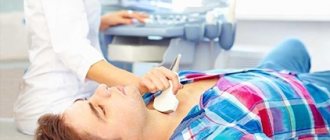
Ultrasound examination of the eye occupies an important place in ophthalmological practice - it is one of the main tools that complements generally accepted methods for diagnosing eye pathologies. Ultrasound of the eye is a highly accurate, painless and safe examination method that allows you to diagnose the condition of the structures of the eyeball - the retina, eye muscles, and lens. The echoophthalmoscopy technique helps to establish an accurate diagnosis and detect various ophthalmological diseases in the early stages.
Ultrasound of the eye is used not only to identify and confirm various ophthalmological pathologies, but also to measure specific biometric parameters and determine a number of quantitative values. Using ultrasound, it is possible to carry out high-precision measurements of the eyeball, obtain information about the state of the structures and elements of the eye, the optic nerve, and assess blood flow in the vessels of the retina and orbit.
Ultrasound examination of the eye
Instrumental examination methods are used in cases where visual pathologies were identified during examination, but it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis due to lack of data. Sometimes ultrasound is the only available method in ophthalmology for studying the structures of the eye, since it is done without exposing the body to ionizing radiation or invasive intervention.
Who is prescribed an eye ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the eye is prescribed when the size of the orbit changes, because it shows areas that are inaccessible to most other types of diagnostics. Also indicated may be diabetes, eye injuries, hypertension, suspected tumor, thyrotoxicosis, retinal detachment and a number of other diseases, including lens pathologies. Ultrasound of the orbits or retina may be prescribed to monitor treatment, assess the dynamics of changes, or when planning surgical intervention.
Combination of ultrasound with other diagnostic methods
The high information content of ultrasound does not exclude the need for additional diagnostic methods. In general cases, ultrasound is preceded by taking an anamnesis and conducting a general clinical and ophthalmological examination by the doctor.
If the presence of a foreign object is suspected, an x-ray of the eye is first taken. If the patient is suspected of having intraocular tumors, ultrasound is preceded by diaphanoscopy of the eyeball. To confirm the presence of a space-occupying lesion in the orbit, exophthalmometry and radiography are additionally performed.
Fill out an application on the website, we will contact you as soon as possible and answer all your questions.
Make an appointment
How is an ultrasound examination of the eye performed?
For an eye ultrasound, the patient sits in front of the specialist while he performs the examination. Sometimes local anesthesia is necessary for the examination. The specific method of performing the procedure depends on the area being examined and the method of examination.
A-mode
A-mode shows tissue; the method allows you to take basic measurements of the eye. Ultrasound of the eyeball is often done in this way to obtain additional data for planning surgery.
During an ultrasound examination of the eye, the transducer comes into contact with the surface of the eye. Therefore, before the procedure, the patient is instilled with an anesthetic drug. It relieves pain and temporarily immobilizes the eye.
B-mode
Ultrasound of the eyeball in this mode is called two-dimensional echography. The examination shows the structure of the eye. The method does not require the use of an anesthetic, so it is performed without prior anesthesia. Before the examination, the specialist applies a contact solution to the patient’s eyelid.
A+B
Sometimes a combination of both methods described above is used to most accurately diagnose an eye condition.
Color duplex scanning
The examination provides an image of the eye as well as information about the speed and pattern of blood flow in the blood vessels in and around the eye.
Three-dimensional echoophthalmography
Three-dimensional echoophthalmography is performed when an image of the eye in three dimensions is needed. An ultrasound of the eyeball shows whether blood circulation in the eye is normal.
Ultrasound of the eye orbit using the method of three-dimensional echo-ophthalmography requires large computing power, for which an ultrasound machine is connected to a computer.
Ultrasound eye diagnostic methods: scanning modes A and B
In ophthalmological practice, several ultrasound diagnostic methods (scanning modes) are used, each of them has its own technical features, differs in diagnostic capabilities and is intended for specific medical cases.
Ultrasound in A-mode . Scanning the eye in one-dimensional mode. The data on the monitor is displayed in the form of a graph, based on which the specialist assesses the biometric parameters of the eye. Ultrasound scanning in A-mode is classified into a separate direction - echobiometry.
Examination in A-mode allows you to accurately measure the axial length of the eye, the depth of its anterior chamber, and lens parameters. These data are crucial in preparing for cataract extraction, for accurately calculating the optical power of an artificial lens, and in diagnosing refractive errors. Ultrasound diagnostics in A-mode also makes it possible to detect and evaluate intraocular tumors.
Ultrasound in B-mode . Advanced scanning method. With its help, the monitor no longer produces a graph, but a two-dimensional image detailing the internal structures of the eyeball: lens, retina, eye muscles, etc. Research in B-mode allows highly accurate assessment and differentiation of intraocular changes: determining the nature of the pathology, its shape , length. Unlike the static A-mode, B-scan displays the intraocular picture in dynamics, which significantly expands its diagnostic potential.
Along with these two methods, which are considered to be the gold standard of ophthalmological diagnostics, other scanning modes are also used:
Combined method is a mode that combines the capabilities of A- and B-diagnostics.
Ultrasound biomicroscopy is an ultrasound method that allows high-resolution study of the structures of the anterior segment of the eye - we are talking about the cornea, iris, lens, and anterior chamber angle.
Three-dimensional echography is a highly informative method that provides three-dimensional acoustic visualization of intraocular structures. The image is given in volume. It is broadcast in real time, which allows you to assess the general condition of the eye over time.
Doppler ultrasound is a method that allows one to evaluate blood flow parameters in the orbital vessels.
