Gamma-glutamyltransferase (gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase) is one of the enzymes of the liver and pancreas that is involved in certain biochemical reactions. Directly in the blood, GGT can be contained in minimal quantities, since the cells are constantly renewed, and their breakdown products penetrate into the bloodstream.
However, an increase in GGT levels above normal (a certain indicator for different age categories and gender) is always evidence of a pathological process in the liver, pancreas, and kidneys.
Gamma GT is increased - what does this mean?
The greatest activity of gamma-GT is observed in the kidneys, bile ducts, and liver, but the enzyme is also found in minimal quantities in other organs and systems (in the tissues of the brain, heart, skeletal muscles, intestines, spleen, prostate).
When the amount of GGT in the blood increases sharply, there may be several reasons for this:
- cholestasis (stagnation of bile);
- cytolysis (death of liver cells);
- exposure to alcohol;
- taking medications;
- oncological processes;
- pathologies of other organs.
In some cases (alcohol or drug intoxication), elevated GGT levels are temporary and can normalize without treatment. Therefore, repeated testing for GGT is recommended.
When is a test for GGTP prescribed?
The amount of enzyme in the blood serum is most informative when:
- diagnosis of pathologies of the liver, gall bladder, bile ducts;
- monitoring of oncological processes;
- monitoring the treatment of diseases of the hepatobiliary system;
- alcoholism monitoring;
- identifying the causes of increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP);
- the appearance of symptoms of damage to the liver, bile ducts, gall bladder (jaundice, itching, dark urine, etc.).
Important! An analysis for GGT can also be prescribed in the diagnosis of extrahepatic pathologies as one of the elements of a comprehensive study.
Indications for the study
A blood test for GGT—the level of gamma-glutamine transferase—is prescribed if there is suspicion of liver cell damage. The causes of such damage can be different (for example: a number of diseases, poisoning with toxic substances, alcoholism, drug use). This test is currently the most sensitive indicator of liver damage.
The analysis is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- decreased appetite;
- skin itching;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- change in color of stool and urine;
- fast fatiguability.
Also, a GGT test is prescribed at certain intervals to patients who are being treated for alcoholism. Based on its results, the doctor can judge how much the patient follows his recommendations (whether the patient has given up alcohol or not).
Gamma-GT is elevated - reasons
Diagnosis of a disease that has caused a change in GGT levels is the prerogative of specialists, but exceeding the norm is always a signal from the body about the unfavorable condition of the liver.
Thus, an excess of GGT level by 5 times is observed when:
- taking certain medications;
- drinking alcoholic beverages;
- post-infarction state;
- congestive heart failure.
5-10 times – at:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- other lesions of the liver and biliary tract.
10 times and higher – at:
- hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholangitis;
- oncological lesions of the liver;
- alcohol intoxication;
- blockage of the intrahepatic bile ducts or bile ducts;
- liver failure.
With all the variety of possible pathological conditions, only a few of them are diagnosed in the vast majority of cases.
Cholestasis syndrome
Stagnation of bile can be caused by disorders at any level of the hepatobiliary system.
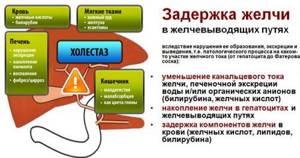
There are 2 main variants of this condition:
- Intrahepatic cholestasis - develops with pathology of the bile ducts inside the liver or dysfunction of the cells themselves. In these cases, stagnation of bile may be due to a disorder in the process of bile formation, as well as an increase in the permeability of bile capillaries;
- Extrahepatic cholestasis - observed in the presence of a mechanical obstruction inside the large bile ducts (stones, parasites, tumors) or when they are compressed externally (cancer, cyst, acute pancreatitis). Other possible causes of the pathological condition may be postoperative scar narrowing or congenital pathologies of the bile ducts.
Characteristic symptoms of cholestasis (indigestion, itchy skin, dark urine, enlarged liver, etc.) may have varying degrees of severity depending on the severity of the underlying disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcohol or drug intoxication, sarcoidosis, etc.).
Treatment
When choosing treatment tactics, extensive diagnostics are carried out (blood biochemistry, urine analysis, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, studies of the patency of the biliary tract and the degree of damage).
The general treatment regimen consists of several mandatory points:
- If possible, eliminate the cause of the pathology;
- A special diet that involves consuming a certain amount of neutral fats;
- When identifying a violation of the permeability of cell membranes, Heptral, Metadoxyl, and antioxidants are used;
- To normalize the composition of bile, Rifampicin and ursodeoxycholic acid preparations are prescribed;
- Corticosteroids can be used as cell membrane stabilizers.
