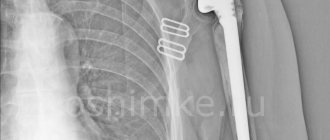
The ankle ranks third in terms of the incidence of osteoarthritis (9-25%), second only to the hip and knee joints.
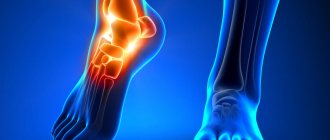
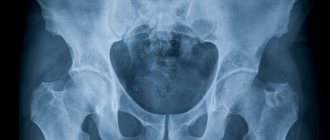
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint on x-ray.
The main cause of arthrosis of the ankle joint (crusarthrosis) is traumatic damage to its anatomical structures - the talus and tibia, the inner or outer ankles. Less commonly, the disease develops as a result of damage to the ankle by rheumatoid arthritis. And even less often, arthrosis occurs spontaneously, as a result of degenerative-dystrophic changes in cartilage and bone tissue.
What is osteoarthritis of the ankle joint
Arthrosis (deforming osteoarthritis, DOA) is a general name for a large group of diseases characterized by wear and tear of the ankle joint with progressive loss of its functions. The reasons for the development of diseases can be different. However, most often the pathology occurs as a result of severe injuries accompanied by damage to the articular cartilage. As a result, the gliding of articular surfaces is disrupted, which leads to further destruction of cartilage and bones. This is how osteoarthritis develops.
In rheumatoid arthritis, synovitis first occurs - an autoimmune inflammation of the synovium of the ankle joint. Cartilage, bone and periarticular tissues are affected later.
Osteoarthritis of the left (right in the picture) ankle joint
Arthrosis is characterized by the following changes in the ankle joint:
- degeneration of cartilage and deterioration of their shock-absorbing function;
- aseptic inflammation and swelling of the synovial membrane;
- softening and ulceration of cartilage, exposure of underlying bones;
- subchondral sclerosis of bone tissue;
- narrowing of the joint space and the formation of bone exostoses;
- hypotrophic and fibrous-sclerotic changes in periarticular tissues;
- progressive deformation of the joint with impairment of its functions.
Characteristic symptoms of crusarthrosis:
- "Starting" pain.
Typical for the initial stages of the disease. They occur after periods of rest, when a person begins to move. They disappear 15-20 minutes after you start walking. - Mechanical type pain.
They can appear in both early and late stages. Caused by stress on the ankle. They disturb a person during the day and disappear at night. - Constant pain.
They occur in the later stages of the disease, when reactive synovitis and reflex spasm of nearby muscles develop. - Decreased range of motion in the ankle.
It is typical for late stages, when the joint is deformed and can no longer cope with its functions.
With concomitant synovitis, patients are concerned about morning stiffness, a local increase in temperature, and swelling in the ankle area. In rheumatoid arthritis, the synovial membrane becomes inflamed primarily, in post-traumatic crusarthrosis - secondarily, in the later stages of the disease. Over time, relapses of synovitis occur more often and have more severe symptoms.
What kind of disease is this?
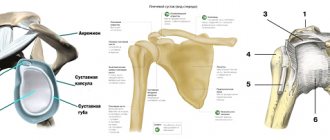
The ankle joint is a rather complex joint in the human body. Participating in its education are:
- talus, femur and tibia;
- several articular ligaments;
- lateral and medial malleolus.
On the left is a schematic representation of the structure of the normal ankle joint,
On the right is destruction of the joint due to arthrosis.
Thanks to the correct functioning of this joint, a person has the opportunity to make many movements in the foot, soften the impulse from the plantar part of the legs when jumping, walking, and running. Also, this joint largely provides maneuverability of movements.
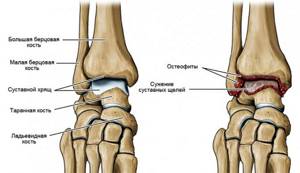
Like any joint in the human body, the ankle joint is equipped with cartilage layers. They reduce friction and provide shock-absorbing function. If an inflammatory process develops in the cartilage, accompanied by gradual degeneration and destruction of tissue, they speak of the development of arthrosis of the ankle joint.
The gradual thinning of cartilage tissue increases the load on the bones. Over time, when cartilage ceases to protect bone tissue, deformation of the joint affected by the disease begins.
Stages of deforming osteoarthritis of the ankle
There are up to ten classifications of the disease. Let's look at the main ones.
