Laparoscopy
Video Useful information Questions and Answers
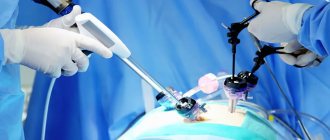
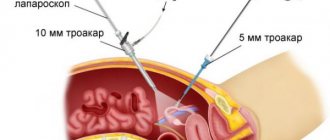
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive method in which access to the pelvic organs is carried out through punctures 3–5 mm in size, through which instruments and an endoscope are inserted (enlarges the image 12 times). This surgical technique allows for gentle treatment and a short recovery period. Check out the prices in the price list. Make an appointment at a clinic in Moscow and check the cost of the procedure on the website.
| Services list | Price |
| Diagnostic laparoscopy | 80,000 - 100,000 rubles |
| Cauterization of the ovaries | from 70,000 rubles |
| Ovarian cyst removal | from 80,000 rubles |
| Removal of uterine fibroids | from 100,000 rubles |
| Supravaginal hysterectomy | from 100,000 rubles |
| Hysterectomy | from 120,000 rubles |
| Surgical treatment of infiltrative form of endometriosis | from 120,000 rubles |
| Fallopian tube removal | from 70,000 rubles |
| Promontofixation (sacrovaginopexy) | from 150,000 rubles |
| Extended hysterectomy with pelvic-iliac lymphadenectomy | from 150,000 rubles |
| Lightweight promontofixation | from 100,000 rubles |
Order a call Make an appointment
Dear girls and women, I am an obstetrician-gynecologist, and I am very sensitive to my patients, I try to help them even in the most difficult situations. I would like to draw your attention to the fact that prices for the service may vary depending on the complexity of the case and diagnosis. Due to the specifics of the field, it is impossible to accurately and immediately describe everything on the website; consultations and initial examinations, tests, ultrasound, etc. are required. Based on their results, the final cost of the service is calculated.
When is laparoscopy necessary in gynecology?
The procedure can be planned, urgent or emergency. Planned surgery is prescribed in the following cases:
- primary and secondary infertility;
- pelvic pain of unknown origin;
- intra-abdominal bleeding;
- symptoms of uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts and tumors;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- removal of submucosal nodes;
- preparation for IVF (and in case of unsuccessful attempts).
Urgent laparoscopy in gynecology is performed for pathologies that threaten the patient’s life. Including, if acute inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries does not stop within 6–8 hours of conservative therapy in a woman. Emergency intervention is necessary in case of intra-abdominal or uterine bleeding, or acute pain syndrome.
Laparoscopy in gynecology: preliminary examination
Before carrying out the intervention, it is necessary to undergo a series of studies. This can be done in the hospital at your place of residence in Moscow or with us at an affordable cost, spending only 1 day on diagnostics.
List of basic examinations that must be performed before laparoscopic promontofixation (sacrovaginopexy):
- General blood test (expiration date 14 days).
- General urine test (expiration date 14 days).
- Electrocardiogram (expiration date 10 days).
- Chest X-ray or fluorography (shelf life 12 months).
- Consultation with a therapist (expiration date 14 days).
- Blood type and Rh factor (if you plan to have surgery not in our medical institution) - only a stamped form is accepted (expiration date - lifetime).
- Biochemical blood test: blood glucose, AST, ALT, urea, creatinine, total and direct bilirubin, total protein, serum iron (shelf life 14 days).
- Coagulogram, hemostasiogram - assessment of the blood coagulation system: VSC, prothrombin index, APTT, fibrinogen, antithrombin III (shelf life 14 days).
- Hospital complex: blood for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B and C (expiration date - 3 months).
- Smears from the cervix for oncocytology (expiration date 6 months). This analysis is taken strictly in the absence of bloody discharge from the genital tract.
- Smears from the cervix and vaginal mucosa for flora and degree of purity (shelf life 14 days). This analysis is taken strictly in the absence of bloody discharge from the genital tract.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder (shelf life 1 month).
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (shelf life 1 month).
Before diagnostic laparoscopy, you also need to undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, an ECG, fluorography, duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities, and consult a therapist.
For some diseases, we may ask the patient to additionally undergo:
- aspiration biopsy of the endometrium (including as part of hysteroscopy);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- EchoCG;
- forced spirometry;
- FGDS;
- colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy;
- extended colposcopy;
- blood test for hormones;
- tests for STIs and bacteriological culture from MPP;
- hysterosalpingography;
- CT, MRI;
- consultation with specialized specialists (endocrinologist, pulmonologist, anesthesiologist, etc.).
