At the Road Hospital in Yekaterinburg, laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is performed to eliminate obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
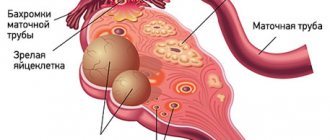
The fallopian tubes connect the uterus to the ovaries. Normally, fertilization of an egg by a sperm occurs in the fallopian tube, after which the fertilized egg moves to the uterus. Obstruction of the fallopian tubes disrupts this natural process and is often the cause of infertility. Typically, obstruction of the fallopian tubes is caused by inflammatory changes (adhesions, adhesions) in the tube and/or the formation of adhesions in the pelvic cavity as a result of diseases, as well as previous operations and manipulations.
Gynecological Clinic | Hospital | Gynecological surgeries | Gynecology, prices | Make an appointment with a gynecologist
The specific type of surgical intervention depends on the cause that led to obstruction of the fallopian tubes, as well as on the level of location and degree of obstruction. Currently, several main types of laparoscopic operations on the fallopian tubes are used, including:
- Removal of adhesions in the pelvis. Laparoscopic removal of adhesions in the pelvis is performed if the adhesive process has led to dysfunction of the pelvic organs. Adhesions, which doctors also call synechiae or moorings, are scar (connective) tissue formed as a result of inflammatory processes, injuries or operations and connecting adjacent organs or surfaces. In the early stages of formation, adhesions can be easily separated, but over time, the “adhesions” become strong, nerves and blood vessels are formed in them, and, moreover, calcium salts are deposited. It can be very difficult to separate such virtually ossified adhesions. There are three stages of the adhesive process. In the first stage, adhesions are located around the fallopian tube, ovary, or other area, but do not affect the function of the fallopian tube, in particular the capture of the egg by the fimbriae (fimbriae) of the fallopian tube. The second stage differs from the first in that the presence of adhesions in the pelvis can interfere with the capture of the egg by the fimbriae. At the third stage, there may be torsion of the tube, disruption of its patency, or inability to capture the egg in the fallopian tube.
- Formation of an anastomosis (connection) between different parts of the fallopian tube. This microsurgical operation is usually performed to restore the patency of the tube after previously performed surgical sterilization, as well as in case of obstruction of a section of the fallopian tube as a result of adhesions. The essence of the operation is to remove the obstructed section of the fallopian tube and then connect the two healthy ends of the tube.
- Salpingectomy (removal of the fallopian tube), or removal of part of the fallopian tube, is performed to improve the success of in vitro fertilization (IVF) in women with hydrosalpinx. Hydrosalpinx halves the success of a live birth after an IVF procedure. The reason for this is not entirely clear. It is believed that in women with hydrosalpinx, either fluid leakage from the tube into the uterus prevents the embryo from implanting, or the fluid itself has a toxic effect on the embryo. Fallopian tube removal is preferred over salpingostomy to treat hydrosalpinx before IVF. In most cases, salpingectomy is performed laparoscopically.
- Salpingostomy is an operation to create a new opening in the part of the fallopian tube closer to the ovary. It is carried out with the aim of restoring its patency in case of its occlusion, including as a result of hydrosalpinx. Unfortunately, after salpingostomy, the adhesive process can again block the fallopian tube.
- Fimbryoplasty (Fimbryolysis) is an operation that is performed for complete or partial obstruction of the fimbrial part of the tube. Unlike salpingostomy, which creates a new opening in the fallopian tube, fimbryoplasty aims to restore the natural opening, preserving and releasing multiple thin fimbriae (fimbriae) that are important for conception.
- A combination of different types of operations (interventions on both pipes, in different sections of one pipe).
Why does body temperature increase after laparoscopy?
There are several explanations for this phenomenon. First of all, the reason for its increase is caused by physiological factors. As a result of laparoscopy, like other surgical interventions, a wound is formed, which is stressful for the body. Why fever after laparoscopy? Regardless of the origin, the wound process has a corresponding course, which is divided into several phases:
- The first one takes about a week. During this period, energy processes predominate, and some individuals lose slight weight. It is during this period that an increase in temperature is observed, and this phenomenon is considered an adequate reaction of the body.