Stages of the disease according to the extent of damage to the articular cartilage:
- 1 — < 10%
- 2 — 10-25%
- 3 — 25-50%
- 4 — > 50%
X-ray stages according to Kellgren and Lawrence:
- 0 - complete absence of radiological signs;
- I — cyst-like changes in bone tissue, subchondral linear osteosclerosis, small marginal osteophytes;
- II — narrowing of the joint space, more pronounced osteosclerosis;
- III - massive subchondral osteosclerosis, severe narrowing of the joint space, large osteophytes;
- IV - massive osteophytes, deformation of the epiphyses of bones, almost complete absence of joint space.
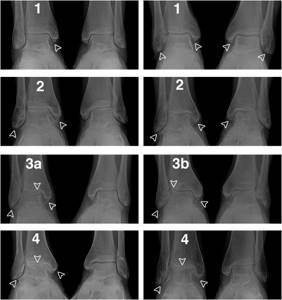
Stages of osteoarthritis of the ankle joint
Classification by N.S. Kosinskaya:
- Initial stage.
Characterized by damage only to articular cartilage. Radiographs may show a slight narrowing of the joint space, which is only noticeable when compared with a symmetrical joint. - Stage of pronounced changes.
The degenerative-destructive process involves bones with the development of subchondral osteosclerosis. X-rays reveal marginal osteophytes and uneven narrowing of the joint space by at least 50%. - Stage of pronounced changes.
It manifests itself as a pronounced limitation of ankle mobility. X-rays show large areas of osteosclerosis, massive osteophytes, bone deformation and a violation of the congruence of articular surfaces.
In clinical practice in Russia and the CIS countries, N.S.’s classification is most often used. Kosinskaya.
Reasons for development
Arthrosis of the ankle joint is a disease that not all people experience during their lifetime. Doctors identify a number of factors that contribute to the development of pathology. The main roles in the gradual destruction of the ankle joint are played by 5 main factors.
- High loads
First of all, physical activity has an impact on the joint. If it exceeds the joint's ability to adapt, articular cartilage begins to gradually deteriorate. That is why athletes and people suffering from obesity most often suffer from the disease.
- Defect in juxtaposition of articular surfaces
If the articular surfaces involved in the formation of the ankle joint are not aligned correctly, this leads to the development of the disease. It is explained primarily by the uneven distribution of the load. Various injuries to the ankle area, arthritis, diabetes and some other diseases contribute to the formation of defects.
- Shoes
Women are primarily at risk. High-heeled shoes have a negative impact on the joint. However, men can also be affected by this factor if they wear uncomfortable shoes for a long time.
- It has been proven that hereditary predisposition also plays a role in the development of the disease.
- Fractures of the ankle joint.
Diagnostics
To diagnose DOA, imaging methods are used that allow one to see pathological changes in the ankle. For secondary arthrosis caused by rheumatoid arthritis, gout, etc., laboratory methods are additionally used. With their help, the cause and nature of degenerative-inflammatory changes in the joint are revealed.
Instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Radiography.
Informative in the later stages of the disease, but does not always allow early changes to be detected. Using radiography, you can visualize subchondral osteosclerosis, osteophytes, bone deformities, and narrowing of the joint space. - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
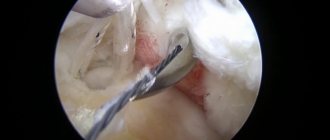
A modern, highly informative research method that allows you to identify almost any defects in cartilage tissue. MRI is informative in the early stages of arthrosis. - Arthroscopy.
An invasive procedure that requires penetration into the joint cavity. Allows you to study the morphology of cartilage and clarify the diagnosis using targeted biopsy. Rarely used.
Benefits of X-ray
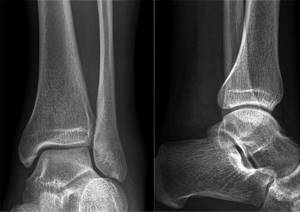
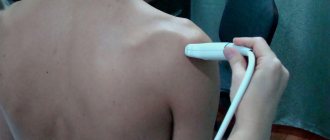
Radiography is one of the main diagnostic methods. It has a large list of indications, high reliability and information content, comparative ease of implementation, and there is no need for preparation. During the x-ray, the integrity of the skin is not damaged, everything is painless. The examination will take 5-10 minutes.
