Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the renal pyelocaliceal system and its parenchyma, predominantly of bacterial origin. Most often, children under 8 years of age and women become ill due to the presence of a short urethra. In men, pyelonephritis is less common, but the likelihood of developing the disease increases if there is prostate adenoma. Untreated or neglected acute pyelonephritis can become chronic, which is fraught with many complications, including the occurrence of renal failure.
Medical helps patients perform a complete medical examination, conduct an informative diagnosis and receive effective treatment. The clinic employs exclusively qualified and experienced urologists who provide effective and safe treatment and make competent recommendations for the prevention of exacerbations.
Causes
There are a number of reasons why this disease occurs:
- hypothermia;
- concomitant pathologies (for example, diabetes mellitus);
- immunodeficiency state;
- urolithiasis disease;
- developmental anomalies of the genitourinary system (several renal pelvis, duplication of ureters);
- vesicoureteral reflux (reflux of bladder contents into the kidney);
- scars or strictures (for example, after surgery on the bladder and/or ureters);
- hypovitaminosis;
- chronic focus of infection (furunculosis, caries, sinusitis);
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- pregnancy, childbirth;
- BPH.
Symptoms
Acute pyelonephritis can begin gradually and instantly, hence its division into serous and purulent forms. In the first option, a person may feel pain in the lower back even a day before the onset of the disease, notice a change in urine in the form of cloudiness and the appearance of a specific odor. Then comes the intoxication syndrome: headache, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting. The purulent form is much more severe, hectic fever (up to 41 degrees), the pain syndrome is pronounced, and signs of intoxication are more pronounced. Chronic pyelonephritis has a stage of exacerbation and remission. In the acute stage, the clinical picture may have either the same course or more mild symptoms, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult.
Pyelonephritis is also divided into obstructive and non-obstructive. Obstructive is a pain similar to renal colic, the patient cannot find a place for himself due to severe pain in the lower back, is restless, and is in a feverish state. With a non-obstructive variant of the course, the patient adheres to bed rest more, tends to lie down and cover his back in order to reduce discomfort in the projection of the kidneys (in some cases, the pain is nagging or aching in nature).
Diagnostics
In our clinic you can undergo all the necessary diagnostic examinations to exclude kidney pathology, namely:
- General blood test (with pyelonephritis, there is a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, leukocytosis, and an increase in ESR).
- Biochemical blood test (C-reactive protein increases during the inflammatory process; urea, creatinine will be increased especially with the formation of renal failure).
- General urine test (bacteria, mucus, white blood cells, sometimes red blood cells and protein).
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko (will allow more detailed identification of damage to the collecting system and renal parenchyma; bacteria, mucus, leukocytes, and the presence of pus will also be detected).
- Bacteriological culture of urine (isolation of the pathogen for proper antibiotic therapy).
- CT, MRI.
- Scintigraphy.
- Biopsy.
- Survey radiography of the abdominal organs.
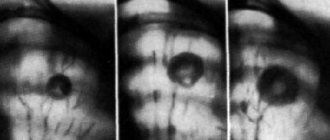
Ultrasound is also used to determine the disease. Using an ultrasound, the doctor can determine other kidney diseases: glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, benign and malignant neoplasms, etc.
Pyelonephritis on ultrasound
in the acute period of the disease looks like this:
- An uneven contour of the affected kidney is noted.
- The size of the kidney is increased due to edema. If one kidney is affected, the doctor indicates an asymmetry in the size of the kidneys.
- The echogenicity of the kidney tissue is reduced due to inflammatory edema.
- The mobility of the affected kidney is reduced.
- If pyelonephritis is of secondary origin, in particular in the presence of kidney stones, stones are visualized, as well as an expansion of the pyelocaliceal system.
- The parenchyma of the diseased kidney is thick. There is also thickening of the renal papillae.
Pyelonephritis on ultrasound
may not be detected so clearly when the inflammatory process begins. As the disease progresses, echo signs become more obvious.
