Laboratory diagnostic methods in obstetrics and gynecology are an important component of assessing the health status of the female body.
Among their diversity, a simple smear on the flora has stood apart for many decades.
Its other names: smear for the degree of purity, smear for GN, gynecological smear, bacterioscopy of discharge from the genitourinary organs, microscopy of discharge from the urethra, vagina and cervix.
This study allows you to assess the composition of the microflora, count the number of leukocytes and epithelial cells, and also diagnose some STDs (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis).
This is a routine, non-invasive, economical and quite informative method, widely used in the work of a gynecologist.
Based on its results, the doctor has the opportunity to determine further tactics for managing the patient and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Why take a smear for biocenosis?
The content of the article
A woman’s vagina is sterile only during the first few hours of life after birth. Then various microorganisms begin to populate it. Beneficial bacteria form a protective biofilm on the mucous membrane, preventing the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and supporting the local immune system to preserve reproductive function. When the quantitative and qualitative composition of the bioflora is disturbed, the mucous membrane is colonized by pathogens that cause gynecological diseases.
As a result, the woman feels pain, itching, an unpleasant odor, and inflammation develops, leading to serious complications, for example, infertility.
Symptoms of diseases caused by a shift in the norms in the composition of the flora (vaginosis, colpitis, thrush, etc.) do not appear immediately. Therefore, gynecologists take a smear on the biocenosis before any procedure, so as not to introduce an infection, for example, when treating erosion. It is also necessary to take a smear test if you suspect infertility or other gynecological diseases.
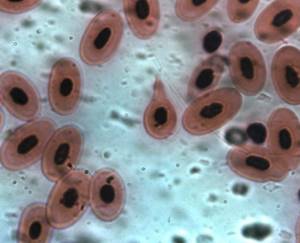
What are red blood cells?
Normally, there should be no red blood cells in the flora smear, or there should be no more than 3 of them in the field of view. But what is it? The red blood cell is a non-epithelial element of the vaginal smear. The norm for red blood cells in a smear for flora is not to be located in the mucus, but directly in the blood, where these bodies carry oxygen from the lungs to the body tissue, and also transport carbon dioxide in the opposite direction. Red blood cells are the most numerous cells in the human body. Statistics show that every 4th cell in our body is an erythrocyte.
Every second, more than two million red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow, which are found in the blood and perform their important functions. Red blood cells in human blood are extremely small cells, shaped like discs, slightly concave on both sides.
This shape and size allow these red blood cells to move freely through the smallest capillary and have a fairly large surface area, thus allowing gas exchange.
What is vaginal biocenosis?
Every woman has microflora, but it is not constant in its composition and changes throughout life. A woman’s body is inhabited by the following groups of microflora:
Gram-positive obligate anaerobic
Propionic bacteria, lactobacilli, clostridia, lactic acid bacteria, peptostreptococci.
Gram-positive bacteria are most often the causative agents of diseases. They were called Gram-positive for their ability to absorb blue dye into the cell wall and retain a purple color when washed with an alcohol solution using the Gram method. This flora is designated Gram (+).
Human pathogens include at least 6 genera of gram-positive microorganisms. Cocci - streptococci, staphylococci - have a spherical shape. The rest look like sticks. They, in turn, are divided into those that do not form spores: Corynebacterium, Listeria and those that form spores: Bacilli, Clostridia.
Gram-negative obligate anaerobic bacteria
Fusobacteria, bacterioides, porphyromonas, prevotella, porphyromonas, veillonella). They do not turn blue on a Gram test and do not form spores, but in some cases they are pathogenic and produce life-threatening toxins. Gram-negative bacteria are classified as opportunistic flora, which are activated and become dangerous only under certain conditions, for example, when the immune system is sharply weakened.
Diseases caused by gram-negative bacteria are difficult to treat because they have a thick shell and are resistant to antibiotics.
Facultative anaerobic
Mycoplasmas, Candida fungus (thrush), streptococci, staphylococci, enterobacteria. They adapt perfectly, so they can exist both in an oxygen-free environment and in the presence of oxygen. Some of them, for example, candida, also belong to opportunistic microorganisms.
