The birth of a new life and the formation of a person is a mysterious and amazing process hidden from the eyes of ordinary people. However, scientists are lifting the veil of secrecy, and today much in this process has already been studied. What happens to the unborn child in the first days and weeks after conception? How does it develop? What is a fertilized egg, what does it consist of? What pathologies are possible in its development?
When does the fertilized egg appear after fertilization?
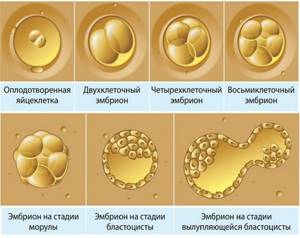
After the fusion of the egg and sperm, the zygote is covered with a fertilization membrane, which prevents the penetration of other male gametes, and remains dormant for about a day. On the second day, its crushing begins. The division of the zygote lasts about 6 hours and ends 30 hours after fertilization - 2 blastomeres are formed. After another 10 hours there are 4 of them, and after 4–4.5 days there are 58.
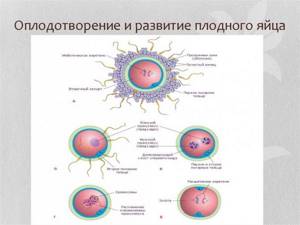
From the very beginning, “light” and “dark” blastomeres are formed. The first, which fragment faster, will subsequently form the outer layer - with its help the embryo will feed and breathe. From the “dark” ones, the body of the embryo and its extra-embryonic organs are subsequently formed.
On the 3rd–4th day, the formation of a hollow vesicle with liquid—a blastocyst—begins. It travels through the fallopian tube for three days and then enters the uterine cavity. It consists of 100 or more cells. The future embryo is a cluster of dark cells in the form of a kind of nodule, attached from the inside to one of the poles of the blastocyst.
For two days, the process of preparation for the upcoming implantation into the uterine wall takes place in the vial. At this time, the blastocyst intensively produces special enzymes, the task of which is to destroy the tissues of the uterus, making a kind of hole in them. Implantation (nidation) occurs in 2 stages:
- the outer layer of cells “sticks” to the endometrium;
- enzymes destroy the endometrial layer of the uterus, the resulting villi destroy epithelial, connective tissue and vascular walls.
For 2 days, the embryo feeds on the decay products of the tissues destroyed by it, then receives nutrition and oxygen from the mother’s blood. Around this time, the germinal nodule changes shape and becomes disk-like. He is preparing for a new stage of his development.
Stages of fertilized egg formation
Cells move and differentiate. The formation of extraembryonic organs begins. At this stage, the following are formed:
- Amnion (future amniotic sac). The transparent membrane produces amniotic fluid, which is designed to be a nutritious and environmental medium for the embryo, promote the proper formation and growth of body parts, and protect against trauma.
- Chorion (future placenta). This is the outer membrane of the fertilized egg, in direct contact with the wall of the uterus. Through this shell, until the formation of the child's place is completed, the embryo receives nutrition and oxygen for breathing.
- Yolk vesicle. From it, the yolk sac is formed - the main hematopoietic organ until the formation of the placenta is completed, in which the first blood vessels appear and germ cells are produced.
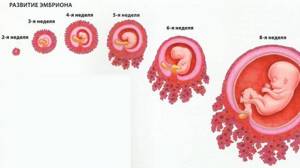
On days 14–15 after fertilization, 3 germ layers, a neural tube and a notochord – the future spine – are formed. The allantois develops, from which the umbilical cord and bladder are then formed. From the 15th to the 20th day, the separation of embryonic tissues from extra-embryonic organs and the formation of the trunk fold continue.
Until the 35th day, the cells of the embryo are divided and receive “specialization” - 43–44 segments are formed, from which the skeleton and rudiments of all organs will be formed before the end of the second month of intrauterine life. At 8–9 weeks, the embryo looks like a man and weighs about 5 g and is 40 mm tall.
First trimester of pregnancy: norm, risks, sensations
Pregnancy lasts 280 days and is usually divided into trimesters. The first trimester is the most important, as all the organs and tissues of the fetus are formed, as well as the placenta and the vessels that nourish the fetus.
First trimester. 1-3 weeks of pregnancy
Reproductive health
For couples who are planning a child, we have developed a diagnostic program for a quick health check. Based on the results, either a more in-depth diagnosis will be prescribed or recommendations will be given. The program allows you to quickly and inexpensively find out your reproductive health status.
