Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that occurs due to Koch bacilli entering the human body. The disease is dangerous because it affects the respiratory system. Less commonly susceptible to tuberculosis are the bones, skin, lymphatic, genitourinary, nervous, lymphatic systems, as well as other organs and systems.
The immune system (the body's natural defense against infection and disease) of most healthy people kills the bacteria without causing symptoms. Sometimes the immune system cannot kill bacteria, but can stop it from spreading in the body. In this case, no symptoms develop, but the bacteria remain in the body. This is called latent (hidden) tuberculosis.
What happens when the TB pathogen (bacterium) enters the lungs?
There are 2 options:
- If your immune system functions well, the tuberculosis pathogen will be destroyed and the disease will not occur;
- Your immune system can control the infection, but it cannot kill the bacteria that causes TB. The body isolates the infection in the lungs and there will be no clinical manifestations. This condition is called infection. In Russia, about 70% of people over 30 years of age are infected. At any time, bacteria can begin to multiply (for example, when the immune system is weakened).
When the bacteria that causes tuberculosis begin to actively multiply in the lungs and destroy them, they speak of active tuberculosis.
Other treatments for tuberculosis
Surgery
The goal of therapy is the elimination of tuberculosis foci in the lungs with ineffective treatment, elimination of the consequences of pulmonary tuberculosis, and elimination of organ damage. All this is necessary to prevent the recurrence of the disease and to exclude the occurrence of complications.
Indications for surgical intervention can be any form of respiratory tuberculosis, especially in the case of complications that threaten a person’s life.
Chemotherapy
used with an optimal combination of anti-tuberculosis drugs aimed at eliminating mycobacteria and suppressing their reproduction. The duration of such treatment can reach up to a year - it all depends on the form and stage of development of the pathology.
If chemotherapy is stopped early, exacerbation or complications of tuberculosis may occur. Therefore, it is important to follow all doctor's recommendations. And the doctor, for his part, must draw up a detailed treatment plan and make adjustments throughout the entire therapy.
A patient who is indicated for chemotherapy as a treatment for tuberculosis must be prepared for the negative consequences of such an aggressive method. Side effects on the action of medications often occur. There are 2 types of adverse reactions: toxic and allergic. Dysbacteriosis may also occur.
The doctor may prescribe outpatient treatment if the disease is detected at an early stage and there is no infection to others. In this case, you need to regularly visit your doctor and undergo diagnostics. Most often, the patient is transferred to outpatient treatment after observation in a hospital and undergoing an extensive course of therapy in a tuberculosis clinic. At this time, the patient is no longer contagious.
Who is at risk for developing active tuberculosis?
The following groups of people are most susceptible to the disease:
- persons without a fixed place of residence;
- released from prison;
- living in shelters, boarding schools for the elderly;
- refugees, migrants;
- patients of drug treatment and psychiatric institutions.
There is a high probability of developing tuberculosis in people with chronic diseases of the respiratory system and cardiovascular system; receiving treatment with drugs that weaken the immune system; patients with diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, drug addiction; infected with HIV and patients with AIDS.
Course and prognosis
Primary tuberculosis
- in persons with unimpaired immunity usually ends in spontaneous recovery
- In immunocompromised individuals, primary tuberculosis has a progressive course.
Post-primary tuberculosis
- represents the reactivation of a persistent pathogen and is usually characterized by a progressive course
- With proper treatment of the Koch bacillus, the causative agent of tuberculosis, and a preserved immune system, the disease often ends in recovery
- Patients with active TB who are shedding bacteria should be isolated.
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Signs of pulmonary tuberculosis are nonspecific, that is, they can also appear in other diseases.
If you suspect tuberculosis, your doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- X-ray of the chest organs (if necessary, computed tomography of the lungs);
- Examination of sputum to determine the presence of the tuberculosis pathogen in it. If the cough is dry, then you have to use various methods of obtaining sputum for research (inhalation with substances that dilute sputum, etc.). The study must be carried out at least three times on different days;
- Tuberculin skin test (Mantoux test). The nurse will inject you subcutaneously into the forearm area with a special drug containing antigens (parts of protein molecules) of the tuberculosis pathogen. This test DOES NOT cause illness. After 72 hours, the doctor will determine the size of the papule (a red round lump slightly raised above the skin) on the forearm, which will help make a more accurate diagnosis.
Based on the results of the studies, a conclusion will be drawn about the presence or absence of the disease.