- Second, in this phase the concentration of hormonal substances in the blood increases, recovery processes become more active, the balance of electrolytes and metabolic processes, as well as temperature, return to normal.
- Third – the individual regains the lost weight, the body is completely restored.
How long does the temperature last after laparoscopy? In most cases, it returns to normal within a week after the operation. It should be noted that with this type of surgical intervention the temperature rarely exceeds 38 degrees. For example, after laparoscopic surgery to remove an ovarian cyst, gallbladder or appendicitis, body temperature can reach 37.5 degrees in the evening. This moment is directly dependent on the severity and scale of the surgical intervention. This is explained by the course of the wound process. If the individual has had drainage installed, then after laparoscopy the temperature remains at 37 degrees or higher for more than a week. This phenomenon is also not considered abnormal, but is a response of the body. The temperature returns to normal after the drainage is removed. However, there are situations when serious complications arise, despite all the efforts of the medical staff.
When should you sound the alarm?
Complications after surgical interventions are caused by damage to internal organs, nervous tissue, blood vessels, infection and other factors. You should contact a medical facility in the following cases:
- After laparoscopy, the temperature rose and did not subside for more than a week.
- Increased sweating, chills.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Pus oozes from the wound, its edges are reddish and dense.
- There is intense pain in the puncture area.
- The individual has developed symptoms reminiscent of the development of an infectious process, for example, pneumonia: wheezing in the chest, cough or signs of intoxication - rapid pulse, dry mouth, as well as signs of peritonitis.
What happens in the operating room? Stages of the operation.
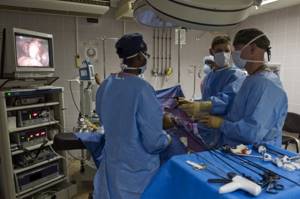
When the woman is already under anesthesia, the surgeon makes several punctures in her abdominal wall. Through one of them, usually in the navel area, a laparoscope is inserted - an instrument with a video camera and a light source. It broadcasts the image to the screen.
Through the remaining punctures, special instruments for laparoscopic interventions are inserted. The surgeon makes an incision in the wall of the uterus, enucleates and removes the fibroids, cauterizes the vessels and stops the bleeding. Stitches are then placed on the wall of the uterus. To better visualize the uterus and other anatomical structures, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
The operation is completed by suturing the skin at the puncture sites. In the future, small, barely noticeable scars remain.
Recovery period after laparoscopy
The rehabilitation period after surgery should be supervised by medical professionals who monitor the recovery process and, if necessary, make the necessary appointments in the form of additional examinations and correction of pharmacotherapy, including assessing the advisability of using antipyretic and analgesic medications. How long does the temperature last after laparoscopy, and is it possible to take medications to reduce it? This question interests many patients who have undergone surgery. In the absence of postoperative complications, the patient's elevated temperature is recorded within a week. The decision to take antipyretics is decided by medical personnel individually, depending on the individual’s condition. In practice, they mainly use drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which, in addition to antipyretic, have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy, of course, is not a disease, but a pleasant state in a woman’s life, which can sometimes manifest as unwanted pain symptoms in the presence of concomitant diseases. Confirmation or refutation of this condition is carried out after clarification of anamnestic data, physical examination, pregnancy tests, as well as additional instrumental methods. If, in the absence of menstruation, after an ultrasound, a neoplasm is discovered in the pelvis, then this is one of the indications for laparoscopy.
Preventive actions
Any complication, including constant (for a month after laparoscopy) temperature, is easier to prevent than to treat. This can be achieved subject to certain conditions:
- Minimal hospital stay - both before and after surgery.
- Prevention of nosocomial infection. Strict compliance with sanitary and epidemiological requirements.
- Timely detection and treatment of various infectious processes in an individual before surgery.
