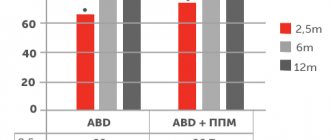
09.12.2020
The recovery process after arthroscopy may vary depending on the condition for which the surgery was performed. For example, usually the limb is not immobilized after the intervention, but if it was done for chronic instability of the shoulder joint (habitual shoulder dislocation), then immobilization can last up to a month. However, in most cases, the recovery period after arthroscopy is standard.
Why is rehabilitation needed?
Rehabilitation measures are carried out to normalize regenerative processes and prevent muscle atrophy, which inevitably occurs in the case of prolonged immobilization.
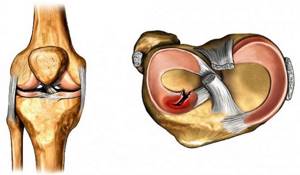
High-quality rehabilitation is especially important in professional sports, as it allows you to quickly return to training and competition. The goal of modern orthopedics is to preserve as much of the damaged meniscus as possible. Very rarely it is completely removed. Basically, partial removal (resection) is performed. This is due to the fact that the meniscus performs a shock-absorbing function, reducing the impact load on the hyaline cartilage. Therefore, in its absence, the risk of developing deforming osteoarthritis of the knee in the coming years after surgery increases sharply.
The quality of meniscal healing is influenced by many factors:
4-6 MONTH:
- Continuation of activities aimed at strengthening muscles and coordination of movements.
- Jogging on a flat surface is possible.
- Using a knee brace during loads, the danger of awkward movements (transport, travel) and exercise therapy.
It is necessary to avoid premature increased loads, early return to sports, sudden leg extensions, especially straight leg movements, jumping, running on hard or uneven surfaces, twisting loads, falls, and uncontrolled movements during sports exercises.
Limiting sports activities after ACL surgery is necessary for up to 4-6 months. Limiting contact or team sports to 9-12 months.
I would also like to emphasize that the selection of a rehabilitation program should be carried out individually and take into account many factors. This is a fairly long and important stage of treatment, without which it is unlikely that good functional treatment results will be achieved.
rehabilitation
rehabilitation
- anatomical type of rupture;
- rupture zone (the closer to the capsule, the faster the recovery);
- extent of damage;
- duration of injury;
- the patient’s age and state of physical health;
- associated damage to intraknee structures.
The quality of medical care provided is of no small importance. In different clinics, after arthroscopic removal of the meniscus, complications develop in 0.2-10% of patients. As you can see, the spread is quite significant. Relatively speaking, in the worst clinic complications occur 50 times more often than in the best.
Indications
For diagnosis, arthroscopy is done if other research methods do not provide a clear picture. Most often today, MRI is used for diagnostic purposes. Using this technique, the following pathological conditions can be identified:
- ligament ruptures;
- meniscus injuries;
- cracks and fractures;
- inflammatory and degenerative processes affecting the joint;
- synovitis;
- damage to the cartilage tissue of the joint.
The following reasons are indicated:
- popliteal fossa cyst;
- synovitis;
- ruptures of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments;
- meniscus lesions;
- cartilage diseases;
- deforming arthrosis;
- arthritis;
- Hoffa's disease (inflammatory process of fatty tissue of the joint);
- Koenig's disease (osteochondritis dissecans);
- post-traumatic proliferation of bone tissue.
Directions of rehabilitation
After removal of the meniscus of the knee joint, the patient's recovery is required so that the person can not only walk without experiencing pain. In most cases this is not enough. The overwhelming number of meniscus injuries occur in the age group of 18-30 years. The majority of those injured are men involved in sports.
Thus, recovery aims not only to restore working capacity, but also to allow further full physical activity on the knee. Basic principles of rehabilitation that allow you to achieve all your goals:
- start rehabilitation activities as early as possible;
- complex methods of knee restoration (physical therapy, physiotherapy, arthrotherapy and other methods should be used at the same time);
- phasing – there are 4 main stages of recovery, which replace each other and set different goals;
- correct dosage of physical activity and its prompt correction, depending on the patient’s well-being, the condition of the knee and the results achieved;
- long-term planning of the rehabilitation process;
- the possibility of an expert assessment of the current functional state of the knee joint.
Recovery after meniscus removal should be not only clinical, but also functional. Incomplete rehabilitation is the main reason for re-traumatization of a person.
Medication provision
No knee rehabilitation is complete without medication. After any type of orthopedic surgery, three main types of medications are prescribed:
- antibiotic against local infection;
- an anticoagulant that thins the blood and has an antithrombotic effect;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
It may be necessary to prescribe dietary supplements or products from a series of chondroprotectors to replenish articular tissues with valuable nutrients, which will help activate reparative and regenerative reactions.

