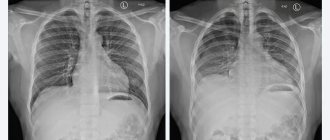
Instrumental studies are often used in the diagnosis of diseases of the thoracic cavity. One of the most effective methods is CT of the mediastinum with contrast. Computed tomography allows you to visualize the structure of internal structures without invasive manipulation. The exception is the intravenous administration of a “coloring” iodine-containing solution.
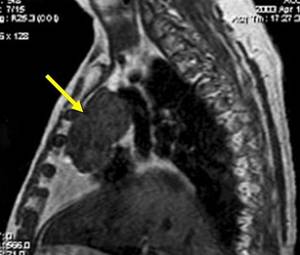
CT scan of the mediastinum, axial, sagittal and frontal projections
Ionizing flows are used to examine tissues. Unlike linear radiography, during CT a given area can be scanned at a certain depth. As a result, photographs of thin (from 0.5 mm) sections of the area under consideration are obtained. Computed tomography of hard tissues (bones, cartilage) and hollow organs is more effective. To increase the information content of scanning, bolus amplification is used.
CT scan of the mediastinum with contrast is prescribed for visualization of soft tissues, the vascular system, and neoplasms. The method provides a detailed study of the internal organs and anatomical structures of the chest cavity.
What will a CT scan of the mediastinum show?
Computed tomography visualizes the shape, size, structural features of internal organs and morphological formations of the chest cavity. Based on the CT results, the condition of three parts of the mediastinum is assessed:
- prevascular (anterior);
- vascular (central);
- retrovascular (posterior).
Each space has conventional boundaries and includes certain anatomical structures. In the study protocol, the doctor indicates the department being studied with a further description of the condition of the internal organs.
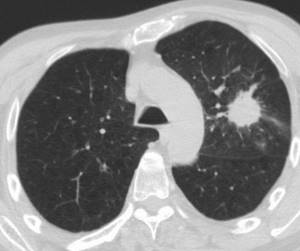
Metastatic lung disease
The scanning area for CT scans of the mediastinum and chest includes:
- heart and pericardium;
- thymus (thymus gland);
- coronary vessels;
- trachea, bronchi, lungs;
- esophagus;
- ascending section and arch of the aorta;
- The lymph nodes;
- superior and inferior vena cava;
- fatty tissue of the mediastinum;
- pulmonary veins and arteries;
- nerves;
- pleural cavity;
- sternum and ribs;
- muscles;
- thoracic spine.
Bone structures in CT images have a light tint, anatomical formations with low density appear as darkened areas.
The thymus is clearly visible on tomograms in childhood. After 25 years, the process of replacing the gland with adipose tissue begins. The maximum thickness of an anatomical formation in adults normally does not exceed 1.3 cm.
Lymph nodes are isolated soft tissue elements of a round shape. Pathological processes lead to an increase in size, and sometimes fusion of organs is observed.
CT scan of the mediastinum with contrast shows disturbances in the blood supply to the chest cavity, vascular pathologies, areas of ischemia and necrosis. The method allows you to identify the slightest changes in the structure of the organs being studied. The photographs show inflammatory, degenerative, neoplastic phenomena of bone elements, epithelial membranes, and lung tissue.
Computed tomography of the chest and neck visualizes the patency of the airways, shows the presence of sputum, foreign bodies, formations in the lumen of the trachea and bronchi. Based on instrumental research, the volume of lung damage and the functionality of the respiratory system are assessed.
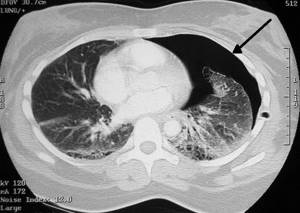
Pneumothorax on CT scan (arrow points to air-filled area)
Tomograms reflect the accumulation of gas in the pleural or chest cavity. In case of injuries, images can be used to determine ruptures in the walls of blood vessels, areas of internal hemorrhage and the consequences of hemorrhages.
