It
is known that thyroid diseases are very common in the Chelyabinsk region.
The most common problem faced by our fellow countrymen is thyroid nodules. What to do if a nodule is found in the thyroid gland, which means the conclusion of THIRADS and Bethesda, our interlocutor, candidate of medical sciences, specialist in endocrine surgery, oncologist surgeon, doctor of the highest category, Sergey Anatolyevich Lukyanov, will tell you today.
— Sergey Anatolyevich, what is a thyroid nodule and why is it dangerous?
- Nodes are various formations that are found in the thyroid gland. Most thyroid nodules do not cause any symptoms. However, if they grow quickly enough, they can cause swelling in the neck and lead to difficulty breathing, swallowing, and pain. Some nodes produce excess amounts of thyroxine, the main thyroid hormone. When this occurs, symptoms of the disease are similar to those of hyperthyroidism and may include: rapid pulse, nervousness, increased appetite, tremors, weight loss, sweating.-
How common are thyroid nodules and how common is cancer?
- Nodules in the thyroid gland are very common. I will list a few basic facts about knots that will be useful for our readers to know:
• Thyroid nodules are three times more common in women than in men.
• 30% of 30 year old women will have a thyroid nodule.
• Every 40th young person most likely also has a thyroid nodule.
• Some thyroid nodules are actually cysts that are filled with fluid rather than thyroid tissue.
• Purely cystic thyroid nodules (thyroid cysts) are almost always benign.
• The prevalence of thyroid nodules increases with age: 50% of 50-year-old women will have at least one thyroid nodule. 60% of 60-year-old women will have one thyroid nodule. 70% of 70-year-old women will have at least one thyroid nodule.
• The main good news is that more than 95% of all thyroid nodules are benign (not cancerous).
— How are thyroid nodules detected?
— Some nodes are visible on the neck and can be felt by the person. However, about 50% of people have knots that are too small to feel. Usually, nodes are detected by chance - during medical examinations and in examination rooms. Most often, nodes are detected during ultrasound performed for other diseases (for example, during ultrasound of the vessels of the neck).
— Is it possible to understand from an ultrasound whether the node is dangerous or cancerous?
— Recently, the quality of ultrasound has increased significantly, and doctors have even encountered an “epidemic” of thyroid nodules. The main diagnostic task of the doctor is to assess the malignancy of the neoplasm, while the size of the node is not a determining factor. Thyroid cancer can be suspected only on the basis of a node biopsy/puncture (FNA). It is not advisable to carry out mass TAB of nodular formations, since these nodules are very common. In this regard, there was a need to create a new ultrasound classification of thyroid nodules, which could help the doctor choose surgical tactics - observation or puncture of the node. And such a classification was created, it is called THIRADS or TI-RADS.
Most specialized clinics have already switched to this system, and therefore, in the conclusion of the ultrasound protocol, we increasingly see one of the following categories:
• THIRADS 1 – normal thyroid gland
• THIRADS 2 – benign changes in the thyroid gland.
• THIRADS 3 – probably benign changes in the thyroid gland.
• THIRADS 4 – suspicious for malignant changes in the thyroid gland. This group is classified into 4a and 4b depending on the increased risk of malignancy.
— If an ultrasound revealed a THIRADS 4 node, does that mean we need to operate?
- No, it’s not necessary, since ultrasound is not a diagnosis yet. The THIRADS classification only helps the endocrinologist surgeon decide from which node the puncture should be taken. The different categories according to THIRADS are just risks. For example, with THIRADS 2, the risk of cancer is less than 5%, THIRADS 3, the risk increases to 10%, and with THIRADS 4, the risk of node malignancy is already about 15%.
- Then when should you operate?
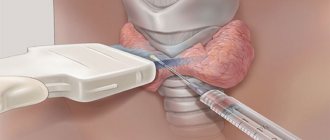
— If after puncture of this node there is a suspicion of a tumor based on the results of the cytological report (the patient can find out how to perform a puncture of the thyroid gland in my article on the website).
— How dangerous are thyroid tumors?
— The most common types of thyroid tumors are colloid nodes and cysts; they are harmless and do not require surgical treatment. Less commonly detected are follicular tumors - neoplasms that need to be removed. Even less common is cancer, in which case the oncologist surgeon removes the affected lobe or the entire thyroid gland. To understand before surgery how dangerous a nodule is, endocrinology surgeons currently use the Bethesda cytology system.
- What is this, the Bethesda system?
