For women's health, you need to take care of your body. This especially applies to the uterus. This organ is responsible for bearing a child, and if abnormalities, infections or pathologies occur, it is necessary to undergo timely treatment.
A woman needs to know about her body, and what sizes of the uterus are normal, and what sizes indicate problems with the health of the reproductive organ.
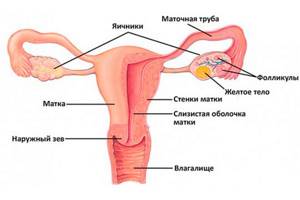
Its structure and main functions
The uterus is shaped like a pear. Its peculiarity is compression in the front and back.
Structure of the uterus:
- At the back it is adjacent to the rectum. The front is covered by the bladder. It is held between these organs by strong flexible ligaments. They are penetrated by a network of blood vessels and nerve endings.
- The uterus has three openings or exits. From below, the cervix passes into the vagina. At the location of the bottom of the organ there are exits to the right and left fallopian tubes.
- The bottom of the reproductive organ is located above the line where the fallopian tubes exit. The body itself has the outline of a triangle. They taper as they become the round cervix. It is an extension of the body.
- The cervix has a third of the length of the entire organ . The outer end exits into the upper part of the vagina. This segment is called the supravaginal part. There are edges on the back and front walls. They separate them from each other.
- The visible part of the cervix in the vagina is covered with epithelium . This part contains an important zone in which inflammation processes can occur. The ecclesiastical canal has a mucus plug. A secret comes out of it. It prevents viruses and infections from entering the uterine cavity.
The structure of the walls of the uterus is presented in the form of three layers of tissue:
- The mucous membrane, which is the inner layer.
- Muscle tissue that forms the middle layer.
- The serosa is the outer layer of the reproductive organ.
The uterus in the female body has the following important functions:
- Protection of the genitals and peritoneum from infections that can come from the vagina.
- Cleansing the vagina and uterus of dead tissue or blood cells through menstruation.
- Creates conditions for sexual intercourse and transports sperm to the fallopian tubes.
- Creates conditions for the development of the embryo and implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterus.
- Strengthens the pelvic floor.
Surgical treatment for fibroids
The “golden” standard for the treatment of fibroids in leading European and American clinics is myomectomy—removal of nodes followed by suturing of the uterus. The presence of a capsule around the node allows it to be removed using the “husking” method, while the myometrium surrounding the capsule is practically not damaged.
The operation is performed using laparoscopy - through several small incisions on the anterior abdominal wall, the size of which does not exceed 10 mm. To eliminate the risk of intraoperative complications (bleeding, the need to switch laparoscopy to open access, etc.) for the safe removal of large fibroids, Professor Puchkov developed a unique organ-preserving technique - myomectomy with temporary occlusion of the uterine arteries.
During the operation, the vessels of the uterus are blocked, which leads to a temporary cessation of nutrition to the organ. Thus, the nodes are removed in a “dry” surgical field. In addition to eliminating the development of bleeding, the intervention area is clearly visible, which allows you to match the muscle layers as accurately as possible, suturing the wound efficiently and reliably. In the future, the formation of a defective scar is practically excluded. At the final stage, the blood supply to the uterus is completely restored.
The use of modern instruments and equipment (ultrasonic scissors, the LigaSure device, the V-lock system (Covidien), the latest generation suture material, anti-adhesion barriers, etc.) allows the operation to be performed quickly and bloodlessly, while recovery also takes much less time than with open access.
Thanks to organ-sparing myomectomy, a woman planning to have a child in the future has every chance of becoming a mother. Patients who do not plan to conceive can maintain menstrual function until the onset of natural menopause, which makes it possible to maintain the same quality of life.
If there are contraindications to organ-sparing myomectomy, the patient may be recommended a radical operation - removal of the uterus either along with the cervix, or with preservation of the appendages and cervix - in this case, it is possible to maintain the hormonal status, avoiding the development of undesirable consequences associated with disturbances in hormone levels. By the way, radical surgery is also usually performed using laparoscopy, which has a number of advantages.
