The basis for diagnosing the human body is the well-known blood and urine tests. While many people are familiar with the examination of the first biomaterial, not everyone can say something intelligible about the examination of the second.
Almost all indicators of urine analysis represent a kind of veil of secrecy for the majority of patients at the clinic who have undergone this diagnosis on the instructions of a doctor. One of the parameters that many patients are interested in is the level of red blood cells in the urine. We will talk about them in more detail, their norm and the danger of deviation in the article below.
Functions in the body
Red blood cells are fairly small, biconcave, round-shaped cells that are also called red blood cells. There are 2 types of these cells in the body - changed and unchanged.
The former almost always arise as a result of some disease, do not contain hemoglobin and are ring-shaped. They are not present in the systemic circulation. In most cases, they appear in biological fluids and are pale in color.
Unchanged red cells have a regular shape and contain hemoglobin, and are colored bright red. They are present in human blood and, with various abnormalities, can appear in other biological fluids.
It is worth noting that in the human body, red blood cells occupy almost 25% of the total volume of all cells.
Red blood cells perform several important functions in the human body:
- They supply hemoglobin and oxygen to the tissues, due to which metabolism is carried out.
- They help transport carbon dioxide from cells, which facilitates gas exchange and speeds up metabolism.
- They normalize the acid-base balance in the body, which prevents various diseases associated with its disturbance.
- They stimulate the formation of important enzymes and other substances in the body that ensure normal metabolic processes.
- Relieves symptoms of intoxication and prevents re-development of the condition.
- They help transport nutritional components supplied with food to cells.
Thanks to the complex effects of cells, many processes take place in the human body, which is very important for the normal functioning of internal organs.
How and under what conditions are they produced?
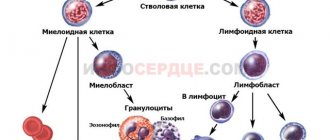
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine cannot appear without the production of cells in the body. Every few seconds, red bone marrow produces more than 2 million red blood cells. Normally, they are in the systemic circulation for 100-120 days, after which they are absorbed by macrophages, and newly formed cells enter the blood.
The formation of red blood cells occurs in the red bone marrow of large bones, such as the pelvis, vertebrae, ribs and even the bones of the skull. This process requires normal functioning of the organ.
It is worth noting that cell formation occurs in several stages, each of which follows from the previous one:
- The initial stage is accompanied by the formation of erythroblasts. These cells resemble red blood cells in appearance, but are larger in size and have some differences in the membrane.
- Erythroblasts form pronormocytes, which are smaller in size, but also do not resemble full-fledged red blood cells.
- Basophilic normocyte is the next stage of cell formation. These cells already have an uneven pinkish color.
- In polychromatophilic normocytes there is a high concentration of hemoglobin.
- Oxyphilic normocyte is more reminiscent of an erythrocyte in shape and size, and has a bright pink color.
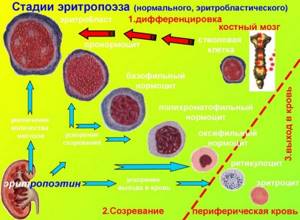
- The reticulocyte is the precursor of a full-fledged red blood cell, but has a different color.
- A mature red blood cell is called a normocyte. It is these cells that enter the systemic circulation and perform various functions.
After all functions are completed, cell absorption occurs in the liver and spleen. This process is normal, but can be disrupted by various diseases.
Clinical manifestations
The fact that unchanged red blood cells in the urine is elevated does not provide grounds for making a specific diagnosis. The final cause of hematuria is determined in accordance with clinical manifestations and data from other diagnostic examination methods.
Elevated unchanged red blood cells in the urine are not always accompanied by symptoms. Asymptomatic or painless hematuria is distinguished. It most often occurs suddenly. It is the release of large blood clots along with urine. There are no pains or other unpleasant symptoms. In this case, it is first necessary to exclude a tumor of the bladder or kidneys.