Severe forms of pyelonephritis or developing complications are usually clearly detected by ultrasound. Acute apostematous pyelonephritis is characterized by a violation of the boundaries of the cortical and medulla layers of the kidney. A kidney abscess appears as an anechoic (dark) formation with a fluid level.
Chronic pyelonephritis during ultrasound examination has the following signs:
- kidney size is normal or, conversely, reduced,
- the echogenicity of the renal tissue is increased due to the replacement of areas of inflammation with connective tissue,
- the thickness of the cortical layer is reduced.
Thus, an ultrasound of the kidneys for pyelonephritis helps the urologist confirm the diagnosis, so this study should not be neglected.
The medical clinic has the latest diagnostic equipment and has the ability to quickly and accurately conduct instrumental and laboratory tests. The cost of tests starts from 300 rubles, which is quite affordable for most patients. The results of many studies can be obtained on the same day of treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of pyelonephritis in our medical institution can be carried out both on an outpatient and inpatient basis, but with the mandatory use of antibacterial drugs. Typically, urologists at the clinic prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in combination with cephalosporins, since Escherichia coli is a common causative agent of kidney disease. The course of treatment averages 10 days.
Patients are recommended to remain in bed for several days until the intoxication syndrome is relieved. At the same time, it is necessary to take painkillers and antipyretics, drink large amounts of water and fortified compotes, fruit drinks throughout the day (up to 2-2.5 liters per day). It is advisable to use herbal diuretics, exclude salt from the diet, and limit protein foods. After stopping the acute stage, physiotherapeutic treatment can be carried out - electrophoresis on the kidney projection, UHF.
Surgical intervention is used only in cases of severe pyelonephritis, the formation of large abscesses or renal failure.
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis is an infectious process that affects the pyelocaliceal apparatus and renal parenchyma. Improper treatment of the pathology contributes to its transition to a chronic form.
The medical specialist treats acute pyelonephritis using optimal methods to achieve recovery in a short time with maximum efficiency. The clinic provides an individual approach to the patient and accurate diagnostics.
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis is carried out by highly qualified urologists and includes antibiotic therapy, the use of NSAIDs, antispasmodics for obstruction, and herbal diuretics. The urologist selects medications taking into account the sensitivity of the bacteria identified in the urine. The duration of antibacterial therapy can range from 5 days to two weeks. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe medications that promote detoxification, as well as immunostimulants. For each patient, the urologist chooses an individual treatment strategy for pyelonephritis.
In case of acute pyelonephritis, bed rest and drinking plenty of fluids up to 2-2.5 liters per day are recommended. Home-made compotes, especially berry ones (rose hips, lingonberries, cranberries), give good results.
If there are abscesses or carbuncles in the kidney, then surgical intervention is necessary.
Successful treatment of patients with pyelonephritis is facilitated by an integrated approach and the use of modern methods.
This is interesting
Interesting facts about pyelonephritis:
- In the United States, 1 in 7,000 people are sick each year. 192,000 patients require and receive hospitalization each year.
- It has been established that female representatives suffer from pyelonephritis 5 times more often than males. The acute form of the disease is diagnosed more often in women of reproductive age who are sexually active.
- With adequate treatment, up to 95% of all patients report significant improvement within the first two days.
- You should not refuse to drink plenty of fluids due to painful sensations during emptying the bladder, since this is the only way to remove bacteria from the body. You should urinate as often as possible to avoid serious complications such as blood poisoning, which can result in death.
- Drinking plenty of fluids is an essential condition for treating the disease. For drinking, it is necessary to use clean water, which normalizes the balance in the body, thins the blood, and promotes the rapid elimination of pathogenic microorganisms and toxic products of their vital activity. The effect is achieved by increasing the number of urinations as a result of drinking heavily.
- Alcoholic drinks, coffee, carbonated water - all this is prohibited for pyelonephritis. It is believed that cranberry juice can help fight the disease. It is consumed in pure form or diluted with water.