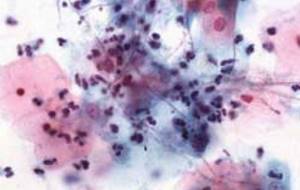
Routes of infection
The main route of transmission of gonococci from humans is sexual. Moreover, you can become infected through vaginal, oral, and anal contact. At risk are women and men who are sexually promiscuous, often change partners, and neglect barrier protection measures. The second most common route of infection is transmission of gonorrhea pathogens from mother to child. This happens during pregnancy, but more often when passing through the birth canal. Immediate treatment of the newborn is required, otherwise there is likely to be a delay in both physical and mental development.
Very rarely, but there are cases of transmission of infection through household means. For example, when wearing the wearer’s underwear, using his towel, razor, washcloth, while visiting public baths, swimming pools, toilets.
Lactobacillus is a major part of healthy flora
The most important of all bacteria is Lactobacillus. Its colonies make up approximately 95% of the normal microflora in a healthy woman. It is lactobacilli that maintain a high level of resistance of the vaginal biocenosis to foreign infections.
Thus, a normal biocenosis can be considered as the absence of gram-negative cells and the dominance of lactobacilli. The number of anaerobic microorganisms to aerobic ones is determined by the proportion from 2:1 to 5:1.
When the number of lactobacilli decreases or disappears completely, bacterial vaginosis occurs. This disease is characterized by the predominance of cocci and a sharp increase in the number of anaerobes.
Lactobacilli as part of the vaginal microflora
In healthy women, lactobacilli predominate in the vagina. There are more than 130 species of lactobacilli that live in different environments and have the common ability to produce lactic acid. 20 species of them can live in the vagina.
Unlike most other areas of the body, healthy vaginal flora includes only one or two species, the most common of which are Lactobacillus iners, Lactobacillus crispatus, Lactobacillus jensenii and Lactobacillus gasseri.
Lactobacilli have several mechanisms for suppressing colonization of the vagina by other bacteria:
- Vaginal epithelial cells produce glycogen, which lactobacilli use to produce lactic acid.
Some types of lactobacilli produce hydrogen peroxide under artificial conditions; At the same time, recent research suggests that in the hypoxic conditions that exist in the vagina, lactic acid concentrations may not reach levels that are inhibitory to other bacteria.
Thus, the growth of bacteria responsible for the development of bacterial vaginosis can be suppressed by lactic acid, but not by hydrogen peroxide.
- Some species of lactobacilli also produce bacteriocins, which can directly kill other species of bacteria.
- Lactobacilli may also likely compete with other organisms for nutrients and receptors on epithelial cells.
These mechanisms differ between different species of lactobacilli. Comparative genomic analyzes of L. crispatus and L. gasseri, L. iners and L. jensenii provided evidence that each species of lactobacilli has its own unique set of proteins, which may influence adaptation mechanisms.
Future studies aimed at characterizing the functional roles of these proteins and genes could provide important information about their impact on women's health.
- Lactobacilli can also inhibit the growth of infectious agents by competing for host cell receptors used by urogenital pathogens such as Gardnerella vaginalis, gonococci, Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, group B streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus agalactie, Escherichia coli, and Prevotella bivia.
Thus, lactobacilli with a higher affinity for host cell receptors can displace pathogenic species.
- In addition, it is assumed that some lactobacilli may bind to the pathogens themselves, for example, Gardnerella vaginalis, Candida albicans and Escherichia coli, thereby preventing their binding to host cells.
Glycogen in the vagina and the constant desquamation of epithelial cells to which bacteria attach contribute to the mechanisms of innate immunity against colonization by pathogens.
How the biocenosis changes throughout a woman’s life
A certain period of a woman’s life is characterized by the dominance of one or another group of microorganisms. In a newborn baby, microorganisms begin to appear in the vagina on the second day of life. Estrogen hormones received from the mother maintain an acidic environment in the vagina. Its walls secrete glycogen, a polysaccharide that is an excellent breeding ground for lactic acid bacteria (lactic acid bacteria, bifidum bacteria).
Opportunistic microorganisms appear after the third week of life, because the immunity received from the mother gradually weakens. The protective properties of a girl’s biocenosis are not stable, so the hymen plays an important role, preventing pathogenic microflora from entering.