What does an ultrasound of the eye show?
Ultrasound of the eye orbits provides a large amount of data about the condition of the eye, due to the fact that it shows the dynamics of the processes occurring inside it. The examination provides information about the structure of the eye, its size, lens injuries, foreign bodies or tumors. Using ultrasound, retinal detachment and some other pathologies are diagnosed. Ultrasound of the eyeball is often used to monitor the patient’s condition; deciphering examination data, for example, allows one to assess the rate of progression of myopia. In addition, an ultrasound of the eye is often prescribed before surgery is performed.
Decoding the results
At the end of the study, the ultrasound doctor draws up a conclusion, on the basis of which he will make a diagnosis, draw a conclusion about the course of the disease and/or the effectiveness of treatment, draw up a surgical plan, etc. For these purposes, the following indicators are assessed:
- visibility of the lens (normally it is not visible; if there is clouding, ultrasound waves no longer pass through it);
- visibility of the vitreous body (similarly with the lens, it is noticeable only when clouded);
- refractive power of the eye in diopters;
- data on the vitreous body;
- eye axis length;
- shell thickness;
- width of the optic nerve.
Using ultrasound, you can examine the bottom of the eye, measure the thickness of its structures (anterior chamber, muscles, cornea), identify congenital anomalies (NIARMEDIC performs ultrasound of the eye of a child, including an infant, to identify abnormalities in the development of the eyes), diagnose tumors in different parts of the eye and periocular space (orbits, appendage apparatus), analyze the blood supply (an apple can be absolutely healthy, but obstructed blood circulation causes discomfort, pain, and nonspecific symptoms).
Normally, the eye has a spherical shape, the blood flow is linear, its speed does not fall below 0.38 m/s, the arteries are not tortuous, and loose tissue containing oculomotor muscles is located in the peribulbar space. These indicators may be disturbed, for example, low blood flow speed may indicate ischemia and angiopathy, an increased amount of parabulbar fiber is observed with pathology of the thyroid gland.
Indications
Ophthalmoechography is performed when the initial examination is not enough. The procedure is indicated for the following problems:
- retinal detachment;
- injury to the organs of vision;
- cataract;
- myopia or hypermetropia;
- congenital glaucoma;
- intraorbital or intraocular neoplasms;
- anomalies of the eye sockets and apples;
- intraocular hemorrhages;
- anterior ischemic neuroopticopathy.
Ultrasound examination is indicated for diagnosing and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy for vascular pathologies, monitoring the condition after surgical intervention on the organs of vision.
Ultrasound of the eyeball at the Miracle Doctor clinic in Moscow

- Fast Diagnostics takes about 20–30 minutes, a description of the results is prepared immediately.
- Painless ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure during which the patient does not experience discomfort.
- Informative For some eye diseases, ultrasound is the only approved diagnostic technique.
Indications for ultrasound diagnostics
- suspicion of foreign body penetration;
- intraocular inflammatory processes;
- retinal detachment;
- tumor processes of any nature;
- identifying the causes of clouding of the optical media of the eye;
- pathologies of the extraocular muscles and vitreous body;
- before surgery to clarify the location and extent of eye damage;
- checking the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
As a rule, a study is prescribed if the initial examination by a doctor does not allow making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment.
Contraindications for ultrasound of the eyes
Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the most gentle and comfortable methods, so it has practically no restrictions. The examination is not scheduled or postponed in the following cases:
- the patient is in serious condition;
- there are open injuries (wounds, burns) on the eyelids;
- acute inflammatory process on the cornea of the eye.
In all other cases, diagnosis is carried out. Pregnant women and children can also be tested.
Why get diagnosed?
Doctors recommend undergoing vision diagnostics annually, even if the patient is not worried about anything. Only in this case can eye diseases be identified in time and brought under control in a timely manner.
With the right correction or treatment, the progression of diseases can not only be slowed down, but also completely stopped! The effect will depend on the stage of development of the visual disorder or eye pathology at which treatment began.
However, in the early stages of development, many diseases are asymptomatic. And even with symptoms, not all patients realize the seriousness of the situation and turn to a specialist.
This is why it is important to undergo a diagnostic examination every year, especially if you are at risk for:
- The presence of visual impairment (myopia or farsightedness) in one or both parents;
- Previously diagnosed diseases and disorders;
- Age - over 50 years old;
- Daily computer use for more than 2 hours.
conclusions
An eye test includes painless procedures that help identify not only visual impairments, but also pathologies of the organ of vision.
There are three types of vision tests at the Happy Look optical salons:
- Express - includes a visual acuity test, takes no more than 15 minutes;
- Complete - includes a comprehensive vision examination with the selection of glasses or contact correction. Does not provide for the detection of eye pathologies;
- An appointment with an ophthalmologist includes a vision test and additional examination methods aimed at identifying pathologies of the visual organ.
Ultrasound forms
There are three types of ultrasound examination. The doctor chooses the method, depending on the situation.
Mode “A” - with the eyes open - is not often used, for example, before operations. An anesthetic is dripped to prevent discomfort and blinking. The mode distinguishes deviations and problems of functioning, determines the dimensions.
In mode “B,” anesthetics and open eyes are not required. The closed eyelid is lubricated with a transparent substance that conducts the signal. The result is a two-dimensional image.
The third option is Doppler scanning to study blood vessels. Indications for the Doppler method are the formation of venous blood clots, pathologies of the carotid artery, spasms, etc.
Sometimes methods are combined so that the doctor receives a variety of data for further diagnosis.