Some people calculate the gestational age from conception, but this is incorrect. From 1 to 3 weeks, only the fertilization of the egg occurs, its descent into the uterus through the fallopian tubes and implantation. Only after implantation of a fertilized egg can we say that pregnancy has occurred. During its journey through the fallopian tube, the cell actively divides and by the time of implantation there are already about 30 of them. Ultrasound is usually not done at 3 weeks of pregnancy, since it is not very informative, and implantation may not have occurred yet.
If you are planning a pregnancy and want to know exactly about your condition, you can take a pregnancy hormone test. It will show the presence of pregnancy within 2 weeks after fertilization. Usually women do not feel any changes during this period; some may experience implantation bleeding, which lasts no more than one day.
First trimester. 4-6 weeks of pregnancy
At this stage, women experience the main symptom – delayed menstruation; in addition, tests for home use will also show pregnancy. Some women experience breast swelling, nausea, and perhaps slight drowsiness. During this period, the fertilized egg turns into an embryo: the rudiments of all systems, even tooth enamel, are formed. And it is especially important to lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid contact with infection and hazardous substances. If you are taking medications, it is important to check with your doctor about taking them.
You can do an ultrasound if there is a risk of ectopic pregnancy - the doctor will see that the fertilized egg is in the uterine cavity and the pregnancy is developing normally. The risk of miscarriage remains very high. This may be due to weak implantation of the fertilized egg - endometrial diseases, frequent abortions and childbirth can thin the endometrium and the fertilized egg will not be sufficiently attached. An ultrasound at 6 weeks of pregnancy will already show a heartbeat, the length of the embryo from the crown to the sacrum is 2-4 mm, and the volume of amniotic fluid is 2-3 ml.
First trimester. 7-8 weeks of pregnancy
The fetus is developing rapidly, if you do an ultrasound at 7 weeks, it still has a “tail”, but by the end of the 9th week you will no longer see it on an ultrasound. The liver is already working, it produces blood cells and the unborn child acquires its own blood type. An ultrasound at 7-8 weeks will show a clear and well-audible fetal heartbeat. Fingers form on the rudiments of the limbs, and the fetus already “knows how” to bend the elbow and wrist joints. The risk of miscarriage remains high. Recommendations:
- Change your eating style, this will help you avoid gaining excess weight in the future;
- Watch your eating behavior, all the extra pounds gained in the first trimester will remain with you after childbirth;
- Visit a gynecologist for an individual selection of a vitamin regimen, since uncontrolled use can worsen the condition;
- Register for pregnancy at an antenatal clinic or private medical clinic.
First trimester. 9-11 weeks of pregnancy
An increased level of pregnancy hormones affects the well-being of the expectant mother: women become emotionally unstable, drowsiness increases, and there may be changes in appetite. The brain of an unborn child grows very quickly - 500,000 new neurons appear every two minutes.
By the end of the 10th week, the final formation of building blocks occurs and, if there were no errors, then congenital anomalies are excluded. For this reason, at 9-11 weeks of pregnancy there is a very high risk of miscarriage - this is how the body reacts to an embryo that has serious abnormalities. The muscle fibers of the fetus begin to work, so far randomly and chaotically, but if you do an ultrasound at 9-11 weeks of pregnancy, the ultrasound will notice them. The length of the fruit is 40-60 mm, and its weight is about 8 g.
First trimester. 12-13 weeks of pregnancy
The placenta is finally formed, the risk of miscarriage is reduced to a minimum, and nausea and toxicosis recede. At this time, the first control ultrasound is performed as part of diagnostic screening for congenital anomalies and Down's disease. You can have an ultrasound done at 12 weeks, both in the antenatal clinic and in a private clinic. By the end of the 13th week of pregnancy, the placenta itself can produce the necessary hormones, the fetus begins to swallow amniotic fluid, and the desired type of chest movement is formed. The weight of the fruit is 14-20 g, and its length is 65-78 mm.
During the first trimester of pregnancy, the main risk is miscarriage. Pain in the sacrum and lower back indicate increased muscle tone of the uterus; you should definitely consult a doctor.
Medical Center named after. Speransky has licenses for pregnancy management and all diagnostic procedures. We will take care of your health and reduce all possible risks to a minimum. You can make an appointment by calling +7 (391) 205-20-35 or through the online registration.
We have installed the latest diagnostic equipment, which allows us to see even minor disorders and prevent more serious pathologies. There is a diagnostic department so that you can undergo all the necessary examinations on the day of your visit.
Methods for diagnosing the condition and parameters of the ovum
The only method for diagnosing the condition and assessing the parameters of the ovum today is ultrasound. It can be detected already at the 3rd week of embryo development, or at the 5th obstetric week. Normally, it looks like a round or oval echo-negative formation 3–5 mm in diameter. At the 7th week, an embryo 6-7 mm long is visualized in the fertilized egg as a strip with increased echogenicity. From 6.5 weeks, the indicators of normal development of the embryo are its mobility and heartbeat.