Alternative diagnostic methods
To date, medical equipment development engineers (America) and Rentgenprom CJSC (Russia) have developed a new type of tomograph - tomosynthesis.
The uniqueness and value of this development for people with tuberculosis is:
- in the frequency of examinations and low radiation dose relative to CT, which is ~40-70 µSV per procedure. On new CT scans the dose is up to 4000 µSV, on old ones up to 20,000 µSV. The difference is obvious.
- in the low cost of the procedure relative to CT. Tomosynthesis is comparable in price to a fluorograph apparatus. The problem is that the devices are not widespread throughout the Russian Federation, and not everyone will be able to find it in their city.
What to do if you have been diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis?
- DO NOT PANIC! In most cases, the disease can be cured with the help of modern highly effective drugs;
- Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis with folk remedies without the use of special anti-tuberculosis drugs is UNACCEPTABLE! None of the folk remedies can cure tuberculosis; for this purpose, special highly effective anti-tuberculosis drugs (antibiotics and antimicrobial drugs) have been developed. Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis only with folk remedies can lead to death. A clear, but at the same time sad example is famous people of the 19th and 20th centuries. (Chekhov, Perov, Belinsky, Kustodiev, Kafka, Napoleon II Bonaparte, Vivien Leigh, etc.), who died from this disease due to the lack of highly effective anti-tuberculosis drugs at that time;
- Strictly follow all treatment recommendations of a phthisiatrician (a doctor who treats tuberculosis).
Medical Internet conferences
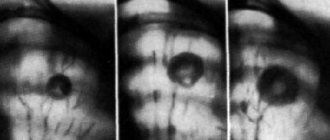
Computed tomography in the diagnosis of miliary tuberculosis
Vdovkina N.G.
Scientific supervisor: Ph.D. Associate Professor Ilyasova E.B.
GBOU VPO Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Department of Radiation Diagnostics and Therapy
Relevance. Recently, there has been an increase in the number of morbidity and mortality from miliary tuberculosis (MT), while at the same time its diagnosis is difficult.
Computed tomography in the diagnosis of miliary tuberculosis
Vdovkina N.G.
Scientific supervisor: Ph.D. Associate Professor Ilyasova E.B.
GBOU VPO Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Department of Radiation Diagnostics and Therapy
Relevance. Recently, there has been an increase in the number of morbidity and mortality from miliary tuberculosis (MT), while at the same time its diagnosis is difficult.
The goal is to clarify the capabilities of computed tomography (CT) in the diagnosis of MT.
Material – 7 patients who were treated at the Clinical Hospital named after. S.R. Mirotvortseva SSMU, whose MT was subsequently confirmed.
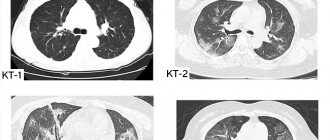
Research methods: analysis of case histories and shadow images of fluorography (FG), radiography (RG) and CT of the chest organs.
Results. FG upon admission: in 4 cases no changes were detected, in 3 cases there was bilateral small-focal dissemination, which the phthisiatrician excluded as specific, clinical suspicion of bronchopneumonia (leukocytosis, cough with sputum, increased body temperature). The RG confirmed the FG data in 3 patients, but additionally similar dissemination, in the absence of clinical symptoms of lung disease, was detected in another 1 patient and suspected in the remaining 3 patients. In 3 cases suspected of pneumonia, X-rays gave the impression of fairly clear contours of the lesions and no changes in the lymph nodes were detected, which gave reason to suspect MT. The other 4 patients were in the surgical clinic: 1 with thyroid cancer, so metastases were suspected in the lungs, 2 with a ventral hernia, 1 with calculous cholecystitis. CT scanning in all patients confirmed the presence of the above-described changes in the lungs, which were regarded as MT, as a result of which they were transferred to anti-tuberculosis institutions. All patients had a negative Mantoux test; MBT was not isolated in the sputum.
Conclusions. If FG or RG reveals dissemination, with clinical signs of inflammation or an asymptomatic course, CT is necessary to obtain additional signs of MT.
Forms of pulmonary tuberculosis.