Clinical picture of the adhesive process in the pelvis
In the vast majority of cases, provided there is no current chronic inflammatory process, patients do not present any complaints. In case of pronounced changes, there may be moderate pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen. Pain may intensify in the middle of the cycle and during menstruation. In these situations, it is always important to carefully collect anamnesis, where you can find references to previous inflammation or surgical interventions. At the same time, often previously suffered inflammatory processes, especially if they occurred subacutely, may not leave a trace in a woman’s memory. The disease is more often detected either by chance, or as a result of the fact that a woman does not become pregnant, and she begins to be specifically examined in order to identify the causes of infertility.
Diagnosis consists of an ultrasound scan, as well as a number of specific studies that allow you to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes: hysterosalpigography (X-ray and ultrasound). The final diagnosis is made based on laparoscopic findings. With ultrasound, you can pay attention to changes in the normal topographic values of the pelvic organs and identify gross deformations. The adhesions themselves are usually not amenable to visualization.
Hysterosalpingography usually makes it possible to clearly understand the nature of the fallopian tube lesion, but it is possible to assess the true picture only after a laparoscopic examination.
Preparation for diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy
The patient must follow a slag-free diet for 2–3 days before the intervention. Before a diagnostic laparoscopy operation, 1-2 enemas are given (the night before and on the day of surgery). Drinking is allowed without restrictions, up to 8 hours before the procedure.
Immediately before laparoscopy, shaving of pubic and labia hair is performed in the gynecology hospital.
After the intervention, the patient may be recommended compression stockings, which should be purchased in advance. We also use the Swiss hardware compression system Kendell, which stimulates blood flow in the legs. This helps to avoid thrombosis after diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy.
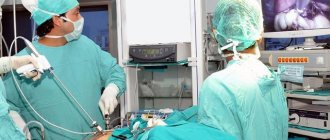
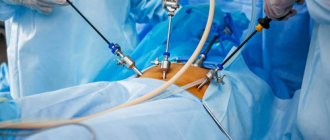
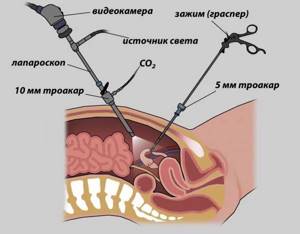
Laparoscopy technique
The intervention is performed under general anesthesia. During laparoscopy, a puncture is made below the navel, through which a trocar with a camera at the end is placed into the abdominal cavity, visualizing the operation process. Next, two more incisions are made, through which trocars equipped with a light source, a gas pump and instruments for manipulation are inserted.
Diagnostic laparoscopy in a hospital in Moscow can be performed with a biopsy. During the procedure, using a special instrument, the doctor takes a small piece of tissue from the pathological focus for subsequent analysis.
Laparoscopy in gynecology takes from 10-30 minutes to several hours, the price and duration depend on the complexity of the intervention.
At the end of the procedure, the doctor performs an inspection and removes blood or fluid that accumulated during the intervention. The gas is then removed and the instruments are removed. The incisions are closed with stitches.
Postoperative period
After laparoscopy, the patient receives antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and infusion drugs, as well as drugs that contract the uterus. It is recommended to take antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs for 5 days after discharge. Sutures after laparoscopy are processed once a day. On days 7–10, you need to visit a doctor for a control ultrasound and treatment of surgical wounds.
Salpingectomy
Salpingectomy
is a type of surgery during which the fallopian tube is removed. The operation is performed laparoscopically, which reduces the patient’s rehabilitation period due to the absence of abdominal incisions. Indications for salpingectomy are anatomical features or functional disorders of one or two fallopian tubes that pose a threat to the patient’s health or cause infertility. The main reasons for removing the fallopian tubes:
- diagnosed ectopic pregnancy
- undisturbed repeated tubal pregnancy on the same side
- chronic inflammatory processes - hydrosalpinx (accumulation of fluid in the fallopian tube), salpino-oophoritis, sactosalpinx (accumulation of inflammatory exudate), pyosalpinx (accumulation of purulent contents in the tube)
- planning pregnancy using IVF with a diagnosis of infertility, which is caused by the presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the appendage area
- adhesions in the pelvic organs with pronounced spread to the appendages.
