Most people become interested in leptin when they are diagnosed with chronic inflammation or an autoimmune disease. What is leptin and how does it affect health? The article has a lot of useful information about leptin.
The article is based on the findings of 75 scientific studies
The article quotes authors such as:
- Center National de la Recherche Scientifique, Lille, France
- Department of Neurosurgery and Physiology, University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine, USA
- Department of Internal Medicine and Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Michigan, USA
Please note that the letters in brackets (1, 2, 3, etc.) are clickable links to peer-reviewed scientific studies. You can follow these links and read the original source of information for the article.
Detailed description of the study
Obesity is one of the main risk factors for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Adipose tissue secretes a number of active molecules - adipocytokines, which affect food intake and metabolic processes, i.e. have various local, peripheral and central effects. The most studied adipocytokines are leptin, tumor necrosis factor and adiponectin.
The protein leptin is a peptide hormone that is involved in the regulation of energy metabolism, signaling satiety in response to food intake. It was discovered in 1994 in tests on obese mice as the product of a gene that causes obesity (ob).
The hormone is produced to a greater extent by adipose tissue cells (adipocytes), a smaller part is secreted by the placenta, skeletal muscle and gastric mucosa.
The biological action of leptin occurs through specific receptors in the hypothalamus. When leptin interacts with its receptor, the synthesis of biologically active substances that suppress appetite is activated. The formation of appetite-stimulating substances also stops.
As the concentration of leptin in the blood increases, the feeling of hunger decreases. Normally, the concentration of leptin increases significantly after a full meal: the hypothalamus detects changes in the concentration of the hormone in the blood and transmits the so-called. “satiation signal”, as a result of which a person stops feeling hungry.
Leptin levels decrease as a result of prolonged fasting, as well as after intense physical activity.
Excess leptin in the blood can in rare cases be associated with genetic defects. But most often a person stops picking up “saturation signals” due to:
- Immunity to the action of leptin caused by defects in Ob-Rs receptors;
- Excessive synthesis of leptin inhibitors;
- Leptin transport disorders.
An excess of leptin provokes excessive accumulation of adipose tissue in the body, which significantly increases insulin secretion, causing hyperinsulinemia.
Normally, leptin increases insulin consumption by body tissues and reduces its production. Excess insulin caused by hypersecretion of leptin is no longer absorbed by muscles and liver cells, and the number of insulin receptors in tissues decreases, insulin resistance develops, i.e. cell insensitivity to insulin. This condition increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and gestational diabetes mellitus (DM). An increase in leptin levels in early pregnancy, regardless of whether the woman is obese, is considered a prognostic marker of gestational diabetes in late pregnancy.
Obesity caused by overproduction of leptin increases the risk of developing many other pathological conditions:
- Hypertension;
- Dyslipidemia is a pathological syndrome associated with impaired fat metabolism;
- Coronary heart disease;
- Ischemic stroke.
As a rule, this test is most often prescribed to people with a body mass index of more than 30, especially if there is a family history of early onset obesity.
In combination with other studies - lipid profile, assessment of thyroid function, determination of glucose, insulin - assessment of leptin levels in the blood is used to identify the risk of developing diabetes mellitus (type 2), diseases of the cardiovascular system and to find the causes of menstrual irregularities in women.
Leptin is a satiety hormone
Leptin is an indicator of a person’s saturation with the required level of fat. Eating food leads to an increase in fat cells in the body, which begin to produce a special hormone - leptin. This hormone enters the human brain through the bloodstream, namely into its special area - the hypothalamus. This area is responsible for mental processes and the emotional state of a person. When leptin reaches the hypothalamus, it signals the body that there is enough food. There comes a feeling of satisfaction and satiety.
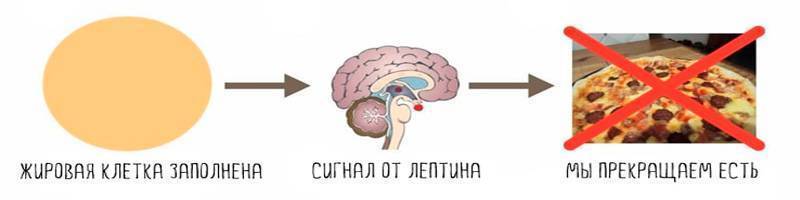
Given the physiological role of leptin, it may seem that the use of this hormone in medicinal form will help obese people lose weight. After all, if a person constantly feels full, he will not have the desire to eat, which means he will lose weight. In fact, this is not true.