Hematuria can also occur with severe symptoms. The discharge of blood is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen or in the lumbar spine. There may be an increase in temperature and deterioration in health. Urine is released in small portions. In this case, the patient most likely has urolithiasis.
Increased unchanged red blood cells in the urine are a common sign of cystitis in women. Then hematuria is accompanied by a constant urge to urinate and a burning sensation during it. The amount of urine is small, blood comes out in drops at the end of urination.
The approximate source of bleeding can be determined by the shape of the blood clot. If it is worm-shaped, it means the red blood cell has passed through the ureter. That is, the source of bleeding must be looked for in the kidney or directly in the ureter.
Table of indicators is normal
Normally, for each age group, the number of red blood cells in the urine is slightly different. Deviation from the norm is considered a disorder that requires treatment.
| Age group | Norm of red blood cells in urine |
| Newborns and children up to 3 years old | From 2 to 5 cells in the field of view |
| Patients from preschool and school age | No more than 4 cells in the field of view |
| Men | Up to 1 unit in field of view |
| Women | No more than 3 units in the field of view |
The absence of cells in the test material is not considered a deviation, but exceeding the permissible norm is a reason to visit a doctor.
Phenomena of changed and unchanged red blood cells
Red blood cells in urine may change even if they were initially normal
It's no secret that human urine is a relatively acidic and alkaline medium. It is precisely because of the specifics of its organization that this biomaterial is capable of modifying the cells that enter it, and red blood cells are no exception.
In official medicine, there are two types of red blood cells in the urine:
- Altered - any cells that have an abnormal shape, color or structural organization for blood. They appear in the urine when left for a long time and may indicate various pathologies of the genitourinary system. Noticeably less frequently, altered red blood cells indicate serious illnesses associated with improper blood formation in the bone marrow.
- Unchanged - cells in the urine that have normal parameters for red blood cells. The presence of such red blood cells in the blood may indicate both their recent entry there (in the absence of a deviation from the norm), and their constant increase due to the presence of serious pathologies of the body in a person (with stable and strong excesses of the norm). For reference, we note that the appearance of unchanged red blood cells in the urine may indicate inflammation, infections and cancer in the human genitourinary system.
In a typical urine test, normal red blood cells are considered to be those that are in a partially altered state. In such a cell, modifications have already begun, but they are not so significant and a standard red blood cell can be seen without any problems.
It is important to understand that for a diagnostician conducting a study of biomaterial, the condition of red blood cells is not of particular importance. The main thing is that they are present in the urine within normal limits.
Causes of cell level growth and its dangers
The phenomenon of hematuria - an increase in the level of red blood cells in the blood - is normal only in three cases:
- when blood enters the urine of a woman during menstruation
- when a girl is pregnant (not always, but the growth of blood cells in the biomaterial usually increases)
- and when examining a baby up to 1 month old
In other cases, when erythrocyte cells “populate” the urine in large quantities, the previously noted hematuria occurs. By the way, this pathology is conditionally divided into two types:
- Microhematuria is urine that appears normal, but the level of red blood cells in it is too high.
- Macrohematuria - the presence of red impurities (blood) is noticeable in the biomaterial.
The development of one of these ailments can be caused by the body’s physiological reactions to external factors. In addition to the cases noted above, excess cell levels occur due to:
- severe overheating
- increased physical activity
- suffered stress
- alcohol abuse
From the video you can find out what blood in the urine indicates:
Read: Urine according to Zimnitsky: how to properly prepare and collect?
However, an increase in the indicator due to such factors is very rare. Much more often, deviations from the norm of red blood cells in the urine are a consequence of the development of certain pathologies. Most often, patients with hematuria of any type experience:
- diseases of the urinary system (glomerulonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis, hydronephrosis, urethritis, etc.)
- injuries to the kidneys, bladder or ureters
- androgenic and gynecological pathologies (prostate adenoma, prostatitis - in men, cervical erosion, fibroids, uterine bleeding - in women)
- infectious lesions of the whole body or individual nodes of the genitourinary system
- hypertension
Surprisingly, improper use of certain medications can also increase the amount of red blood cells in the blood. The parameter is often modified by sulfonamides, vitamin C, anticoagulants and urotropines. However, with simply taking these drugs, an increase in red blood cells is impossible. Something similar happens either with intolerance to the drug or with its excessive use.