- Mandatory prescription of antibacterial agents to the patient in order to prevent possible infectious complications.
- Use of high-quality consumables and medical products, including suture material.
- The fastest possible identification of adverse postoperative consequences and the adoption of measures to eliminate them.
- Early start of physical activity under the supervision of a therapeutic exercise instructor.
Indications for myomectomy - removal of uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids do not always need to be treated. For many women, we can limit ourselves to dynamic observation: they only need to undergo periodic examinations by a gynecologist and ultrasound examinations. Currently, the indications for treatment are clearly defined:
- If uterine fibroids cause symptoms that reduce a woman's quality of life. These may be: pain and excessively heavy periods, anemia, dysfunction of the rectum and bladder as a result of compression by their nodes.
- A woman’s desire to become pregnant, while myomatous nodes will interfere with the onset and gestation of pregnancy.
- If fibroids are growing, based on the results of two or three ultrasound examinations performed over time.
But age is a relative contraindication to surgery. Typically, after menopause, the nodes stop growing and most often decrease in size.
Treatment methods for uterine fibroids vary. And hysterectomy - removal of the uterus - is in last place on this list. Currently, it is used as a last resort when other treatments are ineffective. Many women are candidates for uterine artery embolization , a procedure that does not require incisions or general anesthesia. The doctor makes a puncture in the upper part of the thigh, inserts a catheter through the femoral artery into the vessels feeding the fibroids and injects an embolic drug through it. The latter consists of microscopic particles that block the lumen of blood vessels. Myoma stops receiving oxygen and necessary substances, dies and is replaced by connective tissue.
The third type of treatment is myomectomy, surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus. Surgeries and embolization of the uterine arteries are not competing techniques. Each of them is used in certain cases when it makes it possible to solve the problem of uterine fibroids most effectively and with minimal risks.
Euroonko employs doctors who have extensive experience in performing both uterine artery embolization (UAE) and myomectomy operations, including minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures. Consult our doctor: he will correctly assess your situation and recommend treatment methods that are optimal in your case.
Laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
This method of surgical intervention in gynecological practice is used quite often and is carried out for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is not possible to cure a cyst with medications. Laparoscopy is the most gentle way to access the affected organ. Before the operation, the individual is given general anesthesia. No more than three incisions are made in the peritoneal wall, through which all surgical procedures are performed. The peritoneum fills with air. During the operation, the cyst is cut off along with the ovary or fluid is sucked out of it. Sutures are placed on only two incisions, and a drain is inserted into the third. The surgical intervention lasts no more than an hour. In order to reduce the risk of postoperative complications, which include an increase in temperature after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, contraindications are first identified. The operation is not performed if:
- breathing problems;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- overweight;
- problems with blood clotting;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of an infectious nature.

High blood pressure, adhesions in the abdominal cavity and some other factors are considered relative contraindications to surgery. In these cases, the doctor makes an individual decision.
Preparing for surgery for ectopic pregnancy
Before prescribing surgery for a patient, CELT gynecologists conduct comprehensive studies that are aimed at identifying contraindications:
- Clinical examination will determine its general condition and method of access for surgical intervention;
- Analysis of the level of chorionic gonadotropin in the blood determines treatment tactics (dynamic assessment, conservative therapy or surgical intervention);
- Transvaginal ultrasound scanning of the pelvic organs - detects the location and diameter of the fetal egg even in the first weeks of pregnancy.
If the data obtained does not allow an accurate diagnosis, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. Thanks to it, the gynecologist receives the most accurate data about the location of the fertilized egg. The patient needs to stop eating twelve hours before surgery.
Recovery period
Sometimes women are discharged from the hospital within two days after surgery. However, if complications are detected, the length of stay in the hospital increases. During the rehabilitation period, after ovarian laparoscopy, a temperature within 37 degrees can be recorded for several days, usually no more than five. During this period, the body activates all its forces to heal wounds and restore the reproductive system. On the fourth or fifth day, the drainage is removed and the sutures are removed. Pathological processes are indicated by a sharp increase to 38–39 degrees or prolonged fever during the rehabilitation period.