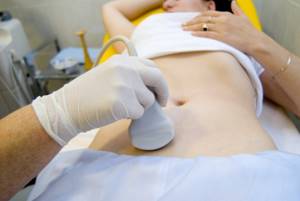
The first ultrasound examination, in the absence of indications for its emergency implementation, takes place at 11–14 weeks. Diagnostic goals:
- clarification of the gestational age;
- detection and measurement of the ovum;
- identification and measurement of the embryo, clarification of the quantity;
- determining the place of attachment of the chorion;
- detection of anomalies of the fertilized egg and embryo.
Transvaginal ultrasound is considered the most informative in the first trimester. It does not require special preparation. The woman needs to wash herself and empty her bladder (the latter is not a mandatory requirement; she will simply feel discomfort with a full bladder during the procedure).
The appearance of the embryo in the fertilized egg
At the blastocyst stage, the embryo undergoes the process of implantation - the introduction of the embryo into the endometrium of the female reproductive organ - the uterus. The chorion is formed and the release of human chorionic gonadotropin begins. Exactly the substance that will act on a pregnancy test and show two cherished stripes. At the third week of embryo development, it measures 4 mm. Of course, at this stage, even with the help of a modern ultrasound diagnostic device, it is quite difficult to visualize it in the uterine cavity.
Right now the formation of all organs and systems begins. At this stage, it is very important to limit the influence of harmful substances, habits or influences. It is during this week that the embryo is so vulnerable that any impact can be fraught with the development of congenital malformations or even termination of pregnancy (oocyte bank).
In the fourth week, the stages of formation and development of human organs and systems still occur, and it is in this week that the heart begins to beat.
It would seem that at this stage the embryo has formed organs, albeit tiny ones, and it seems that in any case a pregnancy can be identified. However, this is not quite true.
Women who really want to get a long-awaited pregnancy make trivial mistakes that make them upset for no particular reason.
The first common mistake is to run for an ultrasound examination on the first day of a missed period. It is this period in the presence of pregnancy that is the level of four obstetric weeks. At this stage of development, although the embryo itself has a heartbeat, it is not always possible to see it on an ultrasound diagnostic machine. And on some devices, even at such a short period of time, it is difficult to visualize the fertilized egg. A woman is worried that the embryo is not developing or is completely upset about the lack of pregnancy.
However, to visualize pregnancy at fairly early stages, as well as identify heartbeats at 5-6 weeks, expert-class ultrasound machines are needed that have the ability to detail images. In fact, ultrasound diagnostics and visualization of the ovum are quite important in gynecological practice, as well as in the practice of reproductology. With the help of ultrasound examinations, it is possible to make diagnoses such as frozen pregnancy, in which there is no heartbeat. The threat of miscarriage, which can be discussed in case of deformation of the contours of the fetal egg, deformation of the contour of the uterus.
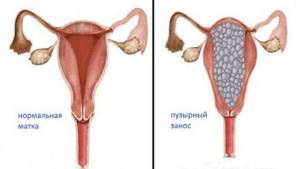
Also a common pathological condition that occurs in women during pregnancy is anembryonia. That is, visualization of an empty fertilized egg without any signs of a developing embryo inside the uterus. Also quite a serious problem is the visualization of the contents of the ovum in the form of a “snow storm” during ultrasound examination. This picture indicates a hydatidiform mole, which can be fraught with serious complications including the development of chorionepithelioma, a malignant neoplasm arising from trophoblast cells.
Therefore, clear visualization of the uterine cavity is a huge diagnostic point in the practice of an obstetrician-gynecologist (how often can you be an egg donor). In the absence of indications for ultrasound examination, the first ultrasound can be performed during the first ultrasound screening at 12-14 weeks of gestation. Each research method, like a medicine, requires its own strict indications. Conducting an ultrasound examination without them can be fraught with danger to the health of the woman and the health of the baby.
A rather big problem is the spread of private practice of ultrasound diagnostics. Every woman can consult a doctor with an ultrasound examination. The fact is that ultrasound, passing through the myometrial tissue, can tone them, causing a condition such as uterine hypertonicity, the threat of miscarriage. No one knows which threat of termination of pregnancy is stopped, and which will be followed by termination of this condition. That is why an ultrasound examination is performed if pregnancy complications are suspected in the form of an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy, impaired tubal pregnancy, frozen pregnancy, after an in vitro fertilization protocol
You just have to follow the recommendations of your doctor, and not engage in amateur activities. In this case, there is a possibility of a good outcome for both your child and the woman.
