Why do you need to do an ultrasound after childbirth?
Ultrasound of the uterus after childbirth, especially if there was a cesarean section, helps specialists monitor the condition of the woman’s internal organs. Having identified deviations from the normal course of recovery in time, the doctor can prescribe a course of treatment.
In addition, during surgery, a scar from the suture may remain on the inner surface of the uterus, which will affect subsequent births. Therefore, experts recommend that an ultrasound scan of the uterine scar after a cesarean section be performed.
How does the uterus change after cesarean section?
The uterus is large and has a damaged inner surface. Over time, the process of healing and reduction occurs. Ultrasound records a decrease in the size and weight of the uterus, but after a cesarean section the process occurs more slowly and is accompanied by postpartum discharge.
It is important for the specialist to monitor the condition of the internal organs after surgery and stimulate the speed of their recovery with the help of medications, if necessary. Therefore, regular ultrasound of the uterus is especially important after a cesarean section.
Pathogenesis
The main links in the pathogenesis of uterine subinvolution are: low activity of the uterine muscles, a decrease in its contractility; severe and prolonged postpartum tissue swelling; slow resorption of collagen fibers in the uterine wall. The myometrium contracts poorly if during pregnancy it was too stretched (large fetus, polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancy) or the neurohumoral regulation of the smooth muscles of the uterus is impaired. This mechanism is the main one when the complication is primary. Low uterine contractility affects not only recovery after childbirth. In such a situation, the infection penetrates more easily into its cavity, causing inflammation that ends in endometritis.
The second mechanism that contributes to the rapid reduction in the size of the uterus is a decrease in tissue swelling. Immediately after childbirth, the inner layer of the uterus resembles a continuous wound. But after 4-10 days it heals, the lumen of the blood vessels narrows, and tissue swelling goes away. If there are foreign bodies in the cavity or it is infected, swelling persists for a long time, blood flow in the capillaries, arterioles and small veins is disrupted. Delayed lysis of collagen is also noted, but this phenomenon cannot yet be fully explained.
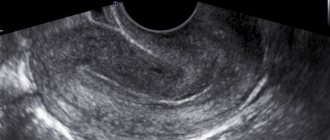
How is an ultrasound of the uterus performed after a cesarean section?
Most often, the examination is carried out on the first day after birth using a transabdominal method.
, that is, through the abdominal wall.
A transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus
is performed after a cesarean section, when a specialist needs to determine the condition of the cervix. Then the sensor is inserted into the vagina. The question of when to perform an ultrasound of the uterus after a cesarean section and how to do the examination is decided by the specialist based on an analysis of the patient’s condition.
Treatment of subinvolution
First, the doctor determines the cause of uterine subinvolution. To do this, a vaginal examination, ultrasound, and smears are taken for pathogenic flora. In complex cases, an MRI may be required.
Treatment is prescribed based on diagnostic results:
- If particles of the placenta or fetal bladder are retained in the uterine cavity, they are removed by vacuum aspiration. This is the name for a gentle type of uterine cleaning performed with special equipment, the principle of which resembles the operation of a vacuum cleaner. Then the uterus is thoroughly washed with a special disinfecting solution.
- To enhance muscle contraction (if they are weak or stretched), the doctor will prescribe hormones - they can be injected intramuscularly or into the uterus.
- In case of infection, antibiotics are prescribed that are not contraindicated during feeding, antipyretic and restorative drugs. The choice of medications is made by the doctor individually, based on test data and the general condition of the patient.
There are other treatment methods; the treating gynecologist will tell you about them in more detail.
Important! It is necessary to start putting the baby to the breast as early as possible - feeding stimulates the uterus, returning it to the physiological prenatal position.
Prevention of subinvolution involves timely treatment of genital and urinary tract infections, proper preparation for childbirth, as well as the right choice of maternity hospital and doctor.
Or sign up by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free)
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
What will an ultrasound of the uterus show after a cesarean section?
The recovery period can last up to 6 weeks after birth. Within a month and a half, involution of the organs of the reproductive system occurs - they return to their pre-birth state. The process can be complicated, so the size of the uterus, shape and other important changes after cesarean section should be monitored by a specialist using ultrasound data.