It is worth noting that in the case of ectopic pregnancy, laparoscopy can remove the pregnancy while preserving the fallopian tube, in the case of early diagnosis (short gestation) and the absence of massive intra-abdominal bleeding. However, maintaining the full function of the fallopian tube after such an operation does not always occur; in some cases, it is impossible to preserve the functionality of the fallopian tubes. Hydro-sactopyosalpinx represent, in fact, different stages in the development of inflammatory disease of the fallopian tubes. They are formed as a result of damage to the fimbriae (villi) of the tube by the inflammatory process, closing the lumen of the tube, and accumulation of fluid. The structure of the pipe wall is also disrupted - it becomes thinner, stretched, and the muscle layer is damaged. The pipe loses its function completely and can serve as a reservoir for a slowly occurring infectious process. If the lumen of the tube towards the uterus is open, then it can pass into the uterine cavity and the opposite fallopian tube. The pregnancy rate in this case is reduced by half, even with the use of ART and an IVF program. In this case, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause before further pregnancy planning.
Is it possible to get pregnant after removal of the fallopian tubes?
After removal of the fallopian tubes, pregnancy is possible with the help of IVF; in the case of removal of only one side, the possibility of natural conception remains in more than 50% of patients. Much depends on the patient’s health status, concomitant diseases and disorders. Competent treatment and timely intervention are the key to a successful pregnancy.
Possible risks after laparoscopy
Among the main dangers of the operation are the consequences of anesthesia and possible damage to internal organs during insertion of the instrument. A preliminary consultation with an anesthesiologist and his monitoring of the patient’s condition during surgery can eliminate the risk of complications.
During laparoscopic procedures, blood vessels, intestines, and the urinary system can be damaged. The risks increase if the woman is overweight, has previously had abdominal surgery, and has intestinal adhesions to the abdominal cavity. The experience and skill of the surgeon eliminate the possibility of injury to internal organs.
Check the price list for the cost of laparoscopy in a clinic in Moscow. You will learn the details of the procedure at your appointment.
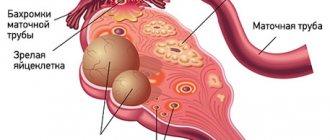
Fallopian tube laparoscopy and pregnancy after surgery
Adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes are one of the factors preventing the conception of a child. Laparoscopy allows not only to detect pathological changes, but also to eliminate them. The operation can be prescribed as an independent examination or as part of other procedures.
After laparoscopy surgery, the recovery period takes 4-5 months. After this time, you can plan your pregnancy.
Despite the low invasiveness and high efficiency of laparoscopy, the operation does not always lead to the expected result. This applies mainly to old adhesive processes. Even after laparoscopy, when the patency of the tubes is restored, negative changes in their walls can be observed.
The adhesive process can affect the inside of the tubes and the ciliated epithelium (it helps propel the egg into the uterine cavity). This risks an ectopic pregnancy.
Sign up for diagnostic laparoscopy at my hospital in Moscow. I use gentle examination and treatment methods to preserve a woman’s reproductive function.
Our experienced gynecologists
Arnaut Svetlana Ivanovna
- More than 27 years of experience, doctor of the highest category
- Obstetrician-gynecologist, mammologist, ultrasound diagnostician
- Performs gynecological operations
- Planning and management of pregnancy
- Diagnosis and treatment of miscarriage
- Infertility treatment
Mamedova Roxana Zaitdinovna
- 10 years of experience
- Obstetrician-gynecologist
- Ultrasound in gynecology and obstetrics
- Colposcopy. Hirudotherapist
Sofronov Alexey Vitalievich
- More than 15 years of experience, Ph.D.
- Obstetrician-gynecologist
- Reproductologist
- Mammologist
- Ultrasound in gynecology and obstetrics
- Laparoscopic operations
- CTG
- Videocolposcopy
Azizova Gulnar Azizovna
- 8 years of experience
- Obstetrician-gynecologist
- Ultrasound organs
- obstetrics and gynecology
- Colposcopy
- CTG
There are several ways to cleanse the organ, one of them is recanalization of the fallopian tubes. This procedure is carried out by highly qualified international multidisciplinary specialists. A small catheter with a balloon is inserted into the uterine cavity. The latter swells as it passes through the pipe and thereby expands it.