The second common mistake is performing a pregnancy test in the early stages, that is, even before a missed period, with a low level of sensitivity to hCG. With late implantation, the level of hCG has not yet increased enough for the test to show the presence of this very chronic human gonadotropin. For example, if a test with a sensitivity of 25 international units, and with late implantation in the first days of delay, the level may be 15-20, which does not reach the threshold value of the test. In such a situation, the second strip may not appear. However, this does not exclude the possibility of pregnancy. The sooner you try to determine whether you are pregnant or not, the more sensitive the test must be used to identify the “interesting position”.
Possible anomalies and their causes
During an ultrasound scan, the following developmental disorders of the ovum and embryo can be detected:
- abnormal localization of the chorion (presentation, attachment outside the uterus - in the fallopian tube, ovary, cervix, abdominal cavity);
- absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg (anembryony, which is diagnosed in approximately 15% of pregnant women);
- death of the embryo and frozen pregnancy;
- structural anomalies, deviations in size;
- Hydatidiform mole (occurs as a result of fertilization of an egg that does not have chromosomes, or when one female cell merges with two male cells, while the chorionic villi degenerate into bubbles with liquid, the embryo does not develop or dies).
Signs and features of embryo implantation
The birth of a new life is a truly wonderful event. After all, so many things must happen at the right time and in the right place for fertilization of the egg to occur, that one can only marvel at nature’s foresight. The embryo faces a very important test - its implantation (introduction) into the uterus. What it is, how and on what day it happens, what sensations it causes - all this is necessary to know not only for pregnant women, but also for women planning a pregnancy, including with the help of IVF.
The fertilized egg, protected by a special membrane formed around it by the sperm, begins its movement from the fallopian tubes, without ceasing to divide. At the same time, it, now called morula, secretes a special enzyme trypsin, which signals the uterus to prepare the “landing site.” In order for the embryo to be implanted into the uterus successfully, an intact and normally functioning endometrium is required, as well as a favorable hormonal background in the woman’s body and, in particular, the production of progesterone in the required quantity. This hormone will further maintain pregnancy until the placenta is formed.
On what day does embryo implantation occur?
Around 3-4 days, the fertilized egg reaches the uterine mucosa and, having gotten rid of the membrane, begins implantation, which lasts up to 40 hours. During this time, the embryo, or rather the part called the trophoblast, penetrates the endometrium, “joins” the capillaries and continues its development. In the future, the trophoblast will turn into the placenta and begin to protect and feed the child, and the endometrium will provide it with all the necessary nutrients.
In some cases, the journey of the egg from the fallopian tubes may last longer than the specified time - about 10 days. This phenomenon is called late implantation.
Signs of implantation
A pregnant woman experiences virtually no special sensations during embryo implantation. Only in rare cases may the expectant mother notice irritability, tearfulness, discomfort in the lower abdomen, a metallic taste in the mouth and mild nausea. Doctors consider these signs not directly related to the implantation of the fertilized egg itself and chalk it up to hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). This hormone begins to be produced in the body of a pregnant woman just after the implantation of the embryo into the endometrium.
In some women, a sign of embryo implantation in the uterus will be spotting. Unlike menstruation, they are very scanty, almost invisible to a woman and pass quickly. These discharges appear when the egg penetrates the lining of the uterus and destroys the walls of the capillaries. But if they are abundant and accompanied by pain, you should immediately consult a doctor, because miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis and some other serious diseases can manifest themselves in this way.
Also, the day of implantation of the embryo into the uterus can be calculated by measuring basal temperature. This will be evidenced by its slight decrease and subsequent increase. This method will reliably report the fact of pregnancy even in the case of late implantation. Basal temperature is measured in the morning in the rectum. And if the expectant mother, planning a pregnancy in advance, measures her basal temperature every day, she can calculate both the day of ovulation and the implantation of the embryo into the uterus, which will indicate the successful occurrence of the long-awaited pregnancy.
Not every fertilized egg is implanted in the uterus
Sometimes implantation does not occur after fertilization. This happens, for example, with genetic abnormalities or the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg. We can say that natural selection is carried out in this way. Implantation of the embryo into the uterus may not occur if the outer membrane of the morula is too strong or if there are disorders in the endometrium itself. However, sometimes the “test” itself can go wrong and a healthy embryo fails to implant. On the contrary, a fertilized egg with genetic abnormalities will be able to easily attach to the endometrium.