Possible negative consequences after removal of an ovarian cyst
Complications and such a phenomenon as high temperature after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts are quite rare in medical practice, occurring in approximately two percent of females. Due to the weakening of the body, the risk of infection increases. Serious consequences, such as adhesions leading to infertility, damage to large vessels, as well as nearby organs, are usually associated with errors made by medical personnel during surgery.
An urgent visit to the doctor is necessary if, after laparoscopy, cysts:
- the temperature rises to 38 degrees and above, or there are sharp jumps, i.e. it is unstable;
- there is redness in the suture area;
- heavy bleeding;
- increasing weakness;
- vaginal discharge that is brownish or yellow-greenish in color.
In some cases, new formations appear at the site of the removed cyst. To prevent them, doctors recommend hormonal therapy. Taking antibacterial agents significantly reduces the risk of infectious complications. To restore the body, vitamin complexes and preparations from plant materials are indicated.
Indications and contraindications for laparoscopy for fibroids
Often, after a woman is diagnosed with uterine fibroids, the question arises: which treatment method should be preferred: myomectomy or uterine artery embolization? The operation is indicated in the following cases:
- A woman is planning a pregnancy in the near future, not sometime in a few years. This is associated with the risk of relapse. If a woman decides to have a child in the long term, there is a high probability that the problem with fibroids will have to be solved again.
- The nodes are located superficially on the uterus, do not lead to deformation of its cavity, do not occupy the entire thickness of the wall of the organ, and are not located in the area of the isthmus and the confluence of large vessels.
- The surgeon is confident that the uterine cavity will not be opened during the operation.
- The surgeon is confident that after the operation a full-fledged scar will form, and it can be easily monitored using ultrasound during pregnancy.
Accordingly, if these conditions are not met, it is worth considering the possibility of conducting an EMA. Laparoscopically, it is possible to remove nodes no more than 8–10 cm in diameter, and their total number should not exceed four.
In addition, we should not forget that any operation, even minimally invasive, carries certain risks. They can be associated both with the surgical intervention itself and with anesthesia. Severe health problems in a woman may be a contraindication.

Causes of fever after hysterectomy
After laparoscopy of the uterus, the temperature may be elevated for several days after the intervention. During this period, the woman is in a hospital setting. Depending on the patient’s condition, doctors prescribe the necessary treatment. A temperature within the subfebrile range is considered a normal reaction of the body and does not require urgent action. Antipyretics are not indicated in this case. If higher numbers are registered, medical attention is required, as this is one of the symptoms of abnormal processes that arose in the postoperative period. To prevent such a situation, a mandatory course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed after surgery, which reduces the risk of inflammatory reactions in the individual’s body, and, accordingly, temperature. In addition, the reasons for its increase are:
- Infection or pathogenic microflora entering the wound.
- Failure to comply with certain rules recommended by the doctor when using hygiene products. For example, after removal of the uterus, it is prohibited to use tampons, since through them it is easy to introduce microorganisms into the vagina and provoke an inflammatory process.
- Inflammation also develops against the background of low immunity.
Thus, there are several reasons for the rise in temperature, but this phenomenon is not always dangerous. If the temperature has not returned to normal for a long time, i.e. more than a week, then you should visit your doctor.
Ectopic pregnancy
This disease, despite modern developments in medicine, remains one of the main causes of maternal mortality. Diagnosing an early or uninterrupted pregnancy outside the uterus is somewhat difficult, and an accurate diagnosis can only be made after numerous examinations and a series of examinations.
Often, women complain of an irregular menstrual cycle with accompanying spotting discharge from the vagina, and consult a gynecologist one to two months after the last normal menstruation. Information about previous inflammatory processes in the reproductive system or about tubal ligation after laparoscopy, which was accompanied by menstruation, may lead the doctor to think about an ectopic pregnancy.