The size of fat cells affects the amount of leptin produced. The larger they are, the more hormone enters the brain. Excessive leptin content leads to the fact that the brain develops a kind of immunity to it and perceives only a small part of the hormone.
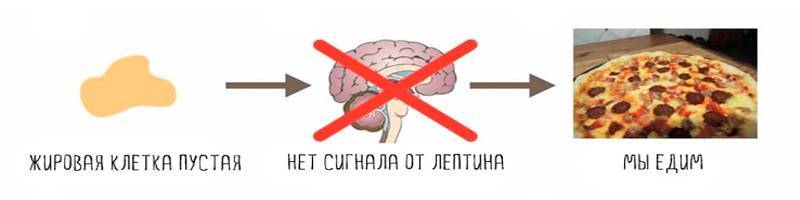
The body receives the opposite signal - it is necessary to replenish the level of nutrients, which, in fact, are more than enough. The person begins to eat even more, and the situation only gets worse. The desire to perform physical activity is reduced to a minimum, as the body feels exhausted and weakened, therefore, you need to conserve your strength. This state of affairs in medicine is called leptin resistance.
Leptin resistance
- This is the brain’s resistance to the perception of the satiety hormone produced by fat cells. It is quite difficult for the body to get out of this state on its own. A person feels a shortage of food and needs to constantly satisfy the feeling of hunger. This leads not only to obesity, but also to disruption of the functioning of all body systems.
Leptin resistance occurs for the following reasons:
- Regular excess food. Systematic overeating leads to excess fructose levels. This monosaccharide increases the number of triglycerides in the body. Elevated levels of these lipids cause leptin to be unable to cross the barrier between the circulatory and nervous systems. This makes it difficult for it to penetrate the brain. The result is only partial release of leptin into the hypothalamus. This leads to a blocking of the feeling of fullness, and the person begins to constantly feel hungry.
- Low-calorie diets + physical activity. A person actively burns calories, while depriving himself of nutrients. The body begins to sense danger and rebuilds itself. The proper functioning of organs is disrupted, which leads to a decrease in sensitivity to leptins.
- Chronic lack of sleep. The body begins to function in an unnatural mode. As a result, only part of the produced leptins enters the brain and the feeling of satiety is deformed.
- Anomaly of hypothalamic receptors. This is an individual feature of the body in which the human brain is not able to respond correctly to leptins.
Leptin resistance appears in the body unnoticed and is asymptomatic. It is important to eliminate the disease in a timely manner and prevent its further development. Do you know your leptin levels? Do you have leptin resistance?
Specialists from the MU “FNPR Polyclinic” will answer all your questions. The necessary studies will be carried out in the clinic’s own laboratory. In the shortest possible time you will receive reliable results, and most importantly, recommendations for the treatment and prevention of the disease.
Leptin levels in blood tests
The level of leptin in the blood depends on the patient’s gender and age. Normal indicators for females aged:
- 0-3 years – from 2.2 to 3.0 ng/ml;
- 3-6 years – from 1.2 to 2 ng/ml;
- 6-9 years – from 6.6 to 10.6 ng/ml;
- 9-12 years – from 10.2 to 17.4 ng/ml;
- 12-15 years – from 11.42 to 17.82 ng/ml;
- 15-20 years – from 6 to 27.6 ng/ml
- over 20 years old – from 0.5 to 13.8 ng/ml.
Normal indicators for male patients aged:
- 0-3 years – from 2.8 to 3.6 ng/ml;
- 3-6 years – from 3.6 to 6.0 ng/ml;
- 6-9 years – from 10.4 to 19.2 ng/ml;
- 9-12 years – from 19.2 to 28.8 ng/ml;
- 12-15 years – from 26 to 42 ng/ml;
- 15-20 years – from 27.6 to 38 ng/ml
- over 20 years old – from 1.1 to 27.6 ng/ml.
Increased leptin in blood test
If the level of leptin is exceeded, this may indicate the presence of:
- obesity;
- development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
Decreased leptin in blood tests
Low content (lack) of the hormone is observed when:
- anorexia;
- long-term adherence to a strict low-calorie diet;
- obesity caused by genetically determined low levels of leptin production.