As a means of symptomatic treatment and in the chronic course of the disease, Naloxone or Ondansetron, vitamins A, E, K, as well as vitamin D are prescribed simultaneously with calcium supplements.
Cytolysis
The death of liver cells can go unnoticed for a long time and is expressed only by side symptoms of an implicit etiology:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea;
- flatulence;
- heaviness in the area of the stomach or right hypochondrium, especially obvious after eating;
- constipation or diarrhea.

In most cases, the cytolysis process starts when:
- poor nutrition;
- alcohol abuse;
- viral hepatitis (type B and C);
- autoimmune diseases;
- parasitic infestations (ascariasis, giardiasis, echinococcosis);
- uncontrolled use of hepatotoxic drugs.
Treatment
As in the case of cholestasis syndrome, the first and main point of therapy is to eliminate the cause of the pathological condition:
- Taking antiviral drugs (Ribavirin, Viferon);
- Antiparasitic drugs (Mebendazole);
- Refusal to drink alcohol;
- Stop taking hepatotoxic drugs;
- Immunosuppressive therapy.
To normalize the condition, it is possible to use hepatoprotectors (Heptral, Karsil), detoxification solutions, sorbents, and vitamins.
Important! Particular importance is attached to diet: split meals, avoidance of unhealthy foods (fatty, salty, rich, sour, etc.), limiting salt, increasing fluid intake.
Effects of alcohol
The release of GGT is directly related to the consumption of alcohol - even when determining the initial high levels of the enzyme in the blood, giving up alcohol reduces the GGT content by 2 times after 10 days.
If after a month the GGT level returns to normal, this means there is no pathology. If the indicators are close to exceeding the norm, it is worth thinking about completely giving up alcohol, since it is this that causes alcoholism and such serious conditions as cirrhosis, injuries while intoxicated, and delirium tremens.
A test for GGT, done in conjunction with other studies of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), can determine not only alcoholism, but also alcoholic steatohepatitis - an inflammatory process with the parallel formation of areas of necrosis under the influence of ethanol metabolic products. In other words, a penchant for drinking alcohol that has not yet developed into alcoholism. Help with treatment here https://rnd.emerkon.ru/
Important! Some companies have made such a test mandatory during a medical examination, and in case of a positive result, it becomes a reason for recognizing professional unsuitability.
Taking medications
When diagnostics do not reveal pathological causes for increased GGT in the blood, an excess of enzymes can be triggered by taking certain medications that cause liver intoxication. These may be drugs from the following groups:
- Antibiotics, antiviral, antifungal;
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- Anesthetics;
- Anticoagulants;
- Hypotonic agents;
- Diuretics;
- Statins, etc.
The list of these medications is far from complete; it is possible to determine exactly which of them caused changes in the composition of the blood based on the patient’s information about what medications he took the day before. More accurate information will be provided by additional blood testing.
Oncology
The formation of tumors in the liver causes an increase in GGT levels several times higher than normal. Primary liver cancer, as well as metastases from other affected organs, can be detected when GGT is activated in the blood.
Other reasons
Sometimes a biochemical blood test shows a deviation from the norm towards an increase in GGT in other pathologies:
- Pancreatitis (inflammatory processes in the pancreas);
- Thyrotoxicosis (increased levels of thyroid hormones);
- Diabetes;
- Heart failure;
- Renal failure, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis;
- Neurological diseases;
- Pathological conditions of the brain;
- Injuries;
- Burn lesions;
- Hormonal drugs for the treatment of the thyroid gland.
Treatment and adjustment of indicators
If, according to the test results, gamma-GT is increased, how to correct this indicator must be determined with a doctor. After all, it is not the enzyme level that needs to be treated, but the reason that caused its increase. So, if it is increased due to excessive alcohol consumption, then there is only one way out - to give up alcohol.
In other cases, it is impossible to do without consulting a specialist. If we are talking, for example, about pancreatitis, then a diet is important, in which you should give up fried and fatty foods, chocolate, and coffee. It is also a good idea to take medications that affect liver function. Some patients with hepatitis are prescribed a drug such as Ursofalk. It can also be used for jaundice in newborns to help establish normal liver function.
Increased Gamma GT in women
Standard GGT levels in women may be slightly increased in the following cases:
- oncological formations in the mammary gland;
- use of hormonal contraceptives or drugs to maintain the balance of female hormones;
- during pregnancy.
In any case, the treatment regimen is drawn up by the attending physician, depending on the magnitude of the excess of GGT, as well as the severity of the primary disease.