The pain can be either dull or acute, but unlike a miscarriage, in which the patient clearly notices pain in the middle of the abdomen, with an ectopic pregnancy it is one-sided.
Ultrasound examination in combination with the quantitative determination of human chorionic gonadotropin in blood plasma also has excellent diagnostic value. To determine the final diagnosis after a delay in menstruation and the presence of additional symptoms, laparoscopy or laparotomy is recommended.
Laparoscopy in such cases is one of the only and low-traumatic methods of eliminating an ectopic pregnancy without the risk of developing serious complications.
Consequences of surgery to remove appendicitis
An increase in temperature after laparoscopy of appendicitis at an early stage is considered a normal process and indicates the body’s natural reaction to the stress associated with surgery. The reasons for this phenomenon lie in the following:
- formation of toxic tissue breakdown products;
- loss of fluid due to bleeding;
- drainage to improve the outflow of secretions from the wound;
- decreased defenses in response to stress caused by tissue damage from medical instruments.
Thus, if after laparoscopy the temperature is 37 degrees, then this indicates the natural resistance of the individual’s body. The temperature normalizes on its own within a week, since this is approximately the time it takes for the wound to heal.

A dangerous sign is fever that lasts for a long period against the background of symptoms such as:
- constipation;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- dysbacteriosis;
- sweating;
- attacks of loss of consciousness;
- vomit.
In addition, prolonged hyperthermia or increased temperature a week after laparoscopy is observed in the following situations:
- In inflammatory processes and sepsis, the temperature rises sharply a few days after surgery. In these cases, repeated surgery is sometimes resorted to, and antibacterial and other medications are also prescribed.
- During the postoperative period, the individual has low immunity. Infections and viruses easily penetrate into an insufficiently well-protected body, causing the development of a pathological process, which is accompanied by a rise in temperature.
- After laparoscopy, a temperature of 37 degrees or higher is observed in the presence of drainage, which was installed for the patient during the operation. When it is removed, the temperature returns to normal; antipyretics in this case are prescribed quite rarely.
It is important to remember that an elevated temperature after discharge from the hospital is a reason to contact a healthcare facility.
Laparoscopic surgery: advantages and disadvantages
The main, obvious advantage of laparoscopic removal of uterine fibroids is that it is a minimally invasive operation. It is performed without incisions, through several punctures in the abdominal wall. At the same time, tissue is less injured, bleeding is minimized, and the recovery period is shortened. The woman can be discharged from the hospital earlier and return to her normal life.
When using laparoscopy, compared to open interventions, in the postoperative period there is less pain, and body temperature increases less frequently and less strongly. Lower risk of adhesions forming.
The disadvantage of laparoscopic interventions for the removal of uterine fibroids is that the possibilities of their use are limited. This operation cannot be performed on all women. Using laparoscopy, it is possible to remove only nodes that are subserosal (protrude externally above the surface of the organ) or intramural (in the thickness of the wall), are relatively small in size (up to 8–10 cm), and if there are no more than four of them.
The problem with any myomectomy is the relatively high risk of recurrence. Studies show that in 14% of women operated on, the nodes return within a year. Thus, after 4–5 years, approximately half of the patients are diagnosed with uterine fibroids again. After UAE, the risk of relapse is very low.
The advantage of a myomectomy over a hysterectomy is that the woman's uterus is preserved and she can become pregnant in the future. In addition, the uterus plays an important role in the body. posthysterectomy syndrome may develop , which manifests itself in the form of metabolic, neurovegetative disorders, and reduces the quality of life.
Gallbladder removal
The occurrence of consequences after surgery, including an increase in temperature, depends on the method of performing the operation to remove the gallbladder. The following methods of cholecystectomy are known:
- transgastric or transvaginal;
- open minimally invasive;
- traditional open;
- laparoscopic.
