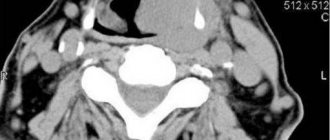
X-ray of the temporal bones, what is it?
An X-ray examination is a radiation diagnostic procedure, the result of which is an image of internal organs and tissues, for example, on photographic film. If a digital X-ray machine is used, the images are displayed on the monitor; they can be recorded on any digital media. X-rays can be used to assess the condition of bone tissue and partially soft tissue quite well.
The temporal bone has a complex anatomical structure. It houses the human hearing and balance organs. It is connected to the lower jaw and serves as a support for the masticatory apparatus.
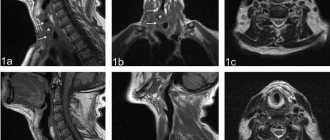
X-ray examination allows us to evaluate the anatomical structure and integrity of the temporal bone. The images show the bony walls of the internal and external auditory canals, the middle ear and the mastoid process.
Since the temporal bone is quite modest in size, it is preferable to choose a digital X-ray method, as it allows you to enlarge images and examine their details.
- This is an extensive study, the result of which is a visual, quite informative snapshot.
- Speed of execution - the procedure, including preparation and decoding, lasts 10-15 minutes.
- Availability. Almost every medical institution has an X-ray machine that will allow you to remove the temporal bone in various projections.
- Simple technique.
Decoding the results
X-ray images are prepared within 1 day. If the result is high-quality, the doctor determines the pathological conditions that have arisen.
What diseases are detected using x-rays?
- If the patient has acute otitis, the transparency in the area of the middle ear, as well as the cells of the mastoid process, will be reduced.
- In acute mastoiditis, pneumatization of the mastoid cells will be reduced or completely absent.
- Foci of bone tissue destruction signal advanced otitis media.
- If the mastoid areas are darkened, this may indicate purulent inflammation.
- Cholesteatoma is determined by the enlargement of the cave area.
- Large-scale formations are visible on their own in the image.
X-ray examination is recommended for all patients. This method accurately identifies pathological changes and conditions in the ear.
When is the examination scheduled?
- bruises, blows, injuries, temporal bone fractures;
- ear diseases: acute otitis with complications, chronic inflammation of the middle ear, cholesteatoma and others;
- suspicion of tumor growths in the temple area.
Today, CT and MRI are more effective and safe techniques than x-rays. This is why there is such a narrow range of indications for x-rays. However, this study helps to reliably identify the presence of pneumatization in a patient (in other words, cavities filled with air), as well as to study the position of intra-ear implants.
X-rays are also prescribed for other indications, when CT and MRI machines are not available in the medical institution.
Computed tomography of the ear
Various pathologies of the inner ear lead to a decrease or complete loss of auditory activity. The use of modern diagnostic methods allows us to determine the condition of soft and hard tissues, as well as the vascular system of the area being studied. Ear CT is one of the most informative diagnostic methods, which is necessary for making a diagnosis and prescribing appropriate treatment.
Computed tomography belongs to the category of advanced radiographic methods. Using a special apparatus, ionized radiation is captured, after which a graphic image is displayed on the monitor screen.
Modern cone beam scanners significantly reduce examination time. It only takes a few seconds to get an accurate picture.
Content
- Indications for the procedure
- What are the contraindications?
- Preparing for CT
- Can it be done for children and during pregnancy?
- Ear CT scan: what does this study show?
- How is the examination carried out?
- Features of CT with contrast
- How often can a CT scan be done?
- Decoding the results obtained
- Which is better - CT or MRI?
- Where can I get a computed tomography scan of the inner ear in St. Petersburg?
Indications for the procedure
A computed tomography scan of the ear is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- The patient's hearing acuity sharply decreased. Symptoms can occur for no apparent reason, or after inflammation of the nasopharynx or otitis media.
- Discharge of purulent or serous fluid from the ear.
- Painful sensations of varying degrees of intensity.
- The patient complains of frequent dizziness, and there is a lack of coordination when walking. All this indicates a dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus.
- Suspicion of the presence of tumors in the ear area and nearby tissues.
- Suspicion of a temporal bone fracture.
In addition, computed tomography is prescribed as a monitoring measure. We are talking about planned procedures to evaluate previous treatment, as well as preparation before surgery in connection with neoplasms.

What are the contraindications?
Contraindications to CT scanning of the inner ear are explained by the specifics of the procedure itself:
- Impact of gamma radiation on humans.
- The need to use a contrast agent.
- During the procedure, the patient must remain motionless.
