If a gynecologist has diagnosed you with an ovarian cyst, do not be alarmed: as a rule, these formations are benign and do not pose a danger; surgery is not required. Often they do not need to be treated at all and disappear on their own within a few months. It is enough to periodically visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound examination.
- What types of ovarian cysts are there?
- When is laparoscopy performed?
- When is laparoscopy not performed?
- Benefits of laparoscopy
- Preparation
- How is laparoscopy performed?
- Postoperative period
- Complications
- Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
Sometimes ovarian cysts still have to be removed. Operations can be performed without an incision, through several punctures in the abdominal wall - laparoscopically. Euroonco employs expert-level gynecological surgeons who have extensive experience in performing such interventions. Come for a consultation with our specialist: he will tell you whether surgery is necessary in your case, and prescribe an examination that will help distinguish a benign neoplasm from a malignant one.
A cyst is not a specific disease. This term refers to any pathological cavity with fluid. The reasons for its formation are different. According to statistics, ovarian cysts are diagnosed in every tenth woman. They most often occur during puberty and menopause. Some girls have them from birth.
What types of ovarian cysts are there?
All ovarian cysts are divided into two large groups: functional , which occur in most cases, and pathological , which doctors have to deal with much less frequently.
Functional cysts are the result of disturbances during the menstrual cycle. Usually they do not cause complications and disappear on their own. They come in three types:
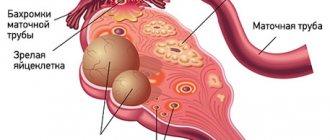
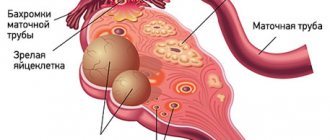
- Follicular . follicle matures in a woman’s ovaries . Normally, it should open and release the oocyte. If this does not happen and the follicle continues to grow, it turns into a cyst.
- Corpus luteum cysts . After the follicle releases the egg, it turns into a special gland - the corpus luteum . It produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum atrophies. And if fluid accumulates in it, it turns into a cyst.
- Theca-luteal cysts often develop as a side effect of infertility treatment with hormonal drugs.
Pathological ovarian cysts are not associated with the menstrual cycle. They are always characterized by the appearance of “wrong” cells that should not be present normally. The most common types of pathological cysts:
- Endometrioid . This is a form of endometriosis, a condition in which endometrial tissue (the lining of the uterus) gets into unusual places and grows there. In the ovaries, it can form cavities with fluid. They often appear as “chocolate” cysts filled with dark blood.
- Dermoid cysts , or teratomas , are a special type of benign tumors made from embryonic cells. There may be different tissues inside them, for example, skin, hair, nails. Dermoid cysts become malignant very rarely.
- Cystadenomas are benign neoplasms of epithelial cells. Usually they are filled with contents of a mucous or watery nature.
For more information about malignant cysts, please visit the ovarian cancer page on our website.
Preparation for laparoscopy
Preparation for this operation for ovarian cysts is standard. Before such laparoscopy, the patient needs to undergo a series of examinations (ECG, ultrasound of the lungs and pelvic organs) and undergo blood and urine tests. If a woman has heart problems, consultation with a cardiologist will be necessary. The patient should also visit an anesthesiologist, who will identify any allergies to medications and select appropriate medications. Laparoscopy for ovarian cysts does not depend on the day of the cycle. However, during menstruation the operation is not performed.
When is laparoscopy performed?
If the ovarian cyst is small, does not cause symptoms and does not look cancerous, it can be left alone. No surgery needed. The gynecologist will prescribe periodic examinations and control ultrasounds. Moreover, postmenopausal women will have to do this more often, because they have a higher risk of malignant tumors.
Are there effective medications?
In some cases, hormonal contraceptives may be helpful. They help prevent the formation of new cysts in the ovaries, but do not affect the growth of existing ones. If a woman is bothered by pain, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). But this is only symptomatic treatment. The only way to get rid of the formation is surgery.
If the cyst is “problematic,” then the doctor will definitely say that it needs to be removed. Indications for surgery:
- Large size of formation. In most cases, ovarian cysts have a diameter of 1–3 cm. Very rarely they reach 15–30 cm.
- Presence of symptoms: abdominal pain, pelvic pain, bloating, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, heavy periods, vaginal bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle. A large cyst can compress the intestines and bladder. This leads to problems with stool and urination.
