If a child has a lot of leukocytes in his urine, in 95% of cases this may indicate problems with the health of the genitourinary tract. But it is important that the analysis is collected correctly - only then can the correct diagnosis be established ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists ETERI KURBANOVA Candidate of Medical Sciences, pediatrician, nephrologist of the highest category, associate professor, deputy chief pediatrician at SM-Clinic
Leukocytes in the urine of children of any age is always an alarming sign. Especially if the standard values are exceeded several times and this cannot be explained by collection defects.
What is leukocytosis in a child and its classification
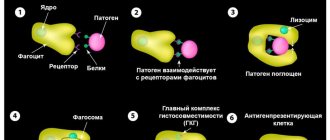
White blood cells are synthesized by the bone marrow to provide the body's immune response to the penetration of infectious agents. They rush to the site of injury, capture pathogenic microorganisms, destroying their cellular structure, and produce antibodies, which promotes rapid recovery.
The detection of a high number of leukocytes in the blood of a child indicates the development of pathologies characterized by inflammation of various parts of the body, and its fight against infectious agents. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based only on the level of white blood cells, so doctors prescribe additional diagnostic methods.
Doctors classify leukocytosis in the blood of children according to the type of etiological factor:
- physiological. It is caused by the influence of external factors and is not associated with the development of diseases;
- pathological. It is a sign of various diseases. To relieve symptoms, drug therapy is necessary, which is prescribed after confirmation of the preliminary diagnosis.
When taking a general blood test, you must follow certain rules, since neglecting them leads to distorted results. If the doctor identifies such factors during the survey, the study is recommended to be repeated.
How to treat leukocytosis?
Treatment can be prescribed only after the exact cause of this phenomenon has been established, for example, physiological leukocytosis is considered to be the norm. As soon as the causative agent of the infection is detected, the following drugs may be prescribed to the small patient:
- Antiviral agents that effectively fight viruses.
- In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed, but they are taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Chemotherapy drugs that are aimed at maintaining the immune system.

Sometimes, when leukocytosis is detected in children and the blood has a viscous consistency, leukapheresis is prescribed, during which the blood is purified.
Norm
The value of the parameter depends on the age of the child, so a special table is used to interpret the results. In the first days of a baby’s life, the cell level will be at its highest, as the child’s body adapts to new living conditions.
Standard indicators of leukocyte levels in a child’s blood test
| Age | Value, x109/l |
| Newborn | 10-30 |
| 5th day | 9-15 |
| 10-30 days | 8-14 |
| 1-6 months | 6-12,5 |
| 6-12 months | 6-12 |
| 1-2 years | 5,5-11 |
| 2-5 years | 5-11 |
| 5-10 years | 5-10 |
| 10-15 years | 5-10 |
| Over 15 years old | 4-9 |
Attention! An increased level of leukocytes in the blood of a newborn is often associated with a stressful state of the body that occurs during a difficult birth.
These table values are conditional, because different laboratories have their own reference intervals. Therefore, the analysis should be deciphered by a specialist who will take into account the patient’s age and the influence of endogenous and exogenous factors.
Reasons for the increase

White blood cell levels vary throughout the day. Often its increase is observed in the evening due to the influence of various external factors. Therefore, tests are taken in the morning so that the concentration of blood cells normalizes after sleep. Pathological causes of deviation from the norm are considered more dangerous, as the risk of developing serious complications and the need for long-term treatment increases.
An increased level of leukocytes in a child’s blood is considered safe in the following cases:
- excessive physical and emotional stress;
- prolonged exposure to the sun or cold;
- change of climatic zones;
- the presence of a large amount of meat in the diet;
- introduction of complementary foods, transition from breast milk to artificial formula;
- period after vaccination;
- stress;
- poor sleep;
- taking a number of medications;
- premenstrual and postoperative period.