Cost of endoscopy
| Brush biopsy during video bronchoscopy | 800 | rub |
| Bronchial diagnostic lavage | 2000 | rub |
| Taking a biopsy during endoscopic examination (more than 4 pieces) without histology | 3000 | rub |
| Taking a biopsy during endoscopic examination (up to 3 pieces, swabs) without histology | 1500 | rub |
| Video epipharyngolaryngoscopy | 3000 | rub |
| Intrabronchial therapeutic instillation | 1000 | rub |
| Congo test (pH measurement during gastroscopy) | 1000 | rub |
| Needle biopsy during videobronchoscopy | 1600 | rub |
| Sigmoidoscopy | 3400 | rub |
| Esophagoscopy | 3400 | rub |
| Tracheoscopy | 7400 | rub |
| Rhinoscopy | 2700 | rub |
| Selective forceps biopsy during videobronchoscopy | 800 | rub |
| Sigmoidoscopy | 4100 | rub |
| Test for Helicobacter pylori (express method) | 800 | rub |
| Fiberoptic bronchoscopy | 10900 | rub |
| Fibrogastroduodenoscopy | 5600 | rub |
| Fibercolonoscopy | 7600 | rub |
| Fibrolaryngoscopy | 4400 | rub |
| Fibrorhinolaryngoscopy | 4900 | rub |
| Fibrorhinoscopy | 3900 | rub |
| Fibertracheoscopy | 4900 | rub |
| Chromoendoscopy | 2100 | rub |
| Endoscopic insertion of a balloon into the stomach (anti-obesity) | 1200 | rub |
| Video endoscopic assistance during surgery | 3000 | rub |
| Endoscopic sanitation (instillation of solutions) | 1500 | rub |
| Operative endoscopy | ||
| Balloon dilatation of the upper gastrointestinal tract | 36000 | rub |
| Bougienage of the esophagus (1 session) | 18000 | rub |
| Stopping bleeding: application of drugs | 2000 | rub |
| Stopping bleeding: argon plasma coagulation | 8000 | rub |
| Stop bleeding: diathermic loop | 3400 | rub |
| Stopping bleeding: applying clips | 5000 | rub |
| Stopping bleeding: applying ligatures | 4000 | rub |
| Stopping bleeding: needling | 5000 | rub |
| Stopping bleeding: electrocoagulation | 3000 | rub |
| Endoscopic papillotomy | 5000 | rub |
| Polypectomy (up to 0.5 cm) category 1 | 7000 | rub |
| Polypectomy (from 0.6 to 1.0 cm) category 2 | 10000 | rub |
| Polypectomy (from 1.0 - above and more than three) category 3 | 14000 | rub |
| Polypectomy (removal of large multiple polyps) category 4 | 20000 | rub |
| Removing a bezoar | 10000 | rub |
| Removal of a foreign body from the stomach | 10000 | rub |
| Installation of an esophageal stent | 20000 | rub |
| Percutaneous gastrostomy | 29000 | rub |
| Electrocoagulation in the colon | 6000 | rub |
| Electrocoagulation of polyps of the esophagus and stomach | 6000 | rub |
| Endoresection of the mucosa | 28000 | rub |
Cost of treatment
Our operating rooms are equipped with the latest equipment, allowing manipulations to be performed as painlessly as possible. We can perform the procedure in parallel with hysteroscopy. This is an X-ray examination of the condition of the fallopian tubes using a contrast fluid with which they are filled.
The price of fallopian tube recanalization starts from 10 to 59 thousand rubles, depending on the complexity. On the website you can find and print a 10% discount coupon. We constantly have new promotional offers. We have developed comprehensive programs in many fields, including gynecology. This will allow you to get your health in order and prepare for successful conception in the future.
Driving directions
+7(495)500-93-90
Shchelkovskaya
Pervomayskaya
12 minutes from Shchelkovskaya and Pervomaiskaya metro stations
Make an appointment
Laparoscopy and pregnancy
Physiotherapy is recommended after surgery. The patient can be referred for magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, or laser therapy. If diagnostic laparoscopy in a hospital in Moscow showed a severe form of obstruction of the fallopian tubes, damage to the inner surface of the tubes by adhesions, or hydrosalpinx, then the tubes can be removed. Such a woman can become pregnant with the help of IVF.
As a result of the adhesive process, an ectopic pregnancy may develop. This is a situation in which the embryo exits into the abdominal cavity or remains in the fallopian tube. Laparoscopy can eliminate ectopic pregnancy. Surgery performed at an early stage of embryo development helps prevent fallopian tube rupture and other serious complications.
In particularly severe cases, one or both tubes may be removed. Conception in this case is possible in the IVF protocol. You can check the prices for laparoscopy in gynecology on the website. I provide detailed consultation at the appointment.
Treatment of adhesions in the fallopian tubes and ovaries
Treatment of adhesions is only surgical. Currently, tubal plastic surgery methods are used using laparoscopic techniques. Today, methods of blowing out the fallopian tubes are practically not used due to their low efficiency. After surgery, anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapeutic treatment and combined oral contraceptives are used (for a period of 3 months). The most favorable conditions for pregnancy occur 3-4 months after surgery. It is worth saying that it is not always possible to completely eliminate the adhesive process; in addition, relapse of the disease often develops, which is often an indication for IVF.