What does the analysis determine, what antibodies to COVID19 are tested for?
A blood test for antibodies reveals 2 types of immunoglobulins - proteins that the body produces in response to infection:
- IgM antibodies are the first to appear in the blood of an infected person, from the moment of infection, as a reaction to the virus, and help fight the infection. Their identification means that the person is currently infected. In the first days, the concentration is low, so it may not be detected in a blood test. By the fifth day, the content increases, determined during testing.
- IgG antibodies are produced later, after the tenth day of the disease. The maximum concentration is determined by the fourteenth day, then decreases. These are memory immunoglobulins; with their help, the body remembers the encounter with the virus. The presence of G antibodies means that a person has already encountered a coronavirus infection and has developed immunity.
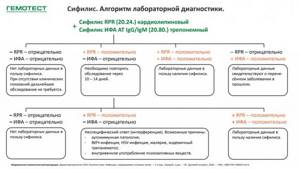
Treponemal tests
Treponema pallidum immobilization reaction (TPIRT). A prerequisite is that before the examination the patient does not take antibiotics, which have a toxic effect on Treponema pallidum, causing their nonspecific immobilization.
Positive results of RIBT are detected approximately from the middle of the secondary fresh period of syphilis, and can persist for a long time after treatment. If necessary, the method is used to detect AT in the CSF; this study is characterized by high specificity, but low sensitivity (about 40%).
RIBT is of little use for diagnosing early forms of syphilis due to the late (no earlier than 8–9 weeks from the moment of infection) appearance of AT-immobilisins; the method can give false-positive results, especially in patients with autoimmune pathology, malignant diseases, and diabetes. In addition, RIBT is a rather complex, labor-intensive and expensive analysis that requires highly qualified personnel and the presence of a vivarium, and therefore in recent years it has been used only in certain laboratories. In diagnostics, RIBT is used as a reaction-arbiter when there are discrepancies in the results of other serological studies, to differentiate false-positive results and when establishing a diagnosis of late forms of syphilis.
Complement fixation reaction with treponemal antigen (RSC with TA)
The sensitivity of the method is about 80%, specificity is 98%. The method was part of a set of standard serological reactions for syphilis, regulated by Order of the USSR Ministry of Health No. 1161 of September 2, 1985 “On improving the serological diagnosis of syphilis.” Currently, the use of this reaction, like CSC with cardiolipin antigen, is limited to individual laboratories.
Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF)
. To diagnose syphilis, several modifications of RIF are used: RIF-c - to detect AT in the CSF, RIF-200 (the test serum is diluted 200 times before the reaction); RIF-abs (RIF with absorption), IgM-RIF-abs (for determining IgM AT). In terms of sensitivity and specificity, RIF-abs is not inferior to RIBT, but the implementation of this method is much simpler. The results of RIF-abs become positive from the 3rd week after infection (before the appearance of chancroid or simultaneously with it), this is a method for the early diagnosis of syphilis. Positive research results are often found many years after complete treatment of early syphilis, and in patients with late syphilis – for decades.
Indications for performing RIF-abs:
- positive results of NTT in pregnant women in the absence of clinical and anamnestic data indicating syphilis;
- examination of persons with various somatic and infectious diseases, in which positive results of NTT are noted;
- examination of persons with clinical manifestations characteristic of syphilis, but with negative NTT results;
- early diagnosis of syphilis;
- in some cases - as a criterion for the success of anti-syphilitic treatment: the transition of a positive RIF-abs to a negative one after treatment is a 100% criterion for the cure of syphilis.
IgM-RIF-abs is used for separate detection of Ig class ATs, which is of particular interest in the diagnosis of congenital syphilis, when Treponema ATs synthesized in the child’s body are represented by IgM, and IgG ATs are of maternal origin. Indications for this study are: diagnosis of congenital syphilis; assessment of the results of treatment of early syphilis.
RIF has high sensitivity (98.5%) and specificity (99.6%) for almost all forms of syphilis. The disadvantages of the RIF are: the impossibility of automating the research and recording the results; difficulties in preparing high-quality antigen from a suspension of Treponema pallidum obtained from the testicle of an infected rabbit; subjectivity in evaluating results.
Passive hemagglutination reaction (RPHA). A comparison of the results obtained using RPGA and RIBT, RIF-abs, CSR, MRP showed high sensitivity and specificity of RPGA in diagnosing syphilis, coinciding with the results of RIF-abs.
