According to the Ministry of Health, in Russia there is one hearing-impaired child per 1,000 newborns. More than 1.3 million children were diagnosed with hearing loss in 2021, and this number is growing.
Sustained hearing loss leads to critical impairments in psycho-speech development, up to complete absence of speech with intellectual impairment. They have a bad effect on the psycho-emotional development of the child if the problem is not diagnosed and corrected in a timely manner. Violations identified and corrected before 6 months of age provide an excellent chance that the feature will have virtually no effect on the child’s development. But it is in infancy that the problem is most difficult to notice.
How to tell if your child has hearing loss
In Russia, since 2008, doctors have tested the hearing of all children in the maternity hospital on the 2nd–3rd day of life. This is an audiological screening, which, according to the letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 2383-РХ dated April 1, 2008, is carried out by recording evoked otoacoustic emissions (OAE). If problems are identified during the check, the doctor prescribes additional examinations for the child.
OAE registration is performed using a special device within a few minutes. The procedure is painless and safe.
Positive screening result
Thanks to audiological screening, the likelihood of “missing” congenital hearing impairments and deafness is reduced. However, screening is not a final diagnosis, but only one of the tests. If for some reason the baby did not pass the UAE in the maternity hospital, this is a reason to schedule an extended study. Most often, this is an objective diagnosis of KSVP (we will talk about this below).
But in any case, parents should notice warning signs that may indicate hearing problems in the baby, and consult a doctor. This primarily applies to children with risk factors for hearing loss:
- Premature and post-term babies.
- Low birth weight.
- Intracranial birth injuries.
- Asphyxia, hypoxic lesions of the central nervous system.
- Severe toxicosis in the mother during pregnancy.
- Administration of ototoxic (negatively affecting the condition of the hearing aid) medications to a newborn or infant.
- Hereditary factor (hearing loss in blood relatives).
Hearing problems in a child can be noticed already in the first days of life. Normally, newborns (children up to 28 days old) react to sound: they turn their heads towards the voice, wake up due to loud sounds, flinch in response to clapping their hands or other sharp sounds. If there is no reaction, you need to talk to your doctor.
At 2–3 months of age, babies recognize and respond to their parents' voice. They also listen to other sounds: rattles, musical toys, dog barking, and so on.

The baby listens to the babble of another child, which he hears from the speaker of the phone. Source: YouTube
At the age of 3-4 months, hearing problems can be indicated by the absence of humming, and at the age of 5-6 months - by the absence of babbling. Here the influence of hearing loss on psycho-emotional and speech development is already evident: it is delayed.
Booming and babbling are sounds that babies make. The first one is like “ah-ah”, “oo-ah”, “ah-uh”. The second one is similar to “ba-ba-ta”, “ta-ta-ta”, “da-ba-ba”.
By the end of the first year of life, the child understands simple words, for example, “mom”, “dad”, “yum-yum”, “drink”, “yes”, “no”. If not, parents should consider getting their child's hearing tested.
Cochlear implantation
Cochlear implantation surgery—installation of an electrode into the cochlea of the inner ear that produces electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve—is performed for patients with bilateral sensorineural deafness. In case of congenital deafness, it is critical to perform this operation and begin auditory-speech rehabilitation as early as possible - in this case, the potential effect will be maximum. The audiological indication for cochlear implantation is the state of sound perception thresholds corresponding to severe hearing impairment and deafness.
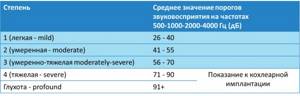
To diagnose hearing, an extensive audiological examination is carried out, on the basis of which the type and degree of hearing loss is determined; Patients with identified sensorineural deafness undergo hearing aids - installation of hearing aids. 6 months after hearing aid, based on deaf-pedagogical testing, a conclusion is made about the feasibility of cochlear implantation.
What to do if you suspect hearing loss in a child
An audiologist deals with hearing problems. But in Russian realities, parents should start with a visit to the pediatrician. Tell your doctor if you have any suspicions and ask for a referral to an audiologist. With a referral from a pediatrician, you will not have to pay for a consultation with a specialist if the child has a compulsory medical insurance policy.
Please note that you need to consult an audiologist, not an otolaryngologist (ENT). An audiologist is an additionally trained otolaryngologist. He knows everything about diagnosis and treatment of hearing, unlike the usual “ear, nose and throat”. Traditional methods of ENT treatment for hearing loss are not effective.
What will the doctor do?
First, the audiologist will check to see if the child actually has a hearing loss. If the diagnosis confirms hearing loss, the doctor will prescribe treatment. It is important to know that sensorineural hearing loss cannot be cured; it can only be corrected with the help of hearing aids (HA). In case of severe losses, CA may be ineffective, then cochlear implantation will be recommended for the child.
How do audiologists diagnose hearing loss?
The doctor will first talk to you and then examine the child. The specialist will check the child’s hearing condition using objective diagnostic methods.
There are also subjective methods - these are tonal or game audiometry. A basic method that is great for adults. But there are nuances: patient participation. When the patient is under 3 years old, he cannot consciously follow the doctor’s orders, which means that the result of such a test will be unreliable.

