongly increases hemoglobin (it contains not only iron and herbs (parsley, dill, basil), but also B-group vitamins). It is better to temporarily stop using them altogether.
- Cherries and sweet cherries. These berries raise hemoglobin levels no worse than pomegranate and pomegranate juice.
Authorized Products
A diet for high hemoglobin includes the following in the diet:
- Dietary poultry (turkey, chicken) and rabbit, mainly boiled/baked.
- Vegetable soups with the addition of a small amount of cereals/vegetables.
- Vegetable oils (sesame, linseed, olive, mustard, rapeseed, nut) cold pressed.
- Rye bread and containing bran, flax seed, sesame.
- Fermented milk products with low fat content. Sour cream/cream may be added in small quantities to prepared dishes.
- Chicken eggs, hard-boiled/soft-boiled.
- Porridge (oatmeal, wheat, corn, pearl barley), cooked in water, brown rice.
- Vegetables/fruits containing little vitamin C (tomatoes, red peppers, cucumbers, grapes, cherries, raspberries, strawberries) and vegetables containing salicylates (beets, onions, garlic, gooseberries, cranberries, cherries, apples, prunes). Potatoes in skin and baked.
- Herbal teas (hazel leaves, licorice, sweet clover, hawthorn, sage), ginger tea, coffee, black/green tea, still water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| squash | 0,6 | 0,1 | 4,3 | 19 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| sesame | 19,4 | 48,7 | 12,2 | 565 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| Cherry juice | 0,7 | 0,0 | 10,2 | 47 |
| grapefruit juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 30 |
| strawberry juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,0 | 41 |
| cranberry juice | 0,4 | 0,3 | 11,0 | 46 |
| raspberry juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 24,7 | 100 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Other recommendations
Doctors with elevated hemoglobin also recommend:
- Minimize physical activity. This will help normalize the water-salt balance, reduce blood pressure and blood viscosity.
- Drink as much water as possible. And most importantly - without gas, since the carbon dioxide contained in such water slightly increases the bioavailability of iron (due to stimulation of the gastrointestinal mucosa).
- Refusal of multivitamin complexes. It is especially important to avoid taking B vitamins.
The best products that lower hemoglobin: TOP 3
The best foods that lower hemoglobin are:
- Dairy. You need to eat cottage cheese, kefir, yoghurts, preferably with a high fat content. Dairy products are high in calcium, which reduces the absorption of iron from other foods.
- Brown rice. It contains tannins that destroy iron molecules. Rice contains a lot of fiber, and it helps cleanse the intestines, speed up metabolism, that is, it reduces hemoglobin.
- Legumes. Beans, peas, and lentils contain some amount of iron. And also B vitamins that promote its absorption. But legumes also contain tannins that destroy iron. And if you eat porridge made from them with butter, the effect will be double.
What can you drink to reduce hemoglobin?

You can drink cow's milk, kefir, and yogurt to reduce hemoglobin. The same effect is exerted by some herbal preparations, the effect of which is to thin the blood. And rosehip, which also changes its viscosity, is used for low hemoglobin.
Rose hip
Rosehip is harmful for too high a hemoglobin volume, because it contains iron, and most importantly, ascorbic acid. A decoction of the fruit thins the blood. But at excessively high levels, it acts as a catalyst for iron absorption. And it is also found in berries.
Milk
Cow's milk contains:
- calcium, which makes it difficult to absorb iron from other foods;
- vitamin D, which slows down the formation of blood elements on which hemoglobin levels depend.
Therefore, it helps to normalize the amount of the latter.
Goat's milk is not suitable for this task, since it itself contains a lot of iron. There is also calcium and vitamin D. The balance of the components will not allow hemoglobin to rise, but will not drop it either.
You can drink milk, cook porridge with it, and eat products made from it:
- kefir, preferably with a fat content of 3% or more, it contains more calcium and vitamin D;
- natural yogurt, but without fruits and berries, but with cereals or without anything;
- cottage cheese, also fatty, contains more components that reduce the absorption of iron;
- cheeses, among which the percentage of calcium is higher in the varieties Parmesan, Emental, Gruyère, Edam, Dutch, Cheddar, Brie;
- sour cream, which is not inferior in the level of substances necessary for normalizing blood composition to cow's milk.
Butter contains less calcium than other foods. Therefore, it does not have a big effect on hemoglobin, especially when baked.
Herbs
Some herbs also help stabilize too high levels:
- Fireweed, woodlice, moth. They can be added to vegetable salads, but the herbs must be fresh.
- Chamomile, mistletoe, veronica. The collection is used to prepare an infusion. Herbs are taken in equal quantities, measure 1 tbsp. l., pour in 250 ml of water and heat until boiling. Then the liquid is removed from the heat and kept covered for 30 minutes. After straining and cooling to a comfortable temperature, you can drink it. The infusion is taken after meals, the course should be 2 weeks.