Symptoms of increase
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine can appear against the background of absolute health of a child or adult. However, as the condition progresses, the disorder necessarily manifests itself with various symptoms, the severity of which depends on the organism and the characteristics of the pathological process.
Externally, the disorder can be manifested by pallor of the skin, dark circles under the eyes, as well as skin moisture, which is associated with increased work of the sweat glands. In addition, hematomas may appear on the patient’s body even with light pressure or bruising. This indicates a vascular disorder, causing capillary fragility and hemorrhage under the skin.
In addition, patients experience weakness and fatigue. Depending on the cause of the appearance of red blood cells in the urine, the patient may report pain in the abdomen, as well as in the kidney area.
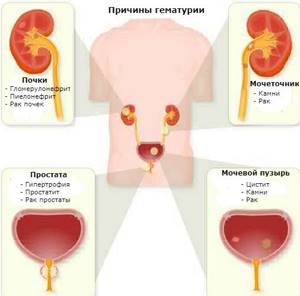
In medicine, the appearance of unchanged red blood cells in urine is called hematuria . It may be accompanied by pain in the bladder area, as well as discomfort when urinating.
Additionally, many patients experience an increase in body temperature, possible pain in the heart, and a decrease in blood pressure. If the appearance of cells in urine is associated with pathologies of the reproductive system, pain appears in the lower abdomen, which intensifies when urinating. This symptom is typical for men suffering from prostatitis and other diseases.
In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and pathological vaginal discharge may appear. Additionally, almost all patients with hematuria experience weakness, fatigue, and headache. The child's condition with this disorder usually does not worsen.
There may be a slight decrease in motor activity and an increase in body temperature. Only when the disorder lasts for a long time does the child develop general symptoms in the form of weakness, dizziness and loss of appetite.
The nature of the symptoms and the severity of the manifestations depend on the cause that provoked the hematuria.
Reasons for the appearance of altered red blood cells in the urine
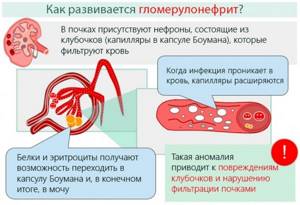
As noted above, altered red blood cells in urine indicate pathology of the kidneys themselves. Violation of the structure of the renal capillaries is caused by the following diseases:
- glomerulonephritis - autoimmune inflammation of the glomeruli of renal capillaries;
- tuberculous kidney damage;
- oncological neoplasms;
- pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys of a bacterial nature;
- autoimmune vascular diseases (hemorrhagic diathesis);
- taking drugs that have a toxic effect on the organ - sulfonamides, anticoagulants;
- prolonged increase in blood pressure.

Reasons for the increase
Unchanged or changed red blood cells may appear in the urine of patients as a result of various reasons.
The most common of them are the following:
- Injuries to the kidneys and bladder of varying severity.
- Bruises of internal organs, causing deterioration in the functioning of the liver, kidneys, and digestive tract.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system in patients of different ages. Red blood cells in urine can appear with pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma. In women, the symptom may be associated with endometritis, endometriosis, fibroids, cycle disorders, and inflammatory pathologies of the appendages.
- Pathologies of the red bone marrow, in which the process of production of red blood cells is disrupted, and immature cells enter the systemic circulation.
- Malignant neoplasms of internal organs.
- Blood diseases accompanied by impaired blood clotting.
- Infectious pathologies accompanied by a febrile state.
- Damage to the kidneys by the tuberculosis bacillus, rupture of the ureters, bladder.
- Severe urolithiasis.
- Overheating of the body as a result of prolonged exposure to open sunlight, in a bathhouse or sauna.
- Stressful situations in which all metabolic processes in the body are disrupted.
- Poor nutrition with a lot of spicy, fatty and sour foods in the diet, as well as abuse of alcoholic beverages on an ongoing basis.