In Russia, a clinical classification is widespread, which includes a large number of forms. We will look very briefly at the following:
- focal tuberculosis (single lesions up to 1 cm in size, usually in the upper lobes of the lungs);
- disseminated tuberculosis (extensive bilateral lung damage);
- infiltrative tuberculosis (localized damage to the lung tissue, reminiscent of pneumonia within several segments, lobes of the lung);
- fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis (severe damage to the lungs with destruction, compaction (fibrosis) and the formation of cavities (cavities) in the lung tissue and disruption of lung function);
- cirrhotic tuberculosis (the outcome of fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis with gross compaction of the lungs (fibrosis), the formation of non-collapsing cavities (cavities) in the lung tissue and severe impairment of all lung functions).
The most unfavorable in terms of prognosis are fibrous-cavernous and cirrhotic pulmonary tuberculosis. One of the reasons is the development of severe respiratory failure due to fibrosis (hardening) of the lungs. Less commonly, massive fibrosis occurs after infiltrative or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis. Dyspnea in all these cases, as a rule, progresses, which requires long-term oxygen therapy. In case of hypoxemia (decreased oxygen concentration in the blood), which arose due to impaired pulmonary function, the only effective method of improving the prognosis is long-term oxygen therapy using oxygen concentrators. This treatment allows you to maintain the oxygen concentration in the blood at an acceptable level, which helps reduce shortness of breath, increase physical activity and sleep, and improves the prognosis. Unfortunately, lung transplantation for tuberculosis is contraindicated, which further increases the relevance of long-term oxygen therapy.
Call us right now and get quality advice regarding the choice of equipment!
Pneumonia and tuberculosis. CT examination
Nowadays, many people suffer from tuberculosis without knowing it, so diagnosis of the disease begins only when obvious symptoms are already visible. Also, tuberculosis can be confused with pneumonia-pneumonia (due to similar symptoms). To understand what you got sick with, you need to know how both illnesses begin. Let's look at the symptoms that occur with pneumonia:
- The disease begins with a sharp increase in temperature;
- Chest pain when inhaling, shortness of breath appears;
- Lethargy and weakness appear;
- Cough with expectoration of mucus.
It is worth noting that pneumonia can begin after bronchitis, viral diseases, or after severe hypothermia.
A number of indicators associated with tuberculosis:
- Loss of appetite, hence weight loss;
- Sweating during sleep;
- Cough with purulent mucus;
- An unhealthy shine appears in the eyes and a blush on the cheeks.
Unlike pneumonia, tuberculosis may not appear for up to several months, but a slight cough will be present. There are cases that the disease begins with a high temperature, so doctors recommend not to ignore your body’s signals and contact a medical facility immediately. You also need to undergo fluorography every year in order to be sure that you do not have any disease. To diagnose the disease, you will need to undergo a series of tests:
- Blood test for increased ESR, leukocyte and hemoglobin levels;
- Triple culture of sputum with a time interval;
- A test is performed for the Mantoux reaction;
- X-rays of light. As a rule, even the most experienced diagnostician will not be able to distinguish between diseases, since inflammation can also occur with lung cancer.
After all the examinations, treatment is prescribed; if in the future it does not help, then doctors recommend doing a CT scan of the lungs. This procedure will allow you to consider:
- The primary symptoms of tuberculosis are growth to the root, which is inflammatory in nature. This process occurs due to the entry of mycobacteria into the bronchi.
- Inflammation inside the chest lymph nodes. It is divided into 3 types: infiltrative (diameter of lymph nodes reaches 10 mm), tumor-like (diameter more than 30 mm), small (diameter 9 mm).
- Miliary, focal, infiltrative, cavernous inflammatory processes. The most dangerous is the miliary one, as it grows very quickly and throughout all organs.
- Tuberculomas. These are “capsules” with a diameter of 10 mm, which are located in the upper part of the lungs.
- Fibrosis and cavities. When cavities appear (their contents are called fibrosis), the lung becomes smaller.
The procedure does not require any preparation, only in the case of contrast, an analysis for an allergic reaction to iodine is required. When making an appointment on our website “link”, pay attention to the convenient functions that allow you to choose a 24-hour clinic or a diagnostic center that is open on weekends. The price of a lung CT scan varies depending on the qualifications of the doctor, the level of the hospital and the geographical location of the medical facility.
What diseases have symptoms similar to pulmonary tuberculosis
Lobar pneumonia
— Tuberculosis has a longer course and is more difficult to treat
Chronic fungal infection
— Based on radiological data, it is impossible to clearly differentiate tuberculosis from the semi-invasive form of aspergillosis and other fungal pneumonias
Sarcoidosis
- Primary damage to the apical segment of the lung and calcification of the lymph nodes is also possible