- Pyelonephritis affects children, both girls (in 3% of cases) and boys (in 1% of cases). In childhood, the disease is dangerous due to its complications. Thus, cicatricial changes in the kidney parenchyma are diagnosed in 17% of children who have recovered from the disease, hypertension in 10-20% of children.
Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis
Medical is a multidisciplinary medical institution that offers patients a wide range of services in many areas. The clinic provides precise diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of chronic pyelonephritis. The clinic’s highly qualified urologists not only effectively provide comprehensive treatment, but also make recommendations for the prevention of exacerbations of chronic diseases.
Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis is based on timely treatment of exacerbations. During the manifestation of the clinical picture, the urologist prescribes antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and herbal diuretics to the patient. The course of therapy is regulated by a urologist depending on the degree of advanced disease and kidney damage.
In addition to drug treatment, home-made fortified drinks based on berries (fruit juice, compote, jelly) must be included in the daily diet. A person should drink up to 2 liters of liquid per day, while limiting salt intake. For high blood pressure, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
Our clinic is ready to provide you with its services at a reasonable price (the cost of complex treatment starts from 4,000 rubles). Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis is carried out using a comprehensive method by highly qualified urologists with extensive experience. An individual treatment regimen is developed for each patient.
Possible complications
In the absence of adequate therapy, pyelonephritis faces the following consequences:
- renal failure (to protect the body from intoxication, it is necessary to regularly resort to the use of an artificial kidney device);
- sepsis (in case of penetration of bacteria into the bloodstream);
- chronicity of the process (painful exacerbations are periodically observed);
- severe kidney damage;
- development of urolithiasis (renal colic is periodically observed);
- death (as a result of blood poisoning - sepsis or kidney failure).
Consequences of pyelonephritis
If therapy is not started on time or was not carried out in full, unpleasant consequences are possible, so consultation with a urologist is necessary.
Acute pyelonephritis after treatment is characterized by minor signs of inflammation in a urine test, which disappear after some time: there may be a slight increase in the level of leukocytes and bacteria. After acute pyelonephritis, the patient’s well-being returns to normal; nothing will remind you of the past illness. With chronic pyelonephritis, everything is different: changes in the general urine analysis can be constantly present, the kidney tissue undergoes a number of pathological changes that progress from year to year. Periodically, exacerbations of the inflammatory process occur, which then go into remission (periods of subsidence of clinical signs). Remission of pyelonephritis lasts longer, the milder the form of the disease. The regimen followed by the patient is important: you need to follow a certain diet and avoid hypothermia.
Complications of acute pyelonephritis are:
- kidney abscess;
- acute renal failure;
- transition of an acute process to a chronic one;
- formation of a kidney carbuncle, etc.
Complications of chronic pyelonephritis:
- the development of nephrosclerosis, in which normal kidney tissue is replaced by connective tissue;
- chronic renal failure;
- pedunculitis, papillitis (inflammatory processes in kidney tissue), etc.
What is secondary pyelonephritis?
This is a chronic process that develops against the background of various pathologies of the urinary system. It can be obstructive or non-obstructive.
Obstructive secondary pyelonephritis
is formed as a result of urinary disorders of various nature: hereditary, congenital, acquired (developmental anomalies, kidney tuberculosis, urolithiasis, etc.). Non-obstructive pyelonephritis is the cause of a deficiency in the immune system, metabolic disorders, diseases of the endocrine system, etc.
Timely consultation with a urologist is very important to prevent the development of secondary pyelonephritis. After all, very often people self-medicate, not wanting to see a doctor, but this treatment can become not only ineffective, but also dangerous. Pathogenic bacteria are not completely suppressed, and the inflammatory process becomes prolonged. In addition, existing concomitant diseases play a role.
The earlier the disease is detected, the easier it is to cope with it and avoid complications.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of acute pyelonephritis include:
- Pain in the lumbar region on the affected side. With non-obstructive pyelonephritis, the pain is usually dull, aching in nature, can be low or reach high intensity, and take on a paroxysmal nature (for example, with obstruction of the ureter by a stone with the development of so-called calculous pyelonephritis).