- Excessive and constant physical activity.
Various factors lead to the appearance of cells in the blood. Their number also depends on the pathology and the degree of its neglect.
Factors that influence the appearance of hematuria
Age. Blood in the urine in men over 50 years of age is very often associated with the development of benign prostate dysplasia. Young men are more likely to suffer from urolithiasis, Alport syndrome, than other age groups. Inflammation of the kidneys after a viral or bacterial infection (post-infectious glomerulonephritis) is considered one of the leading causes of visible blood in the urine in children.
Floor. Blood in the urine in women most often occurs due to urinary tract infections. More than half of all women have experienced cystitis at least once in their lives. This is due to anatomical features: the urethra in women is shorter and wider than in men.
Family history. In 10-15% of cases, hematuria is familial.
Indications for the study
In some cases, the appearance of cells in the urine is a temporary problem that does not require treatment. But more often the condition requires diagnosis and treatment in order to prevent complications.
Main indications for the study:
- A large number of cells in the urine, increasing as the disease progresses.
- Severe pain in the kidney area or lower abdomen.
- Foreign impurities in urine in the form of pus, sand.
- Deterioration of general condition.
- Fever.
- The appearance of complications from internal organs.
These indications are considered a reason to immediately visit a doctor. As a rule, it is recommended to contact a therapist who will prescribe a test.
How to determine
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine are determined by clinical examination of urine in the laboratory. Other methods are not used, since general analysis is the most informative and reliable.
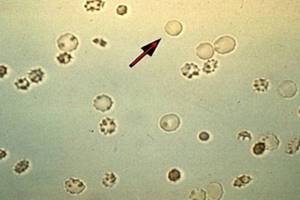
Unchanged red blood cells in urine
If necessary, a clinical blood test is prescribed, which allows you to get a complete picture of the patient’s general condition and determine the need for other studies.
Pathogenesis of hematuria
Pathogenesis is a step-by-step description of the development of a particular disease. Knowing how altered and unchanged red blood cells appear in urine will help in understanding the symptoms and treatment of hematuria.
Red blood cells enter urine through one of the following mechanisms:
- When the wall of the capillary membrane that supplies blood to the kidneys is damaged. Their structure can be destroyed due to injury, inflammation, or tumor growth.
- With stagnation in the veins of the small pelvis, which occurs with phlebitis, external compression of the veins by pathological neoplasms.
- In case of a violation of the structure of the organs of the urinary system: ureters, bladder, urethra. It develops when the mucous membrane of these organs becomes inflamed.
The presence of unchanged red blood cells in urine indicates that the pathology is below the level of the kidneys. That is, the ureters, bladder or urethra are affected. And if the presence of altered red blood cells is noted in a general urine test, it is worth suspecting the pathology of the kidneys themselves. This is due to the fact that with kidney disease, red blood cells change their structure as they pass through the capillary membrane.
Preparing and conducting analysis
Special preparation for collecting biological material is not required, but doctors recommend following certain rules. 10-14 days before urine collection you should not drink alcohol. 3-5 days before, it is better to give up sour, salty, spicy foods, which can negatively affect the condition of the kidneys and also distort the diagnostic result.
It is important not to overwork and also avoid stressful situations. The collection of material must be carried out in the morning when you first visit the toilet and after washing the genitals with warm water and soap.
Experts recommend not collecting urine for the first 2 seconds after the start of urination, and starting collecting urine after 2 seconds. The urine container must be dry and clean. It is better to give preference to sterile pharmaceutical jars with a lid, which are designed for the material.
After collection, urine should be sent immediately to the laboratory. But if necessary, you can store it in the refrigerator. Doctors recommend examining the material directly on the day it is collected, which makes the result more accurate.
In laboratory conditions, urine is examined under a microscope, the number of pathological cells and other components normally present in the material is calculated.
Decoding the results
The results of the study can be obtained the very next day after submitting the material.

Normally, it contains the following parameters:
- The volume of test material, which depends on how much urine the patient has collected.