Under the influence of these factors, leukocytes in the blood are slightly increased, their level quickly returns to normal. Physiological leukocytosis does not require therapeutic intervention.
Pathological reasons for the excess of leukocytes in a child’s blood test:
- infections of viral, bacterial and fungal nature;
- acute and chronic course of inflammatory diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- poisoning;
- allergic reactions;
- injuries accompanied by large blood loss;
- malignant tumors;
- kidney diseases provoked by hormonal and antibacterial therapy;
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- infections accompanied by purulent inflammation;
- extensive burns;
- diseases characterized by increased secretion of leukocytes in the bone marrow;
- rickets;
- parasitic infections.
It is possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and narrow down the number of possible causes of deviation only by considering other parameters of a general blood test. With a simultaneous increase in platelet concentration, the development of a tumor process (erythremia, myeloid leukemia) is assumed. An increase in the level of neutrophils indicates a bacterial infection, lymphocytes - a viral infection, and eosinophils - a parasitic infection. With an increase in monocytes, the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the bone marrow is assumed; basophils - the negative effects of allergens.
Attention! If the etiology of leukocytosis is unclear and there are no symptoms of the disease, it is recommended to exclude all provoking factors and periodically repeat the clinical study.
Diagnosis of leukocytosis
Why does a child under one year bleed from the nose?
With leukocytosis, the number of “white” blood cells increases compared to their normal value. The increase may be slight or severe.
Thus, the level of leukocytes increases after eating or during exercise. These are physiological processes and do not pose any danger. After a short period of time, the indicators return to normal. If such growth is considered as a pathological reaction of the body, we are talking about an inflammatory process.
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky recognizes the need for a general blood test. It, first of all, allows you to determine the nature of the disease, bacterial or viral. This is the basis for subsequent treatment. If the body is attacked by bacteria, then it will be difficult to cope without antibiotics, but they have no effect on viruses. Therefore, their use does not make sense, just like the use of antiviral drugs. Immunity to them is usually developed on days 6-7, and the body copes on its own. If this does not happen and the disease develops, most likely a bacteria has joined.
Possible symptoms in a child
When a child's white blood cell count is elevated, it not only indicates that he or she is sick, but also that the immune system is active. The body's defenses began to fight pathogenic microorganisms.
- Why do women have an increase in leukocytes in the blood?
The following symptoms may indicate leukocytosis in a child:
- Increased body temperature without identifying the cause;
- Weakness and dizziness;
- Indigestion, lack of appetite, weight loss;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Headache and migraine;
- Aches in joints and muscles;
- Sleep disorder, most often insomnia. The child becomes anxious and shudders;
- Increased sweating;
- Moodiness and irritability.
An infant will not be able to talk about his health; parents only have to guess about existing problems. What should alert you is that the baby’s behavior has changed, he is not the same as before. When this happens once, and then the baby becomes himself again, then there is no need to worry. If the condition drags on, behavior and well-being worsen, then you need to consult a pediatrician.

Upset child
We must remember! In a baby, a temperature of up to 37.5° is considered normal. At the same time, he is calm and active, no unpleasant symptoms are observed. This is often due to uncomfortable indoor conditions and too warm clothing. If the temperature is higher and the baby begins to act up, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms

The clinical picture of the deviation is often accompanied by signs of concomitant pathology. When the level of leukocytes in the blood is higher than normal in children, the following symptoms are noted:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- loss of appetite;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- weakness;
- poor sleep;
- sudden changes in weight up or down;
- increased sweating;
- joint and muscle pain;
- decreased vision;
- high body temperature;
- fast fatiguability;
- causeless appearance of bruises, hematomas;
- fainting.
Toddlers usually become whiny and capricious, and older children have a sharp drop in concentration, which causes problems in learning. With minor deviations from the norm, symptoms may be mild and any deterioration in health is attributed to the manifestation of the underlying pathology.
Diagnostics

