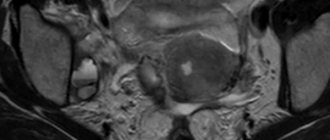
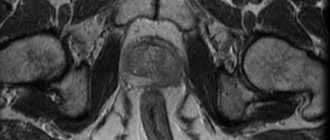
CT scan of the pelvic organs allows you to examine both the bone base and the internal organs of this area. Thanks to CT examination of the pelvic organs, it is possible to carefully examine the condition of the bladder, ureters, the structure of the rectum, prostate gland in men, as well as examine the appendages and uterus in women. Thanks to the three-dimensional images that the tomograph takes, you can see the lymph nodes and even the deep tissue of the pelvis. This diagnosis is irreplaceable during examination if cancer is suspected; it is also used in surgery, gynecology, urology and proctology. CT is the most effective diagnostic method, which deservedly occupies one of the first places in the world.
MSCT of the pelvis
| CT scan of the pelvis is prescribed to diagnose diseases of the pelvic organs, rectum, blood vessels, pelvic bones, as well as to identify the causes of abdominal or pelvic pain. Indications to perform computed tomography (CT) of the pelvic organs:
A CT scan of the pelvic organs is performed to:
CT scan of the pelvic organs in men is one of the methods for examining the pelvic organs. The method is of greatest value for diseases of the bladder and is prescribed for identifying and staging tumors. Also, CT of the bladder is used to identify postoperative complications, injuries, diverticula, ureteroceles, fistula tracts, etc. The study is carried out with a full bladder using a contrast agent to obtain the most objective information. The information content of a CT examination of the prostate gland is significantly inferior to an MRI examination and is used only when the latter is impossible. More often, this study is prescribed for oncopathology and is included in a complex with CT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, the urinary system, which provides additional information for assessing the prevalence of the process, the relationship of the formation with adjacent organs, diagnosing urodynamic disorders, identifying damage to the lymph nodes and bone structures. A CT scan is performed using a contrast agent to obtain the most objective information. CT scan of the pelvic organs in women. The “gold standard” for examining the pelvic organs in women is MRI; CT is prescribed only if it is impossible to conduct an MRI examination. CT examinations of the pelvic organs are performed using a contrast agent to obtain the most objective information. CT examination is most often prescribed for oncopathology in combination with CT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, which provides additional information for assessing the extent of the process, the relationship of the tumor with adjacent organs, and identifying damage to the lymph nodes and bone structures. Also, CT of the pelvis is prescribed for diseases of the bladder - tumors, developmental anomalies, ureterocele, etc. A CT scan is performed with a full bladder, in women in the first decade of the menstrual cycle, and may require special preparation (for example, vaginal tamponing). When vesical-vaginal fistulas form, fistulography is possible, then additional injection of a contrast agent into the fistulous tract is required with the participation of the attending physician or a specialist. |
When is an appointment required?
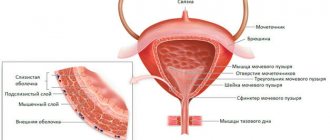
Computed tomography provides an excellent assessment of the condition of not only the female reproductive organs. With its help you can explore:
- bladder;
- urinary tract;
- ovaries;
- uterus;
- fallopian tubes;
- vagina;
- part of the intestine;
- the area located directly behind the uterus (the pouch of Douglas).
Reasons for examination may be injuries that affect the pelvis. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, it is also advisable to attach the results of an identical examination of the kidneys and abdominal cavity to the results of pelvic tomography.
Among other main reasons that prompt the attending physician to send a patient to undergo such a study, the following problems and diseases are identified:
- accumulation of blood or any other fluid in the pelvis;
- inflammatory processes such as salpingoophoritis;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs;
- pain in the lower abdomen of unknown etiology;
- menstrual irregularities for no apparent reason;
- ovarian cysts;
- abscesses;
- neoplasms of malignant and benign nature;
- metastases in the lymph nodes;
- tumors growing into organs and bones;
- preparation for planned surgery;
- anomalies of congenital or acquired properties.
Various acute surgical pathologies are also added here. A striking example of this is ovarian rupture or torsion of the cyst stalk. And the results obtained will then become a significant help for guidance during emergency surgery.
Against the background of the above, it becomes clear that CT can detect not only serious visible injuries, such as fractures of any severity. Tomography helps to deal with hematomas and internal hemorrhages, which are quite problematic to diagnose.
CT is also very informative for detecting foci of the inflammatory process, even if we are talking about the initial stages of endometritis or myometritis. Soft tissue defects are also included in the list of what can be seen in the image.
Due to the fact that the visualization is as detailed as possible, it makes it possible to identify the disease at the initial stage of its development, which is especially important for cancer patients.
Other diseases that can be diagnosed based on CT data include:
- rectal polyps and cysts;
- urethral fistula;
- deviations in the structure of the genital organs;
- cancerous uterine tumors;
- neoplasms in the urethra or bladder.
And with the involvement of other analyzes and taking into account hereditary predisposition, it will even be possible to find foci of diseases that have a genetic predisposition and may not make themselves felt for the time being.
Preparing for a pelvic CT scan
To obtain informative CT results when diagnosing pelvic organs, a prerequisite is a full bladder . Do not urinate for 1 hour, and also drink 1 liter of water an hour before the tomography;
You must come for the test with an empty bowel. 3 hours before the examination, it is necessary to empty the intestines using a cleansing enema or the drug Microlax
General requirements for contrast-enhanced CT:
To perform the test, you must have the result of a blood test with you.
for creatinine, the statute of limitations is no more than 30 days from the date of submission of the biomaterial.
Be sure to tell the radiologist before the examination with contrast:
- Do you have allergies to iodine, medications or food?