During adolescence, a girl’s body itself produces estrogens, which maintain an optimal acidic environment in the vagina. Conditionally pathogenic microflora is washed away by actively secreted mucus. By the age of 16, a unique biocenosis has already been formed, which persists throughout the childbearing period.
At the age of 16 to 45-50 years (before menopause), about 40 different microorganisms are present in the vagina of a healthy woman, 95% of which belong to the group of non-pathogenic lactic acids, and 5% belong to opportunistic pathogens.
During menopause, the production of the female hormone estrogen, which maintains the acidic environment of the vagina, stops. During this period, lactic acid bacteria die, giving way to staphylococci, candida, and E. coli. This is why cases of vaginitis (inflammation of the vaginal walls), thrush and dysbiosis are common in older women.
Factors influencing normal flora
Many factors influence the stability of the vaginal microbiota. The composition of the vaginal microflora can fluctuate depending on age, puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, infections, contraception and sexual behavior.
- Exposure to spermicides, β-lactamases, or other antibiotics may reduce the number of lactobacilli and, as a result, increase susceptibility to vaginal infections.
- Vaginal contamination occurs shortly after or during childbirth. In utero, the fetus was once thought to exist in a sterile or nearly sterile environment, but some studies have shown the presence of small numbers of microorganisms in the placenta.
During vaginal delivery, the newborn is exposed to a variety of microbes. Recent research shows that newborns are contaminated with microorganisms from the vagina and rectum of their mothers.
- Changes in the composition of the vaginal flora may be due to hormonal changes that occur throughout a woman's life.
In early childhood, the pH in the vagina is neutral or slightly alkaline. As estrogen levels rise during puberty, glycogen becomes more abundant, leading to the predominance of lactic acid-producing bacteria.
These bacteria have the ability to ferment glycogen into glucose and ultimately form lactic acid. As a result, the pH level decreases, which creates an unfavorable environment for many pathogenic, “not so good” bacteria.
Traditionally, a high level of lactic acid bacteria is considered the hallmark of a healthy vagina, and in most women of reproductive age, lactobacilli predominate in the vagina.
When a woman goes through menopause, estrogen and glycogen levels decrease and, as a result, the number of lactobacilli in the vagina decreases. As a result, less and less lactic acid is formed, and the pH level increases.
Hormone replacement therapy during and after menopause counteracts this effect and contributes to a significant reduction in vaginal pH compared to postmenopausal women.
- The composition of the vaginal microflora differs significantly among women of reproductive age of different ethnic groups.
- Also, the dynamic balance of the vaginal microflora can be changed under the influence of environmental and external factors (for example, taking antibiotics, vaginal hygiene, sexual intercourse, hormonal therapy, etc.). These changes can lead to microbial imbalance or dysbiosis in the genitourinary tract.
In a review of studies published between 1966 and 2003, bacterial vaginosis was diagnosed based on clinical presentation in 22–50% of cases, vulvovaginal candidiasis in 17–39%, and trichomoniasis in 4–35% of cases. In approximately 30% of cases, it is not possible to make a diagnosis based on complaints.
The absence of itching makes the diagnosis of vulvovaginal candidiasis unlikely. The absence of a specific, unpleasant, “fishy” odor of vaginal discharge makes bacterial vaginosis unlikely.
The presence of signs of inflammation and the absence of an unpleasant odor is more often associated with vulvovaginal candidiasis.
To confirm/exclude the diagnosis of “bacterial vaginosis” and “vaginitis”, visual assessment of microflora disorders in the vagina, microscopy of smears for flora is used (otherwise - a smear for the degree of purity, a smear for GN, a microscopic examination of the discharge of the genitourinary organs of women (microflora)).
During microscopy, 4 main patterns can be observed, which were previously called “degrees of vaginal cleanliness.” Now they use different terminology and classification, but the essence of the study remains the same.
What composition of vaginal bioflora is considered normal?
Normally, in the vaginal microflora, the ratio of anaerobic to aerobic bacteria should be from 2:1 to 5:1. During inflammation, the microflora changes to levels from 100:1 to 1000:1. Also, leukocyte and epithelial cells are normally absent.