What is hemoglobin and its role in the children's body
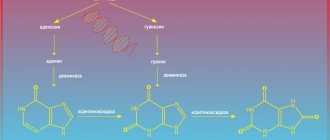
Hemoglobin is a complex protein containing a divalent iron atom. It is found in red blood cells (erythrocytes), which are shaped like a biconcave disc. Iron itself, in addition to hemoglobin, is present in myoglobin, which is deposited in muscle cells. At the same time, in children the level of hemoglobin is higher, and the amount of myoglobin is lower than in adults. As you grow older, its level gradually approaches adult levels.
In infants up to 4-6 months, there is additional fetal hemoglobin HbF, which gradually gives way to the usual form of HbA.
The main function of hemoglobin is to carry out gas exchange. Due to the iron atom, it is able to bind oxygen entering the blood from the lungs, forming the so-called oxyhemoglobin. Together with the blood flow, it spreads throughout the body, delivering oxygen to all tissues and organs. By giving it away, in return it attaches molecules of carbon dioxide, transforming into carbohemoglobin. Then, again entering the lungs with the bloodstream, it gives it away, making room for oxygen. Thus, hemoglobin plays a very direct role in cellular respiration, supporting the vital activity and normal functioning of all cells of the human body.
Hemoglobin is able to bind with carbon monoxide, turning into carboxyhemoglobin, as well as with other toxic substances. This negatively affects the functioning of the body, since the cells do not receive enough oxygen, and can cause death.
In addition, it is involved in cell division, the correct course of a number of redox processes, as well as DNA synthesis. Therefore, a decrease in hemoglobin, especially for children, poses a serious danger and can lead to very undesirable consequences. In such cases, anemia is diagnosed. Depending on the level of hemoglobin, there are 3 degrees:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
But since children of different ages have their own norms for hemoglobin content in the blood, we can only talk about the presence of anemia when comparing actual indicators with normal ones.
Who should not consume milk
Among people there are those for whom drinking milk is contraindicated for a number of reasons. A common cause is lactose intolerance, or rather lactose intolerance. It is transmitted genetically and is characterized by the inability to digest lactose, which is rich in all dairy products. There are allergies to proteins contained inside - determined by measuring IgE antibodies.
Attention! With goat's milk things are a little different. People become intolerant to this drink not at the chemical level, but rather due to the specific smell and taste.
The sweetness of the drink is influenced by the herbs that the animal eats, and the taste is influenced by the care taken in caring for the camp and the herd. Doctors prohibit those with thick blood from drinking goat milk, because its consumption increases the presence of coloring proteins in the blood.
Possible consequences
Anemia should not be perceived as a harmless condition that will go away on its own, especially if it occurs in a child. Indeed, with a reduced amount of hemoglobin, the quality of cellular respiration decreases. As a result, all organs and the brain in particular constantly experience a lack of oxygen.
Therefore, in addition to deterioration of the child’s general condition, this can lead to:
- delayed intellectual development;
- decreased immunity, which will be manifested by an increased incidence of acute respiratory infections and other infectious diseases;
- decreased memory, attention and other disorders of the nervous system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The most severe complication of low hemoglobin in children is hypoxic coma. Today this is rare, but not impossible.

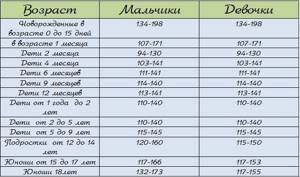
Hemoglobin - what is the norm for a child
Each blood indicator has a norm, including hemoglobin. The World Health Organization gives the following hemoglobin standards for children:
- newborns up to 2 weeks of life - not lower than 150 g/l;
- children from 2 to 4 weeks of life - 120 g/l and above;
- children aged 6 to 59 months - 110-140 g/l;
- children aged 5 to 11 years - 115-140 g/l;
- children aged 12 to 14 years - 120-150 g/l;
- children and adults over 15 years old - 130-160 g/l.
Anything below is considered mild (below normal, but above 90 g/l), moderate (70-90 g/l) or severe (below 70 g/l) anemia. Each of the three degrees of severity has its own symptoms and treatment tactics.
How does low hemoglobin manifest?
Signs of low hemoglobin levels manifest themselves in different ways. They can be divided into groups of symptoms: asthenic, epithelial, cardiovascular, muscular and secondary immunodeficiency syndrome.
Asthenic symptoms are manifested by increased fatigue, irritability, emotional instability, lethargy, and absent-mindedness. Children sleep poorly, eat little or do not want to eat at all. Children may complain of tinnitus, dizziness and headaches.
Epithelial symptoms: children have a pale face, areas of the legs and nails, pale ears and oral mucosa. The skin is dry and often flakes. Hair becomes brittle and may fall out. “Sticks” appear in the corners of the mouth. The child may complain of a burning tongue and dry mouth, difficulty swallowing and nausea.
Cardiovascular symptoms: increased heart rate, rarely shortness of breath. Sometimes the child complains of pain in the heart area.
Muscle symptoms: muscles weaken, the child quickly gets tired of simple activities, and may involuntarily defecate day and night due to weakness of the sphincter muscle.
Secondary immunodeficiency syndrome is manifested by the fact that the child often suffers from colds. He often experiences otitis media, pneumonia and intestinal infections. Rare symptoms of low hemoglobin levels are an increase in body temperature to 38 0C, red-tinged urine, swelling on the face.