If the child is over 3 years old, his hearing can be tested using pure-tone audiometry
Game audiometry is a hearing diagnostics in which a teacher of the deaf is involved. He helps the doctor and, using gaming techniques, determines how the baby reacts to sounds of a certain tone.

Game audiometry is carried out with the participation of a teacher of the deaf.
Therefore, in the case of young children, the “gold standard” is objective audiometry, that is, OAE, KSVP, ASVP, ASSR tests and others. At the same time, in comparison with the traditional registration of short-latency auditory evoked potentials (SLEP), the registration of acoustic brainstem evoked potentials (ASEP) differs in its automatic algorithm, when a specialist is not involved in data analysis.
At the appointment, audiologists usually begin by examining the external auditory canal and eardrum using an otoscope. This device literally allows you to look into your ear. Otoscopy is a painless and safe procedure, but a small child may be afraid of a stranger and actively protest.
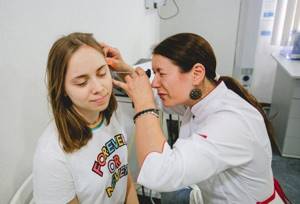
Otoscopy allows you to visually assess the condition of the ear canal and eardrum
The physician then measures the evoked otoacoustic emissions. Measuring OAE allows you to assess the condition of the inner ear and diagnose sensorineural hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs due to disturbances in the perception of sound as a result of damage to the structures of the inner ear or auditory analyzers of the brain.

OAE measurement is a quick and painless procedure
Another hardware diagnostic method is acoustic impedance measurement. The essence of the method: using the device, the doctor measures the acoustic conductivity of the middle ear. There are two types of impedance measurements: tympanometry and acoustic reflexometry.
This is also a safe and painless diagnostic procedure. Allows you to identify dysfunctions of the middle ear, pathology of the facial nerve and auditory analyzers.
The most reliable method for diagnosing hearing in newborns and infants is recording short-latency auditory evoked potentials (SLEPs). Using special equipment, the doctor records brain stem impulses that occur in response to sounds. The child must sleep during the procedure. To record the CVEP, the doctor places the device’s sensors on the baby’s scalp after treating the skin with a special scrub. This is perhaps the only moment in preparation that a small patient may not like.
Outwardly, this resembles recording a cardiogram.