By the end of 3 days, the shape of the uterus should become round. In the future, changes in the contours of the uterus on ultrasound will be more and more noticeable; by the 5th day after cesarean section it should become oval. With normal postpartum recovery, the uterus will be pear-shaped within a week.
Another important indicator of normal involution is the position of the uterus. On the 4th day, it takes a position between the navel and pubis. On an ultrasound of the uterus, done on the 9th day after a cesarean section, it will be higher than the womb.
Uterus dimensions
Normally, a decrease in uterine ultrasound is more and more noticeable every day after a cesarean section. On the 2nd day, its normal length and width will be 13.6-14.4 cm and 13.3-13.9 cm, respectively. On an ultrasound of the uterus on the 4th day after a cesarean section, it should normally be 11.5-12.5 cm in length and 11.1-11.9 cm in width. On the 8th day it should not exceed 10.6 cm in length and 10.5 cm in width.
An ultrasound can determine the weight of the uterus; every day after a cesarean section it should decrease. On the 7th day, the organ should weigh 500-600 g, after two weeks - 350 g. On the 3rd week, the normal weight for the uterus is 200 g, and after six weeks - 60 g.
Clots in the uterus after cesarean on ultrasound
Clots on an ultrasound of the uterus immediately after a cesarean section are concentrated in the upper sections. With normal recovery, after seven days there should be fewer clots and they should move downwards.
If clots continue to appear on an ultrasound of the uterus for a long time after a cesarean section, an inflammatory process has most likely begun. Then the uterus will contract more slowly than it should, and its internal cavity will be deformed and expanded.
Symptoms: what does a woman feel with uterine subinvolution
The symptoms of this pathology are clearly expressed:
- uterine contractions when breastfeeding a baby are not felt or are weak;
- prolonged bleeding from the genital tract, the color of the discharge is closer to burgundy;
- possible fever, weakness, poor health, headache, palpitations.
During the examination, the gynecologist will notice an enlargement of the uterus, swelling and opening of the cervix by 2-3 fingers. When blood or lochia (postpartum discharge) is retained in the uterine cavity, its shape becomes spherical and the consistency of the tissue becomes elastic. Sometimes the position of the organ changes, and an anterior or posterior bend is formed.
What kind of discharge is normal after cesarean section?
Immediately after surgery, constant monitoring is required. Specialists watch the patient’s standing and carefully monitor the amount and nature of discharge from the uterus. In the first 5-7 days, they resemble discharge during menstruation, but are more abundant (up to 500 ml). The discharge is usually red and contains clots.
Over time, the number of lochia decreases and their color becomes darker. By 4-5 weeks there are very few of them. The color of the discharge is dark. The process of restoration of the uterine mucosa ends by 6-8 weeks. By this time, the discharge should not differ from the discharge before pregnancy.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. When should a woman perform it and how to prepare?
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a mandatory, annual and safe procedure for women, which allows you to assess the condition of the organs quickly and accurately!
Diseases of the pelvic organs can already manifest themselves in adolescence, so if you have complaints, you should immediately sign up for an ultrasound examination of the pelvis. An ultrasound diagnostic doctor evaluates and describes the condition of the uterus, cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes, the presence and determination of the gestational age.
What complaints should be addressed to an ultrasound diagnostic doctor:
1. Menstrual irregularities
2. Painful menstruation, intermenstrual spotting, that is, in the middle of the cycle, or spotting before and after menstruation
3. If pregnancy is suspected, that is, absence of menstruation at the usual rate
4. Pain in the lower abdomen
5. Uterine bleeding
6. Suspicion of formations in the ovaries (cysts), fallopian tubes, uterus (fibroids, adenomas, etc.), cervix (cysts)
7. After surgical interventions, after childbirth, after abortions.
For examination of the pelvic organs, ultrasound diagnostics is the most informative, fast and relatively inexpensive service. But for a gynecologist, this is simply an irreplaceable procedure for clarifying the diagnosis and prescribing treatment!
