Today, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are the most informative and highly accurate methods of instrumental diagnostics. They create a layer-by-layer three-dimensional image of internal organs and allow one to make reliable conclusions about the processes occurring in the patient’s body.
The smallest abnormalities in the tissues will be reflected in the image and will allow you to quickly make an accurate diagnosis. However, MRI and CT are fundamentally different both in applications and scanning methods.
Which is better - CT or MRI?
Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages when examining a particular part of the body. The choice of tomograph primarily depends on the expected pathology and clinical task. However, most doctors often recommend MRI.
Magnetic resonance imaging provides more contrast images of internal organs and is good at identifying areas of pathological density. In addition, it does not emit X-ray radiation, and therefore can be used repeatedly.
Modern multislice CT devices also have high scanning accuracy and well visualize any anatomical structures. CT is an ideal option for identifying the consequences of injuries, fresh hemorrhages, and space-occupying lesions. However, radiation exposure somewhat limits its use in children or debilitated patients.
Benefits of medical examination
Many patients are faced with the fact that when an ultrasound detects or suspects a pathology, further examination using CT or MRI methods is postponed for several days or weeks.
If you need to undergo an examination promptly, please contact the Department of Instrumental Diagnostic Methods of Medicine. To speed up and optimize the algorithm for examining patients, we have combined the department of functional and radiation diagnostics.
To conduct additional studies, our patients do not need to re-register for subsequent dates. The schedule of the clinic’s specialists is structured in such a way that, if necessary, we can conduct additional examinations immediately.
In each specific case, the decision to choose one or another diagnostic method is made by the doctor: it is he who decides what is better - MRI or CT. Medical specialists will answer your questions and select an adequate diagnostic method. To do this, call the phone number listed on the website, or leave a request in the feedback form. Let's take care of your health together!
Low-field tomographs
These are old models of devices, but nevertheless they are installed in many medical institutions of St. Petersburg, of a special state type. Their magnetic field strength ranges from 0.3 to 0.5 T (tesla).
Despite the relatively low cost of examination with a low-field tomograph, many specialists do not recommend it to their patients. Low magnetic field strength does not make it possible to obtain good image contrast and to detect the smallest changes in the tissues of the brain or spine. Such devices can only diagnose gross changes: large tumors, herniated intervertebral discs or significant traumatic injuries.
CT scan of the chest organs for children
CT scans are performed for children in exceptional life-threatening situations
Low-dose CT of the chest organs is performed in children for health reasons, if other imaging methods not related to X-ray exposure are not available. A referral for a CT scan is given to a child by a council of doctors; more often, the diagnosis is performed during hospitalization in specialized pediatric clinics. The main reasons for undergoing a CT scan in children:
- tumor of the chest organs;
- mediastinal injury;
- pneumonia;
- pulmonary form of tuberculosis;
- diagnosis of congenital malformations of the respiratory tract;
- inhalation of a foreign body.
Ensuring immobility during the study at an unconscious age requires sedation. The diagnostic procedure is carried out under the supervision of a resuscitator-anesthesiologist.
Closed-type tomographs
This is the most common model of machines for magnetic resonance imaging. Most centers have these types of tomographs installed. Outwardly, they resemble a short tunnel; inside it there is a movable table on which the patient is placed. Considering that scanning time for some anatomical areas lasts up to thirty minutes, some people experience discomfort when being in a confined space. And for people suffering from claustrophobia, such an examination instills a certain fear.
In addition, closed tomographs have some restrictions on patient configuration. People with a large body weight are not always able to conduct an examination due to the impossibility of placing it in the tunnel of the device.
However, modern medicine and technology have found a way out of this situation. The latest models of closed-type MR devices have a significantly larger “tube” diameter and, accordingly, much more space remains for the patient than in older models. Anxiety about examinations and fear of confined spaces can also be addressed with mild sedatives.
What are the disadvantages of MRI and tomography?
The main disadvantage of MRI is the need for a long stay in the confined space of the tube. This method is not suitable for patients suffering from claustrophobia, as it causes panic attacks in them. To obtain a clear image, doctors recommend remaining motionless throughout the entire examination; therefore, if necessary, parts of the subject’s body are secured with special devices.
A magnetic field can damage pacemakers; the presence of metal prostheses negatively affects the operation of the tomograph. Patients with implants and implanted electromagnetic devices should inform their doctor about this.