— In accordance with clinical recommendations, doctors need to use 6 standard categories of cytological reports of the modern international Bethesda classification:
• Category I – uninformative puncture (done when there is insufficient material or the presence of only a cystic and colloid component), in some cases it requires repeated puncture of the node.
• Category II – benign formation (colloid and adenomatous nodes, chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, subacute thyroiditis), most often there is no need to remove such a node.
• Category III – atypia of uncertain significance (difficult to interpret
• puncture with suspected tumor lesion), it is necessary to repeat the puncture after 2-3 months.
• Category IV – follicular neoplasia or suspected follicular neoplasia. It is advisable to remove such a node.
• Category V and VI – suspected malignant or malignant tumor (suspicious papillary cancer, medullary cancer, metastatic carcinoma or lymphoma). With this conclusion, surgery is necessary.
—
What is the long-term prognosis for people with thyroid cancer?
— Patients diagnosed with cancer in the early stages of the disease generally respond well to treatment, and relapses are extremely rare (five-year survival rate is almost 97 percent). Some types of thyroid cancer have a higher recurrence rate.
— Where in the Chelyabinsk region can a thyroid puncture be performed in order to recognize a tumor as early as possible?
— Very often, the patient requires not only a puncture, but also a consultation with an endocrinologist surgeon to determine further tactics, draw up a treatment and observation plan, and, if necessary, referral for hospitalization.
An endocrinologist surgeon provides consultations in the CITYMED network of expert clinics.
A stranger among his own
I was diagnosed with autoimmune thyroiditis. But I'm only 28 years old. Don't such diseases arise with age?
Polina, Moscow
– Autoimmune thyroiditis (inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland of an autoimmune nature) can occur at any age. Its essence lies in the fact that, under the influence of one factor or another, antibodies produced by the immune system begin to mistake thyroid cells for foreign and cause destructive changes in the gland, which ultimately leads to a decrease in its function (hypothyroidism) and a decrease in production thyroid hormones.
For what reasons does such auto-aggression occur? We do not know a clear answer to this question. It is only known that most often women become victims of this disease. One of the risk factors for them is childbirth.
Article on the topic
A visit to the endocrinologist: why sausage is dangerous and iodized salt is useful
Approximately 8–15% of new mothers experience autoimmune destruction of the thyroid gland after the birth of a child. After all, during pregnancy, a woman’s immune system seems to “fall asleep” and “tolerate” everything so as not to harm the fetus through its activity. But as soon as the baby leaves the mother’s body, a powerful restructuring of her immune and endocrine systems begins, as a result of which the thyroid gland, which is quite vulnerable in this regard, may suffer.
But not everything is so sad. In 80% of women, thyroid function is restored after childbirth. What caused this disease in you, you need to figure out. But I can console you: autoimmune thyroiditis can be successfully controlled with drugs.
There is an alternative
Recently, triiodothyronine preparations disappeared from pharmacies, while taking them I had very good results (I suffer from hypothyroidism). I made inquiries. It turned out that these drugs... were discontinued. What do i do?
Elena, Murmansk
– Only no more than 8% of women need combination therapy using triiodothyronine preparations (a biologically active form of thyroid hormone), therefore such therapy is used extremely rarely in the world and the drug has no longer been supplied to our country.
But there are no hopeless situations. A thinking endocrinologist (I hope you have just such a doctor) can find effective approaches to treatment with thyroxine preparations. The main thing is to choose the exact dosage and take them correctly: long before meals (at least 30 minutes) and in no case combining them with milk or coffee. Some medications are also incompatible with thyroxine. Such as valocordin (phenobarbital produces a protein that interferes with the bioavailability of this medicine) or iron supplements.
A special article is the use of thyroxine drugs by pregnant women. It is no secret that this medicine must be taken in the morning, but expectant mothers often vomit at this time. In such cases, taking thyroxine is transferred to the late evening, before bedtime and as far as possible from meals. However, in any case, the subtleties of treatment are the prerogative of the doctor.
Important
Thyroid diseases are much more common in women. The reason for this is hormonal fluctuations (during menstruation, during pregnancy, during menopause). Experts recommend that women regularly visit an endocrinologist and have an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Up to 30 years old - once every five years, from 30 to 45 years old - once every three years, after 45 years old - once a year. Diagnosis of hypothyroidism in pregnant women is especially important, since a lack of thyroid hormones in the mother is fraught with disturbances in the formation of the central nervous system in the child.