RPGA can be performed in qualitative and quantitative versions; there are their macro- and micromodifications. The quantitative RPGA method allows one to assess the concentration of specific treponemal antibodies in the blood. Titers of 1:640 and below are typical for patients treated for syphilis in the past. Higher titers are common for active, untreated infection.
Positive results of RPGA are usually noted 3 weeks after the appearance of chancre and then in patients who have had syphilis for many years, often for life.
The sensitivity of RPGA is 76% for primary syphilis; 100% for secondary syphilis; 97% for latent syphilis; 94% for late syphilis. The specificity of RPGA is higher than the specificity of RIF–abs, being 99%.
Due to the ratio of high specificity, sensitivity, ease of performance, and standardization of reagents among treponemal tests for the serodiagnosis of syphilis, RPGA consistently occupies a leading place in clinical practice in the world.
Special advantages of ELISA
are: high sensitivity and specificity of the method; automation of reaction setting; high degree of standardization; the ability to study a large number of serum samples; in quantitative accounting and objective documentation of the results obtained; the possibility of simultaneous determination of the titer of antitreponemal antibodies of different classes (IgG and IgM) in one sample; suitability for early diagnosis of syphilis and diagnosis of congenital syphilis; in ease of use for testing blood in the blood transfusion service; applicability as a confirmatory specific treponemal test. ELISA sensitivity is 98–100%, specificity is 96–100%.
The disadvantages of ELISA include: unsuitability for studying single samples; longer period before obtaining the result, and shorter shelf life of ELISA kits, for example, compared to RPGA.
Immune blot (IB).
One of the modern methods for diagnosing syphilis is IB to determine IgG or IgM antibodies to certain Treponema pallidum antibodies.
The method has high sensitivity (up to 100%), specificity (98%) and reproducibility (100%). The study makes it possible to study the spectrum of antibodies to several T. pallidum antigens at once, using highly purified recombinant and peptide antigens that reduce nonspecific serum reactivity to a minimum.
All this determines the possibility of preferring the use of the IB method over other treponemal tests for verifying the diagnosis of syphilis in difficult cases, in particular, for diagnosing syphilis in the second half of the incubation period, latent congenital syphilis in the first days of a child’s life, for identifying latent syphilis in persons with weak humoral answer, as well as to differentiate false-positive results from other tests.
What does antibody testing do?
There are two types of blood tests for COVID-19:
- Qualitative. Express testing only detects the presence of antibodies in the blood.
- Quantitative. Laboratory diagnostics ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) also determines the content (titer) of antibodies in the blood plasma.
Quantitative analysis is more informative; based on the concentration and ratio of immunoglobulins, it allows one to determine the stage of the disease - whether it is just developing or declining.
Additionally, it is recommended to undergo PCR testing to determine the virus itself. The study detects Covid-19 DNA in human biological material (oropharyngeal swabs) from the first day of infection.
Laboratory tests - a way to diagnose chronic heart failure
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a disease in which the pumping function of the heart is reduced. It cannot release the required amount of blood, which causes organs and tissues to suffer. To identify the disease, a consultation with a cardiologist is necessary. But first you can take tests that will help a specialist diagnose heart failure. 1. General blood test. With progressive CHF, iron deficiency anemia may develop due to impaired absorption of iron in the intestine or insufficient intake of iron from food.
2. General urine analysis. Proteinuria and cylindruria may appear as markers of impaired renal function in chronic heart failure.
3.Biochemical blood test: • To diagnose possible liver dysfunction - AST, ALT, total protein, bilirubin. AST and ALT are always given in pairs so that the doctor can see and separate lesions in the heart and liver. Their increase, in most cases, indicates problems with the muscle cells of the heart and the occurrence of myocardial infarction. • LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) and CK (creatine phosphokinase) and especially its MB-fraction (MB-CPK) - increase during acute myocardial infarction. • Myoglobin - increases as a result of the breakdown of cardiac or skeletal muscle tissue. • Electrolytes (K, Na, Cl-, Ca2 ions) - an increase in potassium leads to heart rhythm disturbances, the possible development of excitation and ventricular fibrillation; low potassium levels can cause decreased myocardial reflexes; insufficient sodium ions and an increase in chlorides are fraught with the development of cardiovascular failure. • Cholesterol - its excess serves as a risk for the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. An increase in cholesterol levels (with significant impairment of liver function - hypocholesterolemia), triglycerides, low and very low density lipoproteins, a decrease in high density lipoproteins is possible with coronary heart disease. • C-reactive protein - appears in the body during an inflammatory process or tissue necrosis that has already occurred, since it is contained in minimal levels in the blood serum of a healthy person.
4. Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) - used as a marker in the diagnosis of heart failure. BNP levels are elevated in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. At the same time, the content of BNP in blood plasma significantly correlates with the functional classes of chronic heart failure. Determining the level of BNP in blood plasma helps to assess the severity of chronic heart failure, predict the further development of the disease, and also evaluate the effect of therapy.
5. Coagulogram - will give an idea of the process of blood clotting, its viscosity, the possibility of blood clots or, conversely, bleeding. May be given in addition to other tests.
You can take the necessary tests at the Federal State Budgetary Institution “National Medical Research Center for TPM” of the Russian Ministry of Health. A comfortable treatment room and a fully equipped laboratory are at your disposal. Most analyzes are completed within 1 business day.
More details at the link
What does the analysis show, what does decoding the results mean?
- For IgM antibodies. A positive answer means the person is infected in the acute stage. Negative - absence of Covid-19 or late stage when antibodies are no longer produced. Confirmed by PCR test.
- For IgG antibodies. A positive answer is an infection in a late stage or an already suffered disease with the development of immunity. Negative - there was no infection or the disease was in an early stage. Confirmed by PCR test.
Only a doctor knows how to correctly decipher test results. You cannot draw conclusions on your own. Only a specialist can compare the received data and figures, on the basis of which a conclusion can be made about what result is normal. In case of doubtful tests for the presence or absence of antibodies, repeated testing is prescribed; additional PCR research is required.

Oral rehydration salts
Oral rehydration salts
or
oral rehydration salts
(English
oral rehydration salts
; abbreviations
ORS
,
PRS
or
ORS
) - medications intended to compensate for the loss of fluid and electrolytes in the body during profuse diarrhea, repeated vomiting, exudation from extensive wound and burn surfaces, discharge through drainages and fistulas, frequent use of laxatives. Rehydration salts, in addition, are involved in the correction of the acid-base environment in the patient’s body. Oral rehydration salts are sold in pharmacies in the form of ready-made solutions for drinking or in the form of powders intended for the preparation of solutions for drinking.
According to the pharmacological index, oral rehydration salts belong to the group “Regulators of water-electrolyte balance and acid-base environment in combinations.” According to ATC, oral rehydration salts belong to the subgroup “A07CA Rehydrants for oral administration” of the group “A07 Antidiarrheal drugs”.
The need to take rehydration salts for diarrhea
Dehydration is the cause of many diarrhea-related deaths.
At the same time, dehydration against the background of acute diarrhea of any etiology and at any age, with the exception of its severe forms, can be cured without any risk and very effectively in more than 90% of cases using a simple method, drinking a solution containing glucose and several salts included in the composition. mixtures called “oral rehydration salts.” Oral rehydration salts solution is absorbed in the small intestine even during severe diarrhea, thus replenishing the water and electrolytes that are lost from the body during diarrhea. WHO and UNICEF consider the most important measure for diarrhea to be oral or intravenous administration of solutions of rehydration salts to the patient. WHO (Treatment of Diarrhea, 2006) identifies three patient conditions regarding dehydration in diarrhea: “no signs of dehydration,” “some degree of dehydration,” and “severe dehydration.” If the fluid deficiency of a sick child’s weight is in the range of 5 to 10%, then it is approximately considered that he has “some degree of dehydration.” In this situation, it is necessary to immediately drink a solution of oral rehydration salts (replacement with other salt-containing liquids or products is possible). For severe dehydration, intravenous rehydration is recommended.
Active oral rehydration with saline solutions is a mandatory component of treatment for all types of secretory diarrhea, as it reduces secretion and improves absorption (E.A. Belousova, A.R. Zlatkina).
Composition of oral rehydration salt solutions
For several decades, WHO and UNICEF have recommended for use a single formulation of oral rehydration salts based on glucose, sodium and potassium chloride and sodium citrate, having an osmolarity of 311 mOsm/L. These oral rehydration salts have shown to be highly effective for diarrhea, however, based on research, WHO and UNICEF have now (since 2006) clarified the characteristics of the ORS solution and recommend it, especially for children with acute diarrhea not caused by cholera, instead of the previously recommended standard solution, use the so-called “low osmolarity” ORS solution, approximately 245 mOsm/l (see table below).