When choosing a technique and volume of intervention, an individual approach to each patient should be followed. We always strive to perform organ-preserving surgery using a unique proprietary technique, which is now included in the standard of surgical treatment in the best clinics in France, Switzerland and Germany.
What is ultrasound used for?
The use of ultrasound helps to distinguish the 3 layers of the uterine cavity. Doctors usually pay attention to endometrial tissue. It is he who is updated monthly when a woman gets her period. During pregnancy, a fertilized egg is located in this layer.
It is the violations in the structure of the endometrium that will help determine the use of ultrasound. Ultrasound examination reveals muscle tissue and allows you to detect a violation in its layer.
How is an ultrasound of the uterus performed?
During a transabdominal ultrasound, the patient needs to expose her stomach and lie on her back. The doctor will apply an ultrasound gel to the surface to be examined and begin the examination with the sensor. During transrectal diagnosis, the woman should take a lateral decubitus position. The doctor will use a special thin sensor (inserted into the rectum).
During a vaginal examination (a sensor is inserted into the vagina), you need to remove your underwear and lie on your back with your knees bent. For hygienic purposes, a sterile condom is placed on the sensor during transvaginal and transrectal diagnostics.
Types of examinations for women
A woman seeks help from a gynecologist when unusual abnormalities appear in the menstrual cycle or when planning pregnancy.
When diagnosing a problem, a specialist may resort to the following examinations:
- Manual examination;
- Examination using a gynecological speculum;
- Smear analysis for vaginal microflora;
- Analysis of material to identify viruses and infections;
- Colposcopy;
- Ultrasound examination;
- Hysteroscopy and laparoscopy;
- Taking blood for hormone analysis.
Clinical manifestations and complications
Uterine fibroids for 4-5 weeks are not accompanied by any characteristic symptoms, however, as the formation grows, painful sensations may appear in the lower abdomen, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and uterine bleeding occurs. As a result of prolonged bleeding, anemia develops. Large myomatous nodes can compress neighboring organs, which is accompanied by constipation, frequent urination; due to compression of the ureter, the outflow of urine may be impaired, which can cause severe kidney disease.
Myomatous nodes can also cause infertility, but if conception does occur, there is a high risk of miscarriage, premature birth or complications during childbirth. In addition, frequent complications include torsion of a pedunculated myomatous node; then, if the blood supply is disrupted, necrosis with the development of peritonitis is possible.
With submucous fibroids, the uterus may contract and a myomatous node will be “born,” which is accompanied by intense pain and bleeding. The risk of malignancy should also be considered; degeneration of fibroids into a malignant formation is observed in 2% of patients.
The size of the uterus is normal according to ultrasound during reproductive age
The normal uterine size indicators for each nulliparous woman look different. It is individual in nature. It all depends on the size of the organ. This is considered a third of the length of the uterus.
Basic indicators
The following factors can influence the indicators:
- Endocrine system disorders;
- Number of times of conception, pregnancy and past births;
- Individual indicators of a woman’s body;
- Phases of the menstrual cycle.
Indicators during menstruation can fluctuate from the beginning of the cycle to the end. The minimum values may be on the first day, and the maximum on the last. Normal condition during ultrasound examination of the uterus, the thickness of the mucous membrane depends on the menstrual cycle. On days 5 or 7 this figure does not exceed 6 mm. After two weeks it increases from 7 to 14 mm.
Uterus dimensions
| Group of women | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm |
| Women of reproductive age | 47 | 35 | 50 |
| Women who have not given birth but were pregnant | 54 | 38 | 55 |
| Women after childbirth | 61 | 42 | 60 |
Indications for surgery
- Uterine bleeding or menstrual dysfunction;
- Active growth of nodes (more than 4-5 weeks per year);
- Large and giant fibroids, uterine size more than 11 weeks;
- Pain syndrome;
- Submucosal, subserous nodes, atypical location;
- Development of complications: anemia, necrosis, disruption of various organs, infertility, etc.;
- Risk of malignancy.