Ultrasound signs of thyroid disease
When assessing the results of an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland, the doctor describes a lot of parameters that are important but general in diagnosis - for example, the location, contours, structure and volume of the thyroid gland. The description of general signs allows us to make a number of diagnoses (for example, an enlargement of the thyroid gland in combination with its dark color on an ultrasound image and heterogeneity of the structure often indicates either the presence of a hypertrophic form of autoimmune thyroiditis, or the presence of a diffuse toxic goiter in the patient - the final diagnosis is established after assessment hormonal function of the gland and antibody titer in the blood). At the same time, there are a number of ultrasound signs that, even during a cursory examination of the gland by an experienced doctor, immediately catch his eye and with very high reliability (doctors say “with high specificity”) indicate a disease of the thyroid gland. Let's try to describe some of these signs.
Absence of the thyroid gland in the typical location and below it in the absence of evidence of previous neck surgery
indicates either that the thyroid gland did not develop in the prenatal period (agenesis), or that the thyroid gland is located in some atypical place (for example, at the root of the tongue - the so-called lingual goiter). When performing an ultrasound on an adult patient in the absence of the thyroid gland due to agenesis, the patient usually warns the doctor about this, since he has known about his diagnosis since childhood and takes a daily hormonal drug that replaces the function of the thyroid gland. If the position of the thyroid gland is atypical, the patient may not know anything about his diagnosis, since he has a thyroid gland and most often functions normally. At the same time, when the thyroid gland is located at the root of the tongue, it partially blocks the lumen of the pharynx and complicates the act of swallowing, plus patients often complain of a feeling of a “lump in the throat” that constantly interferes with them. In general, a lump in the throat is one of the main complaints of patients with thyroid diseases, but with lingual goiter it is also combined with complaints of difficulty swallowing food. In all cases of the absence of the thyroid gland according to ultrasound in a typical location and the absence of evidence of hormonal deficiency, patients are advised to perform a computed tomography scan of the neck and chest in order to search for either a high or low located thyroid gland.
The presence of a cystic formation in the midline of the neck above the isthmus of the thyroid gland
, below or near the hyoid bone, most often indicates the existence of a median neck cyst in the patient. A median cyst is formed in the prenatal period due to the incomplete disappearance of the thyroglossal duct, which connects the isthmus of the thyroid gland with the root of the tongue, where the thyroid gland is initially formed in utero and from where it begins its “journey” to the neck. The diagnosis of a median neck cyst is not difficult - often patients with a similar finding on ultrasound of the thyroid gland complain of a periodically increasing space-occupying formation in the neck, located quite high. It also happens that patients experience signs of suppuration of the contents of the cyst (redness of the skin, pain when palpated, increased temperature). Typically, a median neck cyst needs to be surgically removed. At the same time, an experienced doctor should always take into account that a cystic formation in the midline of the neck can also be a cystic metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer to the lymph node. When removing a cystic metastasis of thyroid cancer, it is not enough to remove only the cyst - it is important to remove the entire thyroid gland with the surrounding tissue, since this is the only way to ensure that the tumor does not recur in the future. That is why, when a mid-located cyst is detected on the neck, it is necessary to perform a biopsy to exclude cancer.
Thyroid nodule with uneven, unclear contours, a pronounced decrease in echogenicity, with microcalcifications
– typical picture of thyroid cancer on ultrasound. The absence of a dark rim along the edge of the node (the so-called “halo”) indicates tumor growth into the tissue of the surrounding thyroid gland. Microcalcifications (i.e. small light dots on a dark background of the node tissue that do not have ultrasound shadows) are a reflection of the formation of psammoma bodies during the development of papillary cancer. In some cases (but not always), increased blood flow is detected in the node tissue during a Doppler study, indicating an active blood supply to the node tissue and its active growth. If suspicious signs are detected during ultrasound of the thyroid gland, a fine-needle biopsy of the node is required, even if it is small (less than 1 cm) in size. Only after a biopsy can a decision be made on the need for surgical removal of the node, since in rare cases suspicious signs can also be found in benign nodes that have existed in the patient for a long time and therefore have changed their internal structure.