Fears about the dangers of X-rays are unfounded if the examination is carried out on a digital machine. It has a minimal load level, and the images are highly accurate and detailed. With such a device, you can take several pictures in a row (in different projections) in one procedure and undergo examination several times a year as needed. Digital X-rays are not only safer than analog ones, but also more convenient. There is no need to wait until the pictures are printed, all the results are stored on digital media, they are convenient to use, enlarge while viewing, and store. Therefore, when choosing a clinic where to have an ankle x-ray done, check the type of equipment used for the procedure.
Is it possible to treat conservatively?
In the initial stages, arthrosis is treated conservatively, with the help of medications, intra-articular injections and exercise therapy. However, the disease tends to progress despite timely and effective therapeutic measures. Therefore, most patients sooner or later have to lie on the operating table.
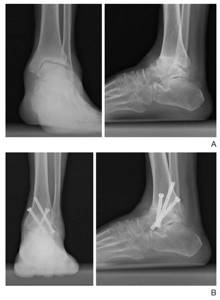
Arthrodesis of the ankle joint.
Previously, the gold standard of surgical treatment was arthrodesis - an operation aimed at completely immobilizing the ankle. On the one hand, it helped get rid of chronic pain. On the other hand, it changed the biomechanics of the foot and the entire limb, which disrupted the dynamics of walking and often caused lameness. Therefore, arthrodesis was abandoned, and endoprosthetics began to be performed instead.
How the research works
There is no need to prepare for an ankle x-ray. Typically, an x-ray of the ankle joint is taken in two projections: direct and lateral. The examination in direct projection is performed with and without rotation of the foot. The image shows the tibia, ankle, talus and ankle joint. In the lateral projection, the patient lies on his side, the healthy leg is bent at the knee and tucked towards the stomach. The images show: tibia, ankle, talus, calcaneus, navicular, ankle. In some cases, the doctor recommends an x-ray with a load - forceful flexion - to assess the condition of the ligaments. If necessary, such a study is performed under local anesthesia.
Decoding is carried out by comparing the images with the standard standard. The size, shape, bone structure, height and angle of the arch of the foot and other criteria are determined.
Conclusions about the norm or detected pathologies are recorded in a conclusion, which serves as the basis for making a final diagnosis.
Endoprosthetics
Endoprosthetics is a complex high-tech operation during which doctors remove a damaged joint and replace it with an artificial endoprosthesis. Surgical intervention allows you to completely eliminate pain, restore ankle mobility and the ability to support the limb. Today, endoprosthesis replacement is the method of choice in the treatment of DOA.
Now patients are fitted with the latest, third generation endoprostheses. They do not have the disadvantages of their predecessors and therefore provide good functional results. Their installation today is much preferable to traditional arthrodesis.
Types and degrees of pathology
Arthrosis of the ankle joint is a disease that does not develop immediately. The formation of the disease occurs gradually, in stages. There are 4 stages of the process in total.
- First stage . The doctor, conducting an objective examination, cannot detect any objective signs of changes in the joint. There are no changes on the radiographs.
- Second stage . Its development is most often triggered by trauma. The ankle area swells, movements become limited, and deformity is observed. The pain may gradually intensify. On an x-ray, the doctor will notice that the size of the joint space has significantly decreased. If we consider the lateral projections, we can note that the articular surface has become longer (bone growths), and the block of the talus has become flatter.
- Third stage . The third stage of the process is characterized by a clear change in the shape of the joint, which can be determined even without the help of radiographic examination. An atrophic change in the lower leg is noted. Movement is severely limited. The patient prefers to avoid movements in the damaged area.
- Fourth stage If treatment of the disease is not started on time, the process reaches a stage characterized by extreme narrowing and sometimes complete disappearance of the joint space. The bone contour can be deformed due to extensive growths. Subluxation is often observed.
Additionally, it is customary to divide the degenerative process in cartilage into primary and secondary. In the first case, initially intact tissues are damaged for some reason. In the second case, the joint is already subject to serious degenerative processes, and arthrosis only aggravates them. Some doctors understand secondary arthrosis as a post-traumatic form of the disease.
Let's sum it up
In the later stages of arthrosis, surgery is the only solution to the problem. Today, the best method of surgical treatment is total arthroplasty - replacing a damaged joint with an artificial implant. If performed successfully and without complications, the operation allows you to restore the mobility of the limb and restore your ability to work. As a rule, after 4-6 months a person returns to his usual lifestyle.
Endoprosthetics is a high-tech surgical intervention, the implementation of which requires the use of modern equipment and instruments. Therefore, it is better to have surgery in hospitals with a good material and technical base. And you should trust your health to highly qualified surgeons with extensive experience in endoprosthetics of large joints.
