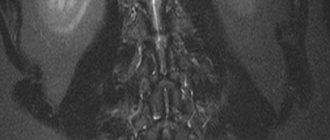
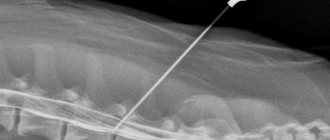
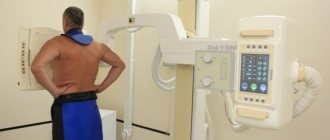
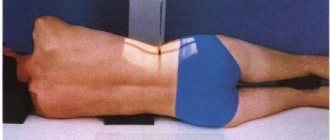
An x-ray, or x-ray, of the lumbosacral spine is an imaging test that helps the doctor see the anatomy of the lower back.
The lumbar spine consists of five vertebral bones. The sacrum is the bony “shield” at the back of the pelvis. It is located below the lumbar spine. The coccyx is located below the sacrum. The thoracic spine is located above the lumbar spine. The lumbar spine also has:
- large blood vessels
- nerves
- tendons
- ligaments
- cartilage
X-rays use small amounts of radiation to visualize bones. X-rays of the lower spine can visualize the presence of injuries, abnormalities, or bone pathologies in this region.
X-rays of the lumbosacral spine can visualize the presence of arthritis or bone fractures, but cannot visualize other muscle, nerve, or disc problems.
Your doctor may order an X-ray of your lumbar spine for a variety of reasons. The test can be used to diagnose injury due to a fall or accident. X-rays can also be used to monitor the progress of the disease, or to determine the effectiveness of treatment.
Purpose of X-ray
- Essentially, x-rays of the lumbosacral spine are used to evaluate back injuries as well as low back pain.
- This method is also used to identify problems in the lower back if there is weakness and persistent numbness.
- X-rays of the lumbosacral spine are used to detect other back injuries such as bone spurs, spinal deformities, fractures, spinal dislocations, osteoporosis, and slipped discs.
- Another goal of the study is to identify the cause of low back pain and numbness.
Indications for the procedure
A two-dimensional image determines the degree of damage to the spine: fractures, cracks, bruises. Compression and compression of the vertebrae are clearly visible in the image obtained after radiography. The method is used to diagnose back curvature, as well as for osteochondrosis and osteoporosis. Developmental anomalies that were not detected after the birth of the child are clearly visible in the photographs.
X-rays are ordered to determine the extent of damage due to injury. Images can refute the diagnosis or confirm the fears of the attending physician. Direct indications for the procedure are frequent headaches (migraines, for which painkillers do not help) and dizziness. In such cases, a study of the cervical spine is prescribed. Choking pain in the chest area is a problem that is also investigated using x-rays. The direct purpose of the procedure is partial or complete numbness of the lower and upper extremities. To confirm an accurate diagnosis, additional research methods are prescribed (soft tissues and healthy internal organs are examined).
When is an X-ray of the lumbosacral spine recommended?
- If a person has lower back pain, they should undergo x-rays of the lumbosacral spine.
- Also, indications for x-ray are persistent pain in the legs and hips
- If a person experiences lower back pain while driving a car or sitting in one place for a long time, he should consult a doctor immediately. The doctor may order an x-ray of the lumbosacral spine.
- If a person experiences pain in the hips and numbness in the legs, they need to undergo an x-ray of the lumbosacral spine.
Research results
The image – the diagnostic result consists entirely of dark and light segments of different contrasts. The light areas are bones, and the dark areas are soft tissues. The outline of fat and muscle tissue is almost invisible (they completely transmit x-rays).
The study is carried out in a specialized room equipped with an X-ray machine. Medical staff performs the procedure and develops the images (the electronic version is downloaded to removable media).
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
What do abnormal results mean?
An X-ray of the lumbosacral spine may show:
- Abnormal curvatures of the spine
- Abnormal wear and tear on the cartilage and bones of the lower spine, such as bone spikes and narrowing of the joints between the vertebrae.
- Cancer
- Fractures
- Signs of thinning bones (osteoporosis)
- Spondylolisthesis
Although some of these findings may be visible on x-rays, they are not always the cause of back pain.
Sample procedure
A functional study is suitable for examining the moving areas of the spine. The body is scanned in a lateral projection with the patient completely motionless. Then the patient begins to bend and unbend with maximum bending. Functional diagnostics are carried out: standing and sitting. This research method helps to study all moving areas of the spine and determine even minimal damage.
Three-dimensional imaging allows you to thoroughly examine every area of the spine. Projections for diagnosis: posterior, extension, flexion. Each position must be recorded. Tests are carried out only if the patient is able to take opposite body positions. Together with the position of the body, the correct tilt of the apparatus tube is selected.
Other reasons for x-rays
Other factors may cause your doctor to order x-rays to determine low back pain lasting up to six to eight weeks. These include:
- the patient is over 65 years of age, under 18 years of age, or is a student-athlete,
- if you have a history of osteoporosis,
- if you have a history of cancer,
- the presence of severe pain during rest or it intensifies at night,
- when pain is combined with fever,
- if back pain is accompanied by rapid and unexplained weight loss
- if the patient has been injured or there have been repeated stress impacts on the spine
- if the person has a history of spinal surgery or fracture.