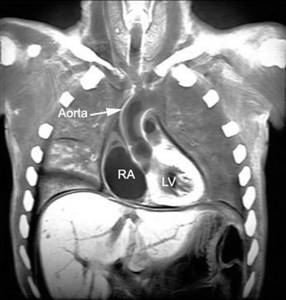
A CT scan of the mediastinum shows what is happening in the pericardial region. The procedure allows you to assess the condition of the chambers, coronary vessels, and determine the degree of functionality of the heart muscle
If a tumor is present, computed tomography helps to clarify the location and size of the tumor, and determine the nature of the oncological process. In contrast-enhanced photographs you can clearly see:
- structural features of the hearth;
- presence of inclusions;
- interaction with surrounding healthy tissues.
In relation to the bone frame, the homogeneity and shape of solid structures are assessed. Based on the scanning results, displacement of morphological elements, violations of the integrity of hard tissues, and degenerative phenomena are determined.
Tomography results
The results of the mediastinal area are deciphered by the attending physician or an independent medical expert of the appropriate specialization. In the conclusion, they indicate which doctor should be consulted.
What will a tomography of the mediastinum show:
| Norm | Pathologies |
| There are no deformations of the heart, blood vessels, glands, nerves, esophagus, trachea, bronchi | There are deviations from the norm (structural disturbances, changes in wall thickness, organ size, dissection of the choroid, and so on) |
| There are no foci of uneven color, tumors, cysts, or other formations in the image | Pathological changes with blurred boundaries or clear contours were identified |
| There are no thickenings of the walls of hollow organs and vessels | An infiltrative focus and impaired blood flow were detected |
MRI images reveal the location and extent of pathological changes.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, previous results of laboratory tests, hardware studies, and the patient’s individual and family history are needed.
Indications and contraindications for mediastinal CT
Computed tomography of the chest is used in the diagnosis of diseases of the respiratory, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal systems. The reason for hardware examination are characteristic symptoms:
- dyspnea;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, fingers and toes;
- pain in the chest cavity;
- wheezing in the lungs;
- persistent cough;
- weakness, chills, increased body temperature.
CT is prescribed in the presence of shadows, expansion of the boundaries of the mediastinum and roots of the lungs on radiographs.
Computed tomography of the chest cavity is used to diagnose:
- aortic aneurysm;
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis);
- systemic diseases (sarcoidosis, lymphogranulomatosis);
- pleurisy;
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- abscesses, mediastinitis;
- diverticula or stenosis of the esophagus (Schatsky rings);
- lymphadenopathy (reactive and infectious);
- pneumo- and hemothorax;
- atherosclerosis;
- vascular tumors;
- consequences of chest injuries;
- neoplasms;
- heart disease;
- congenital anomalies;
- diaphragmatic hernia, etc.
The indication for the study is the need to assess the condition of the mediastinum in preparation for thoracic surgery.
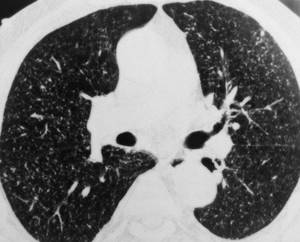
Pulmonary tuberculosis on CT (multiple foci)
A special feature of computed tomography is the radiation exposure to the patient’s body. The restrictions to the native procedure are:
- early childhood;
- pregnancy;
- health condition that precludes the use of x-rays (radiation sickness).
Contraindications to the contrast procedure are associated with the use of iodine-containing solution. The substance can cause allergies and affects the functioning of the excretory and endocrine systems.
CT scan of the mediastinum with contrast is not prescribed in the following cases:
- renal failure - the process of drug elimination increases the load on the excretory system;
- individual iodine intolerance – an allergic reaction may occur;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland - the introduction of contrast enhances the clinical signs of thyrotoxicosis;
- therapy of diabetes mellitus with drugs based on Metformin - simultaneous use with iodine provokes an increase in the concentration of lactic acid and increases the load on the kidneys.