Based on this, a CT scan is not performed if a person is in an alcoholic, drugged or unconscious state. During the examination, the patient may make involuntary movements, which will inevitably distort the information obtained. Various implants and pacemakers are sensitive to gamma rays, so they can also be an obstacle to the procedure.
If we are talking about a contrast agent, then there are certain limitations. The fact is that the contrast contains iodine and barium, which are eliminated from the body naturally within a few days after the CT scan. If the patient has acute or chronic pathologies in the kidneys, then the contrast agent is not used.
Preparing for CT
Computed tomography is performed on an outpatient basis. It is advisable to arrive 30 minutes before the start of the examination. The main requirement is the absence of metal objects on the body and clothing:
- Bracelets, chains and other jewelry.
- Bracket systems.
- Dental jaws (if they contain metal elements).
- Hearing Aids.
Can it be done for children and during pregnancy?
Most experts agree that a child can only undergo a CT scan of the ear from the age of 14. Before this age, it is also possible to use computed tomography, but only if there is an urgent medical need.
For pregnant women, CT scanning is not advisable, especially in the first and last trimester. During the examination, the patient receives a certain dose of radiation, which can negatively affect the formation of the fetus.
Ear CT scan: what does this study show?
Every patient who has been prescribed a CT scan of the inner ear probably wants to know what this procedure shows? It allows:
- Assess the condition of the facial nerve.
- Show a clear picture of the structure of the middle ear.
- Determine the type of hearing loss in the patient (congenital or acquired).
- Visualize various neoplasms (neurinomas, angiomas, abscesses, etc.).
- Identify infectious and inflammatory processes.
- If an injury occurs, a CT scan determines the displacement of the bones and the general condition of the hard tissues.
How is the examination carried out?
Regardless of what exactly is being examined, computed tomography is performed as follows:
- The patient is positioned standing in a special scanning area (tomograph).
- The jaw, chin and head are installed statically using clamps. This is necessary to prevent involuntary movements of the patient.
- After this, the procedure itself begins. The tomograph ring rotates around the patient’s head (the operation of the device may be accompanied by characteristic sounds).
- The image is immediately transferred to the monitor. The specialist can immediately assess the presence or absence of pathologies from the images.
- The entire procedure takes 1-2 minutes, and the scanning itself takes about 15-20 seconds.
Features of CT with contrast
Certain clinical cases require the use of a contrast agent consisting of barium or iodine salts. The solution itself is administered intravenously immediately before the procedure.
Before computed tomography using a contrast agent, the following requirements must be observed:
- Restriction of food and water 4 hours before the examination.
- Diet for three days before the procedure. It is necessary to exclude any flour, fatty, spicy and smoked foods.
- It is advisable to refrain from smoking on the day of the examination.
- If you have an allergy to iodine, you need to warn about it in advance.
When ingested, the contrast gives the vessel a brighter hue, so they are better visible in photographs. This method is most often prescribed for studying blood circulation in veins and arteries, as well as for complex diagnosis of neoplasms.
How often can a CT scan be done?
A diagnostic test that would not only be accurate, fast and informative, but also absolutely safe for the human body, has not yet been invented. A CT scan of the middle ear allows you to quickly determine the pathology, but frequent use of this procedure can negatively affect the functioning of the internal organs.
The maximum permissible radiation dose is about 150 mSv per year. If this level is exceeded, the consequences for the body can be extremely negative. But if the clinical picture of the disease requires re-examination, then repeated images are possible, especially since cone-beam computed tomography at maximum load produces an exposure of 0.1500 mSv per procedure.
Decoding the results obtained
During the examination, X-ray pulses are converted into electrical signals, which undergo computer processing, resulting in an image appearing on the monitor screen.
The resulting images are interpreted by a specialist. When making a diagnosis, the radiologist pays attention to the following parameters:
- Dimensions of the internal auditory canal.
- Condition of the bone labyrinth.
- The presence of inflammation and neoplasms.
Depending on the area being examined, foci of pathology and neoplasms may appear on the image as light or dark spots.
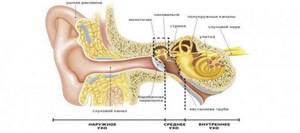
Which is better - CT or MRI?
One of the possible alternative diagnostic methods to CT is magnetic resonance imaging. It is based on magnetic resonance, which is not accompanied by gamma radiation. In this regard, MRI has fewer contraindications, which is a definite advantage.
Additionally, middle ear cholesteatoma is not as visible on CT as it is on MRI. Magnetic resonance therapy also better demonstrates intracranial pathologies, meningocele and facial neuritis.