Various factors can disrupt the normal biocenosis of the vagina:
- weakened immunity due to stress or illness, hypothermia;
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, abortion, taking contraceptives);
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- diarrhea, dysbacteriosis, vitamin deficiency;
- sudden climate change;
- genitourinary infections;
- synthetic underwear, nylon tights (they do not allow air to pass through and create conditions for the development of anaerobes), daily use of pads.
Red blood cells in biomaterial for cytology
In some cases, red blood cells in a smear in women can be detected in the biomaterial for cytology. This happens due to the fact that the specialist took the material for the smear roughly and accidentally destroyed the vessels that pass through the delicate tissue of the cervix.
In this case, after taking a smear, a woman may experience a slight discharge with a small admixture of blood for several hours. Of course, under these circumstances there will be a large number of red blood cells in the smear.
In this situation, the presence of blood cells will not be a pathology. The doctor who took the material for the study noted on the form accompanying the microslide the real reason for the presence of red elements - red blood cells in the smear, which normally should be absent. The reasons for the appearance of these bodies can be different, ranging from the area where biomaterials were taken and ending with circumstances independent of the patient’s health status.
How to understand that the biocenosis is disturbed
Disturbance of biocenosis occurs not only in adult women, but also in preschool children. In Soviet times, all children wore inelastic cotton tights, because other products simply were not sold. But a violation of the girl’s microflora was rare
Today, all sexually mature women have experienced microflora disturbance to one degree or another. The deviation of the biocenosis from the norm is evidenced by the following facts:
- cheesy or gel-like vaginal discharge;
- unpleasant pungent odor;
- burning when urinating, itching in the vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen as during menstruation;
- feeling of discomfort during sex.
Corpuscles in a smear from the urethra
Red blood cells that were found in a smear from the urethra may be symptoms of a tumor or stones in the urinary tract. Blood in urine will never be normal. This condition indicates acute inflammation, including inflammation of a bacterial nature. The most common reason for the appearance of bodies in a smear from the urethra is traumatic urethritis. The cause of this pathology is often a certain medical procedure associated with mechanical entry of blood into the urethra.
Which biocenosis analysis is the most informative: femoflora smear 16
One of the most effective tests for identifying the picture of vaginal biocenosis is Femoflor screening. This technique is based on the polymerase chain reaction PCR technique. This is a molecular biology method that allows you to isolate the DNA of a particular virus, fungus or bacteria. As a result, the doctor receives a picture of the composition of microorganisms - pathogenic and beneficial.
The most popular is the microflora smear, known as Femoflor 16. It helps to identify 16 bacteria that live on the walls of the vagina and separate healthy microbiota from pathogenic microorganisms. This analysis is a scraping from the mucous walls of the vagina.
From minor children under 16 years of age, material can only be collected for study under the supervision of an adult. Pregnant women with a gestational age of more than 22 weeks do not take a smear for bioflora due to the high likelihood of complications.
What doctors don't see with microscopy
- Pregnancy.
To determine it, a smear is not needed and it does not matter what result it shows. It is necessary to take a blood test for hCG, undergo a gynecological examination by a doctor, or do an ultrasound of the uterus. It is possible to detect human chorionic gonadotropin in urine, but not in genital discharge! - Cancer of the uterus and cervix.
To diagnose malignant degeneration of the endometrium, histological material is needed, and in large quantities. And they take it directly from the uterus during separate diagnostic curettage.CC and other pathologies (erosion, leukoplakia, koilocytosis, HPV infection, atypical cells, etc.) are diagnosed based on the results of a cytological examination. This analysis is taken directly from the cervix, from the transformation zone, using a certain method with Papanicolaou staining (hence the name of the analysis - PAP test). It is also called oncocytology.
- Does not show infections (STDs) such as
:- herpes;
- chlamydia (chlamydia);
- mycoplasmas (mycoplasmosis);
- ureaplasma (ureaplasmosis);
- HIV.
The first four infections are diagnosed using the PCR method. And it is impossible to determine the presence of the immunodeficiency virus from a smear with high accuracy. You need to take a blood test.
Back to contents
Preparing to take a smear
Preparation for the study includes the same steps that are carried out in preparation for any other gynecological procedure. The material is submitted for study approximately on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle. During menstruation, a smear is not taken due to changes in the population of the vagina with microbial flora due to blood discharge.