Taking antibiotics is critically important; without this, very unpleasant consequences can occur in the form of an infectious complication.
Anti-pain medications should be used only as needed, and should not be overused if the discomfort in the knee is not severe. In the first 3 days, in order to avoid frequent use of harmful medications, doctors advise applying an ice bag to the knee joint every 30-40 minutes. Cold dry compresses are quite effective in soothing pain and reducing swelling. Drugs from the NSAID category should not be used immediately before exercise, so that you can feel your leg well during training. If the pain is dulled by medication, there is a danger of making the wrong movement and causing unwanted injury to the still vulnerable limb.
Is it painful to work out an operated knee without prior anesthesia? Of course, what to hide, at first it will not be easy, what to do exercises, what to move around. But there is no escape from pain; this is a normal reaction of the body to temporary intervention. Every day you will feel better and better, and after about 7-10 days the unpleasant sensations will stop bringing you such suffering. The main thing is don't give up! Do not stop following the instructions given by the specialist. Naturally, immediately inform your supervising doctor or physical therapy trainer about all your sensations, especially if the unpleasant symptoms begin to intensify.
Physiotherapy

Includes the first day after surgery to remove the meniscus. It is characterized by acute post-traumatic inflammation of the joint. The pain intensifies. The tone of the quadriceps femoris muscle decreases. During this period, isometric and dynamic exercises are indicated. Full weight bearing on the operated limb is indicated.
Phase 2
This is the initial stage of soft tissue healing. These are the 2nd and 3rd postoperative days. The pain decreases and the tone of the quadriceps muscle increases. The patient is placed on bed rest. The range of movements is significantly increased. It is recommended to walk 4 times a day for 5 minutes.
Phase 3
The late healing phase begins 4 days after surgery. It lasts up to 3 weeks. There is no more pain. Thigh muscle tone is slightly reduced. Isometric exercises predominate in therapeutic exercises. Walking is recommended 3 times a day for 15 minutes. Patients exercise in the pool and on an exercise bike.
Phase 4
The last phase of rehabilitation begins 3 weeks after meniscus removal. The main task of the recovery period is to restore normal range of motion in the knee joint and improve exercise tolerance. Muscle strength and volume are completely restored.
The duration of the fourth phase reaches one and a half months. The patient exercises on exercise machines, does isokinetic exercises, and walks a lot. After this phase of rehabilitation is completed, the average person does not require further recovery. If we are talking about an athlete, then he is shown a gradual increase in load in order to reach the previous level of physical fitness. This period is called training and recovery. It can last from one and a half to six months (it lasts longer in patients with combined injuries, for example, with a concomitant rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament).
Elastic bandaging
For 6 weeks after surgery, there is a risk of blood clots and swelling. Therefore, a specialist prescribes elastic bandaging in the early period, and compression stockings in the later period. The degree of compression of these medical devices is selected by the orthopedist, taking into account the volume of intervention and the predisposition factor to thrombosis. Applying an elastic bandage and wearing compression garments prevents the development of deep vein thrombosis.