On the other hand, MRI is good at visualizing soft tissues, but may have problems identifying changes in hard tissues. This method is not used for emergency diagnosis because it takes about 1 hour.
Thus, answering the question of which is better - MRI or CT of the ear, it is impossible to give a definite answer. The appropriateness of a particular examination method is determined by the attending physician, but in most cases, MRI is used when confirmation of the diagnosis is required after a computed tomography scan.
Where can I get a computed tomography scan of the inner ear in St. Petersburg?
X-ray - has been conducting X-ray studies since 2015. We understand the importance of timely diagnosis, so with us you can undergo a computed tomography scan of the inner ear, as well as a number of other studies, as soon as possible.
At your request, the examination results can be recorded on digital media or sent by email. Leave your online application or call the contact phone number to make an appointment.
Sign up for a study by phone
+7 (812) 332-52-54
Methodology
Extraoral, or also called “extraoral,” X-rays of the facial bone can be taken with dental or stationary devices. Using an extraoral technique, they diagnose the bones of the facial skeleton: zygomatic
, temporal - as well as the upper and
lower jaws
. In practice, three types of radiography techniques are most often used.
Schuller projection
X-ray photography to obtain an image in the lateral Schüller projection is performed with the patient lying on his side. Projects the area of the mastoid process, helps to clearly display in the image the cavity of the middle ear, the bulb of the jugular vein, and the tympanic part of the pyramid of the temporal bone. Tumor, inflammatory, and bone-destroying processes are identified by Schuller placement.
Mayer projection
Using the Mayer projection, an axial view of the temporal bone is obtained on the image. Pathologies of the tympanic cavity, the entrance area to the antrum and adjacent structures can be identified. Also, such an examination helps to diagnose purulent-inflammatory diseases and identify foci of destruction in the area of the temporal bone.
Stenvers projection
The Stenvers projection is an overview method of examination, performed in a transverse projection. The X-ray image clearly shows the upper part of the pyramid of the temporal bone. The internal auditory canal, the structural units of the inner ear, is identified.
This research method makes it possible to detect purulent-inflammatory diseases and destructive changes in the hearing organs.
In addition to the above methods of laying and shooting, they also use clarifying ones:
- Two-moment isolated or tangential shot. It visualizes the mastoid process (essentially, this is a modified oblique Stenvers projection).
- Two-stage lateral image with a downward displacement of the labyrinth - Lysholm placement.
- Lateral image with anterior displacement of the labyrinth – Lange-Sonnenkalb method.
How the research works
Before carrying out an x-ray examination, it is important to find a professional specialist. Usually people do this based on the advice of relatives and friends. Many people believe that in an expensive clinic, X-rays are done better than in a municipal medical institution. This judgment has logical confirmation, since private hospitals have better and more modern equipment. But this does not affect the professionalism of the staff. Sometimes doctors in city clinics are more competent than in expensive hospitals.
How is an X-ray examination performed?
- The patient lies on his stomach.
- Turns his head in the direction that will be examined.
- The hand should be clenched into a fist and placed under the chin (thanks to this position, the head will be clearly fixed).
- Place your free hand along your body.
- During exposure to x-rays, the person should not move.
Before the event, you should remove all accessories consisting of metal. The event lasts on average 2-3 minutes. This stage of diagnosis should not be postponed, since thanks to its results it is possible to promptly identify the presence of pathology and begin to eliminate it.
X-ray of the ear with otitis.
Possible complications
Radiography has no complications, since it does not require making incisions on the patient’s body, introducing contrast, or performing other traumatic manipulations.
Contraindications for
- The patient is a pregnant woman (regardless of gestational age).
- The patient is a child under 3 years old. The radiation effect on a child's body is much stronger than on an adult. X-rays can theoretically cause a malignant change in the cells of any of the child’s organs.
- Excess body weight – over 160 kg.
- The patient’s severe general condition or his inappropriate behavior associated with a mental disorder, taking narcotic drugs, etc.
Contraindications to the procedure
X-ray examinations are scary for many people, usually because the person receives a small amount of radiation - 0.12 m3v. It is susceptible to the same irradiation when exposed to the sun for one hour. On average, the radiation dose a patient receives during testing is within normal limits. Even such exposure is contraindicated for some patients. This is one of the contraindications to the procedure.
Who should not undergo X-ray examination:
- pregnant women (even a small dose of radiation can affect the development of the fetus);
- patients with cancer;
- open tuberculosis;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- liver diseases.
The only absolute contraindication to x-ray examination is pregnancy. The analysis is prescribed to pregnant women only when absolutely necessary. In other cases, the procedure is carried out with extreme caution.

Pregnancy.