Registration of CVEP is carried out during the patient’s sleep
The procedure is painless and harmless. Registration of CVEP allows diagnosing hearing impairment, hearing threshold, and is also necessary for selecting a patient for cochlear implantation.
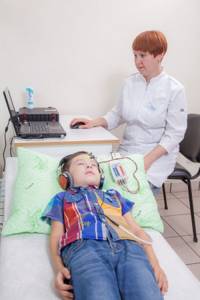
Registration of KSVP can be carried out at any age
Acoustic impedance measurement
This test helps determine the nature of a child's hearing loss and is the main method for detecting infections in the middle ear. When performing this test, movements of the eardrum are recorded after changes in the level of pressure in the ear canal. By measuring the mobility of the eardrum and the level of pressure in the middle ear, the overall condition of the middle ear can be assessed. Acoustic impedance testing is also used to measure the acoustic reflex after certain loud sounds are presented. When the reflex is activated, the eardrum tightens. This is a natural defense against the negative effects of loud sounds. If the reflex is not activated or is activated only when very loud sounds are given. It can be concluded that some part of the auditory system is damaged. This type of test is performed very quickly and does not require the child’s active participation.
The above types of examination are carried out in a special soundproofed cabin, which eliminates the influence of surrounding extraneous noise and obtains 100% reliable results.
How to treat hearing loss in children
The doctor prescribes treatment depending on the diagnostic results: the identified pathology and the individual characteristics of the child.
Remember, the earlier a problem is identified, the easier it is to eliminate its impact on the child’s development. Ideally, hearing impairment should be detected in the first months of life. In this case, proper treatment prevents the negative impact of hearing loss on the baby’s development.
Hearing pathologies are divided into two groups: conductive and sensorineural (sensorineural) hearing loss.
With conductive hearing loss, the transmission of sound along the auditory pathway is impaired. This could be damage to the eardrum as a result of otitis media, tumors, foreign bodies, the formation of cerumen plugs, atresia (infestation) of the ear canal, and so on.
Treatment options for conductive hearing loss depend on your specific situation. This may include surgical restoration of the ear canal, removal of foreign bodies and wax plugs, treatment of infectious diseases and their consequences.
To prevent conductive hearing impairment as a result of infectious diseases, it is important to vaccinate your child in accordance with the national vaccination schedule.
With sensorineural hearing loss, the perception of sounds is impaired due to damage to the inner ear, vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory analyzer (parts of the brainstem and cortex). Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by genetic factors, infectious diseases, the use of ototoxic drugs, injuries, and tumors.
The treatment method depends on the cause of sensorineural hearing loss and its severity. In severe cases bordering on deafness and when hearing aids are ineffective, doctors use cochlear implants. These are devices that perform the functions of damaged or missing hair cells in the inner ear.
A cochlear implant consists of an external microphone and a transmitter that converts sound into electrical impulses. The internal part consists of a receiver, which decodes electrical impulses, and electrodes, which transmit the decoded signals to the cochlea.

The implant allows a child with sensorineural hearing loss to hear
A cochlear implant is placed during surgery. The child is put into medicated sleep, he does not feel pain. The operation is considered safe, and serious complications, such as damage to the facial nerve, are extremely rare.
What is auditory-verbal rehabilitation?
Treatment for hearing loss does not end once the cause is eliminated or a cochlear implant is installed. The child requires auditory-speech rehabilitation, during which he learns to respond to sounds, understand speech and speak.
Several specialists are involved in the rehabilitation of a child after installation of an implant, including an otolaryngologist (surgeon), audiologist, audiologist, teacher of the deaf, psychologist or psychiatrist. Each specialist solves important tasks:
- The otolaryngologist ensures that there are no complications in the postoperative period.
- An audiologist adjusts the cochlear implant processor.
- The audiologist evaluates the effectiveness of implantation.
- Teachers of the deaf teach the child to respond to sounds, understand speech and speak.
- The psychologist creates conditions in which the child adapts to new situations and challenges.
- The psychiatrist, if necessary, corrects defects in the patient’s psycho-emotional development.
After effective auditory-speech rehabilitation, the child can attend a specialized preschool institution and boarding school or a comprehensive school and kindergarten.
Management of patients after cochlear implantation
Hearing-speech rehabilitation after cochlear implantation is a long process, the result of which depends on the consistency of classes with a teacher of the deaf to develop hearing-speech skills. Audiological support consists of regular adjustments to the processor of the cochlear implantation system. The Institute’s specialists have developed proprietary methods for tuning the processor based on recording the responses of the auditory analyzer, which allows for the most effective rehabilitation of young children.