Let's look at the latter in more detail. Laparoscopy is recognized as the best way to remove the gallbladder. This is a safe and effective operation. It is carried out for complications of cholelithiasis, inflammatory processes in the gallbladder and some other pathological conditions. Before surgery, general anesthesia is administered. Next, several small punctures are made in the wall of the peritoneum, through which special tubes are inserted, and through one of them the laparoscope itself is inserted directly. It has a miniature camera with which the image is displayed on the monitor. In addition, carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity. After the operation, which lasts about an hour, the punctures are sutured. The rehabilitation period lasts several days.
Temperature after laparoscopy of the gallbladder is due to a number of reasons:
- postoperative complications;
- abnormal processes of inflammatory nature.
How effective is tubal laparoscopy for infertility?
The effectiveness of the operation depends in part on the level of location and degree of obstruction of the tube, as well as on the presence or absence of other health problems affecting infertility.
- Removing the obstruction in the part of the fallopian tube closest to the uterus (proximal part) is most often successful. In most cases, obstruction in the proximal fallopian tube is due to functional causes (eg, a “mucus plug”) rather than organic causes (eg, adhesions or other obstructions). Up to 60 out of 100 women with proximal fallopian tube obstruction have been reported in studies to have successful pregnancies after fallopian tube surgery.
- The length of the fallopian tube that remains after surgery is critical for the normal functioning of the tube. If a large portion of the tube must be removed to clear the obstruction, the chance of pregnancy after surgery is reduced.
Other factors affecting the effectiveness of the operation include, but are not exhaustive:
- the presence and severity of the adhesive process in the pelvis;
- the presence of other diseases in the pelvic area;
- skill and experience of the surgeon.
Fever after gallbladder removal
An increase in temperature to 38 degrees in the first six days after surgery is not a cause for concern. In addition, in some cases, even 39 degrees is considered within normal limits for the early postoperative period. This phenomenon is caused by the reaction of the individual's immune system to the intervention. This is how the body responds to tissue damage and protects itself from harmful microorganisms when toxic substances are absorbed from the wound into the bloodstream. Complications after removal of the gallbladder are possible with any method of surgical intervention. However, the lowest risk of their occurrence is after using the laparoscopy method. Temperature after removal of the gallbladder serves as a so-called indicator of postoperative consequences. If the temperature lasts more than six days, constantly increases or appears at times for no particular reason, then most likely an inflammatory process is developing in the body.
Reasons for rising temperature
The most common causes of postoperative complications with fever are infections, pneumonia, and diarrhea. The latter after removal of the gallbladder is associated with an intestinal infection, the manifestation of which is due to the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora against the background of a weakened immune system.
Pneumonia can be caused by atypical microflora. Its signs include fever, sore throat, headache, difficulty breathing, pain in the chest area, and dry cough. Infection with fever after laparoscopy of the gallbladder occurs directly in the wound and abdominal cavity. In the first case, the cause is the contamination of the wound surface with pathogenic microorganisms from the dermis, which is caused by errors in the preparation of the surgical field or poor-quality wound care after surgery. Pathogenic bacteria can also be introduced through poorly processed medical products. Also, the reason may be a weakened immune system of the individual, poor cleaning of the wards, operating unit, etc. An infectious process in the peritoneum (for example, peritonitis, abscess) is caused by failure to comply with aseptic rules, damage to the intestines during surgery, and the entry of bile and blood into the peritoneum. Usually the temperature after laparoscopy in these cases is above 38 degrees. In addition to this, the individual exhibits:
- Swelling of the edges of the wound, upon palpation, release of contents from it, pain, redness. These symptoms are inherent in postoperative wound infection.
- Abdominal pain, constipation, bloating, severe itching of the dermis, jaundice, polyuria or urinary retention, deterioration in general health. Such phenomena are characteristic of an infectious process in the peritoneum.

The risk of complications accompanied by fever after laparoscopy of the gallbladder increases if the following conditions are not met:
- the correct preparatory period, which consists of treating existing concomitant pathologies, fasting, intestinal lavage, taking medications to prevent bloating and flatulence, hygienic water procedures before surgery;
- there must be compelling indications for surgical intervention;
- compliance with the diet recommended by the doctor after laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic operations - description

During laparoscopic surgery, two or three one-centimeter incisions are made above the navel and in the groin area. One incision is for the camera, the other for operating instruments.