Before taking a smear, a woman must avoid sexual intercourse 2 days before visiting the doctor, do not douche, do not use panty liners, ointments, etc. The test result will be considered correct if the amount of epithelium in the smear is approximately 105 units, and the total number of bacteria is 106 -108 units
When is the analysis performed?
As a rule, a smear on the flora is taken during any initial visit of a woman to a gynecologist.
Also, indications for taking a smear and its subsequent microscopy are:
- 1Routine preventive examinations and medical examinations.
- 2Pathological leucorrhoea (vaginal, cervical, urethral discharge), its unpleasant odor, profuse nature, color change.
- 3Pre-conception preparation as part of planning natural and IVF-induced pregnancy.
- 4Screening during pregnancy.
- 5Unpleasant, painful sensations in the lower abdomen, which the woman does not associate with the menstrual cycle.
- 6Painful urination, dysuria, including symptoms of urethritis, cystitis. Urological pathology in women, as a rule, requires consultation and examination by a gynecologist.
- 7Completing the course of antibiotics in order to determine the nature of the flora and the possibilities of its restoration.
What pathogens are identified by smear analysis of biocenosis and what data is obtained from the analysis?
The result of a smear test for bioflora can be the identification of microorganisms such as:
- Lactobacilli are the main representatives of normal biocenosis;
- Opportunistic microorganisms: enterococci, streptococci, enterobacteria, hemophilia, corynebacteria, gram-negative bacilli, staphylococci, Candida fungi.
By analyzing a smear for bioflora, the doctor receives information:
- About the growth of pathogenic microflora or its absence.
- About the number of fungi, bacteria and lactobacilli;
- About the degree of sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics (with a number of >104 CFU/tamp.).
A study on the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics is not carried out when the growth of concomitant and opportunistic flora is in low titer.
Treatment methods
An integrated approach to treatment is practiced, aimed at simultaneously destroying infectious agents, improving the patient’s well-being and preventing complications. The first choice drugs are antibiotics mainly from the clinical-pharmacological group of macrolides. Doctors prefer Azithromycin, Josamycin, Clarithromycin, Spiromycin. Cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and penicillins are also in demand in treatment. When choosing antibiotics, the sensitivity of gonococci to them, as determined by smear examination, is taken into account.
Since antibiotic therapy destroys not only pathogens, but beneficial bacteria of the intestinal and vaginal microflora, doctors prescribe probiotics with enterococci, lactobacilli and bifidobacteria - Hilak Forte, Linex, Acipol.
PCR smear - what is it?
The use of such means is also practiced:
- bacteriophages that can penetrate cells and destroy gonococci;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate pain, burning, cutting, lowering temperature, relieving inflammation;
- immunomodulators with interferons or stimulating their production in the body;
- antihistamines to prevent the development of an allergic reaction to medications and eliminate edema.
With advanced gonorrhea, mycoses often develop, which are eliminated by taking antimycotics. To destroy fungi, patients are prescribed Fluconazole and Nystatin.