OAC helps to detect elevated leukocytes in a child’s blood. To clarify the cause of the development of leukocytosis, the doctor carries out the following diagnostic measures:
- physical examination of the patient;
- asking parents about the nature and time of onset of symptoms if the baby is not able to describe them himself;
- study of anamnesis;
- clarification of the presence of external provoking factors.
Additional diagnostic methods are:
- general urine analysis;
- blood culture;
- stool microscopy;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI.
With the results of the examination, the child is referred for consultation to specialists who, together with the pediatrician, determine the treatment method.
In order for the decoding of the CBC to be reliable, it is recommended to follow the following rules before the study:
- exclude spicy and fatty foods from the menu 2 days before blood sampling;
- with the permission of the doctor, stop taking medications that affect the level of analysis parameters the day before the test;
- eliminate the impact of physical and emotional stress. It is recommended to explain to the child in advance how the procedure will take place so that it does not provoke stress;
- The last meal should be taken 8 hours before blood donation (for infants this time is reduced to 2 hours);
- In the morning you are allowed to drink clean water, which does not affect the results of the study.
Attention! It is advised to arrive at the laboratory early so that the child gets used to the hospital environment and understands the safety of the procedure.
What do elevated white blood cells in a child’s urine mean?
If a child has elevated leukocytes in the urine, this indicates inflammation in the kidneys, bladder, ureters or genitals. The largest number of leukocytes (mononuclear) is observed with kidney inflammation and pyelonephritis.
When their increased content appears in a baby, the main reasons are the following pathologies.
- Ureteral infections. Stagnation leads to infection and leukocyturia.
- Cystitis. Inflammation of the bladder due to bacteria. In girls, cystitis occurs more often due to anatomical features. Stagnation of urine also contributes to inflammation.
- Pyelonephritis. Infectious damage to the kidney very often begins in children with inflammation of the bladder, then spreads, reaching the kidney. In children with weakened immune systems, this disease occurs more often, and if not treated correctly, it can become a chronic disease.
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the genital organs. The kidney microflora penetrates the mucosa, so leukocytes increase their activity to destroy the infection and, together with mucus, enter the urine. Also, poor genital hygiene leads to inflammation and diaper rash.
- Glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the kidney glomeruli. It is not only infectious, but also partly allergic in nature, so leukocyturia of this origin has one characteristic feature - mainly cells of the eosinophilic type are released, and not neutrophils, as in other inflammatory processes. Glomerulonephritis can also become chronic, so it also needs to be treated urgently.
- Allergies. They are also characterized by an increase in inflammatory factors and an increase in cells, especially eosinophils.
- Stones in the kidney and ureters. Even in children, salts can be deposited and urinary stones can form in the kidney and ureters. This causes inflammation, infection often occurs, therefore, leukocytes increase.
When there are up to 15-20 leukocytes in the urine, they speak of leukocyturia. If their number is very increased, then the term “pyuria” is used. It is used when the content of leukocytes and pus in it is very high, it changes color and consistency (cloudy, sediment).
Treatment
When pathological leukocytosis is confirmed, the treatment method is selected taking into account the type of pathology that provoked its development. For children, a conservative treatment method is usually used, which consists of taking medications, following a diet, and using folk remedies.
Taking into account the type of disease, the increased level of leukocytes is normalized with the following drugs:
- antibacterial;
- antimicrobial;
- antifungal;
- NSAIDs;
- antiallergic;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
In case of poisoning, sorbents are used that relieve intoxication of the body. Treatment of leukemia and malignant tumors involves chemotherapy. In severe cases, leukophoresis is prescribed, during which leukocytes are extracted from the blood using a special apparatus.
The type of drug, its dosage, and duration of use are determined by the doctor. He can make any changes to the treatment regimen only after re-taking the analysis and deciphering the results. You cannot independently draw a conclusion about the need to stop therapy. If the level of leukocytes has decreased, but has not reached normal, and the medication has been stopped, then a relapse is possible.
Folk remedies that are used only with the permission of a doctor help to increase the effectiveness of treatment and speed up recovery. To reduce high levels of leukocytes, it is recommended to drink decoctions of lingonberries, strawberries, propolis, horsetail, birch buds, and linden flowers.
Plant components can provoke allergies in children, so it is advised to give the first portion of the folk remedy in a small amount and monitor the child’s condition. If his health worsens, you should stop taking such medications and consult a doctor. For this reason, traditional therapy is contraindicated for newborns.
Diet for leukocytosis