Computed tomography takes less time, but this method is based on the use of x-rays. It can cause harm to the patient’s health, so a repeat examination is possible only after a month. Categories of patients who have contraindications to x-ray diagnostic methods are not allowed to undergo computed tomography.
When diagnosing diseases of blood vessels, neoplasms, and inflammatory processes, it is necessary to administer a contrast agent, which is undesirable in patients with an allergy to iodine and in people suffering from renal failure.
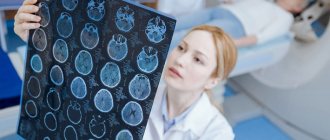
Which tomograph is better for MRI of the brain?
The human brain is a rather complex structure; even minimal, just a few millimeters, changes in it can cause severe neurological disorders. Therefore, to diagnose nervous system pathology, the best option would be an examination using a high-field tomograph.
At a power of 1.5 Tesla, any organic changes in brain tissue, cysts, areas of hemorrhage or ischemia are clearly detected. In addition, this type of study can identify foci of demyelination in multiple sclerosis or degenerative changes in progressive encephalopathy.
An examination with a high-field tomograph is the most informative if vascular aneurysms or cerebral vascular malformations are suspected. The resulting images clearly visualize the walls of arteries and veins, and the introduction of contrast makes it possible to clarify the nature and size of the anomaly, and the degree of its interaction with surrounding structures.
And, of course, magnetic resonance imaging is an extremely necessary examination to identify tumors of the central nervous system. The higher the class of the tomograph, the better the early stages of tumor development, its contours and the degree of growth into surrounding tissues are visible.
Preparing the patient for CT and MRI of the lungs
To resolve the issue of preparation for diagnosis, it is necessary to clarify whether it will be carried out with or without the introduction of contrast. If contrast enhancement is to be used, the following prohibitions must be taken into account:
- It is best to perform the procedure in the morning on an empty stomach; the drinking regimen does not need to be changed. Your doctor will tell you whether you can eat before a CT scan of the lungs without contrast injection. In any case, you should avoid overeating and foods that cause increased gas formation.
- The day before and on the day of CT and MRI, it is prohibited to drink alcoholic beverages.
- Clothing should be loose and not restrict movement. For MRI, it is important that there are no metal parts, be it clothing, jewelry, glasses, etc. They must be removed before the procedure.
CT and MRI with contrast are prescribed only after an allergy test and a blood test for creatinine to exclude possible renal failure.
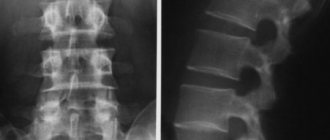
Which tomograph is better for the spine
To diagnose spinal diseases, you can use both low-field and high-field MR machines. However, low-field tomographs are able to detect only gross changes: significant deformations of the bone structure of the vertebrae or large hernial intervertebral protrusions. Therefore, neurosurgeons and neurologists recommend undergoing an examination of the spinal column using a high-field apparatus.
It also helps to identify pathologies of the intervertebral discs, but the images best visualize changes in the bones of the spine: fractures, areas of destruction, tumors. Therefore, this type of study is more preferable after injuries or with a clinical picture of spondylitis.
CT scan of the chest for tuberculosis
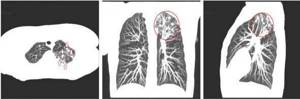
Focal changes on CT scan of the lungs, suspicious for tuberculous lesions (highlighted in red)
Tuberculosis affects patients of any age and gender; the lungs are most often involved in the process. The disease is considered socially dangerous, since if the open form is not diagnosed in a timely manner (release of mycobacteria into the environment when coughing), there is a high risk of infection of surrounding people. Chest CT for tuberculosis is prescribed in the following situations:
- screening radiography showed changes suspicious for the pathology in question;
- the patient has positive results of laboratory tests for tuberculosis (Mantoux test, Diaskintest) with ambiguous signs on the fluorogram;
- tracking dynamics after specific therapy;
- as a preoperative diagnosis to identify the anatomical features of blood supply and innervation of lesions, localization of pathology.
How to choose a CT scanner
First of all, it is recommended to undergo examination on a multislice CT machine. The best option in terms of price and diagnostic quality are 16-slice tomographs, which provide high-quality images with a slice thickness of 1-2 mm. The radiation exposure is comparable to taking a conventional x-ray. Step-by-step CT scanners, despite the low cost of the examination, produce very low-quality images with low diagnostic value.
