The concept of “sexually transmitted infections” (or “sexually transmitted diseases”, STDs) includes not only sexually transmitted diseases, but also urinary tract infections.
A feature of many STDs is the absence of clearly defined symptoms (the so-called “hidden infections”). A woman may not even be aware that she is infected for a long time. Without timely treatment, STDs lead to chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, which, in turn, can cause infertility or spontaneous abortion and other serious consequences (see complications of pregnancy). Don't let the situation go that far! MedicCity diagnoses and treats all major sexually transmitted infections in women.
What microorganisms are “guilty” of causing STDs?
STDs are transmitted by various microorganisms, including:
- fungal infections (candidiasis);
- protozoa (trichomoniasis);
- viral (genital warts, HIV, genital herpes);
- bacterial (chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis).
This group also includes infections caused by opportunistic microorganisms (such as gardnerella, mycoplasma and ureaplasma). In small quantities, these microorganisms live even in completely healthy people, but in large concentrations they lead to urogenital diseases.
1 Surgitron

2 Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections
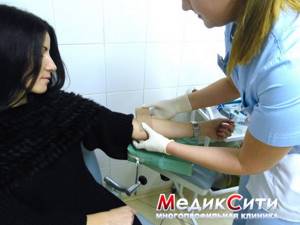
3 Laboratory diagnostics
How are indicators assessed?
The resulting material is sent for bacteriological, cytological and microscopic examination. After staining, the degree of cleanliness of the vagina, the presence of pathogens, and the presence of altered atypical cells are assessed. Bacteriological research is quite lengthy, since it is necessary to grow microflora on a nutrient medium, this is at least 5 days.
In diagnostics, speed and accuracy are important - this is the model of the work of the international clinic Medica24. A quick examination is made possible by precisely calibrated actions of specialists, following a standard algorithm of actions and the absence of a queue for hardware examinations. Error-free work is the credo of professionals, and all our employees are professionals. Sign up for a consultation: +7 (495) 230-00-01
The material was prepared by a gynecologist, oncologist at the international clinic Medica24, candidate of medical sciences Alimardonov Murad Bekmurotovich.
How do women get STDs?
There are no male or female sexually transmitted diseases. There are features of the course of the disease in men and women. The routes of infection are the same: sexual intercourse, infection through blood, close contact with an infected person at home. It is also possible to transmit the infection from mother to fetus during intrauterine development or to a child during childbirth and through milk during breastfeeding.
Diseases can intensify due to such unfavorable factors as:
- reduced immunity;
- stress;
- poor nutrition;
- environmental factor, etc.
It should be remembered that sexually transmitted diseases are very contagious, immunity to them is not developed, that is, re-infection is possible.
Who needs an STI test?
Since many diseases transmitted through sexual contact may not manifest themselves for a long time, almost no person can be sure that he or his partner do not have them. Therefore, checking yourself for infections through a blood test and smear for STIs is recommended in the following cases:
- When planning a pregnancy. To protect the unborn child from the development of congenital diseases and malformations under the influence of STI pathogens, both future parents need to undergo a preventive examination, tests and a smear for STIs. If a disease is detected, the doctor must prescribe a course of treatment that will ensure the normal course of pregnancy in the future and increase the chance of having a strong and healthy child.
- When changing partners or having a casual relationship. Casual sexual intercourse and the absence of a regular sexual partner increases the risk of STDs. Early detection of these diseases makes it possible to avoid unpleasant complications and protect your partner from infection.
- When unpleasant sensations appear in the genital area, discharge and inflammatory processes. If an STI is detected in one of the partners, the other also needs to undergo blood tests and a smear for STIs in order to accurately confirm or deny the presence of the same sexually transmitted infection and to exclude the possible presence of pathogens of other infections that were not transmitted to the partner.