What does a biocenosis smear reveal - Femoflor 16: normal and abnormal indicators
| Group | Name of microorganism | Normal indicators | Pathology indicators | What does it mean |
Facultative anaerobic | Lactobacillus spp (lactobacteria) | 80-95% of the total number of bacteria | Less than 80% indicates the displacement of lactic acid bacteria by pathogenic flora, mainly cocci. In combination with leukocytes, it indicates inflammation. | Responsible for the cleanliness of the vagina. They are present in large quantities in young girls, but tend to decrease with age. Determines the acidic environment of the vagina |
| enterobacterium spp (enterobacteria) | No more than 1% of the total number of microorganisms | More than 1% occurs due to incorrect selection of antibiotics | This anaerobic gram-negative bacterium is opportunistic. In its normal state it does no harm. When immunity decreases, it causes the development of infections. | |
| streptococcus spp (streptococci) | Any detection in a smear is not normal | Detection does not indicate infection | Is opportunistic microorganism, treated with antibiotics | |
| staphylococcus spp (staphylococci) | No more than 1% of the total number of microorganisms | Speaks of weakened immunity, eliminated with antiseptic drugs | Infected as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse or inaccurate hygiene procedures | |
| gardnerella vaginalis (gardnerella), Prevotella bivia, Porphyromonas spp | No more than 1% of the total number of microorganisms | More than 1% indicates infection with another disease | Normally it is not dangerous, but in combination with other infections. The most dangerous form is gardnerellosis, which leads to disastrous results. | |
Obligate anaerobic | Eubacterium (eubacteria) | 0,8% | Indicates bacterial vaginosis if all other indicators are normal | Gram-positive anaerobic bacterium, develops in women |
| Sneathia spp, Leptotrihia spp, Fusobacterium spp | 0,8% | Indicate bacterial vaginosis if all other indicators are normal | Gram-negative anaerobic rods | |
| Megasphaera spp, Lachnobacterium spp, Clostridium spp | 1% | Gram-positive rods cause bacterial vaginosis | ||
| Lachnobacterium spp, Clostridium spp | 1% | Gram-positive rods and cocci develop bacterial vaginosis | ||
| Peptostreptococcus spp. | Less than 1% | Promotes the development of genitourinary infections and abscesses | Anaerobic gram-positive rod. | |
| Atopobium vaginae | Up to 1% | Causes vaginosis | Anaerobic gram-positive rod. | |
mycoplasma | Mycoplasma | Up to 1% | Provokes the development of mycoplasmosis | A bacterium without a cell wall that causes STDs. |
| Ureaplasma | Up to 1% | Provokes the development of ureaplasmosis | A bacterium without a cell wall that causes STDs. | |
Yeast-like fungi | Candida spp. | Up to 1% | If the norm is exceeded, curdled discharge appears | Fungus that causes thrush. |
Based on the results of the analysis, the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the body can be determined. An increase in the content of one or more opportunistic microorganisms indicates an inflammatory process, the presence of a foreign body (fibroids, cysts), STDs (STIs), etc. The Femoflor analysis is carried out quickly and gives instant results. That. at one time the doctor can see the complete picture of a woman’s biocenosis.
The purpose of studying the microflora of the genital tract
The external genitalia, vagina and cervix of a woman are the birth canal through which the fetus passes. If an inflammatory process is detected in smears, there is a risk of infection of the child during childbirth, colonization of the skin and intestines with pathological microflora and the development of intestinal, skin and respiratory diseases.
If the smear results are unfavorable in the 1-2 trimesters of pregnancy, there is a high probability of infection of the membranes and waters (pathogenic microflora easily penetrates the uterine cavity through the cervical canal), damage to the placenta/chorion and intrauterine infection of the fetus. As a result, pregnancy may end in spontaneous miscarriage, premature birth, or the mechanism of water formation (low and polyhydramnios) and/or fetal development (fetoplacental insufficiency and intrauterine growth retardation) will be disrupted.
In addition, the pathological microflora of a woman’s genital tract also affects the course of the postpartum period. The risk of developing purulent-septic complications after childbirth increases (from suppuration of the perineal sutures to endometritis and sepsis). Also, taking control tests allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
A “bad” smear in the third trimester of pregnancy is dangerous due to infection of the membranes and their premature rupture, which leads to premature birth, as well as infection of the fetus. In addition, colpitis in the last trimester of pregnancy loosens the birth canal, it swells and is easily injured, which leads to numerous ruptures of the perineum, vagina and cervix during childbirth.
In addition, the pathological microflora of a woman’s genital tract also affects the course of the postpartum period. The risk of developing purulent-septic complications after childbirth increases (from suppuration of the perineal sutures to endometritis and sepsis). Also, taking control tests allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Examination of smears of the urogenital tract during pregnancy reveals:
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis;
- vaginal candidiasis (thrush);
- bacterial vaginosis;
- cervicitis;
- nonspecific vaginitis.
How to decipher the results of a smear: identified diseases
The interpretation of the results obtained is always carried out by a gynecologist. The doctor compares the data obtained with the results of examination using other methods and the patient’s complaints. There are several states of the vaginal dysbiotic process:
Normocenosis
It is characterized by contamination in the range of 106-108 CFU/tamp. Most of the microflora is represented by lactobacilli. Opportunistic pathogenic microflora (OPM) is completely absent or observed in low titer (<104 CFU/tamp.). When examining epithelial cells microscopically, cells of the superficial layer are found, less often of the intermediate layer. In some cases, “false key” cells are encountered.