X-ray at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center
The medical center is located within walking distance from the Slavyansky Boulevard metro station at the address: Davydkovskogo Street, 5 and offers a full range of medical services. The use of the best international treatment practices, modern equipment, and compliance with service quality standards helped the center become a clinic worthy of patient trust. It is important for us that patients feel cared for, the friendliness of the staff, understand the doctor’s instructions, receive an accurate diagnosis and a correctly prescribed course of treatment. Our prices are affordable - the price of an x-ray of the ankle joint is 2250 rubles. Choose a convenient time and make an appointment at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center.
Also, for a complete diagnosis of problems with the musculoskeletal system of the lower extremities, in our center you can do an MRI of the calf muscle and x-ray of the feet.
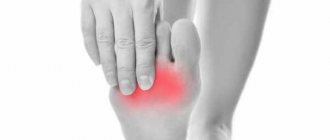
Symptoms of the disease
Ankle damage is considered quite insidious. In the early stages of the disease, symptoms may be completely absent. Naturally, a person who has no complaints does not go to the doctor. A patient visits the hospital for the first time only when signs of pathology begin to significantly reduce his quality of life.
Typical symptoms of the disease include:
- the onset of pain if the joint is forced to cope with significant loads;
- the appearance of sounds such as clicks, crunching, creaking when moving;
- gradual atrophy of muscles located in close proximity to the affected area;
- pain that occurs in the morning;
- rapid fatigue of the limb during exercise, including sometimes even simple walking;
- swelling of the affected area, sometimes a local increase in temperature;
- restriction of movement, which progresses over time to the point that the patient cannot move the foot;
- violation of the axis of the leg.
At the last stage of the disease, subluxations often occur. They are explained by the fact that the supporting function of muscles and tendons is disrupted, and large osteophytes appear.
Diagnosis methods
If you suspect the development of arthrosis of the ankle joint, it is recommended to immediately visit an orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor will conduct an examination and give recommendations on which diagnostic techniques are best to use. Radiography plays the most important role in diagnosing the disease. Using images, you can assess the condition of the joint axis and detect the bones and cartilage involved in the process. It is recommended to take the photo with a load on the leg. Radiography additionally makes it possible to understand whether neighboring joints are involved and, if so, how severe the process is. In some cases, based on radiography, the cause of the pathology can be assumed.
Additionally, computed tomography and MRI can be used.
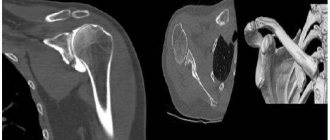
A
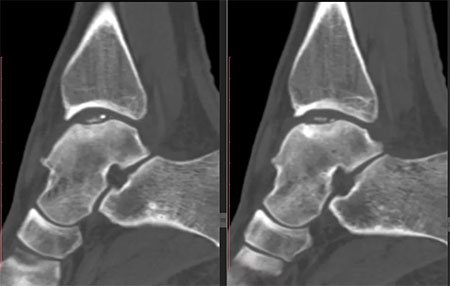
a. on radiographs arthrosis of the ankle joint, b. CT scan of the ankle shows necrosis of the talus.
Preparation and procedure
No special preparation is required for the study. The patient is placed on a special table, the groin area is protected with a lead apron. For children, additional protection is used for the thyroid gland and eyes; the baby is completely covered with an apron, leaving only a limb exposed.
An image of a joint or bone can be taken in one or more projections. To obtain accurate data, it is important to remain still. The study takes just minutes. The doctor sees the condition of the tissues immediately, and a conclusion with a transcript is issued after the procedure.
Excess body weight can become a hindrance - fat cells distort X-rays. This results in the picture not being clear enough. In this case, the attending physician will suggest alternative examinations. Sometimes it is possible to solve the problem by taking pictures from several projections. Some diseases and injuries require only a direct projection, others require a lateral projection, on both sides. Occasionally they resort to a combination of several options. This allows you to get the most accurate picture of the condition of the bone tissue.
Types of X-ray of bones and joints
Depending on the clinical picture and diagnostic need, the specialist chooses the type of x-ray examination. This can even be an isolated examination of any one bone or joint:
- X-ray of the elbow, wrist, knee and hip joints;
- hands and feet, fingers;
- sternum, collarbone;
- x-ray of the shoulder joint;
- pelvic bones;
- sacroiliac joints;
- x-ray of tubular bones.