For a written consultation, in order to choose treatment tactics in your case, you can send me a complete description of the ultrasound of the pelvic organs, indicate your age and main complaints [email protected] [email protected] Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.
The size of the uterus is normal according to ultrasound during menopause
During menopause, women are prescribed an ultrasound of the reproductive organ. This examination is standard for diagnosing pathologies. This method provides fairly accurate information. The ultrasound method is considered safe and women do not dislike the process.
Basic indicators
When a woman enters menopause, an ultrasound scan pays attention to the following indications:
- Density of the reproductive organ;
- Anteroposterior size;
- State of atrophy of the mucous layer;
- Detection of adhesions in the reproductive organ.
During this period, a woman has a thin mucous layer. The thickness is reduced to 6 mm. When the indicator crosses this threshold and continues to fall, this indicates the beginning of a climatic period. Deviations may be several mm. Hormonal disorders and the state of the reproductive system can affect the indicators.
Dimensions
| Period | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm |
| First 5 years | 56 – 58 | 30 – 32 | 41 — 42 |
| After 5 years | 51 – 54 | 26 – 28 | 37 – 39 |
Service cost*
| NAME | PRICE (Kolomenskaya) | PRICE (Vidnoe) |
| Transabdominal ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages (using a Voluson, Mindray, Logiq device) | 1850 rubles | 1850 rubles |
| Transvaginal ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages (using a Voluson, Mindray, Logiq device) | 2050 rubles | 2050 rubles |
| Transrectal ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages (using a Voluson, Mindray, Logiq device) | 2050 rubles | 2050 rubles |
We accept payment:
*Attention! The indicated prices are provided as reference information and do not constitute a public offer. Check current prices by phone and directly in clinics.
Permissible deviations from the norm
The gynecologist usually evaluates the deviation from the normal size of the reproductive organ and prescribes an ultrasound examination on the first day of menstruation.
Deviations in women can be presented in a table
| Length deviation | Width deviation | Thickness deviation | |
| Women of childbearing age, during pregnancy and childbirth | 3 mm | 6 mm | 2 mm |
| During menopause | Length deviation | Width deviation | Deviation of anteroposterior size |
| Before 5 years and after 5 years | Up and down by 30 mm | ||
When cervicometry is performed regularly
If during pregnancy you have previously had problems with premature termination of pregnancy or have undergone cervical surgery, you must inform your doctor about this, who will prescribe cervicometry and, after studying the results, take all measures to preserve the pregnancy.
In case of multiple pregnancy, regular cervicometry is prescribed, which is carried out at the 4D Clinic in Pyatigorsk once every fourteen days, starting from the 16th week.
It is very important to carry out cervicometry during the first pregnancy, since there is no data on previous pregnancies yet. This is necessary in order to ensure that there are no abnormalities and to check the indicators of the internal organs and the fetus.
Size of the uterus during pregnancy and after childbirth
During an ultrasound examination and detection of pregnancy, the size of the reproductive organ will increase.
The main indicator at this moment is the length of the uterus. The gynecologist monitors her indicators starting from the 3rd trimester. Before this period, the size of the uterus is checked by manual examination or ultrasound examination using a vaginal probe.
A specialist is able to determine the gestational age by the size of the reproductive organ. He is able to detect abnormalities using the size of the uterus. The gynecologist is able to use palpation to determine how the organ will increase further.
This happens when a woman begins her 3rd month of pregnancy. With each week, 1 cm is added to the previous size. At the time of birth, this figure can reach up to 40 cm.
If a slight deviation from the norm occurs, this is not a pathology in all cases. The indicators for each woman are individual and if they are good enough, the specialist recommends undergoing a preventive examination once a year.
Causes of uterine enlargement
The uterus consists of muscle fibers that can stretch. This is one of the organs whose size can vary greatly depending on its condition. Enlargement of the uterus is much more common than its reduction.