If the results of the decoding result in an increased (high) or decreased (low) level of leptin in the blood, do not worry about this. It is necessary to consult a doctor to determine the reasons for its increase or decrease and to draw up a treatment regimen in order to normalize leptin levels to reference norms. You cannot independently reduce or increase the level of the hormone in the blood.
So, a test for the level of hunger hormone in the blood may be recommended for patients who have metabolic disorders. If leptin is produced in the body in increased quantities, this may indicate a predisposition to the development of a serious disease - type 2 diabetes.
Factors affecting leptin levels
Leptin increases after eating , more due to carbohydrates than due to fat, in both obese and healthy people. (, )
During psychological stress, the body secretes leptin intensely, and high leptin levels are associated with increased food consumption. () A syndrome of “seizing” of psychological stress is formed.
Diet
Overeating during meals increases leptin production. In contrast, eating smaller meals and a higher proportion of protein, or foods with a low glycemic index, can lead to lower leptin levels. (, )
A low-carbohydrate, low-fat diet may reduce the release of leptin by fat cells. ()
Anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, olive oil, nuts, fruits and vegetables can also reduce leptin production. ()
Some nutritional rules to reduce leptin:
- For breakfast, it is advisable to eat 20-30 grams of protein
- It is better to limit your meal time to 18.00. You need to stop eating at least 3 hours before bedtime.
- Reduce the number of meals by 2-3 times with no snacks between them.
- Reduce the amount of carbohydrates in your diet. Switch only to foods with a low glycemic index.
- Reduce portions when eating. Don't eat your fill.
Starvation
Short-term fasting (24-72 hours) reduces leptin levels. ()
Intermittent fasting is considered the safest and most accessible form of fasting. Talk to your doctor before making significant changes to your diet. You may have contraindications to fasting. ()
Psychological stress
Emotional stress, the stress hormone cortisol, and anti-inflammatory steroid medications (corticosteroids) increase leptin levels. Reducing stress helps lower leptin levels. (, )
Physical activity
Any physical exercise reduces leptin production. (, )
Toxins and inflammation
Endotoxins (bacterial toxins, disturbances in the breakdown and digestion of food, impaired detoxification in the liver) in both rodents and humans lead to an increase in leptin. (, )
Leptin - description and role of the hormone
The peptide hormone leptin is produced by fat cells in the body. This substance performs important functions in the body:
- takes a direct part in metabolic processes;
- regulates appetite;
- Body weight largely depends on its quantity.
The more fat reserves in the body, the more leptin is synthesized, and when losing weight, the production of this hormone decreases. With a lack of leptin in the blood, a feeling of hunger occurs, that is, in this way the body regulates its weight. In addition, in women, leptin is one of the regulators of menstrual function.
Advice! With a critical decrease in the level of this hormone, amenorrhea occurs, that is, the cessation of menstruation.
The amount of leptin in the blood depends on many factors. Thus, increased levels of the substance during puberty are the norm for representatives of both sexes. Leptin is produced unevenly throughout the day.

In overweight people, leptin is produced in large quantities. Moreover, in obese men, the hormone begins to suppress testosterone synthesis, reducing sexual function.
In most cases, the cause of obesity is not a violation of leptin synthesis, but the emergence of tolerance to it, that is, tissues and cells lose sensitivity to this hormone.
Normal leptin levels
Leptin levels can be measured using a blood test. Results are usually reported as a unit of measurement - ng/ml (nanograms per milliliter).
Normal Leptin Levels
are in the range of
4.7 – 23.7 ng/ml,
although they may vary slightly between laboratories. These values may also depend on the person's age, gender and time of day when the test was taken.
- Time of day : Leptin levels may be higher at night than during the day. ()
- Gender : Women have higher leptin levels than men. ()
Research shows that the level of leptin circulating in the blood is directly proportional to the amount of fat in the body, and that it can change depending on food intake. (,, )
A leptin test is usually ordered for overweight/obese people, especially if they have a family history of obesity. It may also be useful for an obese person who has symptoms of frequent, constant hunger.
Sometimes leptin levels are tested along with other tests, such as overall thyroid health, glucose levels, cholesterol and insulin. This list of tests can help determine the health status of an overweight/obese person and identify causes that may contribute to or impair the health of such people.