If restrictive measures are observed, computed tomography does not have a negative effect on the patient’s body.
Photo
|
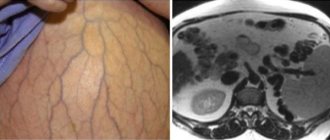
| Neurogenic tumor of the mediastinum |
|
| Neoplasm in the mediastinum |
|
| Mediastinal tumor |
|
| Pathological neoplasm in the mediastinum |
|
| Mediastinal thymoma |
How is a CT scan of the mediastinum performed?
Computed tomography uses sophisticated equipment. The CT machine consists of a movable table and a ring part, inside of which there are emitters and sensors.
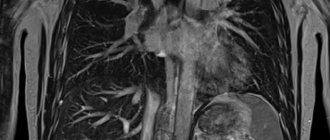
Computed tomography of the lungs and mediastinal organs
The patient lies face up on the conveyor. To improve image quality, you must remain still throughout the entire session. Changing the position of the body leads to distortion of the picture and the appearance of artifacts in the images.
The table with the patient moves inside the tomograph ring. The scanning elements move in a circle, taking several pictures per full revolution. The procedure is called multislice computed tomography. MSCT provides:
- reduction of radiation exposure;
- reduction of scanning time;
- improving image quality.
As a result, photographs of axial sections are obtained, with the help of which sagittal and frontal projections are completed. To clarify the localization of the pathological focus and assess the relative position of the anatomical structures of the mediastinum, a 3D model of the area under consideration is reconstructed.
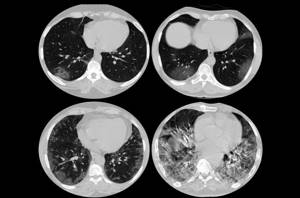
Viral (Covid) pneumonia on a tomogram
A CT scan of the mediastinum and lungs takes 5 to 10 minutes. When using contrast enhancement, the duration of the diagnostic procedure increases. The injection is done after a series of native photographs. The scan is paused and a “staining” solution is injected into the patient through an intravenous catheter. Within 10-15 minutes, the drug fills the lumen of the vessels of the chest cavity, after which scanning is continued.
A CT scan of the mediastinum with contrast takes no more than half an hour. After 1-2 days, the body is completely cleansed of traces of the iodine-containing solution.
Cost of tomography
The mediastinal organs are examined using MRI in public or private medical institutions where there is a magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
In Moscow, the cost of the procedure for December 2021 starts from 4,300 rubles. MRI is the optimal method for obtaining comprehensive information about the condition of mediastinal tissues.
To prevent the procedure from causing harm, the patient is advised to inform about the presence of implants and answer questions asked truthfully. To confirm oncology, other diagnostic methods may be additionally used.
Price
On our website, many clinics list prices for MRI, including MRI of the mediastinum.
To see prices, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
On the page for the list of city clinics, in the form for selecting a clinic based on parameters, in the “Research area” field, select “MRI of the mediastinum.”
The list will be filtered and the clinics will be sorted by ascending price, which will allow you to find out where to get an MRI of the mediastinum cheaper.
|
| List of clinics filtered by MRI of the brain using the example of the city of Moscow |
If prices are not indicated on the website, then you need to call all the clinics and find the best price for you yourself.
When talking with the operator, be sure to ask if there are any promotions or discounts. For example, some 24-hour clinics offer discounts on MRIs at night.
You can get an MRI with compulsory medical insurance or VHI insurance. To do this, you need to find out which clinic does MRI under insurance, using the information on the website or calling the clinics yourself if there is no information on the website. In the form for selecting a clinic by parameters, there is a field “MRI under insurance”. Next, you need to find out the list of documents that the clinic operator will tell you, collect them and you will be able to undergo an MRI with insurance, which will allow you to save a lot.