| Ingredient | Chemical formula | Composition of ORS “with reduced osmolarity” recommended by WHO and UNICEF , g per 1 liter of solution | Contents of glucose and salts in ORS registered in the Russian Federation as medicines, g per 1 liter of solution *) | |||||
| Regidron 1 pack. | Hydrovit 5 pack. | Hydrovit forte 5 pack. | Gastrolit 5 pack. **) | Citraglucosolan 1 pack 24.9 g, 2 packs 12.45 g (or pack 11.95 g) ***) | Trihydron | |||
| glucose (dextrose) anhydrous | C6H12O6 | 13,5 | 10 | 17,8 | 20 | 14,5 | 15 | 5 |
| potassium chloride | KCl | 1,5 | 2,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 3,5 | 1,25 |
| sodium chloride | NaCl | 2,6 | 3,5 | 2,35 | 2,8 | 1,75 | 3,5 | 1,75 |
| sodium citrate | Na3C6H5O7 2H2O | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,65 | 2,95 | 2.5 NaHCO3 | 2,9 | 1,75 |
| Osmolarity of the finished solution , mOsm/l | about 245 | 260 | 240 | 311 | 240 | ***) | ||
Notes.
*) different medications are produced in sachets intended for the preparation of different volumes of oral rehydration salts solution; in the table, next to the name of the drug, the number of sachets required to prepare 1 liter of solution is indicated, and below is the amount of glucose or salts in the indicated number of sachets and required to prepare 1 liter of ORS solution **) Gastrolit contains sodium instead of sodium citrate bicarbonate, as well as dry chamomile extract 0.5 g per 5 sachets (1 liter of solution) ***) Citraglucosolan is (was) produced by various Russian manufacturers, the composition and weight of the sachets may differ from those indicated in the table
Approximate volume of oral rehydration salts solution to take in the first 4 hours for some degree of dehydration
| Body weight, kg | Age (used when weight information is missing) | Volume of ORS solution, ml |
| up to 5 | younger than 4 months | 200-400 |
| 5-7,9 | 4-11 months | 400-600 |
| 8-10,9 | 12-23 months | 600-800 |
| 11-15,9 | 2-4 years | 800-1200 |
| 16-29,9 | 5-14 years | 1200-2200 |
| 30 or more | 15 years and older | 2200-4000 |
Notes.
- The approximate required amount of ORS solution (in ml) is equal to the patient’s body weight in kg, multiplied by 75.
- If the patient wants to drink more ORS solution than in the table above, you need to give him as much as he wants.
- At the initial stages of treatment, when the state of dehydration has not yet been relieved, adults are recommended to take up to 750 ml per hour, if necessary, and for children - up to 20 ml per kg of body weight per hour.
- People with more severe signs of dehydration or those who continue to have frequent, watery stools require more solution than those who have less severe signs of dehydration or have less frequent stools.
In Russia, the following oral rehydration salts with active ingredients are (were) registered as medicinal products:
- dextrose + potassium chloride + sodium chloride + sodium citrate
: Hydrovit, Hydrovit forte, Regidron, Citraglucosolan - dextrose + potassium chloride + sodium chloride + sodium bicarbonate + dry chamomile extract
: Gastrolit (Gastrolit registered in Ukraine)
The American College of Gastroenterology in its "Tips for Food Poisoning (Including E coli)" recommends taking oral rehydration salt solutions for severe diarrhea or vomiting and cites Pedialyte ® and Oralyte ® as examples of such salts. Back to section
Detailed description of the study
Syphilis is an infectious disease caused by Treponema pallidum. Transmission of infection occurs primarily through sexual contact without the use of barrier contraception. However, it is possible to become infected with treponema pallidum through contact and household contact if personal hygiene rules are not observed, as well as transmission of the pathogen from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. Syphilis can affect any organs and systems. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease becomes chronic. Initially, a hard chancre is formed at the site of contact with the source of infection - a painless ulcer with a small amount of transparent content on the surface. Often the body reacts to the introduction of the pathogen by inflammation of the lymph nodes located near the site of the lesion. Within a few weeks, a scar forms in place of the chancre. However, the disease does not recede, and after some time the infected person notices the appearance of a specific rash on the body - the appearance of small bright pink spots (rosacea rash). This stage is called secondary syphilis. The disease is prone to periodic exacerbations with changes in the nature of the rash. Tertiary syphilis is the result of untimely diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Along with the formation of nodes and tubercles on the skin, which are called gummas, prone to ulceration and scarring, damage to internal organs is observed. Diagnosis and treatment of syphilis is carried out by a dermatologist. To confirm the diagnosis, a modern test for determining rapid plasma reagins, or RPR test (Rapid Plasma Reagins), is used. These proteins are antibodies to the lipid components of cells destroyed by the pathogen.