Yalanskaya Nadezhda Petrovna
Gynecologist at Danaya MC
To prevent the abdominal wall from interfering with medical manipulations, it is lifted upward using neutral gas (“inflating” the abdomen). Laparoscopy also requires general anesthesia.
Unlike operations through incisions in the abdomen or vagina, laparoscopy provides a better view and is less traumatic.
Indications for laparoscopic operations
- Infertility - pregnancy does not occur within a year from the start of regular sexual intercourse without contraception. In this case, before the operation, the woman must be examined, the man undergoes a spermogram (the need for treatment of male infertility is determined). In case of hormonal disorders, laparoscopy is indicated for a woman if treatment does not bring results for 1–2 years. If infertility is observed during a regular menstrual cycle, laparoscopy reveals various organ pathologies in 75% of patients (for example, laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes can detect and eliminate adhesions).
- Chronic pain in the pelvic area, endometriotic or adhesive processes are preliminarily diagnosed.
- Ovarian tumor (for surgical treatment of ovarian cysts, benign neoplasms, the method of ovarian laparoscopy is used).
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS, a disease of hormonal etiology; ovarian laparoscopy is necessary if drug therapy is ineffective).
- Endometriosis in the peritoneum, uterine appendages.
- Uterine fibroids (small superficial nodes are removed laparoscopically).
- Surgical sterilization of a woman if desired (laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes allows them to be ligated).
- Emergency: rupture or torsion of an ovarian cyst; apoplexy (rupture) of the ovary and internal bleeding; laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy; purulent-inflammatory processes in the appendages or recesses of the small pelvis (if antibacterial therapy does not have an effect within 1–2 days).
Contraindications
Among the contraindications (complete prohibitions) for laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes, ovaries and other areas of minimally invasive surgical treatment:
- cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in the decompensation stage;
- shock, coma;
- cachexia (exhaustion with severe symptoms);
- disorders in the blood coagulation system;
- hernias (diaphragm, anterior abdominal wall).
Contraindications for the planned operation include:
- acute infectious disease less than a month before laparoscopy;
- deviant results of clinical laboratory research (consultation with a therapist is required to make a decision on surgery or additional examination);
- frequent exacerbations of bronchial asthma;
- high blood pressure (hypertension).
Preparation
Tests that need to be taken before laparoscopy:
- general blood and urine tests (CBC, UAM), coagulogram (blood clotting);
- blood group, Rh factor;
- blood for syphilis (RW), hepatitis types B, C, HIV;
- smear to examine vaginal flora;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
Before the operation, the doctor consults the patient about the extent of the surgical intervention (for example, in some cases the cyst needs to be removed along with part or the entire ovary; the invaluable advantage of laparoscopy for ectopic tubal pregnancy is the high chance of preserving the entire fallopian tube) and possible complications. The anesthesiologist talks about preoperative drug preparation. In both cases, the woman must certify in writing that the conversation was conducted and her consent to the proposed treatment measures.
Preparing for surgery requires a certain dietary regimen. As a rule, the doctor recommends a diet before surgery, taking adsorbents, and possibly enemas to cleanse the intestines. It is necessary to follow these instructions, since a swollen intestine interferes with laparoscopy and is easy to injure during manipulation.
On the eve of laparoscopy, food intake stops at 18:00, water - at 22:00. On the day of surgery, food and water intake is completely prohibited.
Postoperative period
After recovery from anesthesia, indications for a diet remain; if pain is present, the doctor recommends certain medications. At first, the tied seams should not be wetted or touched at all. After removing the bandages (plasters), the stomach is carefully washed, the seams are lubricated with a disinfectant solution (zelenka).
To avoid adhesions, patients are recommended to have early mobility - they can and should get up several hours after surgery.