- Suspicion of a malignant nature of the cyst - the risks are increased in postmenopausal women.
- Continued growth over 2–3 menstrual cycles.
- Pathological ovarian cyst.
What happens if the cyst is not removed?
If the doctor said that the cyst needs to be removed, then delaying the operation is primarily dangerous for postmenopausal women. They, as we have already mentioned, have a higher risk that the formation may turn out to be malignant. And with cancer, time is critical. The later treatment is started, the lower the chances that it will be successful and that remission will be achieved. The prognosis worsens and survival rate decreases.
At the Euroonko clinic you can receive treatment for ovarian cancer according to modern standards. Our doctors perform operations of any complexity; we have access to all the latest generation antitumor drugs registered in Russia. We work according to modern European, American, Israeli treatment protocols. For ovarian cancer complicated by peritoneal carcinomatosis, we use an innovative technique - hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
With benign ovarian cysts, serious complications can also occur, although they are rare. Large cysts may rupture. In this case, severe bleeding develops into the abdominal cavity, and severe abdominal pain occurs.
As the cyst grows, the risk of ovarian torsion increases. Due to compression of the blood vessels, it stops receiving blood supply, severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting occur. The result may be necrosis (death) of the ovary, and it will have to be removed urgently.
If you experience symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or a fever of more than 38 degrees, you should immediately seek medical help.
LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY IN MODERN GYNECOLOGICAL PRACTICE AND, ESPECIALLY IN REPRODUCTOLOGY, PLAYS AN ESSENTIAL ROLE IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF VARIOUS DISEASES OF THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT IS WHEN PERFORMING LAPAROSCOPY THAT IT IS POSSIBLE TO IDENTIFY AND SOLVE WOMEN'S PROBLEMS THAT PREVENT THE NATURAL CONCEPT OF A BABY OR TO CREATE CONDITIONS FOR THE SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE IVF PROGRAM.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive and, therefore, low-traumatic surgical research technique in which the doctor visually examines the abdominal organs and pelvic organs (uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries) through small incisions on the abdominal wall. Typically, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed through one or two of these incisions. To improve the size of the field of view, a small amount of harmless inert gas is injected into the abdominal cavity.
Through one incision, a laparoscope is inserted, which is a thin telescopic tube with a lens at one end and an eyepiece at the other, which is attached to a digital video camera (to transfer the image to the monitor and record it on a medium for later viewing with the patient and discussing the results of the study) .
Through another, even smaller incision, a manipulative instrument is inserted, with the help of which the doctor displaces the internal genital and abdominal organs, studying them in detail.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is often performed under general anesthesia, but can also be performed under local anesthesia in combination with light sedation.
If during such an examination a pathology is revealed that can be eliminated, the doctor will immediately do so. In most cases, diagnostic laparoscopy takes no longer than 15 minutes.
Preparation for diagnostic laparoscopy
Before performing diagnostic laparoscopy, as well as before other surgical interventions, the patient must undergo an appropriate examination.
First of all, a set of standard studies is carried out: urine and blood tests (general, biochemical, coagulogram), electrocardiogram, chest x-ray, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, analysis of discharge from the genital tract. The patient should not take food or liquid 8 to 10 hours before surgery. In addition, it is recommended to limit smoking and alcohol intake. Before the operation, the patient needs to undergo a cleansing enema.
Operative (therapeutic) laparoscopy
For surgical laparoscopy, it is enough for the doctor to make two or three incisions on the anterior abdominal wall, 5-7 mm long. After the operation there are no scars left. In other words, there are no cosmetic problems.
If monoportal laparoscopy, also practiced at the Ferti-Line clinic, is performed, then it is necessary and sufficient to make only one incision 10 mm long in the navel area.
What problems can be solved with surgical laparoscopy?
With the help of laparoscopic intervention, you can perform almost all operations that are performed in the open (laparotomy) way.
First of all, surgical laparoscopy is advisable for removing various cysts and ovarian cysts, separating adhesions and restoring the patency of the fallopian tubes, removing myomatous nodes (with preservation of the uterus), surgery on the fallopian tubes during ectopic pregnancy, as well as for complete removal of the uterine body and uterine appendages.
There are pathological situations, the solution of which is generally impossible without the use of laparoscopy: elimination of foci of genital endometriosis and, therefore, elimination of a powerful factor for the existence of infertility in women. This technology has opened a new era in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility, allowing for significant improvement in results.