- Dysuric phenomena are not typical for pyelonephritis itself, but can occur with urethritis and cystitis, which lead to the development of ascending pyelonephritis.
General symptoms are characterized by the development of intoxication syndrome:
- fever up to 38-40 °C;
- chills;
- general weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting.
Children are characterized by the severity of intoxication syndrome, as well as the development of the so-called. abdominal syndrome (severe pain not in the lumbar region, but in the abdomen).
Elderly and senile people often develop an atypical clinical picture, either with an erased clinical picture or with pronounced general manifestations and the absence of local symptoms.
Prevention
In order not to lead yourself to pyelonephritis, prevention should be carried out taking into account certain rules:
- The use of medicinal herbs as prophylaxis.
- If the pathological process of infectious etiology is located in any other organs, it must be sanitized, since bacteria can spread to the kidneys with the help of blood.
- Getting rid of bad habits, since alcohol and smoking significantly reduce the body’s immune properties, which inhibits the ability to respond to the penetration of bacteria and viruses into the body.
- The body must receive sufficient rest and sleep, since an exhausted body is not able to fight a bacterial infection.
- Persons who are at risk of developing the disease need to regularly carry out laboratory and instrumental research methods in order to prevent pyelonephritis.
Compliance with these rules does not require significant work; you just need to pay close attention to your own health and carry out treatment in the early stages of the pathological process.
Diagnostics
The doctor will recommend that the patient undergo instrumental diagnostics and laboratory tests. These measures will help to correctly diagnose and distinguish pyelonephritis from pathologies with similar symptoms.
Initially, the patient will be recommended to undergo the following tests:
- Biochemistry of blood. Detects increased amounts of urea, creatinine, and potassium. The content of an increased amount of potassium characterizes the development of renal failure.
- Blood test. It will show the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the body (acceleration of ESR, the presence of a large number of leukocytes).
- Urine culture. The liquid is sown on a special nutrient medium. After a while, the growth of a certain bacterium that provokes inflammation will appear. Thanks to culture, the doctor will be able to choose the right antibiotic therapy.
- Analysis of urine. In the case of pyelonephritis, the urine will have an alkaline reaction, with a pH of 6.2–6.9. In addition, the shade of the liquid is assessed. In the presence of pyelonephritis, urine becomes dark, sometimes even reddish in color. It often contains protein.
- Research on Nechiporenko. This method allows us to detect a significant predominance of leukocytes in the urine over red blood cells.
- Prednisolone test. The event allows you to diagnose a pathology characterized by a hidden course. The patient is administered intravenously the drug Prednisolone in combination with sodium chloride. 1 hour after this, the woman needs to collect urine, then after 2 and 3 hours. And after a day. The urine is sent for detailed examination. An increased number of leukocytes will indicate the occurrence of pyelonephritis.
- Zemnitsky's test. The method allows you to detect reduced density of urine. With pyelonephritis, nighttime diuresis (volume of urine excreted) prevails over daytime.
To confirm pyelonephritis and differentiate it from other pathologies, the doctor will prescribe the following measures:
- Excretory urography. Allows you to detect kidney mobility. The study characterizes the condition of the calyxes and the tone of the urinary tract.
- Ultrasonography. To get an idea of the size of the kidneys, their structure, density, and the presence of stones in them, an ultrasound is performed. In the case of a chronic process, the echogenicity (ability to reflect ultrasound) of the parenchyma is increased, while in the acute phase it is unevenly reduced.
- Cystometry. This study allows us to identify pathologies of the bladder. The principle of the examination is based on determining the volume of urine.
- Cystography. This is a radiopaque study to detect vesicoureteral reflux or intravesical obstruction.
- CT scan. Detailed study of the kidney structure. Unlike ultrasound, it allows you to determine the condition of the pelvis, vascular pedicle and perinephric tissue.
In addition, women are definitely recommended to visit a gynecologist. The doctor will take smears to clarify the pathogen and determine the pathologies accompanying pyelonephritis.