What to do if complications are detected after gallbladder removal
If a postoperative complication is detected, you should immediately contact your doctor. He will conduct the necessary types of examinations and prescribe adequate therapy. There is no need to try to cope with the situation on your own or resort to the advice and help of friends and relatives. If you have a fever after laparoscopy, then doctors most often recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as symptomatic therapy:
- "Diclofenac";
- "Voltaren";
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Brufen."
The above drugs have a low level of toxicity and cope well not only with fever, but also reduce inflammation and pain. It is important to remember that an increase in temperature in the postoperative period is not always a complication. According to the observations of practical doctors, after laparoscopy the temperature rises to 39 degrees and lasts for about seven days, after which the individual is fully restored and ready to begin work.
The main reasons for the rise in temperature
Any interference is perceived by the body as something unnatural and alien, and it experiences severe stress, and its protective functions decline. An increase in temperature is one of the body’s possible reactions to such external influences. The main causes of fever are:
- absorption of decay products formed after tissue injury;
- decrease in fluid level in the bloodstream.
If the postoperative period is favorable, a slight increase in temperature returns to normal after a few days. Otherwise, temperature after laparoscopy is a consequence of all kinds of complications that have different symptoms, including hyperthermia. What to do if the body reacted to the intervention in this way? In such cases, you should focus on the nature of the increase:
- If there are no other signs and the temperature increases immediately after the operation, then no measures should be taken, including taking medications that reduce it. This is a natural process and the temperature will return to normal within a few days.
- If, in addition to high temperature, other signs are observed, for example, pain, then consultation with a specialist is required. He will assess all risks and identify possible pathological processes in order to prescribe appropriate treatment in the future.
If the temperature rises after laparoscopy, then this is absolutely natural. However, this point does not exclude control over its values.
Things to remember
- Hysterosalpingography may be performed 3 to 6 months after surgery to check whether tubal obstruction has been resolved;
- You can get pregnant within about a year to a year and a half after the operation. The likelihood that the pipes will again become impassable as a result of the adhesive process is quite high. In addition, the patency of the tubes is not enough; they must fulfill their function of moving the fertilized egg to the uterus. Otherwise, an ectopic pregnancy may occur. Thus, restoration of patency of the fallopian tubes does not guarantee your successful pregnancy;
- If you do not become pregnant within 12 to 18 months after surgery, consult your doctor, he may recommend a diagnostic laparoscopy to check the condition of the fallopian tubes, or refer you for in vitro fertilization (IVF);
- If you are young and there are no other factors that interfere with pregnancy, it makes sense to have laparoscopic tubal surgery. At the same time, if you are over 35 years old and have been trying to have a baby for a long time, talk to your doctor about artificial insemination.
- If fallopian tube surgery is successful, a woman can have more than one pregnancy without ongoing fertility treatment or repeat surgery.
How to measure temperature correctly
Measuring temperature is an absolutely simple procedure, the main thing is to follow some rules. One of the most common mistakes is measuring it incorrectly. In order to correctly assess the readings, you should consider the following points:
- the room temperature should not be lower than 18 and higher than 25 degrees;
- Air should not be allowed to enter the armpit;
- the temperature in the oral cavity is half a degree higher than in the armpit;
- You cannot measure your temperature after eating, smoking, or hot drinks;
- It is not advisable to take a bath with hot water, or engage in sports and physical exercise immediately before the measurement;
- The thermometer is taken out with a smooth movement;
- the dermis in the armpit should be dry;
- It is not recommended to measure the temperature several times to ensure that the thermometer is working properly.
The average time for taking readings from a measuring device is about six minutes, for a mercury thermometer - ten, for an electronic one - three. During illness, the temperature is measured at least twice, in the morning and evening hours. If possible, it is best to do this at the same time to track the dynamics.
If the high temperature does not subside for a long period of time after surgery, then you should immediately consult a doctor. This will help to identify pathology in a timely manner and begin appropriate therapy. You should not self-medicate, as this is dangerous and can harm your health.