- whether you have diabetes, asthma, heart or thyroid disease
Contraindications for examination
Apart from pregnancy and allergic reactions, there are no other serious contraindications for the use of computer diagnostics. Even women during lactation can undergo such a study if, after the procedure involving a contrast solution, they refrain from breastfeeding for 2-3 days.
Relative contraindications include:
- heart failure;
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- mental disorders;
- comatose state;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- diabetes.
But all of the above refers to risks that are not an absolute obstacle to carrying out this diagnosis. This means that the examination may still be recommended if the benefits of the results obtained are greater than the possible harm.
Situations with patients suffering from obesity are considered separately. Typically, a contraindication for scanning involves a weight limit of 150 kilograms. But here everything depends on the specific model of the equipment itself. There are some variations where the weight limit is reduced to 120 kilograms.
Benefits and risks of CT
Advantages
The results of computed tomography allow doctors to make the most accurate, correct diagnosis and timely prescribe treatment. Computed tomography is a non-invasive, painless diagnostic method. Carrying out CT scans very often reduces the required number of studies to a minimum and eliminates the advisability of using invasive techniques.
CT scan:
— allows you to study the state of the bone structure, soft tissues, blood vessels and individual organs layer by layer; - often used in emergency situations, for post-traumatic disorders, for suspected damage to internal organs, bleeding; — can be used if the patient has implanted medical devices of any kind; — used for control during biopsy of organs and pathological areas of the human body. X-rays from a CT scan have no immediate side effects.
Estimated risks and contraindications
The effective dose of radiation from computed tomography is minimal, however, it is always present. The radiation dose is usually specified in the study protocol. In the interests of accurate diagnosis, especially in acute cases, this risk is mitigated. Women are required to inform the referring physician and radiologist about the possibility of pregnancy. Because of the potential risk to the baby, CT scans are not recommended for pregnant women unless there are specific medical indications. It is extremely rare, but allergic reactions to a contrast agent that contains iodine do occur. In such cases, PATERO CLINIC has all the necessary means to stop such reactions.
Manufacturers of intravenous contrast media do not recommend that mothers breastfeed for 24 to 48 hours after receiving or administering contrast media.
How is a pelvic CT scan performed?
The examination is usually performed lying on your back, rarely - lying on your side or stomach. To maintain correct or still body position during the examination, you may be asked to place your arms under your body or raise your arms above your head.
If it is necessary to use a contrast agent, it is administered either orally (orally - swallowed) or administered intravenously, depending on the type of study being performed.
You may be asked to hold your breath during the scan. Any slightest movement of the body can lead to artifacts in the images. After the test is completed, you may be asked to wait a short time while the radiologist checks the quality of the image.
Typically, a CT scan takes about 30 minutes. The administration of a contrast agent during the study lasts from 10 to 30 seconds.
What sensations arise during the study.
A CT scan is a painless and quick procedure that is easily tolerated by the patient. Although the scan itself is not painful, there may be some discomfort from having to remain still for several minutes. If you have pain and find it difficult to lie still, your doctor may suggest painkillers. When a contrast agent is administered intravenously, you will feel a rush of warmth and a slight metallic taste in your mouth. These sensations last no more than two minutes.
The contrast agent may taste unpleasant when administered orally, but almost all patients tolerate the procedure well.
After the CT scan, the patient can immediately return to his normal routine.
How to get a conclusion
A radiologist with relevant experience will analyze the results of the study and draw up a detailed report. The report and images can be sent to the attending physician who referred the patient for a computed tomography scan. The patient will also receive images and a copy of the radiologist's report. It is recommended to study the results of the study together with the attending physician.
How does the procedure work?
The patient is positioned on a special table. It is secured with pads and straps to reduce mobility because movement blurs the image in the photograph. Then the table is sent inside the tomograph. Within 15-20 minutes, the machine scans with X-rays and returns the patient to the office.
The radiologist is in the next room all this time and watches what is happening through thick glass. You can contact him at any time by clicking the contact staff button. The procedure does not bring any unpleasant sensations, and you can protect yourself from noise inside the tomograph with headphones or earplugs.
Sensors transmit cross-sectional images to a computer screen. Pictures can be obtained both on removable media and in printed form.
Indications for CT scan of the pelvis
A pelvic CT scan is prescribed to diagnose diseases of the pelvic organs, rectum, blood vessels, pelvic bones, as well as to identify the causes of abdominal or pelvic pain.
Indications for performing computed tomography (CT) of the pelvic organs:
- Fluid accumulation, abscesses;
- Inflammatory and infectious processes;
- Tumors;
- Aneurysms of the abdominal aorta and large vessels of the pelvis, diagnosis of blood clots and abnormal narrowings (vascular stenosis);
- Damage to the lymph nodes.
A CT scan of the pelvic organs is performed to:
- Urgent detection of damage to the pelvic organs due to trauma;
- Performing a biopsy, as well as draining abscesses and fluid accumulations;
- Assessment of the condition of the pelvic organs at the planning stage of surgical intervention;
- Determining the patency of the fallopian tubes in the treatment of infertility;
- Assessment of the results of a particular treatment, including surgery, radiation and chemotherapy for cancer.
Alternative methods for diagnosing the pelvic organs
Computed tomography, as mentioned above, is usually prescribed to clarify the results of other research methods.
Ultrasound does not provide a complete picture of the disease, and the image on the ultrasound specialist’s computer monitor is only in one plane. With CT, a whole series of layer-by-layer images is obtained in different projections;
MRI in some cases provides more information than CT because CT and MRI images are from different angles. Doctors prefer to combine these diagnostic methods, which complement each other perfectly.