Enlarged cervical lymph nodes with the formation of cysts, microcalcifications or the appearance of increased blood flow
with Doppler examination. The appearance of a cyst in a lymph node is a very alarming sign, almost always indicating damage to the lymph node by metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer. Microcalcifications in the lymph node are another sign of malignant lymph node damage. Increased blood flow in the lymph node can occur not only when the lymph node is affected by thyroid cancer, but in the presence of other tumors in the lymph node (lymphoma, metastases of tumors of other organs). Identification of any suspicious sign dictates the need for a mandatory biopsy of the lymph node with determination of the level of additional laboratory parameters in the washout from the puncture needle (thyroglobulin, calcitonin). Biopsy of lymph nodes, as well as biopsy of thyroid nodes, should be carried out only under ultrasound guidance and in specialized centers.
| Damage to the jugular cervical lymph node by metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer - ultrasound picture | Disappearance of the internal structure of the cervical lymph node on ultrasound when affected by metastasis of papillary cancer |
It should also be noted that even if an ultrasound of the thyroid gland revealed very alarming ultrasound signs, this is not yet enough to prescribe treatment to the patient (for example, surgery). It is mandatory to prescribe clarifying diagnostic procedures (determining the level of thyroid hormones, tumor marker calcitonin, performing a biopsy). At the Northwestern Center for Endocrinology, ultrasound of the thyroid gland is performed by endocrinologists or endocrinologist surgeons, so all recommendations for additional examination of a patient with suspicious ultrasound symptoms can be formulated immediately after the ultrasound.
The thyroid gland is the small battery of our body.
Why is it so important to be attentive to the health of such a small organ of our body as the thyroid gland, says endocrinologist-nutritionist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor Iraida Georgievna Mokhova.
The thyroid gland is part of the body's endocrine system. This organ is shaped like a butterfly and is located on the front of the neck. The important role of the thyroid gland (TG) is the regulation of metabolism, supply of energy to all cells of our body, control of the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, physical and mental development. If a malfunction occurs in this small gland, it affects the functioning of all organs and systems.
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, every third person on the planet has thyroid problems, and they occur ten times more often in women than in men. Thyroid pathology is widespread in regions of iodine deficiency, which include most of the territory of Russia, including the Novosibirsk region.
The most common diseases of the organ are an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, the appearance of nodes, cysts - formations that differ in structure from the rest of the thyroid tissue. Cysts are formations containing colloid fluid that form against the background of iodine deficiency conditions. Small cysts may disappear when the iodine deficiency is replenished.
To prevent iodine deficiency conditions, it is recommended to add iodized salt, seaweed and fish to the diet, and it is possible to take iodine supplements.
During the appointment, the endocrinologist examines the thyroid gland by palpation and can determine the enlargement of the gland or the presence of large nodular formations. Not all nodes can be palpated, especially if their size is less than 1 cm. In this case, ultrasound diagnostics comes to the rescue.
If a node larger than 1 cm is detected, the endocrinologist prescribes a puncture biopsy. Thanks to this most accurate diagnostic method, a diagnosis is established and the correct treatment tactics are selected. A puncture biopsy is always performed under ultrasound control, which eliminates damage to other organs and makes it absolutely harmless. In rare cases, your doctor may recommend surgery. For small formations, the tumor nature of which is excluded, surgery is not required, only dynamic monitoring is necessary.
For our body, the thyroid gland is a source of energy. When organ function is impaired, the rate of metabolic processes changes. Insufficient production of thyroid hormones is called hypothyroidism, excess production is called hyperthyroidism. The normal functional state is designated as euthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism (deficiency)
The symptoms of this condition are very non-specific, similar to other diseases:
- fatigue, drowsiness and/or weakness
- cold intolerance (you tolerate cold worse than those around you)
- memory impairment
- weight gain or difficulty losing weight (despite dieting and increasing physical activity)
- depression
- constipation
- menstrual irregularities and/or infertility
- muscle or joint pain
- thin and brittle hair and nails and/or dry, flaky skin.
Hyperthyroidism (excess)
It is much less common than hypothyroidism.
Key changes to note:
- weight loss even with a normal diet
- anxiety and irritability
- rapid heart rate (often more than 100 beats per minute)
- wide open, protruding eyes
- trembling hands
- weakness
- hair loss
- frequent stool
- thin and very smooth skin
- sweating
- menstrual irregularities.
At the onset of thyroid dysfunction, the symptoms are nonspecific, but dangerous due to the subsequent development of serious complications.
In rare and advanced cases, hypothyroidism can lead to severe respiratory and heart failure, including the development of coma. Uncompensated hypothyroidism is accompanied by an increase in the level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) - “bad” cholesterol (a risk factor for cardiovascular disease), infertility and Alzheimer's disease (the risk is higher in women).
Hyperthyroidism can lead to serious heart rhythm disturbances, including fibrillation, severe heart failure and myocardial infarction. In postmenopausal women, hyperthyroidism is accompanied by an increased risk of osteoporosis and potentially fatal fractures.