When choosing a diagnostic center for examination, you also need to take into account the newness of the equipment installed in it. In some medical institutions, in order to save money, devices that have already been in use are installed. They do not have most modern computer programs, and therefore their diagnostic capabilities are limited.
Which tomograph is best for the brain can also be clarified by calling the single MRI appointment center at 8 (812) 614-16-95. An experienced employee will provide all the necessary information and select the most convenient time for diagnosis.
Differences between MRI and computed tomography
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography have a number of significant differences that must be taken into account when choosing a diagnostic method. When comparing the two procedures, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- the method used to scan;
- recommended scope of tomography application;
- time spending;
- indications and contraindications for the diagnostic method;
- features of preparation for each study;
- types of contrast agent used during scanning;
- information content of the method.
MRI involves scanning tissues and organs using a magnetic field; it penetrates the human body and causes a reaction that depends on the structures. Thanks to this feature, the study makes it possible to assess the condition of the soft tissue structures of the studied area. CT is based on the use of X-rays, which also penetrate tissues and organs, but the intensity of their absorption is determined by the density of the structures of the examined area.
The magnetic field allows you to visualize the condition of soft tissues, so MRI is prescribed for diseases of the muscles and ligaments of the musculoskeletal system, pathological conditions of the nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, pelvic organs and abdominal cavity.
MRI of the abdominal cavity
To evaluate solid structures, CT is used, which is informative in differentiating diseases of bone and cartilaginous formations of the skull, spine, limbs, and thoracic cavity. Computed tomography shows the presence and size of neoplasms, hematomas, is effective in determining pathologies of hollow organs, and clearly visualizes the condition of the pulmonary parenchyma, heart and blood vessels.
Magnetic resonance imaging and CT examinations have many differences, but little or no preparation is required for either. The techniques are simple and comfortable for the patient. Having determined what the difference is between CT and MRI, the patient can independently undergo the procedure at a medical center in order to diagnose possible pathological conditions of the body.
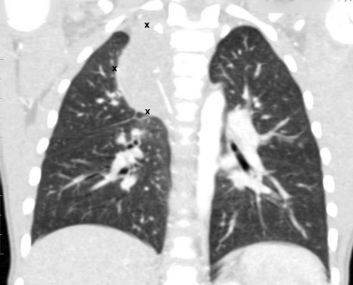
Chest tomography photo
The CT result of the OGK will be ready in 90-120 minutes; at the Magnit diagnostic center in St. Petersburg, the data obtained in doubtful situations are assessed collectively. Let us present several tomograms that demonstrate pathological processes in the chest:
CT scan of the chest demonstrates a mediastinal tumor (the boundaries are highlighted with markers)
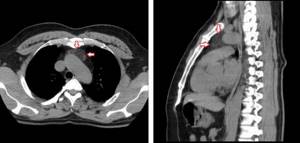
CT scan of the mediastinum. Red arrows indicate lipoma.
Signs of peripheral lung cancer on CT (highlighted in red)
Contraindications
Computed tomography is not a preferred test for pregnant women and children under 14 years of age. They try not to perform CT with contrast in this category of people and in patients with a complicated medical history, which includes:
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- allergy to iodine-containing substances;
- urological and nephrological pathology with impaired renal function;
- cardiovascular diseases in the stage of decompensation.
Indications and contraindications
Before sending for an x-ray examination, the doctor takes into account the risk-benefit ratio of the diagnosis
Indications for CT of the chest are complaints from the lungs and organs and structures of the mediastinum, which cannot be interpreted unambiguously after assessing the results of primary studies: radiography, ultrasound, etc. CT of the chest can be done as an additional diagnosis if there is:
- hemoptysis, shortness of breath, decreased respiratory excursions of the chest, cough, wheezing;
- limitation of mobility and pain in the joints of the shoulder girdle, thoracic spine, palpable formations and post-traumatic pain in the chest area, crepitus of the ribs (characteristic crunching sound during fractures), etc.;
- difficulty swallowing, if esophageal stenosis is suspected;
- chest pain, aggravated by movement, feeling of lack of air;
- enlargement of the cervical, supraclavicular and subclavian lymph nodes.