Bandages are used less and less; they hold up very poorly when moving. This type of compression knitwear is most often used.
The technique of how to bandage a leg will be taught to you in the hospital. First, the bandaging is carried out by a doctor, and when you return home you will have to do it yourself. Be attentive to everything the medical staff says and teaches you while you are still in the clinic or rehabilitation center.
Knee replacement in the Czech Republic: guarantees, prices, rehabilitation, reviews and statistics.
Find out more
Recovery control

Recovery control
- manual muscle testing with evaluation of results using the Lovett scale;
- goniometry – measurement of the angle of flexion and extension of the knee joint;
- centimeter - the circumference of the knee joint is regularly measured in two positions: at the site of the greatest swelling (it can last up to 2 months), and also to the patella between the quadriceps femoris and the knee.
- algesimetry – assessment of the severity of pain (according to the patient’s subjective sensations).
Exercise therapy for the knee after surgery
Only with a comprehensive combination of exercise therapy with other therapeutic and health tactics prescribed by the doctor will you achieve results in normalizing the motor-support potential of the leg.
How long recovery lasts was indicated in previous chapters. Let's repeat, 2-6 months. The duration of the recovery process is influenced by 3 criteria: surgical tactics, the degree of surgical aggression and the personal characteristics of the patient.
The fundamental goals of exercise therapy after knee replacement, arthroscopy to restore ligaments, knee meniscectomy and other surgical treatment methods are to increase muscle tone and endurance, and develop the knee until the most complete recovery possible. A competent physical regimen in stages can be recommended by a highly competent doctor - the operating orthopedic surgeon, rehabilitation specialist or exercise therapy specialist.

Orthosis training.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic techniques are aimed at:
- normalization of microcirculation in the knee joint;
- elimination of tissue swelling;
- improvement of lymph and venous blood circulation;
- normalization of trophism of muscles, ligaments, articular cartilage;
- reduction of pain.
For this purpose, massage is used, as well as many hardware physiotherapy techniques. The treatment process uses a laser, electric fields and magnetic waves, ultrasound and other physical factors. They are able to influence muscle tone, the condition of blood vessels and the regenerative processes occurring in the body.
If your temperature rises
Many people, after arthroscopy of the knee joint, observe that the body temperature has reached 37. The first reaction is that patients begin to panic and suspect complications. In fact, low-grade fever is normal after surgery. This is a peculiar reaction of the body. This temperature can reach 37.3 and is not dangerous. As a rule, it goes away on its own and does not require treatment. If the temperature is higher, this is a good reason to consult a doctor and rule out complications.
Arthrotherapy
To restore patients after meniscus removal, drug treatment methods can also be used. The use of arthrotherapy allows:
- reduce pain and prevent damage to hyaline cartilage by reducing friction of articular surfaces;
- accelerate the regeneration of tissues that have been damaged as a result of injury and during surgery;
- form a better scar in place of damaged tissue.
The procedure uses platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid. This combination has a more pronounced effect compared to using these drugs separately.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
You will be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures:
- laser treatment;
- electromyostimulation;
- UHF treatment;
- extracorporeal shockwave therapy (shock wave therapy);
- ion-galvanization;
- magnetic therapy;
- hot paraffin treatment (only in the later stages!).
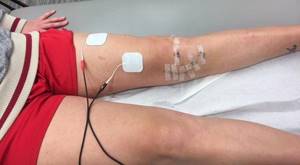
Electrical stimulation is one of the options for physiotherapy.
Exercise therapy and physiotherapy will help:
- relieving spasms from tense muscle structures and increasing the tone of weakened and atrophied muscles;
- activation of microcirculation and blood flow in the lower limb;
- stimulating metabolism in joint structures;
- relief of painful manifestations and swelling.
Diagnostic arthroscopy of the knee joint: contraindications
All disorders that are associated with the cartilage, ligaments, and tendons of the knee joint can be diagnosed using arthroscopy. The decision to diagnose using arthroscopy is made by a specialist; the method requires an individual approach. Before a diagnostic test, the patient must undergo a series of tests. The following conditions are contraindications to the procedure:
- joint diseases (ankylosis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis and others);
- acute inflammatory processes;
- chronic diseases;
- hemarthrosis;
- violation of the integrity of the joint capsule;
- unstable condition of the patient;
- high risk of complications after surgery and anesthesia.