First of all, the root cause is eliminated, followed by strict adherence to the diet and drug support for the liver. In the most extreme cases, surgical intervention is indicated (for oncology).
Diagnosis of diseases
Depending on the overall clinical picture, other blood parameters and test results, the doctor may suspect the development of certain diseases in you. Thus, gamma HT can be increased with the following ailments:
1. Cholestasis - the amount of the enzyme increases in both extrahepatic and intrahepatic forms of the disease. In this case, problems such as gallstones, obstructive jaundice caused by a liver tumor, and cholangitis appear.
2. Acute hepatitis of viral etiology, various toxic diseases.
3. Chronic hepatitis.
4. Pancreatitis - GGT will be increased both in acute and chronic forms.
5. Alcoholism.
6. Oncological diseases of the liver, pancreas or prostate.
In addition, if you are taking oral contraceptives, barbiturates, estrogens, or cephalosporins, your gamma TG levels may also be increased. You should not try to diagnose your illnesses yourself; only a doctor can diagnose them.
Increased Gamma GT in men
For men, the list of gender-specific reasons for increased GGT is most often limited to the following points:
- Prostate cancer;
- Alcohol addiction.
It is worth considering the fact that the standard values for men exceed the women's standards due to the enzyme content in the prostate gland.
Treatment of the identified pathology depends on the stage of the disease and is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. In the case of a single alcohol intoxication, a period of abstinence is sufficient for the indicators to return to normal.
GGT level and age
If you go to donate blood to find out your gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase level, then you need to remember the following. Normally it is low, but the values obtained will depend on gender and age. Also, you should not rely on data from other laboratories; look only at the standards indicated in the research results. The level determined depends on the units of measurement and the equipment used.
Thus, some laboratories indicate that gamma GT will be increased provided that it is more than 36 for women and 64 U/l for men. At the same time, for children it is permissible to increase the amount of enzyme by 2 or even 4 times.
In other laboratories there is a division depending on age. Thus, for adult women the norm will be the amount of enzyme in the range from 6 to 42 units, for men - from 10 to 71. In adolescents aged 12 to 17 years, the amount of GGT in the serum should not exceed 33 U/l in girls and 45 in young men. Regardless of gender, at the age of 6-12 years the upper limit of normal is considered to be up to 17 U/l, from 3 to 6 - up to 23, from 1 year to 3 - up to 18, from 6 to 12 months - up to 34.
The picture is slightly different with newborns, in whom the work of all body systems is just getting better. It's okay if GGT is up to 185 before 5 days of age, and before 6 months it can even rise to 204 U/L.
How is a blood test for Gamma GT performed?
A biochemical blood test for GGT is always prescribed to test for sensitivity to alcohol.
However, the study can be carried out in a number of other cases:
- during preoperative preparation;
- when diagnosing liver problems;
- when the patient develops alarming symptoms: nausea, vomiting, weakness, pain in the right hypochondrium;
- if signs of cirrhosis or hepatitis occur;
- to confirm detected oncology.
How to prepare?
As a rule, blood is taken from a vein for analysis.
To obtain the correct result, the patient must adhere to several recommendations:
- since blood is taken on an empty stomach, eat no later than 8 hours before the time of analysis;
- exclude alcohol and foods with a high fat content from the diet 2-3 days before the test;
- do not expose the body to intense physical activity;
- temporarily stop taking medications after the prior consent of the doctor;
- additional studies (ultrasound, x-ray, etc.) and physiotherapeutic procedures should be carried out after the test.
Norm
The average standards are:
- for men – up to 49 U/l;
- for women – up to 32 U/l.
In children, standard indicators depend on age and gradually decrease. The highest level of GGT is in newborns. Until the age of 12, the indicators for boys and girls are approximately the same, then puberty begins, and the standard for boys gradually increases.
When is it recommended to take GGT?
If you know about your problems with the liver, pancreas, kidneys or other organs of the gastrointestinal tract, then most likely you have already donated venous blood more than once in order to determine the gamma-GT indicator.
It is necessary to control it if you know that you have the following ailments:
- chronic hepatitis, including its forms without jaundice,
- cancer of the pancreas, liver or prostate;
- alcohol addiction that you are struggling with.
In cancer, the GGT indicator is used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment; for the same purposes, it is used when fighting addiction to alcohol.
They find out whether the HT gamma is increased or not, also in order to diagnose liver damage that is accompanied by cholestasis. This can be, for example, with viral or congenital hepatitis and obstructive jaundice, biliary atresia. This indicator is monitored after myocardial infarction. In addition, it is possible to find out whether the level of gamma HT in the blood is elevated or not to check the hepatotoxicity of drugs.