Bacterial vaginosis
Under aerobic conditions, the growth of microorganisms is not observed or a weak growth of UPM is observed. The lactobacilli titer is low (< 104 cfu/tamp.). The microflora of the vagina contains gardnerella and anaerobes. There are “key cells”. Lactomorphotype bacteria are completely absent or detected in small quantities.
Vaginal candidiasis
It is divided into candidal vaginitis, asymptomatic carriage of fungi and a combination of candidal vaginitis with bacterial vaginosis, depending on the number of UPM and fungi. With candidal vaginitis, the number of all microorganisms reaches 108 CFU/tamp., fungi - >104 CFU/tamp., lactobacilli - >106 CFU/tamp. The epithelium is represented by cells of different layers. The microflora is dominated by lactomorphotypes of bacteria. Yeast-like fungi and blastospores are observed. Leukocytes - 10-50 or more in the field of view.
Combination of candidal vaginitis and bacterial vaginosis
Characterized by a low content of lactobacilli and the absence of their growth. Fungi and “key cells” are present. The predominant morphotypes are Gardnerella. Epithelial cells are multilayered.
Asymptomatic carriage of fungi can be determined by an increase in the number of lactobacilli and fungi. The epithelium is represented by cells of the superficial layers. The leukocyte reaction is weakly expressed. Yeast-like fungi are not visualized or are isolated in the field of view.
Nonspecific vaginitis
The increase in the number of one of the UPM representatives is noticeably predominant. The number of lactobacilli decreases sharply or is equal to zero. The epithelium is represented by heterogeneous cells. The microflora is dominated by gram-positive cocci or polymorphic rods.
Cytological vaginosis
The culture shows an increase in the number of lactobacilli in a high titer (> 108 CFU/tamp.). Epithelial cells are presented in a disintegrated form. There is no growth of pathogenic microflora. Lactomorphotypes are visualized in large numbers.
Vaginal atrophy
There are no opportunistic microflora and lactobacilli. When studied in depth, the epithelium is represented by cells of the intermediate layers. This depends on the degree of atrophy. Microflora is practically absent or occurs in isolated cases. The number of leukocytes is 10-15 per field of view.
Intermediate microcenosis
Characterized by a decrease in the number of lactobacilli, there is no growth of microflora. The epithelium is represented by superficial cells. There are no more than 10 leukocytes in the field of view, there are “key cells”. The amount of microflora is moderate. Anaerobes predominate.
Reasons for performing culture in gynecology
- If the smear contains a moderate or large number of leukocytes, but the causative agent of the infection is not known. Since with microscopy there is a lower limit for the detection of microorganisms: 10 to 4 - 10 to 5 degrees.
- If a microbe is identified, to determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- If there are signs of a fungal infection. To accurately determine the type of fungi and prescribe an effective antimycotic drug.
Some types of fungi, for example, Candida albicans (a diploid fungus), are very dangerous for expectant mothers and can cause infection and premature rupture of the membranes.Other types of Candida fungi do not need to be treated if there are no pathological symptoms.
If key cells are found (signs of bacterial vaginosis), but besides them, other microbes are also present. For identification.
Back to contents
Practical advice
Tip #1
Women and men who frequently change sexual partners should be tested for gonococci at least twice a year. Regardless of whether they use barrier contraceptives for protection or not.
Tip #2
Treatment should not be stopped after the symptoms of gonorrhea disappear. A person is considered healthy only after a repeated negative smear test.
Tip #3
In order not to worry about the results of a smear for gonococci, you should refrain from casual contacts and use barrier types of contraception.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Are additional examinations needed? Yes, we do. With their help, it is possible to identify developed complications and determine therapeutic tactics. The doctor may prescribe colposcopy, urethroscopy, or cervicoscopy.
When will the results be ready? The readiness of the research results depends on the workload of the laboratory, but on average does not exceed one day (bacterial culture - up to a week). In case of urgent need, data can be obtained within three hours. The analysis should be deciphered by the attending physician.
Does it hurt when taking a smear? Touching the instruments may cause minor discomfort. Severe pain occurs only with a strong infectious-inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, for example, with ulceration of the cervical canal mucosa.