If the leukocytes in a child’s blood are elevated, then nutrition is selected taking into account the cause of the symptom. To maintain immunity, it is recommended to make easily digestible foods high in proteins and vitamins the basis of your diet.
The diet requires adherence to the following principles:
- daily fluid intake is 1.5-2 liters;
- meals should be frequent and small;
- preference in the menu is given to plant foods, cereals, legumes, nuts, water soups, stewed vegetables, fruits, low-fat fish and fermented milk products.
Attention! If leukocytes in the blood are high, then sweets, spicy, fried, fatty foods, and foods that can cause allergies are completely excluded from the menu. Meat is allowed in limited quantities.
How is the analysis performed?
When testing blood for a general or, as it is also called, clinical analysis, the child should, if possible, be hungry, i.e., the procedure is done on an empty stomach. Typically, blood collection rooms in clinics are open from 8.00. until 9.30. At this time, blood levels in the body are the most optimal.
Blood must be donated on an empty stomach, because after eating, the stomach begins to work actively and the number of leukocytes may increase, and this, in turn, may give the doctor incorrect information about the child’s health status. Also, before taking the test, you should not undergo any procedures, such as x-rays, FGDS and various physiotherapeutic procedures, this can also lead to an increase in leukocytes in the blood. [adsen]
Complications
An increased number of leukocytes cannot be ignored in the absence of pronounced symptoms of the disease. Inflammation that becomes chronic becomes the cause of dangerous complications.
The long course of such diseases leads to disturbances in the psychoemotional and physiological state of the child, which threaten developmental delays and disability. If diagnosed untimely, leukocytosis provokes the transformation of benign tumors into malignant ones, characterized by a high risk of death.
Any deviations in health, accompanied by changes in the level of blood components, can be life-threatening for the child. It is important to promptly determine the cause of their development and begin treatment.
Prevention and prognosis

Most of the reasons that provoke an increase in white blood cells can be prevented by following the following recommendations:
- undergo medical examinations in a timely manner;
- avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- control the level of physical activity;
- avoid stress and injury;
- balance the diet;
- do not neglect therapeutic courses and medications for chronic pathologies;
- do not refuse vaccination;
- support immunity;
- maintain a daily routine;
- limit contact with sick people;
- do not self-medicate;
- be outdoors regularly.
When leukocytes increase, the prognosis of the health condition depends on the root cause of the symptom, the time of contacting a doctor, and compliance with his recommendations. Serious consequences threaten with the development of dangerous pathologies and refusal of treatment.
A lot of leukocytes in the blood is not always a sign of disease. High levels of white cells are observed in children due to exposure to various physiological factors. This phenomenon passes quickly and does not require medical intervention. If their concentration exceeds the norm due to the development of pathology, then the lack of treatment can lead to dangerous consequences. The right decision in this case would be to follow all medical recommendations.
Prevention
To prevent infections of the genitourinary system in children, the symptom of which is often pyuria, it is recommended:
- Do not neglect personal hygiene and do not forget to regularly change your baby’s underwear.
- Replenish your child’s diet with foods that support immunity.
- Give your child enough to drink (clean water is best).
- Prevent constipation in your baby.
- Wash the child towards the buttocks.
Also, to ensure that the increase in leukocytes is not false, it is important to correctly collect urine from the child. First of all, this concerns good washing and sterility of the container in which the urine sample is collected. Urine should be delivered to the laboratory immediately after collection within 1-2 hours. For more accurate results, collect the first urine your child passes in the morning.