Most often, such a genetic “marriage” will end in spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages. It also happens that the fertilized egg is not attached to the wall of the uterus, but, for example, in the fallopian tubes. Then they talk about ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy, which will be manifested by bloody discharge, pain in the lower abdomen, and general poor health. Under no circumstances should you ignore this condition and expect everything to go away on its own. You should immediately consult a doctor to prevent dangerous complications.
The fact of implantation of the egg into the wall of the uterus and its normal development can be confirmed by a gynecologist during an examination, starting from 5-7 weeks of pregnancy. The fact is that by this time the genitals undergo some changes, which are detected by specialists during vaginal examination. Ultrasound also helps make an accurate diagnosis by detecting the fetal heartbeat even in the early stages of pregnancy. Sometimes, with late implantation, ultrasound will not determine the presence of an embryo in the uterus. In this case, the examination must be repeated after seven days, when the fertilized egg will probably be noticeable.
Embryo implantation during IVF
When for some reason it is not possible to conceive or bear a child for a long time, in vitro fertilization (IVF), which has recently become increasingly popular, is possible. However, even this method does not always work and pregnancy failure is possible after artificial insemination. This can happen for many reasons: genetic abnormalities of the embryo, hormonal disorders of the mother, her age and general health. But women dreaming of a child should not despair. The IVF Center clinic in Petrozavodsk performs artificial implantation of the embryo into the uterus, even if attempts in other clinics have failed.
It is worth understanding that IVF is a whole complex of examinations and treatment aimed at successful IVF - implantation of the embryo into the uterus and the further course of pregnancy.
In vitro fertilization is carried out in several stages:
- Stimulation of ovulation using medications
- Retrieval of eggs and sperm
- Selection of the necessary “material”
- Artificial insemination
- Embryo transfer and implantation into the uterine cavity.
An artificially implanted embryo must adapt to the new environment for some time, so the day of implantation will occur later than with natural fertilization. To increase the likelihood of successful transfer, clinic specialists transfer two embryos. In the future, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the expectant mother in order to protect her from spontaneous miscarriage and other complications. A woman should avoid excessive physical activity and stress. It is necessary to get more rest, eat healthy foods and avoid contact with infectious patients. Also, in the early stages, you should not take a hot shower, avoid sexual intercourse, avoid overcooling and spend more time in the fresh air, but without long walking.
The sensations during implantation and during pregnancy itself do not differ from those during natural fertilization. Their difference lies only in the greater susceptibility to various complications of those women who have undergone artificial insemination. After IVF, pregnant women may face intrauterine infections, placental insufficiency, detection of congenital malformations, and immune conflict between mother and child.
The management tactics for pregnant women after in vitro fertilization are more stringent and include receiving hormonal drugs in larger than usual doses; enhanced vitamin therapy; taking metabolic drugs; prevention and timely treatment of infectious diseases and increased attention from the attending physician. But even with such intensive therapy, there remains a risk of complications and pregnancy failure. Often the consequence of artificial insemination is multiple pregnancy, which can also become a problem for the mother. However, with competent management of the clinic’s specialists, strict adherence to their recommendations and a positive attitude, pregnancy after IVF will proceed quite safely and will be resolved with the birth of the long-awaited baby.
If you have any problems with childbirth, you can contact the IVF Center in Petrozavodsk. Our specialists will determine the reason for the absence of the desired pregnancy and select the optimal treatment for you. You will surely be able to experience the joy of motherhood!
Therapeutic tactics when detecting pathologies
The actions of doctors after detecting a particular pathology of the ovum or embryo depend on the nature of the disorder. So, if chorion presentation, a change in the shape of the fetal egg, a discrepancy between its size and the parameters of the embryo with the expected gestational age are detected, specialists take a wait-and-see approach and prescribe a repeat ultrasound in a week.
If an ectopic or frozen pregnancy, anembryonia, or hydatidiform mole is detected, interruption and removal of the fertilized egg and its contents are indicated. Subsequently, the doctor analyzes the situation, looks for the reasons for what happened and prescribes a genetic analysis, determines the state of hormonal levels, etc. Then an individual treatment regimen is developed.
Irregularly shaped fertilized egg
The shape of the fertilized egg is normally oval or round. If it looks flattened on the sides and resembles a bean, this may indicate the tone of the uterus. This condition should be monitored by a doctor. If nothing bothers the patient, then the deformity does not pose a threat to pregnancy. With increased uterine tone, doctors take certain measures (taking medications, bed rest) to remove hypertonicity, as well as return the fertilized egg to its normal, correct shape. This is achieved by relaxing the muscles of the woman’s uterus.
However, if the fertilized egg has an irregular shape, and the patient experiences pain, discharge or symptoms of cervical dilatation, then urgent measures must be taken. In such cases, the woman is admitted to the hospital for further pregnancy.