What is the best way to prepare for research?
There are several ways to examine the pelvic organs using ultrasound:
• The first and most common is transvaginal (through the vagina).
It allows for the best ultrasound. Before it, you need to empty your bladder and the recommended day of the menstrual cycle is from 3 to 7 days of m.c.
• The second method is transabdominal - through the anterior abdominal wall.
This method is usually used for young girls who are not yet sexually active. Here, on the contrary, the study must be performed with a full bladder, that is, before the study it is better to drink 1 liter of water
• The third method is often found with obstetric ultrasound - screening ultrasound during pregnancy, here the indications are a certain stage of pregnancy (in the first, second and third trimester) in specified weeks. You can also drink some water.
How is the research going?
Before any ultrasound, it is better to empty the intestines and try not to eat gas-forming foods, so that the doctor can see better.
Ultrasounds are not performed during menstruation. The results of the study depend largely on the day of the menstrual cycle.
Before the study, it is necessary to pre-register by phone. 8-952-277-71-74, since not all medical doctors do ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
You should take your passport to the examination to complete medical documentation.
During the examination, you lie on the couch on your back (we only use disposable diapers), so you do not need to bring a diaper with you. With transabdominal, the woman frees her lower abdomen, and with transvaginal, she undresses below the waist.
The doctor lubricates the sensor with gel (during transvaginal ultrasound, a disposable condom is always used) and begins the ultrasound, which lasts from 5 to 20 minutes, on average 15 minutes. The procedure is absolutely painless, with the exception of acute inflammatory diseases in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. The patient then wipes off the gel and awaits his conclusion. The doctor prints out a report on the computer and gives recommendations on whether or not to see a doctor. Since the protocol is just a conclusion, and the final diagnosis is made by a gynecologist.
What can we see with ultrasound diagnostics?
- the size of the organs that are located in the pelvic cavity (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix). The size of the uterus depends on the number of pregnancies and births a woman has.
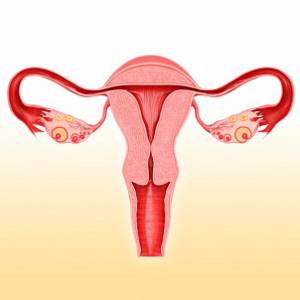
- location of these organs (correct and not, for example, the bend of the uterus)
— developmental anomalies (for example, bicornuate uterus, etc.)
- thickness of the endometrium and its structure
- the number of dominant follicles, their size - important when planning pregnancy (sometimes the doctor prescribes folliculometry - this is a description of the follicles in different phases of the menstrual cycle)
- benign or malignant formations (cysts, polyps, fibroids)
-Features of fetal development during pregnancy, gestational age
- presence of intrauterine contraceptives
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a very important diagnostic procedure! Therefore, dear women, if the doctor recommends it, do not refuse and follow the doctor’s instructions!
Where can I get an ultrasound of the pelvic organs?

In the medical office at the address: Ulyanovka village, st. Pobeda, house 39, Leningrad region, Tosnensky district.
Discounts are provided to pensioners, disabled people, mothers of many children in the amount of 3%. There is also a discount system for accumulating discounts from 3% to 7%.
This study is performed by a gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor Elena Vladimirovna Gubarkova,
Sycheva Maria Sergeevna
Prognosis and prevention
If subinvolution is not complicated by infection, then it is quite treatable. Within a few weeks, the size of the uterus returns to normal, so the prognosis for this type of pathology is quite favorable. For endometriosis against the background of subinvolution and other inflammatory diseases, therapy is more complex, and the consequences can be severe. There is a risk of developing sepsis, peritonitis, and infection of other pelvic organs. Prevention of subinvolution should be carried out in patients with pregnancy pathologies (late gestosis, polyhydramnios), when carrying a large fetus or two or more children. Such women in labor are required to be injected with oxytocin or its analogues, regardless of the course of the birth process and uterine contractions in the first days.