In any case, it is better to entrust the interpretation of the test results to a doctor, and, if necessary, decide on treatment tactics with him.
General symptoms of sexually transmitted infections
Since many sexually transmitted infections do not manifest themselves in the early stages, a woman only begins to experience certain symptoms during an exacerbation of the disease and consults a doctor late. Therefore, it is important to know the main primary signs of sexually transmitted infections , which include:
- discharge from the genital tract, which has a yellowish, greenish and gray color and an unpleasant odor;
- frequent and painful urination;
- pain and burning in the genital area;
- skin manifestations in the form of growths, rashes or sores on the genitals;
- discomfort and pain during or after intimate intercourse;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the inguinal folds.
If you find yourself with similar symptoms, immediately contact your gynecologist and get tested for STDs! It is necessary to begin treatment of sexually transmitted infections as early as possible: in women they are more severe than in men.
Remember that untreated sexually transmitted diseases can cause irreparable damage to the female body!
How is the PCR test performed?
For research, any environment in which the pathogen may be located is taken, but the following are most often used:
- Blood serum or plasma
- to identify many pathogens - hepatitis B, C, D, G viruses, herpes, HIV, cytomegalovirus; - Urine and prostate juice
– for the diagnosis of STDs; - Sputum, pleural fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage
- for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis; - Cerebrospinal fluid
– for diagnosing infections of the nervous system; - Amniotic fluid
– to determine intrauterine infections; - A throat smear
- to identify the causative agents of infectious mononucleosis and diphtheria; scrapings and smears from the mucous membranes to diagnose STDs; cells of the gastric mucosa and gastric juice - to identify the Helicobacter bacterium, which causes gastritis and ulcers.
With one sample of material, several pathogens that have entered the body can be detected at once. This versatility saves the patient from additional examinations and unnecessary expenses. It is possible to detect and identify areas of genetic information using special DNA reference markers (primers) created for each known pathogen. The standard allows you to find “your” fragment among millions of others. If this happens, the polymerase chain reaction is started.
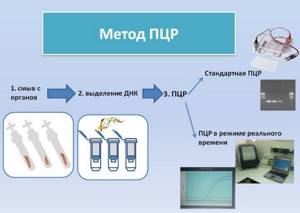
The PCR reaction makes a huge number of copies of the identified section of genetic information (replication). It is important that only the sections of DNA and RNA necessary for the analysis are replicated. Therefore, the cleanliness of the experiment and the ability of the staff to handle equipment and samples are so important. The chain reaction proceeds very quickly; after just two hours, the DNA section increases millions of times, which makes it possible to detect and accurately identify the infection. To work with standards, the test tubes are placed in a special device. Using the program, an algorithm is set that changes the temperature of the medium several times and affects the course of the reaction. The PCR result is visible immediately after the end of the study.
How do various sexually transmitted infections manifest themselves?
Sexually transmitted diseases occur in both men and women. You can read about the peculiarities of sexually transmitted infections in men here, and in this article we will talk about how sexually transmitted infections manifest and are treated in women.
Chlamydia
The causative agent of this disease is chlamydia. The disease is characterized by scanty symptoms - absence or a small amount of mucous discharge with pus, possibly painful urination, accompanied by itching and/or burning in the vagina. The infection poses a great danger for women planning pregnancy, as it can lead to adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes, and, consequently, to infertility or miscarriage, and fetal pathology.
Mycoplasmosis
The disease is caused by a microorganism such as mycoplasma. It manifests itself as transparent discharge and causes discomfort during urination and intimate contact. Can lead to inflammation of the vagina, uterus and appendages, and urethra. If infected during pregnancy, it can cause polyhydramnios, pathology of placental development and miscarriage.