Treatment methods for thyroid dysfunction include taking medications. For hyperthyroidism, when drug therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment methods and radioiodine therapy are used. Effective treatment for thyroid dysfunction can reduce the risk of serious complications; the main thing is to consult a doctor in a timely manner. The American Thyroid Association recommends having your thyroid function checked every 5 years after age 35, even if there are no symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
Take care of your excellent health by making it a rule to visit an endocrinologist on a preventive basis!
Treatment is a must!
My wife was prescribed thyroid hormones (she doesn't have enough). But she is afraid to drink them. What does this mean?
Mikhail, Tver region.
Article on the topic
Thyroid Day. What is hypothyroidism and how to self-diagnose
– Hypothyroidism must be treated. If left unattended, the disease can lead to skin problems, brittle hair, changes in cognitive functions (decreased memory, irritability, etc.), changes in twilight vision, disruption of ENT organs (the appearance of snoring), the formation of a pituitary adenoma (tumor), anemia, and disorders from the gastrointestinal tract, the appearance of discharge from the mammary glands, heavy menstruation.
As you can see, there are enough reasons for mandatory use of thyroid hormone medications. Moreover, with a precisely selected dosage and careful adherence to the rules for taking them, replacement therapy with these drugs does not threaten your wife with any unpleasant symptoms.
Autoimmune thyroiditis - symptoms and treatment
Therapy for autoimmune thyroiditis of the thyroid gland is nonspecific. When the phase of thyrotoxicosis develops, the use of symptomatic therapy is sufficient. When hypothyroidism develops, the main option for drug therapy is the administration of thyroid hormones. Now in the pharmacy chain of the Russian Federation it is possible to purchase only Levothyroxine sodium tablets (L-thyroxine and Euthyrox). The use of tableted preparations of thyroid hormones neutralizes the clinical picture of hypothyroidism and, in the hypertrophic form of autoimmune thyroiditis, causes a decrease in the volume of the thyroid gland to acceptable values.
If a patient has manifest hypothyroidism (an increase in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone and a decrease in the concentration of free T4), it is necessary to use levothyroxine sodium in the treatment at an average dose of 1.6 - 1.8 mcg/kg of the patient’s body weight. An indicator of the correctness of the prescribed treatment will be the confident retention of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the patient’s blood within the reference values.
When a patient is diagnosed with subclinical hypothyroidism (increased TSH concentration in combination with unchanged free T4 concentration), it is necessary:
- After 3–6 months, carry out a second hormonal examination to confirm the presence of changes in thyroid function;
- When an increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone levels is detected in a patient during pregnancy, even with preserved free T4 concentrations, prescribe levothyroxine sodium at the full calculated replacement dose immediately;
- Treatment with levothyroxine sodium is necessary for persistent subclinical hypothyroidism (an increase in the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood above 10 mU/l, and also in situations of at least twice the determination of the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone between 5 - 10 mU/l), but if these patients are over 55 years old and have they have cardiovascular pathologies, treatment with sodium levothyroxine is prescribed only if the drug is well tolerated and in the absence of information about decompensation of these diseases while taking thyroxine;
- An indicator of the sufficiency of treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism is the stable maintenance of TSH levels within the reference values in the blood.
If women, before planning pregnancy, have antibodies to thyroid tissue and/or ultrasound signs of autoimmune thyroiditis, it is necessary to determine the hormonal function of the thyroid gland (thyroid-stimulating hormone concentration and free T4 concentration) and be sure to determine the level of hormones in each trimester of pregnancy.[8]
If autoimmune thyroiditis is diagnosed, but changes in the functioning of the thyroid gland are not detected, the use of sodium levothyroxine is not indicated.[9] It is sometimes possible in exceptional situations of an impressive increase in the volume of the thyroid gland, provoked by autoimmune thyroiditis, and the decision is made for each patient individually.[10]
Physiological amounts of potassium iodite (approximately 200 mcg/day) cannot provoke the formation of hypothyroidism and do not have a negative effect on thyroid function in previously developed hypothyroidism caused by autoimmune thyroiditis.
Nutrition for autoimmune thyroiditis
There are no products that affect the course of autoimmune thyroiditis. Gluten or lactose are not related to hypothyroidism due to AIT. Therefore, dietary recommendations for people with autoimmune thyroiditis are the same as for everyone else: a varied, balanced diet with sufficient water intake.
Are there traditional methods of treatment?
Autoimmune thyroiditis is treated only with medications prescribed by an endocrinologist. The lack of adequate therapy can lead to dangerous complications: impaired reproductive function, severe memory loss (even dementia), anemia and coma, which occurs with a severe deficiency of thyroid hormones.