Classification
Many experts tried to classify uterine subinvolution, but most systems did not take root. This is due to the variety of mechanisms that lead to disturbances in uterine contractility and the influence of concomitant pathologies (preeclampsia, infections) on the course of the process. Most gynecologists now use a classification that is based on the etiology of the disease. Subinvolution is divided into several types:
1. Primary or true . This type of uterine subinvolution is rare. It is diagnosed in cases where there is no evidence of infection of the organ, but the myometrium contracts poorly. Primary pathology is divided into three more subtypes:
- Myogenic . Involution slows down due to the strong stretching of the smooth muscles of the uterus during pregnancy. The main factors that lead to the development of pathology are carrying twins or triplets, polyhydramnios, a large fetus, and rapid labor.
- Microcirculatory . With this subtype, microcirculation in the tissues of the uterus is disrupted, and swelling persists for a long time. The condition is provoked by gestosis in the second half of pregnancy, poor cleansing of the intestines and bladder on the eve of childbirth.
- Endocrine . Associated with disorders of neuroendocrine regulation in the postpartum period. This problem is caused by both the primary pathology of the neuroendocrine system and the late start of breastfeeding.
2. Infectious . One of the most common types of uterine subinvolution, sometimes considered as a stage in the development of endometritis. Viruses or bacteria, including opportunistic ones, act as pathogens in this pathology. The likelihood of subinvolution increases in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases (colpitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis). A favorable environment for the development of infection is created if parts of the placenta or blood clots remain in the uterus.
Types of research
- Transabdominal ultrasound. During the study, the doctor moves a sensor over the patient's abdomen. This type of ultrasound is used when examining virgins. It provides a high degree of accuracy, but requires preparation.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. It involves inserting a special sensor into the patient’s vagina.
- Transvaginal ultrasound with blood flow examination. It is performed in the same way as a regular study and allows you to determine vascular pathologies in the area under study.
- Combined ultrasound. It involves combining several of the above ultrasound diagnostic methods to obtain a comprehensive result.
Establishing diagnosis
Already when observing a pregnant woman with an obstetrician-gynecologist in the prenatal period, it is possible to say with a high probability whether she is at risk for the occurrence of uterine subinvolution. Women with multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios, large fetus sizes, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs, and gestosis require special attention. In the postpartum period, they are carefully examined in order to identify the first signs of pathology in time and begin its treatment. Patients are additionally prescribed:
- Regular examinations by an obstetrician-gynecologist. The doctor asks the woman in labor about the nature and amount of discharge, pays attention to subjective signs (pulling pain in the abdomen, absence of contractions during breastfeeding). If necessary, an examination is carried out in a gynecological chair and other examinations are prescribed.
- Inspection on the chair . During a bimanual examination, it is discovered that the size of the uterus does not correspond to the postpartum period, it is enlarged, and the organ has a pear-shaped-spherical shape. If the consistency of the uterus is elastic-soft, then there are parts of the placenta, fetal membranes or blood inside. In the mirrors, swelling and a purple tint of the cervix are noticeable, the cervical canal is dilated, allowing 1-2 fingers to pass through, and condensed blood can be seen in the lumen.
- Ultrasound . To timely identify a complication, two types of ultrasound examination are used - transabdominal and transvaginal, as well as three-dimensional echography. An ultrasound shows that the uterine fundus is located too high, does not correspond to the period after childbirth, and the walls of the organ are thickened. Ultrasound imaging can reliably reveal placenta remains and blood clots.
- Hysteroscopy . A special fiber-optic device is inserted into the internal cavity of the uterus to study its condition in more detail. In this way, symptoms of subinvolution and endometritis are identified; if necessary, it is possible to take tissue samples and secretions for examination and a more accurate diagnosis.
If the cause of the pathology is an infection, general blood and urine tests and biochemistry . The pathogen can be identified after bacterioscopy and culture of the contents of the uterine cavity and vaginal smears. Blood with the infectious type of subinvolution has typical inflammatory changes - high ESR, leukocytosis, anemia is detected after prolonged bleeding. In difficult cases, an MRI of the pelvic area is performed; the technique makes it possible to more accurately study the size of the uterus, the characteristics of the contents of its cavity, and changes in surrounding organs.