1 Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections

2 Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections

3 Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections
Candidiasis
Candidiasis or “thrush” is caused by yeast fungi of the Candida class. They affect the vaginal mucosa and cause severe itching and cheesy discharge. You can read more about candidiasis here.
Trichomoniasis
One of the most common sexually transmitted infections is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis. This disease is characterized by slightly foamy vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor and pain during intercourse. In its acute form, the infection is extremely dangerous for pregnant women.
Genital herpes
It is considered an incurable disease. When the herpes virus (and its relative, cytomegalovirus) enters the body, it integrates into human nerve cells and remains there for life.
In addition to itching and burning in the genitals, it is characterized by the appearance of a blistering rash, high fever, muscle pain and headaches. Subsequently, it can lead to such unpleasant diseases as conjunctivitis, encephalitis, meningitis, keratitis and damage to the central nervous system.
Human papillomavirus
HPV (and in particular, flat condyloma of the cervix) can be recognized by the following signs: the appearance of warts and genital warts on the genitals and mucous membranes, the occurrence of cervical erosion.
The danger of infection is that the virus cannot be treated. The current approach is to test all women with cervical cytology during mandatory annual screening. It is important to carry out typing of the virus for oncogenic variants and, if detected, take the patient under observation, and not engage in mythical treatment of the human papillomavirus. However, if anatomical changes are detected in the form of condyloma or cervical papilloma, surgical excision is indicated. It must be remembered that oncogenic types of human papillomavirus are associated with cervical cancer.
Staphylococcus
A whole group of diseases caused by pathogenic staphylococci. Often, staphylococcus, together with pathogenic microbes such as gonococcus, chlamydia, and trichomonas, enters the genital tract during sexual intercourse and after a while causes itching, pain and burning.

1 Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections

2 Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections

3 Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
The essence of the polymerase chain reaction method
The method is based on identifying the pathogen by sections of DNA or RNA. PCR is reminiscent of forensic science, when a criminal is found by pieces of skin or hair left at the crime scene. Because every living organism has a unique DNA or RNA structure. The method allows you to accurately identify a microorganism, even if it is present in the test material in minimal quantities. PRC is suitable for identifying latent carriage, atypical, erased and other forms of infectious diseases. Diagnostics is highly accurate and therefore practically does not produce errors or false results. The analysis is often prescribed as an additional examination to identify a specific type of virus or microbe.
Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
To diagnose sexually transmitted infections, you may be prescribed the following STD tests:
- general smear (a smear scraping from the genital organs is taken for examination);
- ELISA (i.e. enzyme immunoassay) - the patient’s biological material is examined. The immunological reaction to certain pathogens is checked;
- PCR (polymer chain reaction, analysis shows the pathogen). DIGENE test - quantitative analysis for HPV allows you to determine the concentration of the virus in the material.
- bacteriological culture (helps to identify the sensitivity of the infection to antibacterial drugs);
- RIF (immunofluorescence reaction) is carried out by staining biological material using various reagents;
- urine test for infections.
At the MedicCity clinic, you can undergo a gynecological examination at a time convenient for you and get tested for any sexually transmitted infections in women. You can find out the cost of testing for HPV, testing for cytomegalovirus infections and other STDs by phone.
Quite often, worried patients search the Internet for answers to their questions (for example, what to do if the blood test for ureaplasma is negative, but the smear test is negative?). However, it is better not to rely on all sorts of Internet forums, but to receive information first-hand during a consultation with a professional gynecologist.
Blood analysis
If during the PCR analysis the patient’s blood becomes the object of study, the rules for preparing for it are as follows.
- The optimal time to donate blood is in the morning; the test must be taken on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours without food). You can drink water freely.
- Quit alcohol one day before the PCR test, quit smoking an hour before it.
- If your health allows this option, it is recommended to stop taking medications for a while.
- Before donating blood samples, you should rest for about 20 minutes.
- On the eve of the PCR test, emotional and physical overload is completely excluded; they can affect the results of the analysis.
Treatment of sexually transmitted infections in women
Treatment of sexually transmitted infections in women, as well as in men, includes taking antibacterial drugs, antiviral, antifungal agents, and immunomodulators. If it is necessary to remove papillomas and condylomas, radio wave methods are used.
When treating sexually transmitted infections, women often rely on advice from friends or advertising. In most cases, this not only does not help get rid of a sexually transmitted disease, but also causes serious damage to the female body! Be sure to consult with a gynecologist who will conduct the necessary tests for STDs and individually select the medications you need.
Even if you follow STD prevention measures, do not forget to visit a female doctor every six months! In our clinic, specialists work on Voluson 10 expert-class ultrasound equipment, which allows them to detect the slightest alarming changes in the female body. Remember: any illness is easier to cure at an early stage!