When asking the question “the uterus is enlarged - what does this mean?”, patients should understand not only the causes, but also the consequences of this process.
The causes of uterine enlargement are physiological and pathological.
The most pleasant reason for an enlarged uterus is pregnancy. But expectations do not always correspond to reality. Therefore, the reasons for an enlarged uterus with a negative pregnancy test can also be:
- approaching menopause;
- benign formations (most often these are fibroids - a tumor developing from the muscular layer of the uterus);
- cyst-like formations;
- uterine adenomyosis (spreading of the endometrium into other layers of the uterus);
- the occurrence of malignant tumors of the uterus;
- so-called molar pregnancy. This is a disorder of the development of the placenta, which can occur at different stages of pregnancy and is accompanied by more or less abnormal hypertrophy of fetal tissue. Molar pregnancy is thought to be due to a genetic error;
- in some women - in the postpartum period. Why is the uterus enlarged after childbirth? This primarily depends on the ability of its walls to contract. With their atony, the uterus may not return to its original size for some time after birth.
Prevention of uterine diseases
To prevent illness, it is better to take care of your health right away. It is necessary to carry out prevention, which consists of certain actions. Every woman needs to do them.
Even minor measures will help prevent the development of a serious disease. In some cases, preventive measures improve intimate life.
To take care of your health you need:
- Visit a gynecologist once a year. Take the necessary tests to detect bacterial microflora of the vagina and other examinations.
- Visit a mammologist once a year. You can observe the mammary glands on your own from the first day of your period.
- It is important for a woman to have sexual relations . During sexual intercourse, more blood begins to flow into the uterus.
- For adult women, it is necessary to do special exercises to strengthen the vaginal muscles.
- You should pay attention to genital hygiene , especially during sexual intercourse.
- When the menstrual cycle begins, it is necessary to take more care than usual about the cleanliness of the genitals.
- You need to ensure timely emptying of the bladder ; if you hold back, the position of the uterus may change.
- It is necessary to maintain proper nutrition , which is dominated by vegetables, fruits and other foods containing vitamins and macroelements.
- You should keep yourself in shape and exercise, but not overwork as much as possible.
Each woman has individual indicators of the normal size of the uterus. However, they are usually rounded and often have minor deviations.
Characteristics of the most common causes of uterine enlargement
The size of the uterus by week of pregnancy is not the only criterion. Fibroids are one of the most common causes of uterine enlargement. Factors that provoke the occurrence of this benign tumor:
- hormonal shift;
- irregular sexual relations;
- lack of satisfaction from sexual life;
- medical abortions;
- traumatic birth;
- genetic predisposition;
- long-term chronic diseases (obesity, hypertension);
- passive sedentary lifestyle.
An increase in the size of the uterus due to enlarging fibroids should cause caution, as unpleasant complications may arise:
- inability to get pregnant;
- miscarriage and termination of pregnancy at different stages;
- malignancy (degeneration into a malignant neoplasm).
According to some authors, a uterine cyst is one of the ten most common causes of uterine enlargement. Often the cyst leads to an uneven, “one-sided” enlargement of the described organ: the uterus itself is small in size, but with a huge protruding cyst.
Rapid growth of the uterus may indicate a malignant lesion, which should cause clinical concern among physicians. Women at risk:
- with obesity of any degree;
- with polycystic ovary syndrome;
- previously nulliparous;
- who have reached menopause earlier than usual.
Therefore, one should not only ask the question of what size the uterus should be normally and how it changes in pathology, but at the same time evaluate the symptoms and associated factors.
When is cervicometry necessary?
Carrying out cervicometry during the period when a woman is pregnant is necessary for the following symptoms:
- If it is determined that the pregnancy is multiple;
- If there have been surgical interventions on the organs of the reproductive system performed before pregnancy;
- If it is diagnosed that the cervix is short;
- When establishing isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
It is worth noting: if the gynecologist who is caring for the patient’s pregnancy gives a referral for cervicometry, it cannot be ignored; it is necessary to undergo an examination.