Timely detection by ultrasound or diagnostic laparoscopy, as well as laparoscopic removal of ovarian tumors, has significantly reduced the incidence of ovarian cancer.
Laparoscopy can be either an independent operation or combined with hysteroscopy or operations with vaginal access (for example, for prolapse of the walls of the vagina and uterus, urinary incontinence).
The advantages of laparoscopic technique are undeniable. the next day after endoscopic surgery ; recovery and recovery after surgery occurs much earlier than in cases with conventional laparotomy techniques.
Patients report less severe postoperative pain or no pain at all compared to patients after laparotomy. The incidence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity and pelvis is minimal, long-term results are much better, since laparoscopy in combination with intraoperative ultrasound allows the removal of formations invisible to the naked eye (fibroids, endometriomas or ovarian cysts), which leads to a decrease in the number of relapses.
Mini laparoscopy
Mini-laparoscopy is a type of laparoscopy that has the following advantages:
1) even smaller incisions are needed on the anterior abdominal wall and, as a result, the patient’s negative sensations in the postoperative period are practically eliminated;
2) the cosmetic effect is even more pronounced than with conventional laparoscopy;
3) such an operation can be called fully outpatient, with a minimum (one-day) stay of the patient in the clinic.
Minilaparoscopy at the Ferti-Line clinic is performed with instruments no more than 5 mm thick. The technique is acceptable for solving most gynecological problems, except for cases of removal of fibroids and cysts of impressive size. Traditional laparoscopy is suitable for solving such problems.
Fertiloscopy or transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy
A type of laparoscopy used to examine the pelvic organs and check the patency of the fallopian tubes.
The essence of this method is that a special thin needle is used to make a puncture in the posterior vaginal fornix, through which a sterile solution is injected into the abdominal cavity in order to straighten the tissue and improve visibility in the pelvis. Then, in the same way, a thin endoscopic instrument, a fertiloscope with a video camera, is inserted through the vagina. With their help, the doctor can examine and evaluate the condition of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes. With fertiloscopy, you can evaluate the patency of the fallopian tubes by injecting a contrast agent into the uterine cavity and directly observing how it distributes through the tubes and exits into the abdominal cavity.
This method is distinguished by almost 100% diagnostic accuracy of the condition of the woman’s reproductive system and, in fact, is not inferior in this regard to traditional laparoscopy. In addition, this procedure is carried out under short-term anesthesia, which allows the woman to leave the clinic after a couple of hours.
Unfortunately, if any pathology is detected in the pelvis: adhesions, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, the method does not allow it to be corrected, which means that you will have to go back to the operating table to eliminate these diseases using traditional laparoscopy. This is perhaps the only drawback of transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy. It is appropriate to emphasize that the degree of mastery and implementation of endoscopic techniques is the key to the proper quality of medical services provided. Patients need to take this into account when choosing a gynecological clinic.
IF YOU HAVE INDICATIONS FOR LAPAROSCOPIC OPERATIONS, YOU CAN SEEK A GYNECOLOGIST AT THE FERTY-LINE CLINIC FOR CONSULTATION.
BE HEALTHY!
Preparation
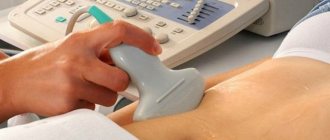
Ovarian cysts are usually detected during an ultrasound examination. In order to better assess the size, location and internal structure of the neoplasm, the condition of the ovary, they usually resort to not only transabdominal (through the abdominal wall), but also transvaginal (using a special sensor inserted into the vagina) ultrasound.
In rare cases, usually when a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, computed tomography and diagnostic laparoscopy are prescribed. of cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) in the blood testifies in favor of cancer . But this analysis is unreliable, since a positive result can be obtained for uterine fibroids, endometriosis and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Based on the examination results, the doctor advises the woman and explains which treatment tactics will be optimal in her case. If laparoscopic surgery is indicated, a date for hospitalization is set. You need to undergo a preoperative examination. It usually includes the following diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood test for hormone levels.
- Tests for infections.
- Cervical smears - cytological, flora.
- Blood clotting study.
- Determination of blood group AB0, Rh factor.
- Electrocardiography.
- X-ray of the lungs.
Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts is performed under general anesthesia - endotracheal anesthesia. The woman is hospitalized in the hospital the day before surgery. You can’t eat anything for 8 hours before surgery, and you can’t drink anything in the morning. Some time before anesthesia, premedication : the woman is given drugs that help her relax and calm down.
Laparoscopic surgery - cauterization of the ovary
Diathermocautery of the ovaries - radial dissection of the ovarian tissue with a hook to the gate to a depth of 7-10 mm (usually 6-8 dissections are performed). Another option for this operation is the formation of 10-15 holes on the surface of the ovary using an electrode, which is placed perpendicular to its surface. Follicular fluid flows out of the affected area; as a result of thermal damage, the medulla shrinks and by the end of the operation the volume of the ovary is reduced to normal size.
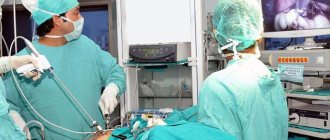
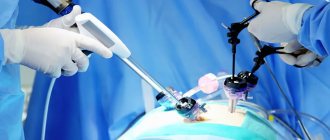
How is laparoscopy performed?
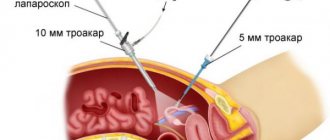
Laparoscopic intervention is performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall. Through one of them, in the navel area, a laparoscope - an instrument with a miniature video camera. It broadcasts an enlarged image onto the screen. For better visualization during surgery, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
Special laparoscopic instruments are inserted through additional punctures, and the cyst is removed with the help of them.
Depending on the specific situation, the scope of the operation varies:
- Often it is possible to remove only the cyst, preserving the ovary.
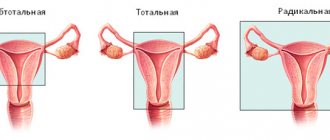
- In some cases, it is necessary to remove the entire ovary - to perform an oophorectomy (oophorectomy) - while the second ovary can be saved. This has to be done if a malignant tumor is suspected, or if the cyst is in an “inconvenient” location, when it is difficult to remove it separately.
- In rare cases, both ovaries may have to be removed. This operation is performed only in extreme cases, especially in women of reproductive age, since menopause occurs after removal of both sex glands. The levels of female sex hormones decrease, and this can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, hot flashes, etc.
Don't hesitate to ask your doctor questions before surgery. Ask what is the likelihood that during the operation you will have to remove both ovaries, what negative consequences this threatens, and how to cope with them.
Laparoscopic surgery – oophorectomy – removal of the ovary
The intervention is carried out as follows. The ovary is grasped with a clamp, traction is created, ensuring visualization of its ligaments and tissue tension. Bipolar coagulation of the ovarian ligament, infundibulopelvic ligament and mesovarum is performed, followed by dissection with endoscissors.
Another method of ovariectomy is to apply a loop ligature to the above formations or to intersect the ligament with the Force Triad “LigaSure” device (Switzerland). The ovary is placed in a plastic container and removed from the abdominal cavity.
Complications
Laparoscopic operations are associated with a low risk of complications. As after any surgical intervention, in rare cases, infection and suppuration in the area of surgical sutures and bleeding are possible. If you are concerned about severe pain, vaginal bleeding, or increased body temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Adhesions may occur after surgery. Very rarely, during surgery, damage to neighboring organs (intestines, bladder) is possible.
At the Euroonko clinic, operations are performed by experienced gynecological surgeons. Our operating room is equipped with modern equipment, multifunctional laparoscopic stands from leading manufacturers. This helps to minimize risks and perform the operation as safely as possible.
After removal, the cyst may recur, in the same ovary or on the other side. Only removal of both ovaries helps to completely eliminate relapse. But such an operation leads to menopause and undesirable consequences, so it is resorted to only in extreme cases.
Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
You can get pregnant even with an ovarian cyst. Most often, they do not interfere with pregnancy, but they can make it difficult to conceive a child.
If during surgery only the cyst is removed or at least one ovary is left, the woman’s fertility is preserved. She may become pregnant in the future. Of course, you need to understand that reproductive function is affected not only by surgery. The ovarian reserve (the number of eggs in the ovaries - it constantly decreases with age) and concomitant diseases play a role.
Get a consultation with a doctor at the Euroonko clinic. Our doctor will tell you whether treatment is needed in your case, what type of surgery is indicated for you, and what is the likelihood that you will be able to conceive and carry a pregnancy in the future.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78