- The color should normally be straw yellow, but with a significant number of red blood cells it can be pink or even red. In addition, urine is normally clear.
- Density normally ranges from 1002 to 1025. With deviations, the indicator may change in one direction or another.
- Normally, there is no glucose in the analysis.
- The amount of protein normally does not exceed 0.03 g/l.
- Ketone bodies and bilirubin are normally absent. In pathologies it can appear in different quantities.
- Normally unchanged red blood cells depend on age. For children under one year old - no more than 5 cells in the field of view, children of preschool and school age - up to 4 cells in the field of view, women - up to 3 cells in the field of view, men - up to 1 cell in the field of view. If this indicator increases, we can talk about hematuria of varying degrees of neglect.
- The amount of squamous epithelium is insignificant or moderate. If the analysis indicates “many”, most likely the patient has some kind of disease.
- White blood cells are normally 1-4 units per field of view. An increase in level indicates the development of inflammation.
- Modified red blood cells should not be present in the material.
- Bacteria, fungi, salts, mucus, columnar epithelium are normally absent.
When studying the result, you should rely on normal indicators. Their deviation indicates illness.
When to see a doctor
Independent study of the study results helps to detect deviations, once the patient is approximately aware of the norm for his age. If any point does not correspond to the norm, but is significantly or slightly elevated, it is worth visiting a therapist.

The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe additional diagnostics to identify the cause of the deviation. Usually a consultation with a urologist, gynecologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, or endocrinologist is required.
How to get it back to normal
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine appear as a result of various factors. However, in most cases, the disorder is associated with pathologies of the genitourinary system. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Medications
Various medications are used in treatment, depending on the specific disease and the presence of complications.
The following groups of funds are considered the most effective:
- Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is used to relieve pain, relieve symptoms of inflammation and reduce body temperature. The patient is prescribed from 1 to 3 tablets per day, the course of treatment lasts up to 7 days. The drug effectively eliminates severe manifestations and significantly alleviates the patient’s condition.

- Spasmalgon is a drug that has analgesic and antispasmodic effects. Used for cystitis and other pathologies of the genitourinary system, it helps alleviate the condition, as well as urination. This allows pathogenic microorganisms that lead to the appearance of red blood cells in the urine to be removed from the organs. Take 1 tablet 2 times a day, repeat the dose for 5-8 days in a row.
- Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that alleviates the patient’s condition when identifying infectious, bacterial diseases of the bladder, kidneys, urethra, and other internal organs. Tablets are taken orally, 1 piece 2 times a day for 3-6 days, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- Urolesan is a herbal remedy in capsule form, which is actively used to eliminate microbes from the urinary system. Capsules are taken 3 times a day, 1 piece for 10-20 days, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- Monural is a very effective antimicrobial medication in powder form, which is often prescribed for hematuria resulting from damage to the kidneys or bladder. The product is taken once in the amount of 1 sachet. The powder is dissolved in 100-150 ml of water, and the solution is taken orally. If necessary, repeat the dose after 5-7 days.
- Dicynone is a drug to stop bleeding, which is prescribed when a large number of red blood cells are found in the urine on an ongoing basis. In this case, the drug is used in courses of 3-7 days, daily the patient is administered 2 ml of the drug intramuscularly 2-3 times a day. This helps stop bleeding, which is associated, for example, with damage to the bladder wall from a stone.
- No-spa is an antispasmodic medication that is used for damage to the kidneys, bladder, liver or urethra. Helps relieve spasms and relieve pain. Tablets are taken 3 times a day, 1-2 pieces for 10 days.
- Cycloferon is an antiviral medication that is prescribed to patients when the appearance of red blood cells in the urine is associated with a protracted course of a viral disease. The patient is administered intramuscularly 2 ml of the drug per day for 10 days. In some cases, an individual regimen is used, which involves breaks between injections.
The treatment regimen in each case may differ, depending on the disease and possible complications. It is important not to self-medicate, as the risk of complications is increased.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies do not help to completely cure the patient, but they can significantly alleviate his condition.