Contraindications to X-rays
Did you know that...
Next fact
Despite the fact that x-rays are used quite often, in some cases this procedure may be contraindicated.
First of all, x-rays pose a great danger to:
- women during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- small children;
- people who are overweight;
- patients in serious condition;
- persons suffering from nervous disorders.
If an X-ray is urgently needed while a woman is pregnant, then during the examination a special protective screen is used to cover the abdomen. In the future, all consultations with a gynecologist should be carried out much more carefully. The procedure poses the greatest danger during the first trimester due to the formation of all organs and systems in the fetus during this period .
By decision of the World Health Organization, the use of x-rays for children under 15 years of age is prohibited. If a procedure is necessary, the child must be covered with a protective oilcloth.
How is the procedure done?
X-rays of the lumbosacral spine may be performed on an outpatient basis or as part of a hospital stay. Procedures may vary depending on the patient's condition.
Typically, X-ray examinations of the spine follow the following process:
- The person will be asked to remove any clothing, jewelry, hair clips, glasses, hearing aids, or other metal objects that may interfere with the procedure.
- The patient is positioned on an x-ray table, which carefully positions the part of the spine to be x-rayed between the x-ray machine and an x-ray film cassette or digital media. Your doctor may also require that x-rays be taken from a standing position.
- Parts of the body that do not need to be examined may be covered with a lead apron (screen) to avoid exposure to X-rays.
- The radiologic technologist will ask the patient to remain still in a certain position for several minutes during the X-ray exposure.
- If x-rays are used to determine injury, special attention will be given to preventing further injury.
- The X-ray beam will be focused on the area to be photographed.
- An x-ray technician stands behind a protective window during an examination.
Although the X-ray procedure itself does not cause pain, manipulation of the body part being examined may cause some discomfort or pain. This is especially true if there has been a recent injury or an invasive procedure such as surgery.
Preparation for lumbar x-ray
The presence of feces in the intestines and excessive accumulation of gas do not allow the radiologist to obtain a reliable picture, therefore, despite its simplicity, the study requires special preparation.
- Three days before the event, it is recommended to exclude foods that cause flatulence from the diet: legumes, carbonated drinks, cabbage and brown bread.
- For better absorption of food, it is recommended to take enzymatic preparations (Mezim, Unienzyme, Pancreatin) according to the instructions.
- The procedure is performed on an empty stomach; the day before it is recommended to take laxatives and perform a cleansing enema.
X-ray examination is not recommended for pregnant women, due to the high sensitivity of the fetus to the teratogenic effects of ionizing radiation.
Limitations of X-ray
Various soft tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and discs between the bones of the spine, are difficult to see on X-rays, so pain or disease in these structures in the lumbosacral spine may not be detected.
Also, a routine x-ray of the lumbosacral spine may not show prolapsed discs or other pathologies that are pressing on the spinal cord or affecting the nerves that exit the spinal canal, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the pelvis or legs.
X-rays may sometimes miss small bone fractures in the spine due to overlapping or blurring of shadows in the image, or may sometimes incorrectly show a bone defect, injury or fracture where there is none, due to overlapping shadows or "artifacts" that are false non-anatomical structures that may be present on the x-ray image.
A CT or MRI of the lumbar spine is often performed when symptoms clearly indicate pathology—even if X-rays of the lumbosacral spine are normal.
This is because the lumbosacral spine is a complex anatomical region and simple radiographs of the lumbosacral spine are of limited use.
Algorithm for X-ray diagnostics
X-rays of the lumbar region can be performed in three projections: oblique, lateral and straight. Images can be taken in a standing or lying position, everything directly depends on the patient’s well-being and the complexity of the diagnosed disease. Most often, the procedure is performed lying down for curvature of the spine. In order to determine the mobility of the department, so-called functional tests are carried out: a series of photographs are taken in different projections with tilts to the right, left, forward and backward.
It is important to protect the reproductive organs from X-ray radiation during the examination. For this purpose, special radiation-resistant plates are used. But their use is not always possible; for example, during the period of examination of the sacrococcygeal region, the plates will simply cover the desired area. It is recommended to discuss all these points with your doctor, and, perhaps, choose a diagnostic method that is safer for the body.
Activated charcoal before abdominal MRI
The use of any medications before the study must be agreed with the attending physician. If dietary recommendations are followed, there is usually no need for additional medications.
If you are prone to bloating, preparing for an MRI of the abdominal organs may involve the use of activated charcoal or other anti-flatulence medications. Medicines against pathological gas formation are taken according to the instructions or as recommended by a doctor. There is no need to exceed the dose.
Taking sorbents for 2-3 days before the study is possible only as prescribed by a doctor. Using such drugs unnecessarily can cause constipation, which is not advisable before an MRI.
In case of excessive intestinal motility, preparation for tomography of the abdominal cavity includes the use of antispasmodics in consultation with a specialist.
MR image of the abdominal organs