A decoction of nettle leaves is considered one of the most effective natural remedies for stopping bleeding. For 500 ml of water you need to take 5 g of dry leaves of the plant, cook for 3 minutes, leave for 1 hour to infuse. After this, the filtered decoction is taken orally, 50 ml 2 times a day for 5 days.
Another effective remedy is douching with calendula decoction. This method can only be used by women when bleeding is associated with inflammatory pathologies of the reproductive system.
For 1 liter of water, take 20 g of dried flowers of the plant and cook for 10 minutes. After cooling, filter the product and use it in the evening for douching. Repeat the procedure 10 days in a row.

Traditional methods can worsen the course of the underlying disease, so their use should be agreed with a doctor.
It is strictly forbidden to visit saunas, baths, or take hot baths if red blood cells appear in the urine.
Other methods
Additional methods of therapy include physiotherapy and surgery. Physiotherapy is used in cases of hematuria associated with kidney damage. Electrophoresis is considered a popular and effective procedure. In this case, special electrodes are applied to the kidney area, which affect the organ and stimulate tissue restoration.
The course consists of 10-15 procedures, once every 3 days. The manipulation lasts up to 30 minutes.
If the ureter is ruptured, bladder tumors are detected, internal bleeding or large kidney stones are detected, surgery is performed. The method is most effective in this case. The features of the operation and the recovery period depend on the disease.
Today, the operation can be performed openly or using endoscopic instruments and performing a minimally invasive procedure. Each case requires an individual approach.
Three-glass sample value
If the doctor finds unchanged red blood cells in the urine, the next step is to determine the level of damage. A three-glass sample comes to the rescue with this.
Before the procedure, the patient must refrain from urinating for 3-5 hours. The patient urinates in three containers alternately. In this case, about 1/5 of the total volume of urine is collected in the first container, 3/5 in the second, and the remaining volume in the third. The urine is immediately sent to the laboratory for testing.
The results are deciphered as follows:
- The presence of blood in the first portion and its absence in the subsequent volume of urine indicates the presence of a source of bleeding in the urethra (urethra).
- Hematuria, which is detected only in the final portion of urine, indicates the presence of pathology in the bladder or prostate disease in men.
- If red blood cells are found in all portions of urine, they speak of kidney or ureter disease.
- Hematuria in the first and last portions, as well as the absence of red blood cells in the second glass, most likely indicates damage to both the prostate and urethra.
Possible complications
Lack of therapy will certainly lead to various complications, so do not put off visiting a doctor.
The most common consequences:
- Worsening of symptoms of the underlying disease.
- Massive blood loss.
- Anemia due to the loss of a large amount of blood.
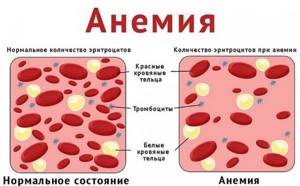
- Spread of the inflammatory process.
- Damage to the kidneys or bladder as a result of stone movement.
- Tumor growth into nearby organs, if the cause is cancer.
Complications also depend on the underlying disease that caused the hematuria.
Unchanged and changed red blood cells can appear in the urine of a child and an adult. The causes of this disorder vary, and in some cases no treatment is required. However, more often the patient needs to immediately consult a doctor to prevent complications.
Hemoglobinuria and myoglobinuria: what is it?
A condition similar to hematuria is called hemoglobinuria. It is manifested by the release of hemoglobin into the urine. It develops with severe destruction of red blood cells inside the vascular bed with the release of hemoglobin. The following situations may cause this condition:
- Hemorrhagic shock due to transfusion of incompatible blood group or Rh factor;
- hydrogen sulfide poisoning;
- infectious diseases with severe course;
- hemolytic anemia of hereditary or acquired nature;
- major burns.
Dark red color of urine can occur when myoglobin enters it. Myoglobin is a protein that is formed during the breakdown of skeletal muscle. This situation often occurs among people who have been under landslides for a long time. This is called long-term compartment syndrome. Myoglobin accumulates in the kidney tubules and damages their function.